Sub 1.5 Body Defence Mechanism
Diunggah oleh
liefeng810 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
4K tayangan17 halamanTo defend the body against disease-causing microorganism (pathogens) pathogens are bacteria, viruses and parasites Transmitted by air, contaminated food and water, animal (vector) and contaminated needles.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PPT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniTo defend the body against disease-causing microorganism (pathogens) pathogens are bacteria, viruses and parasites Transmitted by air, contaminated food and water, animal (vector) and contaminated needles.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
4K tayangan17 halamanSub 1.5 Body Defence Mechanism
Diunggah oleh
liefeng81To defend the body against disease-causing microorganism (pathogens) pathogens are bacteria, viruses and parasites Transmitted by air, contaminated food and water, animal (vector) and contaminated needles.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 17
LEARNING OUTCOMES
• To state another function of the
circulatory system
• To identify the three lines of
defence mechanism
• To describe phagocytosis
• To state the meaning of antigen
& antibody
WHY DO WE NEED THE
BODY’S DEFENCE
MECHANISM?
• To defend the body against
disease-causing
microorganism (pathogens)
• Pathogens are bacteria,
viruses & parasites
• Transmitted by air,
contaminated food & water,
animal (vector) &
contaminated needles. Also
by contact.
MAIN LINES OF DEFENCE
• Non-Specific
Defence : First line
defence & Second
line defence
• Specific Defence :
Third line defence
BODY’S DEFENCE MECHANISM
NON-SPECIFIC SPECIFIC
1ST LINE 2ND LINE 3RD LINE
SKIN : sweat, sebum Phagocytosis by Antibodies produced by
phagocytes lymphocytes
MUCOUS
MEMBRANES :
secretion of mucus
FIRST LINE of DEFENCE
• Skin – physical barrier (dead keratinised
layer difficult to penetrate
• If there is a cut, the blood clots quickly to
prevent blood loss & entry of m/organisms
• Tears secreted by tear gland & acidic sebum
(sebaceous gland) – contain lysozymes
which destroy some bacteria
• Mucus (mucous membrane) in nasal cavity
& trachea traps dust particles & microbial
spores
• The cilia (respiratory tract) sweep the
trapped particles to the pharynx swallow
SECOND LINE of
DEFENCE
• The phagocytic white blood cell are
attracted by chemicals produced at the
sites of infection and move to these
sites.
• Engulf & digest the pathogens
• The soluble products are absorbed &
assimilated by the phagocytes
• May also be destroyed by toxins
produced by the pathogens
• Number of leucocytes increases to try
to destroy the pathogen & neutralise
THIRD LINE of
MECHANISM
• In higher group of animals have a more specific immune
defence mechanism against pathogen IMMUNE
SYSTEM
• Two main types of lymphocytes :
– B-lymphocytes produce antibodies
– T-lymphocytes attack cells infected by pathogen or which
produce certain chemicals to coordinate the immunes response.
• ANTIGENS – large complex molecules
(proteins/polysaccharides) that the immune system recognises
as foreign found on the cell membrane of
m/organisms/dissolved in the blood plasma/interstitial fluid.
THIRD LINE of MECHANISM
(cont…)
• ANTIBODIES – A protein produced by
lymphocytes in response to the entry of an
antigen into the body.
• IMMUNE RESPONSE – interaction
between antibody & antigen which result
in the antigen being eliminated from the
body
MECHANISM TO DESTROY
ANTIGENS
AGGLUTINATION : the clumping of antigens easy
targets for phagocytes to destroy
NEUTRALISATION : toxin are made non-toxic by
reaction with the antibodies
LYSIS : lysin (antibodies) bind to antigens cause
antigens/pathogens to rupture
OPSONISATION : The binding of antibodies to
antigens stimulate phagocytes (macrophage) to
destroy the antigens.
• IMMUNITY : The state in which
the body is resistant to infection
by a disease-causing pathogens
@ the ability of an animal or
plant to resist infection by
pathogens
• IMMUNISATION : The process of
inducing immunity by
administering a vaccine
Defence system
Non specific Divided into
specific
is
Divided into
3rd line
1st line 2nd line through
eg are produce
lymphocyte antibody
Phagocyte
•Skin Carry out gives
immunity
•mucous Phagocytosis
Divided into
membrane passive active immunisation
Divided into Divided into
artificial natural natural artificial
VARIOUS TYPES OF
IMMUNITY
• ACTIVE IMMUNITY : when an
individual’s own immune system
produces its own antibodies to
defend against specific antigens
• Natural Active Immunity : after
recovered from certain disease
(examples : mumps, measles &
chicken pox)
• Artificial Active Immunity :
can be established upon
immunisation or vaccination.
(mumps, rubella, measles &
poliomyelitis)
VARIOUS TYPES of
IMMUNITY
• PASSIVE IMMUNITY : when an
individual is given the antibodies
required to defend against the
pathogen
• Natural Passive Immunity : when
antibodies produced by the mother
are passed across the placenta to the
foetus during development or in
early infancy through breast milk
(breast feeding). Colostrum (1st
formed milk) – rich in antibodies
• Artificial Passive Immunity : ready-made
antibody or serum is injected into the
individual. Prepared from cows or horses.
(rabies, hepatitis, tetanus & snakebites)
Ooo…sleeping in Biology
class ek?
So stubborn la.
Let me ‘teach’ U first before
Mr. FAZLI become angry!!!
Waa….mama!
Help me…. I don’t
want to fall asleep
in the class
anymore!!!
I SWEAR!!!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
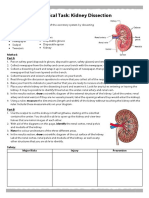
- Kidney Dissection Practical SheetDokumen3 halamanKidney Dissection Practical SheetIvona Matković100% (1)
- The Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationDokumen15 halamanThe Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationShee YingBelum ada peringkat
- Microorganisms: Friend or FoeDokumen14 halamanMicroorganisms: Friend or FoeGeetika100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDokumen27 halamanTransport in Plantspetar starkBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsDokumen12 halaman4 - Unicellular Structural AdaptationsNayani Snigdha0% (1)
- 7th Class Respiratory SystemDokumen14 halaman7th Class Respiratory SystemCas Tan100% (1)
- Patterns of InheritanceDokumen26 halamanPatterns of InheritanceVidhya NairBelum ada peringkat
- 8.cell Structure and FunctionsDokumen10 halaman8.cell Structure and Functionssharvan10Belum ada peringkat
- Start Up: Division OF Gen. Trias CityDokumen4 halamanStart Up: Division OF Gen. Trias CityJune Patrick AlleraBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Exercise 1 FillableDokumen16 halamanLaboratory Exercise 1 FillablePatricia Andrea Alexei FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 6 - CoordinationDokumen3 halamanIGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 6 - CoordinationHisokagen100% (2)
- Tropic and Taxic ResponsesDokumen3 halamanTropic and Taxic ResponsesSFbizBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Theory and Types of Microscopes - Print - QuizizzDokumen4 halamanCell Theory and Types of Microscopes - Print - QuizizzosamaBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Dissection Lab Report Guide (GALO)Dokumen6 halamanHeart Dissection Lab Report Guide (GALO)galo09landivar0902Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 - Media-Based Arts and Designs in The Philippines (Photography&Film)Dokumen28 halamanLesson 1 - Media-Based Arts and Designs in The Philippines (Photography&Film)Dan Alfred IsonBelum ada peringkat
- Test Cross WorksheetDokumen3 halamanTest Cross WorksheetAlbina YulmukhametovaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System WorksheetDokumen3 halamanNervous System WorksheetaBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic Table of ElementsDokumen76 halamanPeriodic Table of ElementsNursaiyidah RoniBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokumen20 halamanCell Structure and FunctionAPS UpdatesBelum ada peringkat
- Activity KMTDokumen3 halamanActivity KMTBoss Malupit sa CodesBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Circulatory SystemDokumen6 halamanLesson Plan Circulatory Systemapi-315857509Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan in SCIENCE 7-WPS OfficeDokumen8 halamanLesson Plan in SCIENCE 7-WPS OfficeBhea GasparBelum ada peringkat
- 5.1 Particle Theory of MatterDokumen1 halaman5.1 Particle Theory of Matterjohn doeBelum ada peringkat
- PDF Cell Structure and Function Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanPDF Cell Structure and Function Lesson PlanDaniel Okazaki0% (1)
- "Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)Dokumen1 halaman"Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)SusanAngDíaz0% (2)
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDokumen63 halamanCell Division Mitosis MeiosisRinBelum ada peringkat
- Mutations PowerpointDokumen40 halamanMutations Powerpointkurrupp k.pBelum ada peringkat
- Monosaccharides Formula Where Found: 4 QTR - Science The Chemistry of LifeDokumen7 halamanMonosaccharides Formula Where Found: 4 QTR - Science The Chemistry of LifeJune Emerson ManalangBelum ada peringkat
- 2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer-SNC2DDokumen2 halaman2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer-SNC2DBob Dharam0% (1)
- Directions: Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of Your Answer. I. Multiple ChoiceDokumen4 halamanDirections: Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of Your Answer. I. Multiple Choicejam syBelum ada peringkat
- Human Biology Part 1 FBDokumen56 halamanHuman Biology Part 1 FBJayjayjay 5Belum ada peringkat
- 16 Learning ObjectivesDokumen5 halaman16 Learning Objectivesapi-309893409Belum ada peringkat
- Land and Sea BreezesDokumen14 halamanLand and Sea BreezesClive John DelesBelum ada peringkat
- Self Desighned Lesson PlanDokumen15 halamanSelf Desighned Lesson PlansimikuttiyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan - Digital Pedagogy - GRADE 11 BIOLOGICAL CLASIFICATIONDokumen7 halamanLesson Plan - Digital Pedagogy - GRADE 11 BIOLOGICAL CLASIFICATIONshamshadBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Class Vii Respiration in Organisms MODULE (1/2)Dokumen2 halamanWorksheet Class Vii Respiration in Organisms MODULE (1/2)yash12312Belum ada peringkat
- Activity 3. CnidariansDokumen62 halamanActivity 3. CnidariansRangel Cuello100% (1)
- Act 7 Science PowerpointDokumen41 halamanAct 7 Science PowerpointBless CotingjoBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptation in PlantsDokumen19 halamanAdaptation in PlantsRACHIT MOHAN GUPTABelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 3 - Laboratory SafetyDokumen1 halamanWorksheet 3 - Laboratory Safetykkuma coupsBelum ada peringkat
- Differentiation Assignment 2-2Dokumen23 halamanDifferentiation Assignment 2-2api-295423685Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Dimensional HomogeneityDokumen4 halaman1 Dimensional HomogeneitySteven Kua100% (1)
- Class 8: Subject: Science Chapter 2-Microorganism: Friend and Foe WorksheetDokumen2 halamanClass 8: Subject: Science Chapter 2-Microorganism: Friend and Foe Worksheetazwin hasyanaBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 w18 QP 21-CIE-IGCSE-BiologyDokumen20 halaman0610 w18 QP 21-CIE-IGCSE-BiologyRahulBansuman100% (1)
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDokumen3 halamanThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJeffrey Selpo BondadBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDokumen62 halamanCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister Count100% (1)
- Class 5 Subject Science Chapter 5 Our Nervous SystemDokumen3 halamanClass 5 Subject Science Chapter 5 Our Nervous Systemhema7 lathaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life Practice Worksheet: (B) Golgi Apparatus (C) Cell Wall (D) Cytoplasm (E) NucleoplasmDokumen3 halamanChapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life Practice Worksheet: (B) Golgi Apparatus (C) Cell Wall (D) Cytoplasm (E) NucleoplasmSarwan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Reproduction Lesson PlanDokumen11 halamanReproduction Lesson PlanSHILPA AGARWALBelum ada peringkat
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures WS Vrishabh 1Dokumen7 halamanElements, Compounds and Mixtures WS Vrishabh 1Anand Kumar ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Mendelian Genetics PowerPoint Presentation - Free To Download - Id - 3b5e0a-NTQwZDokumen1 halamanNon-Mendelian Genetics PowerPoint Presentation - Free To Download - Id - 3b5e0a-NTQwZJuvan PauloBelum ada peringkat
- 16 - Development of Organisms and Continuity of Life: Candidates Should Be Able ToDokumen3 halaman16 - Development of Organisms and Continuity of Life: Candidates Should Be Able ToWeb BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptation in Plants PPT-4Dokumen13 halamanAdaptation in Plants PPT-4ARNAB GHOSH CLASS VBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Organisms-VMDokumen67 halamanClassification of Organisms-VMLee-Anne Lutchman100% (1)
- Chemistry Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanChemistry Lesson PlanLoire Aviles CollamatBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8Dokumen14 halamanGrade 8Dandan Ostria100% (1)
- Kidney Dissection Lab: EvaluationDokumen4 halamanKidney Dissection Lab: EvaluationmauvegamBelum ada peringkat
- (BIOLOGY) Cellular RespirationDokumen12 halaman(BIOLOGY) Cellular RespirationHAJIRA RAMLANBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ImmunityDokumen54 halamanIntroduction To ImmunityHadi Adam100% (1)
- Non Specific and Specific Host Defense MechanismDokumen7 halamanNon Specific and Specific Host Defense Mechanismcheskhadomingo33Belum ada peringkat
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDokumen59 halaman2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliefeng81100% (8)
- 2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inDokumen19 halaman2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inliefeng81100% (1)
- Science Form 1: CHAPTER 1: Introduction To ScienceDokumen3 halamanScience Form 1: CHAPTER 1: Introduction To Scienceliefeng81Belum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Cell OrganisationDokumen41 halaman2.1 Cell Organisationliefeng81100% (4)
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDokumen59 halaman2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliefeng81100% (8)
- 1.3 Steps in Scientific InvestigationDokumen10 halaman1.3 Steps in Scientific Investigationliefeng81100% (2)
- 2.1 - Cell FunctionDokumen29 halaman2.1 - Cell Functionliefeng81100% (2)
- Sub 1.6 CardioDokumen10 halamanSub 1.6 Cardioliefeng81Belum ada peringkat
- Journal Club Hepatitis BDokumen45 halamanJournal Club Hepatitis BMadeeha ArifBelum ada peringkat
- Infectious DermatologyDokumen206 halamanInfectious DermatologyAaron Christian Earl VillosoBelum ada peringkat
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D & EDokumen1 halamanHepatitis A, B, C, D & EMaryam FadahBelum ada peringkat
- Human Rabies in The PhilippinesDokumen2 halamanHuman Rabies in The PhilippinesAngeli SoabasBelum ada peringkat
- Dengue Fever (Nepal) An Emerging Public Health Problem.Dokumen13 halamanDengue Fever (Nepal) An Emerging Public Health Problem.Bzay DhitalBelum ada peringkat
- Infectious Diseases of CatsDokumen39 halamanInfectious Diseases of CatsMelanieBelum ada peringkat
- Viral Exanthem ManagementDokumen4 halamanViral Exanthem Managementrona ellein galoBelum ada peringkat
- The Hot Zone QuestionsDokumen8 halamanThe Hot Zone QuestionsGilbert1322Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 19 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityDokumen68 halamanChapter 19 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityAurea Nazaire100% (2)
- DengvaxiaDokumen1 halamanDengvaxiaAce Bryan Niño LlesolBelum ada peringkat
- Act 366 Poison Act 1952Dokumen124 halamanAct 366 Poison Act 1952saffwanBelum ada peringkat
- Veterinary Partner - VIN PDFDokumen6 halamanVeterinary Partner - VIN PDFsamuel AcostaBelum ada peringkat
- Roseola Infantum (Exanthem Subitum) Pathpophysiology: Infected Saliva by The HHV-6 VirusDokumen7 halamanRoseola Infantum (Exanthem Subitum) Pathpophysiology: Infected Saliva by The HHV-6 VirusElle RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- List of Parasites of Humans - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen12 halamanList of Parasites of Humans - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShailendra YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Dengue PreventionDokumen20 halamanDengue PreventionSharath WankdothBelum ada peringkat
- List of Zoonotic DiseasesDokumen1 halamanList of Zoonotic DiseasesHuyen J. DinhBelum ada peringkat
- AEHK Import Customs Hints PADokumen4 halamanAEHK Import Customs Hints PAKhairul IdhamBelum ada peringkat
- Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) : Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment, Prevention and ControlDokumen19 halamanEbola Virus Disease (EVD) : Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment, Prevention and ControlABc abcBelum ada peringkat
- Canine DiseasesDokumen5 halamanCanine Diseasessambhaji1976Belum ada peringkat
- Imunisasi Record - KennyDokumen1 halamanImunisasi Record - KennyrifiBelum ada peringkat
- Immunobiology NIOSDokumen16 halamanImmunobiology NIOSChetan MitraBelum ada peringkat
- Esumoh4 - Ebola - Specimen - Ar Oct 2014 PDFDokumen32 halamanEsumoh4 - Ebola - Specimen - Ar Oct 2014 PDFAbdulraheem HalawaniBelum ada peringkat
- EBOLADokumen2 halamanEBOLAamirBelum ada peringkat
- WS7 Bachti Alisjahbana - Pendekatan Klinis Demam Akut PDFDokumen47 halamanWS7 Bachti Alisjahbana - Pendekatan Klinis Demam Akut PDFWindy R. PutraBelum ada peringkat
- SodaPDF-converted-PANA LA PAGINA 436 High-Quality, High-Volume Spay and NeuterDokumen860 halamanSodaPDF-converted-PANA LA PAGINA 436 High-Quality, High-Volume Spay and NeuterAndreea MayaBelum ada peringkat
- Vmed 101 General Prinicples of Veterinary Medicine Course OutlineDokumen14 halamanVmed 101 General Prinicples of Veterinary Medicine Course OutlineCyntany poltsBelum ada peringkat
- Covid Vacc - Import Beneficiaries - GJ - Rajkot - IdaDokumen75 halamanCovid Vacc - Import Beneficiaries - GJ - Rajkot - IdaKartik R. MorjariaBelum ada peringkat
- Short Covid-19 Dialog 1Dokumen3 halamanShort Covid-19 Dialog 1karin kamilaBelum ada peringkat
- Iec DengueDokumen3 halamanIec DengueKeith Wesley YbutBelum ada peringkat
- Presentado Por: Pedro MoncadaDokumen10 halamanPresentado Por: Pedro MoncadaPedro Alejandro Moncada VelandiaBelum ada peringkat