Adchem Vapor Pressure
Diunggah oleh
Melvin CabonegroHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Adchem Vapor Pressure
Diunggah oleh
Melvin CabonegroHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
COLLIGATIVE PROPERTY
COLLIGATIVE PROPERTY
- are property that depend only on the number of solute particles in the solution, not on the nature of those particles. - Colligative properties of solutions includes: a. Vapor pressure b. Boiling point elevation c. Freezing point depression
VAPOR PRESSURE OF SOLUTION Consider a solution from two components, A and B. The vapor pressure of the solution (Ptotal) is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of A (pA) and the partial pressure of B (pB): The partial pressure in this equation may be found by means of a relationship known as Raoults law, which pertains to what are called ideal solutions. The partial pressure of A, for example, is given by the equation: pA = XA Where: pA = partial pressure of A (atm) XA= mole fraction of A = vapor pressure of pure A (atm)
Ptotal = pA + pB
VAPOR PRESSURE OF SOLUTION Ideal solution is one I which the intermolecular forces between A and B molecules, A and A molecules, and B and B molecules are essentially the same. -in such a situation, the tendency of an A molecule to escape into the vapor is the same whether it is surrounded by A molecules in a pure A or surrounded by a mixture of A and B molecules in the solution. -the partial pressure of A for the solution, therefore, is equal to the vapor pressure of pure A reduced in proportion to the number of molecules of A present out of the total number of molecules in the solution.
VAPOR PRESSURE OF SOLUTION The partial pressure of B can be found by use similar equation: 0 pB = XB Where: pB = partial pressure of B (atm) XB = mole fraction of B 0 = vapor pressure of B (atm) With this, the vapor pressure of the solution is equal to the sum of the two partial pressures. 0 Ptotal = XA + XB - The vapor pressure of an ideal solution, therefore, can be derived from the vapor pressure of the pure components by taking into account the proportion of the components (by mole) present in the solution.
VAPOR PRESSURE OF SOLUTION Sample Problems: 1. Heptane (C7H8) and octane (C8H18) form an ideal solutions. What is the vapor pressure at 400C of a solution that contains 3 .0 mol of heptane and 5.0 mol of octane? At 400C, the vapor pressure of heptane is 0.121 atm and the vapor pressure of octane is 0.041 atm. 2. Assuming ideality, calculate the vapor pressure of a 1.00 m solution of a nonvolatile, nondissociating solute in water at 500C. The vapor pressure of water at 500C is 0.122 atm
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- G8 DLL Arts Q3Dokumen16 halamanG8 DLL Arts Q3Crys Alvin MaticBelum ada peringkat
- BE Form 5 - RECORD OF DONATIONS RECEIVEDDokumen1 halamanBE Form 5 - RECORD OF DONATIONS RECEIVEDMelvin Cabonegro0% (1)
- Taligaman National High School Taligaman, Butuan CityDokumen1 halamanTaligaman National High School Taligaman, Butuan CityMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson LogDokumen4 halamanDaily Lesson LogMelvin Cabonegro100% (2)
- Substitute FormDokumen1 halamanSubstitute FormMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 9: Name of Student School Last Attended Residence Address Contact Number RemarksDokumen2 halamanGrade 9: Name of Student School Last Attended Residence Address Contact Number RemarksMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Deped Order No. 42, S. 2016 Taligaman National High School Melvin C. CabonegroDokumen6 halamanDeped Order No. 42, S. 2016 Taligaman National High School Melvin C. CabonegroMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- School Base Management Dimensions A. Leadership and Governance B. Curriculum and LearningDokumen2 halamanSchool Base Management Dimensions A. Leadership and Governance B. Curriculum and LearningMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- MAPEH Arts of East AsiaDokumen16 halamanMAPEH Arts of East AsiaShemae Obni89% (9)
- Bi OmegaDokumen7 halamanBi OmegaMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Taligaman National High School Enrolment List for Grade 9Dokumen2 halamanTaligaman National High School Enrolment List for Grade 9Melvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Tnhs Annual Report Finale 1Dokumen44 halamanTnhs Annual Report Finale 1Melvin Cabonegro100% (1)
- SF7 School Personnel Assignment ListDokumen6 halamanSF7 School Personnel Assignment ListMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
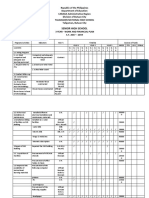
- SHS 3 Years Work and Financial Plan WFPDokumen8 halamanSHS 3 Years Work and Financial Plan WFPMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Sf5 - 2017 - Grade 7 (Year I) - FrondaDokumen3 halamanSf5 - 2017 - Grade 7 (Year I) - FrondaMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Travel Authority: Taligaman National High SchoolDokumen2 halamanTravel Authority: Taligaman National High SchoolMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Final Assignment Mam RuthDokumen21 halamanFinal Assignment Mam RuthMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
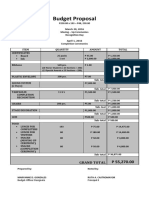
- Budget Proposal: March 29, 2016Dokumen2 halamanBudget Proposal: March 29, 2016Melvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Grain 2016Dokumen12 halamanGrain 2016Melvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Jhs Class Program BlankDokumen45 halamanJhs Class Program BlankMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Conduct of Meetings Policy 2015Dokumen6 halamanConduct of Meetings Policy 2015Melvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- DEPED-Butuan City-Notice of Evaluation-SchoolsDokumen1 halamanDEPED-Butuan City-Notice of Evaluation-SchoolsMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- CSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets FormDokumen4 halamanCSC Resolution No. 1500088 Sworn Statement of Assets Formwyclef_chin100% (6)
- Class ProgramDokumen30 halamanClass ProgramMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Committees and AncillaryDokumen6 halamanCommittees and AncillaryMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Objective TabbingDokumen8 halamanObjective TabbingMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Appearance 3Dokumen2 halamanAppearance 3Melvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Science and Technology Contests SummaryDokumen19 halamanScience and Technology Contests SummaryMelvin Cabonegro0% (1)
- Letterr NewDokumen1 halamanLetterr NewMelvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Grain 2016Dokumen12 halamanGrain 2016Melvin CabonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Liebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VDokumen2 halamanLiebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VsinoBelum ada peringkat
- Kami Export - BuildingtheTranscontinentalRailroadWEBQUESTUsesQRCodes-1Dokumen3 halamanKami Export - BuildingtheTranscontinentalRailroadWEBQUESTUsesQRCodes-1Anna HattenBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperDokumen14 halamanInorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperRuan ReisBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2 - Weather DerivativeDokumen8 halamanAssignment 2 - Weather DerivativeBrow SimonBelum ada peringkat
- Instrumentation Positioner PresentationDokumen43 halamanInstrumentation Positioner PresentationSangram Patnaik100% (1)
- Pita Cyrel R. Activity 7Dokumen5 halamanPita Cyrel R. Activity 7Lucky Lynn AbreraBelum ada peringkat
- Last Clean ExceptionDokumen24 halamanLast Clean Exceptionbeom choiBelum ada peringkat
- GlastonburyDokumen4 halamanGlastonburyfatimazahrarahmani02Belum ada peringkat
- Reader's Digest (November 2021)Dokumen172 halamanReader's Digest (November 2021)Sha MohebBelum ada peringkat
- NewspaperDokumen11 halamanNewspaperКристина ОрёлBelum ada peringkat
- UTP3-SW04-TP60 Datasheet VER2.0Dokumen2 halamanUTP3-SW04-TP60 Datasheet VER2.0Ricardo TitoBelum ada peringkat
- Movement and Position: Question Paper 4Dokumen14 halamanMovement and Position: Question Paper 4SlaheddineBelum ada peringkat
- 15 - 5 - IoT Based Smart HomeDokumen6 halaman15 - 5 - IoT Based Smart HomeBhaskar Rao PBelum ada peringkat
- Java development user guide eclipse tutorialDokumen322 halamanJava development user guide eclipse tutorialVivek ParmarBelum ada peringkat
- Break Even AnalysisDokumen4 halamanBreak Even Analysiscyper zoonBelum ada peringkat
- Reg FeeDokumen1 halamanReg FeeSikder MizanBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics Ecommerce Website: 1) Background/ Problem StatementDokumen7 halamanElectronics Ecommerce Website: 1) Background/ Problem StatementdesalegnBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises2 SolutionsDokumen7 halamanExercises2 Solutionspedroagv08Belum ada peringkat
- 2-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTDokumen5 halaman2-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTIbrahim JaberBelum ada peringkat
- DELcraFT Works CleanEra ProjectDokumen31 halamanDELcraFT Works CleanEra Projectenrico_britaiBelum ada peringkat
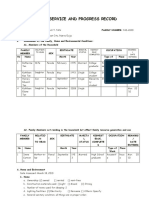
- Family Service and Progress Record: Daughter SeptemberDokumen29 halamanFamily Service and Progress Record: Daughter SeptemberKathleen Kae Carmona TanBelum ada peringkat
- Bluetooth TutorialDokumen349 halamanBluetooth Tutorialjohn bougsBelum ada peringkat
- Federal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestDokumen8 halamanFederal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestAnonymous Pb39klJBelum ada peringkat
- Guiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test BankDokumen16 halamanGuiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test Bankoglepogy5kobgk100% (27)
- DIN Flange Dimensions PDFDokumen1 halamanDIN Flange Dimensions PDFrasel.sheikh5000158Belum ada peringkat
- Tension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisDokumen19 halamanTension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisPrajeesh RajBelum ada peringkat
- AgentScope: A Flexible Yet Robust Multi-Agent PlatformDokumen24 halamanAgentScope: A Flexible Yet Robust Multi-Agent PlatformRijalBelum ada peringkat
- Archlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Dokumen16 halamanArchlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Goh Ka WeeBelum ada peringkat
- En dx300lc 5 Brochure PDFDokumen24 halamanEn dx300lc 5 Brochure PDFsaroniBelum ada peringkat