Telecom Industry: Consulting Club, IIM Calcutta
Diunggah oleh
MARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHI0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
876 tayangan6 halamantelecom
Judul Asli
Telecom
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Initelecom
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
876 tayangan6 halamanTelecom Industry: Consulting Club, IIM Calcutta
Diunggah oleh
MARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHItelecom
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
Telecom Industry
Consulting Club, IIM Calcutta
Industry Statistics
Revenue
Category Growth(%)
in Million
2002-03 2001-02
Access Services
Basic Services 3804 3488 9.05
Cellular Services 1093 726 50.5
Other Services
NLD Services NLD Services 786 991 -20.7
ILD Services 716 902 -20.5
Internet Services 76 148 14.3
VSAT Services (Only services) 30 27 9.7
Radio Trunking Services 6.18 3.42 80.87
Others 23 19 24.1
Grand Total of Telecom Industry 6626 6304 5.11
Others include infrastructure providers,
paging services and unified messaging
services
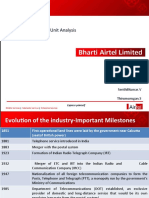
History of the Telecom Industry
1851 First operational land lines were laid by the government near
Calcutta (seat of British power)
1881 Telephone service introduced in India
1883 Merger with the postal system
1923 Formation of Indian Radio Telegraph Company (IRT)
1932 Merger of ETC and IRT into the Indian Radio and Cable
Communication Company (IRCC)
1947 Nationalization of all foreign telecommunication companies to
form the Posts, Telephone and Telegraph (PTT), a monopoly
run by the government's Ministry of Communications
1985 Department of Telecommunications (DOT) established, an
exclusive provider of domestic and long-distance service that
would be its own regulator (separate from the postal system)
1986 Conversion of DOT into two wholly government-owned
companies: the Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited (VSNL) for
international telecommunications and Mahanagar Telephone
Nigam Limited (MTNL) for service in metropolitan
areas.1997Telecom Regulatory Authority of India created.
1999 Cellular Services are launched in India, New National
Telecom Policy is adopted.
2000 DoT becomes a corporation, BSNL
Key Market Players
Company Million % share
Subs
(Nov 2003)
Hexacom
BSNL 40.3 58.8
Fascel Reliance 6.1 8.9
Bharti 5.7 8.3
SP ICE MTNL 4.9 7.2
Hutchinson 2.9 4.2
BPL Idea 2.1 3.0
Cellular
Hutchinson BPL 1.4 2.1
Tata Tele. 1.3 1.9
Bharti SPICE 1.0 1.4
Escotel 0.8 1.1
BSNL
Fascel 8.1 1.1
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Aircel 0.9 1.4
Market S hares Hexacom 0.2 0.3
Constraints
Slow pace of the reform process .
It would be difficult to make in-roads into the semi-rural and
rural areas because of the lack of infrastructure. The service
providers have to incur a huge initial fixed cost to make
inroads into this market. Achieving break-even under these
circumstances may prove to be difficult.
The sector requires players with huge financial resources
due to the above mentioned constraint. Upfront entry fees
and bank guarantees represent a sizeable share of initial
investments. While the criteria are important, it tends to
support the existing big and older players. Financing these
requirements require a little more liberal approach from the
policy side.
Problem of limited spectrum availability and the issue of
interconnection charges between the private and state
operators.
Future Trends
further liberalization,
Increase in the Spectrum.
Consolidation of the smaller players.
convergence of technologies & the
ability of private players to offer it to
the market faster than the incumbent
operator.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mobile Radio Network Design in the VHF and UHF Bands: A Practical ApproachDari EverandMobile Radio Network Design in the VHF and UHF Bands: A Practical ApproachBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Industry in IndiaDokumen12 halamanTelecom Industry in IndiaanuragmsrcascBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Industry: Consulting Club, IIM CalcuttaDokumen6 halamanTelecom Industry: Consulting Club, IIM CalcuttaNitin KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Bharti Airtel Strategy FinalDokumen39 halamanBharti Airtel Strategy FinalniksforloveuBelum ada peringkat
- The Hutchinson Essar Acquisition: International Strategic Management June 1st 2010Dokumen37 halamanThe Hutchinson Essar Acquisition: International Strategic Management June 1st 2010Pritha GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Top 30 Telecom Companies in India by Market CapDokumen2 halamanTop 30 Telecom Companies in India by Market CapcatchvidhBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Industry FinalDokumen35 halamanTelecom Industry FinalyashodhanmundraBelum ada peringkat
- AIRTELDokumen49 halamanAIRTELSaroj MuduliBelum ada peringkat
- Tier 1 Internet ProvidersDokumen2 halamanTier 1 Internet ProvidersdroidBelum ada peringkat
- Public Knowledge Berkman Comments Addenda in FCC GN 09 47 Filed 11-16-2009Dokumen17 halamanPublic Knowledge Berkman Comments Addenda in FCC GN 09 47 Filed 11-16-2009StimulatingBroadband.comBelum ada peringkat
- Top 10 Mobile Operators With Subscribers Wise & Market Share Wise of IndiaDokumen1 halamanTop 10 Mobile Operators With Subscribers Wise & Market Share Wise of IndiaNandeep VermaBelum ada peringkat
- 11 - Chapter 2 PDFDokumen56 halaman11 - Chapter 2 PDFAmrutha gopinathBelum ada peringkat
- BhartiDokumen9 halamanBhartiabhijitBelum ada peringkat
- Annual Report of Airtel: - A.VinaykumarDokumen49 halamanAnnual Report of Airtel: - A.VinaykumarVinay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Bharti 2airtel 1227851581611151 8Dokumen49 halamanBharti 2airtel 1227851581611151 8Ramendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bharti-Airtel StrategyDokumen52 halamanBharti-Airtel Strategyshree0312Belum ada peringkat
- Telecom - Industry - v.1 The Full and FinalDokumen56 halamanTelecom - Industry - v.1 The Full and FinalSanjeev SoodBelum ada peringkat
- TELECOM INDUSTRY FinalDokumen25 halamanTELECOM INDUSTRY FinalShameek ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- General Packet Radio Service: Report Compiled By: Rajeev NavalDokumen19 halamanGeneral Packet Radio Service: Report Compiled By: Rajeev Navalrajeev_navalBelum ada peringkat
- Impact of Increasing Competition in Indian Telecom SectorDokumen17 halamanImpact of Increasing Competition in Indian Telecom SectorSailesh NallapothuBelum ada peringkat
- Thuckalay Approval MergedDokumen4 halamanThuckalay Approval MergedbalaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On Telecommunication Industry - Vodafone vs. BSNLDokumen23 halamanPresentation On Telecommunication Industry - Vodafone vs. BSNLBhavna DuggalBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Telecom SectorDokumen30 halamanAnalysis of Telecom Sectorajay gehlotBelum ada peringkat
- Source: From 20 OCT, 2010 From 20 OCT, 2010Dokumen13 halamanSource: From 20 OCT, 2010 From 20 OCT, 2010nandinee15Belum ada peringkat
- Order: Subscriber Base (In Lakh) Supported by GSM Spectrum in Mhz. (Eligibility For Allotment of Next Step)Dokumen1 halamanOrder: Subscriber Base (In Lakh) Supported by GSM Spectrum in Mhz. (Eligibility For Allotment of Next Step)Ashish KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom SectorDokumen39 halamanTelecom SectorRashmi GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Industry: IndiaDokumen39 halamanTelecom Industry: IndiaskaleemohdBelum ada peringkat
- Information Note To The Press (Press Release No. 66 /2010) Telecom Regulatory Authority of IndiaDokumen10 halamanInformation Note To The Press (Press Release No. 66 /2010) Telecom Regulatory Authority of IndiarohitpsBelum ada peringkat
- Satellite Communications Theory - Book 2Dokumen36 halamanSatellite Communications Theory - Book 2namakoolasolomonBelum ada peringkat
- Nepal Telecommunications Authority: MIS ReportDokumen11 halamanNepal Telecommunications Authority: MIS ReportRejish ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom SectorDokumen39 halamanTelecom SectorPradeep GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Nepal Telecommunications Authority: MIS ReportDokumen12 halamanNepal Telecommunications Authority: MIS ReportRaMesh AdhikariBelum ada peringkat
- Nepal Telecommunications Authority: MIS ReportDokumen12 halamanNepal Telecommunications Authority: MIS ReportRaMesh AdhikariBelum ada peringkat
- Bharti 2airtel 1227851581611151 8Dokumen49 halamanBharti 2airtel 1227851581611151 8mayankvohraBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Telecom IndustryDokumen30 halamanIndian Telecom Industryhahire100% (1)
- Daman 123Dokumen41 halamanDaman 123daman khuranaBelum ada peringkat
- Telecommunication Industry: Presented By:-VishwaDokumen18 halamanTelecommunication Industry: Presented By:-VishwaVishwa Mohan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom: The Latest Breakthrough ExplainedDokumen17 halamanTelecom: The Latest Breakthrough ExplainedAnkapali MukherjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Service ProviderDokumen1 halamanService Providerketan_chananaBelum ada peringkat
- BSNL TrainingDokumen40 halamanBSNL Trainingdaman khuranaBelum ada peringkat
- Pricing Strategies of Reliance TelecomDokumen37 halamanPricing Strategies of Reliance Telecomvenkataswamynath channa100% (9)
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 4. Various Phases of Bs NL Cmts TenderDokumen5 halamanE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 4. Various Phases of Bs NL Cmts TenderAGM CMS&MBelum ada peringkat
- OM38040 MIMO Port Plumbing BTS RET Control Deployment Guide v3 0Dokumen41 halamanOM38040 MIMO Port Plumbing BTS RET Control Deployment Guide v3 0venu100% (2)
- SWOT-The Indian Telecom IndustryDokumen10 halamanSWOT-The Indian Telecom IndustryPalmodiBelum ada peringkat
- AirtelDokumen42 halamanAirtelraghavsaaniBelum ada peringkat
- FIM Final OneDokumen71 halamanFIM Final OneAbhijeet MondalBelum ada peringkat
- Developing Regulatory Ecosystem Enabling NGN - India2006Dokumen41 halamanDeveloping Regulatory Ecosystem Enabling NGN - India2006spmalla31Belum ada peringkat
- Report File On Network SystemDokumen32 halamanReport File On Network SystemUltimate Game ZoneBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Sector ReportDokumen25 halamanTelecom Sector Reportravi_rathi_2Belum ada peringkat
- APACDokumen14 halamanAPACnehaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On Essentials of Marketing: Submitted ToDokumen16 halamanAssignment On Essentials of Marketing: Submitted ToVishal JainBelum ada peringkat
- Country Report On "Wireless Telecommunication in Nepal": Sinamangal, KathmanduDokumen13 halamanCountry Report On "Wireless Telecommunication in Nepal": Sinamangal, Kathmandukks_82Belum ada peringkat
- Dynamics of Indian Telecom Industry 2009 v8Dokumen42 halamanDynamics of Indian Telecom Industry 2009 v8jmadariBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom Sector: Presented by Pallavi.B - 66 Mms MarketingDokumen48 halamanTelecom Sector: Presented by Pallavi.B - 66 Mms MarketingpaalveeBelum ada peringkat
- PrasadDokumen15 halamanPrasadyatheesh07Belum ada peringkat
- Satellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsDari EverandSatellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Profile of the Worldwide Semiconductor Industry - Market Prospects to 1997: Market Prospects to 1997Dari EverandProfile of the Worldwide Semiconductor Industry - Market Prospects to 1997: Market Prospects to 1997Belum ada peringkat
- Telecommunications: Present Status and Future TrendsDari EverandTelecommunications: Present Status and Future TrendsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Telecom in IndiaDokumen19 halamanTelecom in IndiaMARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHIBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom BillingDokumen5 halamanTelecom BillingMARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHI100% (2)
- Telecom 1111111Dokumen2 halamanTelecom 1111111MARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHI100% (2)
- TelecomDokumen6 halamanTelecomMARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHI100% (2)
- PR 23 March 07 No 31Dokumen3 halamanPR 23 March 07 No 31MARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHIBelum ada peringkat
- Telecom in IndiaDokumen10 halamanTelecom in IndiaMARUTI NANDAN TRIPATHIBelum ada peringkat
- The Frankfurt SchoolDokumen12 halamanThe Frankfurt SchoolNinaNC100% (1)
- Sample Works CitedDokumen2 halamanSample Works CitedmrtalmadgeBelum ada peringkat
- PCK 303 Understanding The Lesson 7Dokumen1 halamanPCK 303 Understanding The Lesson 7Japhet BagsitBelum ada peringkat
- BS-EN 12504-1 Cored Specimen PDFDokumen12 halamanBS-EN 12504-1 Cored Specimen PDFArisan IqmaBelum ada peringkat
- Guide To Pre-Week PlanningDokumen3 halamanGuide To Pre-Week Planningjorge samahaBelum ada peringkat
- Review Notes in Introduction To Criminology & Psychology of CrimesDokumen13 halamanReview Notes in Introduction To Criminology & Psychology of CrimesAizha Aizing Zuniga77% (13)
- Telephoning and Writing 4Dokumen42 halamanTelephoning and Writing 4LY HOANG THU NGAN NGAN.L5vus.edu.vnBelum ada peringkat
- Material Requisition For Expansion Joints - Taif SiteDokumen41 halamanMaterial Requisition For Expansion Joints - Taif SiteAnonymous uLAATWpfBelum ada peringkat
- Careers in The Tourism IndustryDokumen18 halamanCareers in The Tourism Industry049 Rista MariantinaBelum ada peringkat
- Operator Guide - Nozzles - ENDokumen16 halamanOperator Guide - Nozzles - ENAlexander SimanovskyBelum ada peringkat
- Student Development Theory Autobiography FinalDokumen10 halamanStudent Development Theory Autobiography Finalapi-541684468Belum ada peringkat
- Happiness Is A Snip Away: Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanHappiness Is A Snip Away: Lesson PlanLucy de la MoraBelum ada peringkat
- Free 3x3 Risk-MatrixDokumen1 halamanFree 3x3 Risk-MatrixTigor Gurning100% (3)
- Rubric Form A3Dokumen2 halamanRubric Form A3Azhan FikriBelum ada peringkat
- Catering Module 1 (Word)Dokumen11 halamanCatering Module 1 (Word)Princess Rolene Mamaradlo100% (1)
- Secrets of Spoken English by Gaurav FulbrightDokumen91 halamanSecrets of Spoken English by Gaurav FulbrightSarthak Singh ChandelBelum ada peringkat
- Eotc Camp Permission Form PDFDokumen3 halamanEotc Camp Permission Form PDFapi-238963120Belum ada peringkat
- U.S. Customs Form: CBP Form 7553 - Notice of Intent To Export, Destroy or Return Merchandise For Purposes of DrawbackDokumen1 halamanU.S. Customs Form: CBP Form 7553 - Notice of Intent To Export, Destroy or Return Merchandise For Purposes of DrawbackCustoms FormsBelum ada peringkat
- CSC Q0405 Designer Mechanical 1 02.07.2018 PDFDokumen73 halamanCSC Q0405 Designer Mechanical 1 02.07.2018 PDFUmair Ft SteynBelum ada peringkat
- Visual Representation of Metaphor SF ApproachDokumen17 halamanVisual Representation of Metaphor SF ApproachramBelum ada peringkat
- MCS Report On Piedmont UniversityDokumen12 halamanMCS Report On Piedmont UniversityKaran Jain100% (3)
- A Guide To CVS, Cover Letters and Application Forms: CareersDokumen35 halamanA Guide To CVS, Cover Letters and Application Forms: CareersFrank MaguiñaBelum ada peringkat
- Service Strategy: Sachin Modgil IMI-KDokumen44 halamanService Strategy: Sachin Modgil IMI-KHarsh VivekBelum ada peringkat
- Organisational Culture of Apple IncDokumen21 halamanOrganisational Culture of Apple IncArpita ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- B) Job Charts of The Principals & Staff at Gurukulam Institutions: I. Job Chart of The Principal: A. AcademicDokumen18 halamanB) Job Charts of The Principals & Staff at Gurukulam Institutions: I. Job Chart of The Principal: A. AcademicKanagaraj RBelum ada peringkat
- MGT1022 - LSM - Final Project Report - Format - 27.11.2020Dokumen7 halamanMGT1022 - LSM - Final Project Report - Format - 27.11.2020Gokul SrinathBelum ada peringkat
- Ab Bank Zambia Agro Finance: Risks, Mitigations and Departmental DevelopmentDokumen12 halamanAb Bank Zambia Agro Finance: Risks, Mitigations and Departmental DevelopmentStephen DiandaBelum ada peringkat
- TLE-TE 6 - Q1 - Mod7 - AgricultureDokumen19 halamanTLE-TE 6 - Q1 - Mod7 - AgricultureMila Macaranas100% (2)
- Business Plan: Executive SummaryDokumen19 halamanBusiness Plan: Executive SummaryAngela HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 415midterm Exam Routine Spring 2020 Update On 23-08-20Dokumen1 halaman415midterm Exam Routine Spring 2020 Update On 23-08-20TanimunBelum ada peringkat