Heart Notes
Diunggah oleh
Michael S. PetryDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Heart Notes
Diunggah oleh
Michael S. PetryHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
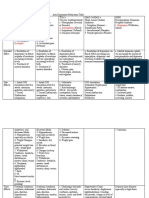
Right Atrium
Left Atrium
Right Ventricle
Left Ventricle
Interatrial septum Interventricular septum Fossa ovalis
Tricuspid (right AV valve) Bicuspid (Mitral) (left AV Valve) Aortic SL Valve Pulmonary SL valve
Prevents backflow into the left ventricle : Aortic SL Valve Prevents backflow into the right atrium : Tricuspid Prevents backflow into the right ventricle : Pulmonary SL valve Prevents backflow into the left atrium : Bicuspid (Mitral) What structural features are added to the AV valves to ensure one-way flow? Chordae tendineae Papillary muscles Why does blood not normally backflow from the great vessels to the ventricles? Semilunar valves, simple with no cords of connective tissue holding them in place Fibrous Pericardium Parietal Serous Pericaridial cavity Visceral peri=epicardium Myocardium Endocardium
What are the functions of the gap junctions? Allow ions to pass from cell to cell , allowing a current to transmit across the entire heart.
What are the other structural modifications of cardiac muscle that ensure proper functioning of the heart? Densemones are cell junctions within the intercalcated discs and anchor adjacent cells preventing them from separating during contraction. How does the presence of the slow calcium channels play a role in the length of cardiac muscle contraction? Na triggers open Ca channels to a low the entry of calcium. They open slowly and stay open longer.
1. action potential of skeletal muscle is caused almost entirely by sudden opening of large numbers of socalled fast sodium channels; remain open for only a few thousandths of a second (a) In cardiac muscle, the action potential is caused by opening of two types of channels: (1) the same fast sodium channels and (2) another entirely different population of slow calcium channels (calcium-sodium channels); slower to open, remain open for several tenths of a second (b) maintains a prolonged period of depolarization, causing the plateau in the action potential; calcium ions that enter during this plateau phase activate the muscle contractile process, while the calcium ions that cause skeletal muscle contraction are derived from the intracellular sarcoplasmic reticulum. Immediately after the onset of the action potential, the permeability of the cardiac muscle membrane for potassium ions decreases about fivefold, an effect that does not occur in skeletal muscle. a. When the slow calcium sodium channels do close at the end of 0.2 to 0.3 second and the influx of calcium and sodium ions ceases, the membrane permeability for potassium ions also increases rapidly
2.
What factors speed up the rate of contraction of cardiac muscle? What factors slow down the rate of contraction of cardiac muscle? Higher Potassium and sodium concentrations slow the heart rate. The charge surrounding the heart becomes more positive. It is harder to depolarize and contracts less often. Calcium increases, the rate increases because it depolarizes more frequently. What factors can cause a variation in these heart sounds?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Heart of The ProblemDokumen6 halamanThe Heart of The ProblemKeaton0% (1)
- Perfusion Review - Nclex TipsDokumen37 halamanPerfusion Review - Nclex TipsMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Perfusion. Shock - DicDokumen45 halamanPerfusion. Shock - DicMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Perfusion. Cad - Acs.miDokumen47 halamanPerfusion. Cad - Acs.miMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Perfusion. Dysrhythmias - Pacemaker.aicdDokumen41 halamanPerfusion. Dysrhythmias - Pacemaker.aicdMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Health Law and EthicsDokumen38 halamanPsychiatric Health Law and EthicsMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Affective Continuum: Depression Suicide BipolarDokumen73 halamanAffective Continuum: Depression Suicide BipolarMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Prozac Venlafaxine Duloxetine Amitriptyline BupropionDokumen3 halamanProzac Venlafaxine Duloxetine Amitriptyline BupropionMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Three Major Divisions of The Brain-Forebrain, Midbrain and HindbrainDokumen1 halamanWhat Are The Three Major Divisions of The Brain-Forebrain, Midbrain and HindbrainMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Cognition Concept .OCD - Schizophrenia.Delirum - DementiaDokumen64 halamanCognition Concept .OCD - Schizophrenia.Delirum - DementiaMichael S. PetryBelum ada peringkat
- Mitral Valve Disease: A Comprehensive ReviewDokumen8 halamanMitral Valve Disease: A Comprehensive ReviewArthurBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid HFDokumen9 halamanRapid HFDoc Tor StrangeBelum ada peringkat
- Case-Based Textbook of Echocardiography (PDFDrive)Dokumen572 halamanCase-Based Textbook of Echocardiography (PDFDrive)Ringo StoneBelum ada peringkat
- ROSELA, ERLAINE MARIE BSN 1F Heart-LabDokumen4 halamanROSELA, ERLAINE MARIE BSN 1F Heart-LabPado100% (1)
- الباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فوراDokumen163 halamanالباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فورانادين مطر0% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen35 halamanRheumatic Heart DiseaseSAYMABANUBelum ada peringkat
- Topic List Q&ADokumen63 halamanTopic List Q&APop D. MadalinaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Abbreviations - Flash CardsDokumen78 halamanNursing Abbreviations - Flash Cardsɹǝʍdןnos100% (4)
- Uia 14 Anaesthesia For Patients With Cardiac Disease Undergoing Non Cardiac SurgeryDokumen6 halamanUia 14 Anaesthesia For Patients With Cardiac Disease Undergoing Non Cardiac Surgerybhaskaracharya dontabhaktuniBelum ada peringkat
- Complications of Mitral Stenosis in PregnancyDokumen3 halamanComplications of Mitral Stenosis in PregnancyJulissapenacBelum ada peringkat
- Mitral Valve SurgeryDokumen2 halamanMitral Valve SurgeryLena MarieBelum ada peringkat
- Diastolic CHF DiagnosisDokumen3 halamanDiastolic CHF DiagnosissamBelum ada peringkat
- De La Salle University Medical Center Department of Obstetrics and GynecologyDokumen3 halamanDe La Salle University Medical Center Department of Obstetrics and GynecologyNehemiah FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Wanis H Ibrahim - Short and OSCE Cases in Internal Medicine - Clinical Exams For PACES, MRCPI, Arab Board and Similar Exams-Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (2020)Dokumen303 halamanWanis H Ibrahim - Short and OSCE Cases in Internal Medicine - Clinical Exams For PACES, MRCPI, Arab Board and Similar Exams-Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (2020)Daniah Marwan Dawood DAWOOD100% (1)
- 5Dokumen47 halaman5Nasti PalilingBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Valve Replacement SurgeryDokumen25 halamanCardiac Valve Replacement SurgeryJamalul AdilBelum ada peringkat
- Carbomedic StandardDokumen26 halamanCarbomedic Standardadel husseinBelum ada peringkat
- ECHO CensusDokumen9 halamanECHO CensusReda SoBelum ada peringkat
- Cvs MCQ Exam 2008Dokumen14 halamanCvs MCQ Exam 2008ZH. omg sarBelum ada peringkat
- Rheumatic Fever 2Dokumen4 halamanRheumatic Fever 2Radin Nurulfathiah RSuleimanBelum ada peringkat
- Four Chambers of The HeartDokumen7 halamanFour Chambers of The HeartJohn TecsonBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology Board QuestionsDokumen86 halamanPathology Board QuestionsJulius Matthew LuzanaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio Intensive ReviewDokumen40 halamanCardio Intensive ReviewAchilles YbarraBelum ada peringkat
- Percutaneous VR 2019Dokumen45 halamanPercutaneous VR 2019rantirunteaBelum ada peringkat
- Se Non-IschaemicDokumen40 halamanSe Non-IschaemicRui FonteBelum ada peringkat
- Soap CardiologyDokumen155 halamanSoap CardiologyTambunta Tarigan100% (5)
- Biology Grade 9 - Lesson NoteDokumen9 halamanBiology Grade 9 - Lesson NotemicahxBelum ada peringkat
- Valvular Heart Disease: Mitral RegurgitationDokumen33 halamanValvular Heart Disease: Mitral RegurgitationjihyooniBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Heart DiseasesDokumen4 halamanTypes of Heart DiseaseslalalallaBelum ada peringkat