Bones Table
Diunggah oleh
NursingNowDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bones Table
Diunggah oleh
NursingNowHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
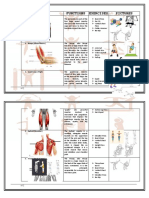
Skeletal Bone Table
Axial Skeleton
Bone Parietal bone Temporal bone Occipital bone Frontal bone Description Above temporal bone. Forms side of cranium. inferior to the parietal bone on lateral skull Most posterior bone of cranium. Forms floor and back wall. In the base is the Foramen Magnum Anterior portion of cranium. Above zygomatic bone. Bat-shaped bone forming the anterior plateau of the middle cranial fossa across the width of the skull. Keystone of cranium because it attaches with all other cranial bones. Feature Description of the feature point of articulation of parietals with frontal bone. forms the lateral portion of the skull base large hole through which the inferior part of the brain connects with the spinal cord. allows the supraorbital artery and nerve to pass to forehead a saddle shaped region of the sphenoid midline. The seat of this saddle, called the hypophyseal fossa, surrounds the pituitary gland. (hypophysis)
The Bones of the Skull
coronal suture petrous region foramen magnum supraorbital foramen (notch)
Sphenoid bone
sella turcica
Ethmoid Bone
Irregular shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid forms most of the bony area between the nasal cavity and the orbits
cribriform plate
punctured by tiny hole called olfactory foramina that allow the filaments of the olfactory nerves to pass from the smell receptors in the nasal cavities in the brain
Lacrimal Bone
the smallest and most fragile bone of the face, is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit small rectangular bones forming the bridge of the nose a paired bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek
lacrimal fossa
passageway for tear
Nasal Bone
none
none
Zygomatic Bone
zygomatic process
Any of three processes that articulate with the zygomatic bone,
Maxilla Mandible
two bones fused in a median structure lower jaw bone which articulates with the temporal lobes in the only freely movable joints. blade shaped bone in the median plane of nasal cavity that forms the posterior and inferior nasal septum
palatine process mandibular condyle
Forms the anterior hard palate meet medially in the inter maxillary suture. Articulation point of the mandible with mandibular fossa of the temporal bone. none
Vomer
none
Bone
Description
Feature
Description of the feature
The Vertebral Column Cervical vertebra first 7 vertebrae-form the neck portion of the vertebral column. the next 12 vertebrae in the spinal columnlarger body than the cervical vertebrae heart shaped the last 5 vertebrae supporting the lower back. Massive block like bodies, short and thick hatchet-shaped spinous processes extending directly backward bone formed from the fusion of five vertebrae. Superiorly articulates with L5 and inferiorly it connects with the coccyx Tailbone - attached to the sacrum by ligaments breastbone, A long flat bone in most vertebrates that is situated along the ventral midline of the thorax and articulates with the ribs. Typical flat bone. A result of the fusion of three bones. concave upper border of the manubrium. Generally at the level of the third thoracic vertebra atlas C1- lacks a body, its lateral processes contain large concave depressions on their superior surfaces that receive the occipital condyles of the skull articulate with the heads of the corresponding ribs
Thoracic vertebrae
costal facets
Lumbar vertebra
superior articular facets
reduce mobility of the lumbar region
Sacrum
sacral foramina
located at either end of the ridges it allows blood vessels and nerves to pass none
Coccyx
none The Bones of the Thoracic Cage
Sternum
xiphoid process
constructs the inferior end of the sternum and lies at the level of the fifth intercostal space.
Jugular notch
part of the sternum
none
Bone
Description
Feature
Description of the feature
True Ribs False Ribs Floating Ribs
the first seven pair of ribs. Attach directly to the sternum by their own costal cartilages the next five pair of ribs that indirectly attach to the sternum last 2 ribs of the 12 that have no sternal attachment
none none none
none none none
Appendicular Skeleton
Clavicle Scapula Humerus The bones of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs collar bone - a slender doubly curved bone the projection that anchors a ligament and provides the convex forward on its medial two-thirds conoid tubercle landmark for determining whether the clavicle is from the and concave laterally right or left side of the body shoulder blades- triangular, flattened body. long bone of upper arm. Its rounded head fits into the shallow glenoid cavity of the scapula the smaller one of the two large bones of the forearm. articulates with the capitulum of the humerus, the radial notch and the head of the ulna. The larger bone of the two bones of the forearm, extending from elbow to wrist on the side opposite the thumb 8 bones of the wrist, inferior to the ulna and radius numbered 1-5 - base of the metacarpals articulate with the carpals of the wrists glenoid cavity greater tubercle a shallow socket that receives the head of the humerus larger of two bump-like projections of the proximal humerus. It is situated lateral to the head and lesser tubercle the point of attachment for the tendon of the biceps muscle of the arm serves as a point of attachment for the ligaments of the wrist restrict movement between the bones none none superior margin of the iliac bone cartilaginous joint at the pubic crest receives the weight of the body when sitting
Radius
radial tuberosity
Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Ilium Pubic bones Ischium
styloid process ligaments none
digits - our fingers 14 bones- each finger none contains 3 phalanges The bones of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs forms major portion of coxal bone iliac crest most anterior portion of the coxal bone "sit down bone" - forming the most inferior and posterior portion of the coxal bone pubic symphysis ischial tuberosity
Bone
Description
Feature
Description of the feature
Femur Patella Tibia Fibula Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges
thigh bone - superior to the tibia and fibula a triangular sesamoid bone enclosed in the tendon that secures the anterior thigh muscle to the tibia Shin bone - larger and more medial of the two leg bones lies parallel to the tibia. Thin and stick like with aq sharp anterior crest 7 bones where body weight is concentrated 5 bones - form instep 14 bones - forms the toes
greater trochanter surface for patellar ligament tibial tuberosity lateral malleolus calcaneus none none
a strong process overhanging the root of the neck of the femur. Site of muscle attachment ligaments, leverage knee joint roughened protrusion on the anterior tibial surface, is the site of attachment of the patellar forms the outer part or lateral bulge of the ankle heel bone none none
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Massachusetts Bay Colony ExcerptsDokumen3 halamanMassachusetts Bay Colony ExcerptsNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- APA Style Notes-2-2Dokumen4 halamanAPA Style Notes-2-2NursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Coping and PreventionDokumen268 halamanCoping and PreventionNursingNow100% (1)
- Basic Tools To Describe DataDokumen9 halamanBasic Tools To Describe DataNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Care Tips For Chronic WoundsDokumen3 halamanCare Tips For Chronic WoundsNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Calculating Central TendencyDokumen9 halamanCalculating Central TendencyNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- EHR DocumentationDokumen7 halamanEHR DocumentationNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Care Tips For Chronic WoundsDokumen3 halamanCare Tips For Chronic WoundsNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- A Conceptual Model of QSEN 1Dokumen1 halamanA Conceptual Model of QSEN 1NursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Experimental ResearchDokumen2 halamanExperimental ResearchNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- 16 Z 4thDokumen15 halaman16 Z 4th1ab4cBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Tools To Describe DataDokumen9 halamanBasic Tools To Describe DataNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Bristol Stool ChartDokumen2 halamanBristol Stool ChartNursingNow100% (1)
- Tests For Differences Between MeansDokumen5 halamanTests For Differences Between MeansNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemical Testing HandoutDokumen13 halamanBiochemical Testing HandoutNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid and Electrolyte Management PDFDokumen10 halamanFluid and Electrolyte Management PDFbalab2311Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Hints PDFDokumen1 halamanDrug Name Hints PDFNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Hints PDFDokumen1 halamanDrug Name Hints PDFNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- IV Drip Calculation Practice ProblemsDokumen3 halamanIV Drip Calculation Practice ProblemsNursingNow100% (3)
- BacterialStaining ProcessDokumen4 halamanBacterialStaining ProcessNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory SafetyDokumen2 halamanLaboratory SafetyNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- BacterialStaining ProcessDokumen4 halamanBacterialStaining ProcessNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Safety Document 2013 JARDokumen2 halamanLab Safety Document 2013 JARNursingNowBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Math Calculations PDFDokumen32 halamanPediatric Math Calculations PDFNursingNow100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy: An Overview of Early Treatment ConsiderationsDokumen7 halamanBrachial Plexus Birth Palsy: An Overview of Early Treatment Considerationsphannghia.ydsBelum ada peringkat
- Oleh: Annisa Maharani 111 2016 2099 Pembimbing: Dr. Muslimin Ali, SP - AnDokumen9 halamanOleh: Annisa Maharani 111 2016 2099 Pembimbing: Dr. Muslimin Ali, SP - AnauliyaanandaBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Assessment Form AnalysisDokumen3 halamanPhysical Assessment Form AnalysisVishal PatleBelum ada peringkat
- Ellen Becker 2014Dokumen5 halamanEllen Becker 2014Nacho Cifuentes BlancBelum ada peringkat
- ABFAS Study GuideDokumen368 halamanABFAS Study GuideMohammed FarhanBelum ada peringkat
- Lower Body TestsDokumen49 halamanLower Body TestsLakshita PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Fundamental PositionsDokumen10 halamanIntroduction To Fundamental PositionsMuhammed Farhan BashirBelum ada peringkat
- Proper Postures for Zhineng Qigong PracticeDokumen70 halamanProper Postures for Zhineng Qigong Practiceeeklşeke kelekşlekBelum ada peringkat
- 2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDokumen3 halaman2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDi CanBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles Functions Exercises Pictures: 2. Biceps (Elbow Flexors)Dokumen5 halamanMuscles Functions Exercises Pictures: 2. Biceps (Elbow Flexors)Spongie BobBelum ada peringkat
- Dorian Yates WorkoutDokumen4 halamanDorian Yates WorkoutFrank Bookhardt100% (1)
- Axial DeformityDokumen58 halamanAxial DeformitynishantsinghbmeBelum ada peringkat
- Musculoskeletal Injuries GuideDokumen38 halamanMusculoskeletal Injuries GuideWindi PradnyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of The Upper and Lower LimbsDokumen67 halamanMuscles of The Upper and Lower LimbsAngel 冯晓君Belum ada peringkat
- Distal Radius FracturesDokumen259 halamanDistal Radius FracturesLuka Damjanovic100% (1)
- YogaRenew Flash CardsDokumen26 halamanYogaRenew Flash CardsKaterina FlegkaBelum ada peringkat
- Modified Duran Hand Therapy ProtocolDokumen4 halamanModified Duran Hand Therapy ProtocolkkBelum ada peringkat
- Management Menyscal PathologyDokumen201 halamanManagement Menyscal PathologyMaricruzhdezaBelum ada peringkat
- The Asics Natural Running GuideDokumen15 halamanThe Asics Natural Running GuideJavalinoshopBelum ada peringkat
- The Skeletal System: By: Jasper C. Pilongo, M.DDokumen110 halamanThe Skeletal System: By: Jasper C. Pilongo, M.Dash_zordickBelum ada peringkat
- Steven Angelo E. Cruz, PTRPDokumen130 halamanSteven Angelo E. Cruz, PTRPJoeBelum ada peringkat
- Chintan Rohitkumar Bhatt, Meenakshi Sanjay Modi, Chandrakant D MehtaDokumen4 halamanChintan Rohitkumar Bhatt, Meenakshi Sanjay Modi, Chandrakant D MehtaChintan BhattBelum ada peringkat
- Peter Duffie - ApplicationsDokumen59 halamanPeter Duffie - Applicationsbobbobov1Belum ada peringkat
- Acl Rehab ProtocolDokumen35 halamanAcl Rehab Protocolmatamea100% (3)
- Upper and Lower Extremities Oina: Vasquez, Eloiza Unice B. First Year Bs Physical TherapyDokumen60 halamanUpper and Lower Extremities Oina: Vasquez, Eloiza Unice B. First Year Bs Physical TherapyJonah DelmundoBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching The Hang Clean and Overcoming Common ObstaclesDokumen5 halamanTeaching The Hang Clean and Overcoming Common ObstaclesPaula BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Exploratory Latin Body PartsDokumen11 halamanExploratory Latin Body PartsKari Kristine Hoskins Barrera100% (1)
- Pocket PodDokumen656 halamanPocket PodchristineBelum ada peringkat
- 09.20-09.35 - DR - Dr.heri Suroto - When To OperateDokumen80 halaman09.20-09.35 - DR - Dr.heri Suroto - When To OperateJoseph WilsonBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Muscle Testing: Left Side Muscles Right SideDokumen2 halamanManual Muscle Testing: Left Side Muscles Right SideVaneet KumarBelum ada peringkat