Nuclear Power Plant
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Ahkam KhanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nuclear Power Plant
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Ahkam KhanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MUHAMMAD AHKAM KHAN (09-6394) MUHAMMAD WAQAR (09-6391)
Nuclear fuel is any material that can be consumed to derive nuclear energy. The most common type of nuclear fuel is fissile elements that can be made to undergo nuclear fission chain reactions in a nuclear reactor.
The most common nuclear fuels are 235U and 239Pu. Not all nuclear fuels are used in fission chain reactions.
When a neutron strikes an atom of uranium, the uranium splits into two lighter atoms and releases heat simultaneously.
Fission of heavy elements is an exothermic
reaction which can release large amounts of
energy both as electromagnetic radiation and
as kinetic energy of the fragments.
A chain reaction refers to a process in which neutrons released in fission produce an additional fission in at least one further nucleus. This nucleus in turn produces neutrons, and the process repeats. If the process is controlled it is used for nuclear power or if uncontrolled it is used for nuclear weapons.
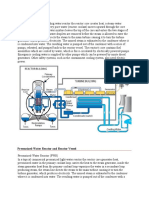
A major design advantage is the fact that fuel leaks, such as ruptured fuel rods, are isolated in the core and primary loop. That is, radioactive material contained inside the fuel is not allowed to go outside of the containment shell. The pressurized water reactor can be operated at higher temperature/pressure combinations, and this allows an increase in the efficiency of the turbine generator system. Another advantage is that it is believed that a pressurized water reactor is more stable than other designs. This is because boiling is not allowed to take place inside the reactor vessel.
The coolant water must be highly pressurized to remain liquid at high temperatures. This requires high strength piping and a heavy pressure vessel and hence increases construction costs. Under certain circumstances, the pressurized water reactor can produce power at a faster rate than the cooling water can remove heat. If this event takes place, there is a high probability of fuel rod damage.
A major advantage of the BWR is that the overall thermal efficiency is greater than that of a pressurized water reactor because there is no separate steam generator or heat exchanger. Controlling the reactor is a little easier than in a PWR because it is accomplished by controlling the flow of water through the core. Increasing the water flow increases the power generated. Because of the nature of the design, the reactor vessel is subjected to less radiation, and this is considered to be an advantage because some steels become brittle with exposure to excessive radiation.
Much larger pressure vessel than for a PWR of similar power, with correspondingly higher cost. This larger pressure vessel also increases the cost of the BWR. The design does allow a small amount of radioactive contamination to get into the turbine system. This modest radioactivity requires that anybody working on the turbine must wear appropriate protective clothing and use the proper equipment.
A nuclear reactor is a device in which nuclear chain reactions are initiated, controlled, and sustained at a steady rate, as opposed to a nuclear bomb, in which the chain reaction occurs in a fraction of a second and is uncontrolled causing an explosion.
Control rods, made of a material that absorbs neutrons are inserted into the reactor to control the nuclear reaction using a mechanism that
can rise or lower the control rods.
The control rods essentially contain neutron
absorbers like, boron, cadmium or indium.
Steam generators are heat exchangers used to convert water into steam from heat produced in a nuclear reactor core.
Either ordinary water or heavy water is used as
the coolant.
A steam turbine is a mechanical device that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam, and converts it into useful mechanical
energy.
Various high-performance alloys and super
alloys have been used for steam generator
tubing.
The coolant pump pressurizes the coolant to pressures of the order of 155bar.
The pressure of the coolant loop is maintained almost constant with the help of the pump and a pressurizer unit.
Steam coming out of the turbine, flows through the condenser for condensation and recirculated for the next cycle of operation.
The feed pump circulates the condensed water
in the working fluid loop.
Condenser is a device or unit which is used to condense vapor into liquid.
The objective of the condenser is to reduce the
turbine exhaust pressure to increase the efficiency
and to recover high quality feed water in the form of condensate & feed back it to the steam generator without any further treatment.
Cooling towers are heat removal devices used to transfer process waste heat to the atmosphere.
Water circulating through the condenser is
taken to the cooling tower for cooling and
reuse.
Nuclear power generation does emit relatively low
amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2). The emissions of
green house gases and therefore the contribution of nuclear power plants to global warming is therefore
relatively little.
This technology is readily available, it does not have to be developed first. It is possible to generate a high amount of electrical energy in one single plant.
The problem of radioactive waste is still an unsolved one. It is technically impossible to build a plant with
100% security.
The energy source for nuclear energy is Uranium. Uranium is a scarce resource, its supply is estimated to last only for the next 30 to 60 years depending on the actual demand.
Nuclear power plants as well as nuclear waste could be preferred targets for terrorist attacks..
During the operation of nuclear power plants, radioactive waste is produced, which in turn can be used for the production of nuclear
weapons.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NuclearDokumen18 halamanNuclearapi-238832008Belum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Plant ReportDokumen9 halamanNuclear Power Plant ReportJIL IbaanBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclearpowerplant SeminarDokumen16 halamanNuclearpowerplant Seminarraghavendra DBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurDokumen27 halamanNuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurNikhil ChopraBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Plant: Seminar ONDokumen18 halamanNuclear Power Plant: Seminar ONAmit Singh DehuryBelum ada peringkat
- Prepared By: Escolano, John John P. Bsme-VDokumen21 halamanPrepared By: Escolano, John John P. Bsme-VJohn John IscoBelum ada peringkat
- What Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Dokumen3 halamanWhat Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Rahul GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantADokumen13 halamanAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantAtheunsung tale100% (1)
- Energy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50Dokumen3 halamanEnergy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50pagal noobBelum ada peringkat
- NuclearDokumen18 halamanNuclearJaat Pankaj BurraBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear MeDokumen20 halamanNuclear MeJaat Pankaj BurraBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantDokumen13 halamanAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantVinay Rai100% (3)
- How Does A Nuclear Power Plant Work?Dokumen4 halamanHow Does A Nuclear Power Plant Work?Cherry ObiasBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water ToDokumen5 halamanNuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water ToYash SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Reactors: Presented To: Sir Aiman ShabbirDokumen33 halamanNuclear Reactors: Presented To: Sir Aiman Shabbirabubakar chohaanBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Reactor and Power Plant:: Research Reactors Are Operated at Universities and Research CentresDokumen19 halamanNuclear Reactor and Power Plant:: Research Reactors Are Operated at Universities and Research CentresNiteshBhuwaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Plant - WikipediaDokumen19 halamanNuclear Power Plant - Wikipediashrawani waghBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear EnergyDokumen4 halamanNuclear EnergyAkshara K VijayBelum ada peringkat
- NuclearDokumen49 halamanNuclearA ABHISHEK MARSHALLBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power PlantDokumen13 halamanNuclear Power PlantlintangellaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power: An Operation Management Presentation OnDokumen5 halamanNuclear Power: An Operation Management Presentation OnArif KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Isotopes U U MevDokumen5 halamanIsotopes U U MevPrasath CkBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power PlantDokumen12 halamanNuclear Power PlantAnil BhattaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power PlantDokumen23 halamanNuclear Power Plantvish0909Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Layout and Working of A Nuclear Power PlantDokumen3 halamanBasic Layout and Working of A Nuclear Power Plantsaranya saiganeshBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Nuclear ReactorDokumen32 halamanTypes of Nuclear Reactorsapna100% (1)
- 2 - Classification of ReactorsDokumen28 halaman2 - Classification of Reactorspothuraju harithaBelum ada peringkat
- NuclearPowerReactors AnOverviewDokumen11 halamanNuclearPowerReactors AnOverviewcdnaveenBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Power PlantDokumen12 halamanTypes of Power PlantJonaz CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Submitted By: M David SamuelDokumen14 halamanSubmitted By: M David SamueltpatruniBelum ada peringkat
- Types of ReactorsDokumen4 halamanTypes of ReactorsPawan PuniaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Reactor: Ejaz Ahmad B.Tech ChemicalDokumen22 halamanNuclear Reactor: Ejaz Ahmad B.Tech ChemicalEjaz Ahmad100% (1)
- 8.1 Nuclear Reactors and Nuclear SafetyDokumen2 halaman8.1 Nuclear Reactors and Nuclear SafetyHAN SEUL SHIMBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear PowerplantDokumen5 halamanNuclear PowerplantAri HariBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear EnergyDokumen2 halamanNuclear Energydhyeypatel2701Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Project - Nuclear ReactorDokumen8 halamanPhysics Project - Nuclear Reactormunmun ghoshBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteDokumen15 halamanNuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteRonald Andrei DaguioBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2Dokumen43 halamanUnit 2A ABHISHEK MARSHALLBelum ada peringkat
- Reactor, Its Components, TypesDokumen32 halamanReactor, Its Components, TypesAzhar AliBelum ada peringkat
- STEAM Script GeoDokumen3 halamanSTEAM Script GeoKHAING LYNNBelum ada peringkat
- The Physics Behind The Working Of: Made By-Taniya Gupta B.SC Phy (H) II Yr. Miranda HouseDokumen19 halamanThe Physics Behind The Working Of: Made By-Taniya Gupta B.SC Phy (H) II Yr. Miranda HouseTaniya GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Sudan University of Science and Technology College of Engineering School of Electrical and Nuclear Engineering Department of Nuclear Engineering Assignment On: Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)Dokumen19 halamanSudan University of Science and Technology College of Engineering School of Electrical and Nuclear Engineering Department of Nuclear Engineering Assignment On: Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)امجداحمدBelum ada peringkat
- IV SolutionDokumen35 halamanIV SolutionAnonymous t3GcHwKMBBelum ada peringkat
- Neuclear Power Plants PresentationDokumen24 halamanNeuclear Power Plants PresentationShreeBelum ada peringkat
- Mining and Processing Uranium OreDokumen12 halamanMining and Processing Uranium OredeesingBelum ada peringkat
- Class 6. Nuclear Power PlantDokumen25 halamanClass 6. Nuclear Power PlantsureshlalBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power PlantDokumen7 halamanNuclear Power PlantzzaanBelum ada peringkat
- Operation of A Nuclear Power PlantDokumen8 halamanOperation of A Nuclear Power PlantMuhamad FaizBelum ada peringkat
- Power Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?Dokumen8 halamanPower Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?Shahrukh123456789Belum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Reactors: Components of A Nuclear ReactorDokumen23 halamanNuclear Power Reactors: Components of A Nuclear ReactorBenjamin LukeBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar On Nuclear Reactor: Bhabani Sankar Hota ROLL NO - 107EE007Dokumen28 halamanSeminar On Nuclear Reactor: Bhabani Sankar Hota ROLL NO - 107EE007Saptarshi Pal ChaudhuriBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power ReactorsDokumen10 halamanNuclear Power ReactorsJos TeixeiraBelum ada peringkat
- Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRS) Constitute The Large Majority of All WesternDokumen3 halamanPressurized Water Reactors (PWRS) Constitute The Large Majority of All WesternAnkit SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Station or Nuclear Power PlantDokumen3 halamanNuclear Power Station or Nuclear Power Plantkkt29Belum ada peringkat
- Types of ReactorDokumen3 halamanTypes of ReactorTariq AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Nuclar Plant OperationDokumen15 halamanBasics of Nuclar Plant OperationPrashant TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- UGC - 9 - Ali HosinDokumen7 halamanUGC - 9 - Ali HosinVIKRAM KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Nuclear ReactorDokumen12 halamanWhat Is A Nuclear ReactorShams ShamsBelum ada peringkat
- of Types of Nuclear ReactorDokumen33 halamanof Types of Nuclear Reactormandhir67% (3)
- Satellite Phone CommunicationDokumen12 halamanSatellite Phone CommunicationMuhammad Ahkam KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Polarization PresentationDokumen17 halamanPolarization PresentationMuhammad Ahkam KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Satellite Phone: Muhammad Ahkam Khan (09-6394)Dokumen11 halamanSatellite Phone: Muhammad Ahkam Khan (09-6394)Muhammad Ahkam KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 1 Introduction To MatlabDokumen4 halamanLab 1 Introduction To MatlabMuhammad Ahkam KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Whether Ordinance On Self-Denial of Nuclear Power Harmful To IndiaDokumen55 halamanWhether Ordinance On Self-Denial of Nuclear Power Harmful To IndiabksubbaraoBelum ada peringkat
- Calibration of Radiation Protection Monitoring InstrumentsDokumen162 halamanCalibration of Radiation Protection Monitoring InstrumentsalbertoprassBelum ada peringkat
- 1112 Cheat SheetDokumen1 halaman1112 Cheat SheetShuyao LiBelum ada peringkat
- Ionization ChamberDokumen42 halamanIonization ChamberRabia AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- ActiniumDokumen7 halamanActiniumKevinBelum ada peringkat
- Class 12 Cbse Physics Syllabus 2012-13Dokumen7 halamanClass 12 Cbse Physics Syllabus 2012-13Sunaina RawatBelum ada peringkat
- 50 Years of Quantum Chromodynamics: A B C DDokumen729 halaman50 Years of Quantum Chromodynamics: A B C DArchana RadhakrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Formation of Heavy ElementsDokumen27 halamanPhysical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Formation of Heavy ElementsMary Ann Isanan89% (46)
- 5 Xray Interaction With MatterDokumen3 halaman5 Xray Interaction With MatterCaution CautionBelum ada peringkat
- Unclassified: Operating Limits and Conditions P-50099Dokumen17 halamanUnclassified: Operating Limits and Conditions P-50099Patrick AyanBelum ada peringkat
- The First Reactor - Chicago Pile 1.CP-1. 40th Anniversary.1982 DOEDokumen51 halamanThe First Reactor - Chicago Pile 1.CP-1. 40th Anniversary.1982 DOEjleydencoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3-2d-3d-nmrDokumen104 halamanChapter 3-2d-3d-nmrMELVINDO JACOBBelum ada peringkat
- RT WordDokumen30 halamanRT WordKarthikeyan P100% (1)
- 5 Chain r1Dokumen13 halaman5 Chain r1Seaw Rio Rj100% (1)
- 4 Atoms - The Inside StoryDokumen4 halaman4 Atoms - The Inside Storypianosheet123Belum ada peringkat
- The War That Must Never Be Fought - Ch. 13-14, Edited by George P. Shultz and James E. GoodbyDokumen96 halamanThe War That Must Never Be Fought - Ch. 13-14, Edited by George P. Shultz and James E. GoodbyHoover InstitutionBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Reactions and Nuclear Structure: P. E HodgsonDokumen1 halamanNuclear Reactions and Nuclear Structure: P. E HodgsonAndrésBelum ada peringkat
- SA Nuke IndustryDokumen25 halamanSA Nuke IndustryMojalefa MurphyBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power Plant Engineering - BUETDokumen79 halamanNuclear Power Plant Engineering - BUET0410058100% (6)
- F2 MAR 01 Electric ChargeDokumen25 halamanF2 MAR 01 Electric ChargeJack OlanternBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Elsus 2Dokumen10 halamanSoal Elsus 2Istinganatun KhoeriyahBelum ada peringkat
- Sas7 STM-005Dokumen6 halamanSas7 STM-005mayasBelum ada peringkat
- SR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XIV (NUCLEI)Dokumen18 halamanSR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XIV (NUCLEI)sojakoj867Belum ada peringkat
- Half lifeSEDokumen4 halamanHalf lifeSERusty WynderBelum ada peringkat
- 6011931b en Radiation Survey Meters WP W - 9Dokumen8 halaman6011931b en Radiation Survey Meters WP W - 9César SánchezBelum ada peringkat
- Fukushima Nuclear Disaster - ScriptDokumen2 halamanFukushima Nuclear Disaster - ScriptRosa SeijasBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 - Basic Notions of Nuclear Reactor PhysicsDokumen43 halamanTopic 1 - Basic Notions of Nuclear Reactor PhysicsSit LucasBelum ada peringkat
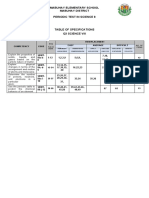
- Science 8 Q3 Periodic Exam Blooms Taxo With Answer KeyDokumen6 halamanScience 8 Q3 Periodic Exam Blooms Taxo With Answer KeyPantz Revibes Pastor100% (1)
- Nuclear Power Plant: A.N.Khudaiwala (L.M.E) G.P.PorbandarDokumen78 halamanNuclear Power Plant: A.N.Khudaiwala (L.M.E) G.P.PorbandarmharitmsBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 - Chemical Kinetics 4b - Half LifeDokumen20 halamanTopic 4 - Chemical Kinetics 4b - Half LifeJoshua LaBordeBelum ada peringkat