Biokimi A
Diunggah oleh
Afrida SahestinaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Biokimi A
Diunggah oleh
Afrida SahestinaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Glandular Cell
Target Hormone Cell Receptor
V V H H H Blood vessel H H H H Hormone H H H H H
Grandular-and target cells
H V H H H H H
Endocrine
Paracrine
Autocrine
Endocrine, paracrine and autocrine effect of hormone
General features of signal
Types Solubility Transport proteins Plasma half life Receptor Mediator Group I Steroids, iodothyronines, calcitrol, retinoids Lipophilic Yes Long (hours to day) Intracellular Signal-receptor complex Group II Polypeptides, proteins, glycoproteins, catecholamines Hydrophilic No Short (minutes) Plasma membrane cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+, DAG, IP3, kinase cascades
The classes of hormones and hormonelike compounds, with some examples Hormone Peptide hormones Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Corticotropin (adrenocorticotropic hormone, ACTH) Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone, ADH) Insulin Glucagon Amine hormones Epinephrine (adrenaline) Thyroxine (Thyroid hormone) Steroid hormones Cortisol Aldosterone -Estradiol Testosterone Progesterone Eiscosonoids (hormonlike) Postaglandins Leukotrienes Thromboxanes Secreting organ/tissue/cells Hypothalamus Anterior Pituitary Posterior Pituitary Pancreas Pancreas Adrenal medulla Thyroid Adrenal cortex Adrenal cortex Ovary Testis Corpus luteum (in ovary) Function or activity Stimulates thyrotropin release from anterior pituitary Stimulates synthesis of aderenocortical steroids in adrenal cortex Increase blood pressure, promotes water reabsorption by kidney Stimulates glucose uptake and utilization Stimulates glucose production by liver Controls responses to stress, increases heart rate Stimulates metabolism in many tissues Limits glucose utilization, increase blood glucose Regulates sodium retention and blood pressure Regulates activity in Female reproductive tissues Regulates activity in male reproductive tissues Regulates activity in Female reproductive organs during menstrual cycle and pregenancy Trigger smooth muscle contraction; fever, inflammation Cause bronchial constriction; involved in hypersensitivity reaction Regulate blood clotting; vasoconstriction; pletelet aggregation
Most tissues Leukocytes (white blood cells), spleen others Platelets and other tissues
Receptor
Plasma membrane
Rec
Second messenger (e.g., cAMP) Altered transcription of specific genes Necleus
Altered activity of preexisting enzyme Altered amount of Newly synthesized proteins
Hypothetical Cell
Receptors for many Peptide hormones, Growth factors, and Amino acid-derived hormones (epineprhine)
Other stereoid hormones and their related receptors Nucleus
Cell membrane
Thyroid hormon receptor Hormone
Cytoplasm
Specifik steroid (glucocorticoid) Hormone receptor
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Daftar PustakaDokumen1 halamanDaftar PustakaAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- ThoraxDokumen32 halamanThoraxAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Early Goal-Direct Therapy in The Treatment of Severe Sepsis and Septic ShockDokumen32 halamanEarly Goal-Direct Therapy in The Treatment of Severe Sepsis and Septic ShockAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- EcgDokumen23 halamanEcgAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Miliary Tuberculosis Is Characterized by A ChronicDokumen1 halamanMiliary Tuberculosis Is Characterized by A ChronicAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolyte and Metabolic DisturbancesDokumen27 halamanElectrolyte and Metabolic DisturbancesAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Miliary Tuberculosis Is Characterized by A ChronicDokumen1 halamanMiliary Tuberculosis Is Characterized by A ChronicAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Controversies in Cesarean Delivery AnesthesiaDokumen4 halamanControversies in Cesarean Delivery AnesthesiaAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- TuberculosisDokumen1 halamanTuberculosisAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Do2 Vo2 FluidDokumen21 halamanDo2 Vo2 FluidAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg T-Wave Changes in The Pacu - Bad or BenignDokumen34 halamanEcg T-Wave Changes in The Pacu - Bad or BenignAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg T-Wave Changes in The Pacu - Bad or BenignDokumen34 halamanEcg T-Wave Changes in The Pacu - Bad or BenignAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Evidence-Based Management of Postoperative PainDokumen1 halamanEvidence-Based Management of Postoperative PainAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency DrugsDokumen22 halamanEmergency DrugsAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- ICE-ACT CPR GuideDokumen12 halamanICE-ACT CPR GuideEsha KohalBelum ada peringkat
- Ekg 1Dokumen23 halamanEkg 1Afrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- DRUGS AND DEFIBRILLATION IN CARDIAC ARRESTDokumen20 halamanDRUGS AND DEFIBRILLATION IN CARDIAC ARRESTAfrida Sahestina100% (1)
- Evidence-Based Management of Postoperative PainDokumen1 halamanEvidence-Based Management of Postoperative PainAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Akses Vena Central: Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi RSUD TasikmalayaDokumen28 halamanAkses Vena Central: Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi RSUD TasikmalayaSaeful AmbariBelum ada peringkat
- A Better Approach To Acid-Base BalanceDokumen1 halamanA Better Approach To Acid-Base BalanceErinne DefrianiBelum ada peringkat
- Update On Perioperative Brain ProtectionDokumen3 halamanUpdate On Perioperative Brain ProtectionAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Gastrointestinal EmergenciesDokumen25 halamanAcute Gastrointestinal EmergenciesAziz AndrianaBelum ada peringkat
- TuberculosisDokumen1 halamanTuberculosisAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Anesthesia For High Risk PatientDokumen5 halamanAnesthesia For High Risk PatientAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- The Role of The AnaesthetistDokumen3 halamanThe Role of The AnaesthetistAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
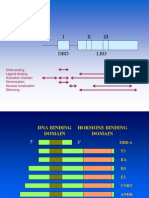
- Nuclear hormone receptors: DNA binding and activationDokumen6 halamanNuclear hormone receptors: DNA binding and activationAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Which Dial Do I Turn!? Essence of Mechanical VentilationDokumen54 halamanWhich Dial Do I Turn!? Essence of Mechanical VentilationKang Wisit TheaBelum ada peringkat
- Update On Perioperative Brain ProtectionDokumen3 halamanUpdate On Perioperative Brain ProtectionAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- RedDokumen49 halamanRedAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- BiokimiaDokumen8 halamanBiokimiaAfrida SahestinaBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Insights Into Veterinary Endocrinology - Diagnostic Approach To PU - PD - Urine Specific GravityDokumen4 halamanInsights Into Veterinary Endocrinology - Diagnostic Approach To PU - PD - Urine Specific GravityHusnat hussainBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Crisis: Case ReportDokumen1 halamanThyroid Crisis: Case ReportJailani FajriBelum ada peringkat
- Veterinary Medical Terminology: Dr.H.HoseinzadehDokumen16 halamanVeterinary Medical Terminology: Dr.H.HoseinzadehJuk CondeBelum ada peringkat
- Project - : Menstrual CycleDokumen20 halamanProject - : Menstrual CycleJIBAN KUMAR DASBelum ada peringkat
- Menstrual DisordersDokumen16 halamanMenstrual DisordersKamran khanBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd (Integumentary Activity)Dokumen3 halaman2nd (Integumentary Activity)Yma FeelBelum ada peringkat
- Eaching THE GE OF DolescenceDokumen14 halamanEaching THE GE OF DolescenceSundeep GargBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen2 halamanDaftar PustakaJalalludin AnBelum ada peringkat
- Powerpoint Templates Medical FreeDokumen25 halamanPowerpoint Templates Medical FreeBen IntosiusBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 8 Science, Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDokumen5 halamanCBSE Class 8 Science, Reaching The Age of AdolescenceR.Shruti 1040-12Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 50Dokumen79 halamanChapter 50latrishahollmonBelum ada peringkat
- The Thyroid ReviewDokumen2 halamanThe Thyroid Reviewwest alabamaBelum ada peringkat
- Graves' Disease Features in 40 CharactersDokumen41 halamanGraves' Disease Features in 40 CharactersVaanipriya RaoBelum ada peringkat
- GP Balance Themethod PaginaDokumen163 halamanGP Balance Themethod PaginaPedro100% (1)
- Thyroid Disorders in Patients With MelasmaDokumen8 halamanThyroid Disorders in Patients With MelasmaIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid ScintigraphyDokumen7 halamanThyroid ScintigraphyadaniBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Toxic Goiter and Its Nursing CareDokumen22 halamanUnderstanding Toxic Goiter and Its Nursing CareJohn Matley Caampued100% (2)
- Hormonal Cycles: Presented By: Miss. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorDokumen23 halamanHormonal Cycles: Presented By: Miss. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorKaku ManishaBelum ada peringkat
- Hormone Role in Reproductive HealthDokumen7 halamanHormone Role in Reproductive HealthLouina Fernandez Atlas100% (1)
- Physiological Control and Mechanism of Salivation: DR Oyetola Elijah Senior Lecturer/Consultant Oral Medicine, OAU/OAUTHCDokumen19 halamanPhysiological Control and Mechanism of Salivation: DR Oyetola Elijah Senior Lecturer/Consultant Oral Medicine, OAU/OAUTHCJoe AjibadeBelum ada peringkat
- Iflash 1800 Kits Quotation For Yhlo ProductsDokumen3 halamanIflash 1800 Kits Quotation For Yhlo ProductsMohad Asdel100% (1)
- Dr. Amit KumarDokumen73 halamanDr. Amit KumarradhikasreedharBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System Review MSDokumen39 halamanThe Endocrine System Review MSMay Chelle ErazoBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine GlandsDokumen3 halamanThe Endocrine GlandsAshtua MandixBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Freeze Dried Extract of Olea Europaea On The Pituitary-Thyroid Axis in RatsDokumen2 halamanEffect of Freeze Dried Extract of Olea Europaea On The Pituitary-Thyroid Axis in RatsyigalbyBelum ada peringkat
- Delamide, Reproductive System Anaphy LabDokumen5 halamanDelamide, Reproductive System Anaphy LabKristine Lorainne DelamideBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy FinalDokumen60 halamanThyroid Disorders in Pregnancy Finalmonica caballes100% (1)
- Humaclia 150 Assay Sheet enDokumen2 halamanHumaclia 150 Assay Sheet enNghi NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Agenda Rapat Bagian: Rabu, 12 Desember 2018Dokumen10 halamanAgenda Rapat Bagian: Rabu, 12 Desember 2018Puspitasari NotohatmodjoBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To A Patient With "Solitary Thyroid Nodule" (STN)Dokumen6 halamanApproach To A Patient With "Solitary Thyroid Nodule" (STN)Jacob Alexander MarpaungBelum ada peringkat