Porter's Generic Strategies
Diunggah oleh
Basant SinghJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Porter's Generic Strategies
Diunggah oleh
Basant SinghHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Presented By:Basant Singh
Introduction Porters Generic Strategy A) Cost Leadership Strategy B) Differentiation Strategy C) Focus or Strategic Scope
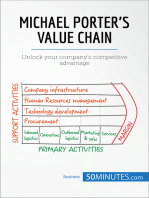
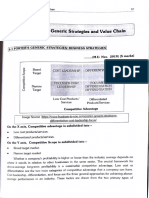
Michael Porter has described a category scheme consisting of three general types of strategies. These three generic strategies are defined along two dimensions: strategic scope and strategic strength. In particular he identified two competencies that he felt were most important: product differentiation and product cost (efficiency). Porter simplifies the scheme by reducing it down to the three best strategies. They are cost leadership, differentiation, and market segmentation.
This strategy appeal to cost-conscious or pricesensitive customers. It is achieved by having the lowest price in the target market. There are three main ways to achieve this: The first approach is achieving a high asset turnover. The second dimension is achieving low direct and indirect operating costs. The third dimension is control over the supply/procurement chain to ensure low costs
Differentiate the products in some way in order to compete successfully. A differentiation strategy calls for the development of a product or service that offers unique attributes that are valued by customers and that customers perceive to be better than or different from the products of the competition.
This dimension is not a separate strategy, but describes the scope over which the company should compete based on cost leadership or differentiation. The firm can choose to compete in the mass market with a broad scope, or in a defined, focused market segment with a narrow scope. In adopting a narrow focus, the company ideally focuses on a few target markets (also called a segmentation strategy). In adopting a broad focus , the firm must ascertain the needs and wants of the mass market, and compete either on price or differentiation depending on its resources and capabilities.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Michael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageDari EverandMichael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantagePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Business Strategy - Lecture 1 - WorksheetDokumen5 halamanBusiness Strategy - Lecture 1 - WorksheetInuy NurhayadiBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionDari EverandMarketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (7)
- Strategy and Competitive Advantage Chapter 6Dokumen7 halamanStrategy and Competitive Advantage Chapter 6Drishtee DevianeeBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management Competitive AdvantageDokumen3 halamanStrategic Management Competitive AdvantageUpendra RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Leadership Porter Generic StrategiesDokumen7 halamanCost Leadership Porter Generic StrategiesRamar MurugasenBelum ada peringkat
- Porter's Generic Strategies and How Firms Position Themselves for Competitive AdvantageDokumen4 halamanPorter's Generic Strategies and How Firms Position Themselves for Competitive AdvantageromirathiBelum ada peringkat
- Building Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyDokumen33 halamanBuilding Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyRizwan Sait100% (2)
- Competitive Strategy and Advantage in The Marketplace: Chapter Learning ObjectivesDokumen23 halamanCompetitive Strategy and Advantage in The Marketplace: Chapter Learning ObjectivesStacie SimmonsBelum ada peringkat
- Porter Generic StrategiesDokumen3 halamanPorter Generic StrategiesbravehorseBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On Porters Generic StrategiesDokumen12 halamanAssignment On Porters Generic StrategiesGeetinder Singh78% (9)
- Strategic Management Module Covers Porter's Five Generic StrategiesDokumen20 halamanStrategic Management Module Covers Porter's Five Generic Strategiesharujadi100% (3)
- Bme4004 Chapter 8Dokumen10 halamanBme4004 Chapter 8saphirejunelBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Mgt. Stratejik EnglishDokumen3 halamanTugas Mgt. Stratejik EnglishGilang PerdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Porter's 3 Generic Strategies ExplainedDokumen2 halamanPorter's 3 Generic Strategies ExplainedEma AkhterBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic PositioningDokumen13 halamanStrategic PositioningleesadzebondeBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3 CSMDokumen31 halamanModule 3 CSMmayankgami27Belum ada peringkat
- Bahria University Islamabad - Generic Strategies ExplainedDokumen8 halamanBahria University Islamabad - Generic Strategies ExplainedjaveriaBelum ada peringkat
- SM Sec 2 PDFDokumen28 halamanSM Sec 2 PDFSUPRIYA MOHANKABelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Mgt Competitive StrategiesDokumen10 halamanStrategic Mgt Competitive StrategiesRezwan SharifBelum ada peringkat
- Bus. Level Stg.-Porter Generic StrategiesDokumen7 halamanBus. Level Stg.-Porter Generic StrategiesJitender KaushalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen21 halamanChapter 5oduniyiabimBelum ada peringkat
- SM Module 4 Rev AnsDokumen4 halamanSM Module 4 Rev AnsLysss EpssssBelum ada peringkat
- Week 13.2 - Business Unit Level StrategyDokumen35 halamanWeek 13.2 - Business Unit Level StrategyPhakpoom NajiBelum ada peringkat
- Strategies For Business & Group MeetingsDokumen8 halamanStrategies For Business & Group Meetingsoreilybrownsworthwbe.ha8.85.8Belum ada peringkat
- Strategic ManagementDokumen2 halamanStrategic ManagementMangesh pandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Porter's Generic Strategies ExplainedDokumen5 halamanPorter's Generic Strategies ExplainedbiswasjoyBelum ada peringkat
- SCM - Module6Dokumen14 halamanSCM - Module6Vissol RibeiroBelum ada peringkat
- Bahria University IslamabadDokumen12 halamanBahria University IslamabadjaveriaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 4Dokumen21 halamanLesson 4Lyra MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- Stratergy-: Features of StrategyDokumen13 halamanStratergy-: Features of StrategyrockyBelum ada peringkat
- Resumen de LecturaDokumen3 halamanResumen de LecturaFabianBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Resumen y CasoDokumen6 halamanChapter 5 Resumen y CasoPolly GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen7 halamanChapter 5ERICKA MAE NATOBelum ada peringkat
- Porter's generic strategies explained in 40 charsDokumen4 halamanPorter's generic strategies explained in 40 charsFarida KalufyaBelum ada peringkat
- Group 8Dokumen8 halamanGroup 8Roy CabarlesBelum ada peringkat
- Competitive AdvantageDokumen3 halamanCompetitive AdvantageAnonymous X8hNvFAyzBelum ada peringkat
- Strat ActDokumen2 halamanStrat ActJael AlmazanBelum ada peringkat
- Porter's Generic Competitive Strategies (Ways of Competing)Dokumen1 halamanPorter's Generic Competitive Strategies (Ways of Competing)suresh.srinivasnBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 8: Business Level StrategiesDokumen35 halamanUnit 8: Business Level StrategiesFlo IglesiaBelum ada peringkat
- Competitive Marketing Strategy: Porter Revisited: Marketing Intelligence & Planning December 1991Dokumen8 halamanCompetitive Marketing Strategy: Porter Revisited: Marketing Intelligence & Planning December 1991awan2008awanBelum ada peringkat
- SU190264W Strategic Management Ass1Dokumen8 halamanSU190264W Strategic Management Ass1Milford Kudakwashe MoyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy FormulationDokumen49 halamanStrategy FormulationAra BellaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management Ass1Dokumen8 halamanStrategic Management Ass1Milford Kudakwashe MoyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Competitive Advantage: Print Page Share On Facebook Share On Twitter Share On Linkedin Share On Google Share by EmailDokumen3 halamanCompetitive Advantage: Print Page Share On Facebook Share On Twitter Share On Linkedin Share On Google Share by EmailAarthi MuthusamiBelum ada peringkat
- Competative StrategiesDokumen9 halamanCompetative StrategiessaiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6Dokumen11 halamanChapter 6NadineBelum ada peringkat
- Porter's 3 Generic StrategiesDokumen4 halamanPorter's 3 Generic StrategiesDave DeBelum ada peringkat
- Five Basic Strategic Approaches: 1. A Low-Cost Provider StrategyDokumen2 halamanFive Basic Strategic Approaches: 1. A Low-Cost Provider StrategyMd. Ismail Hossain Shafi TalukderBelum ada peringkat
- EContent 3 2024 01 05 16 21 17 M3GenericBusinessStrategicModelpdf 2023 12 06 10 13 49Dokumen4 halamanEContent 3 2024 01 05 16 21 17 M3GenericBusinessStrategicModelpdf 2023 12 06 10 13 49Neha SukhdevBelum ada peringkat
- Business StrategyDokumen25 halamanBusiness StrategySarthak BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Competitive Strategy (1980), Competitive Advantage (1985), and Competitive Advantage of Nations (1989)Dokumen3 halamanCompetitive Strategy (1980), Competitive Advantage (1985), and Competitive Advantage of Nations (1989)Kit KatBelum ada peringkat
- Neha 1Dokumen4 halamanNeha 1imdad1986Belum ada peringkat
- Porter's Generic Strategies (cost, diff, focusDokumen2 halamanPorter's Generic Strategies (cost, diff, focusAnthonius TeddyBelum ada peringkat
- STM2 Chapter 7-8 Business Strategies and DiversificationDokumen12 halamanSTM2 Chapter 7-8 Business Strategies and DiversificationMariët KrebsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Strategic Cost Management: MidtermDokumen19 halamanChapter 1 - Strategic Cost Management: MidtermAndrea Nicole De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management Part 5Dokumen7 halamanStrategic Management Part 5aansh rajBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen6 halamanChapter 5rakibulislammbstu01Belum ada peringkat
- Unit III Part II Business Level StrategiesDokumen2 halamanUnit III Part II Business Level StrategiesAbhinav ShrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Value-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1Dari EverandValue-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1Belum ada peringkat