0021
Diunggah oleh
0021rahlulDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
0021
Diunggah oleh
0021rahlulHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Effects of Inflation: 1)Rapidly rise in the prices of goods and services, and 2)Consequntly fall in the value of money
Effects on Production: As very harmful for the economy ,inflation has the following adverse effects on the productive activities. 1)Decrease in Value of Money : After the full employment level, the increase in money supply results in hyper inflation ,which discourages public savings and reduces the cap0ital accumulation. 2)Decrease in Foreign Investment :The inflation has an adverse affects on the foreign investment of a particular country, and thereby leads to decrease the production of wealthy in economy. 3)Decrease in Domestic Investment :The inflation has an adverse affects on the domestic investment due to the reduced capital accumulation and then reduces the volume of production in a country. 4)Business Uncertainties: The inflation causes uncertainties in the business and this discourages the entrepreneurs and business community from taking risks in production of wealth in an economy. 5)Diversoiopn of Productive Resources :The inflation results in the diversion of productive resources from essential goods industries to luxurious goods industries and this creates shortage of the consumer goods. 6)Deteriration in Quality of Goods :The inflation industries the manufacturers to neglect the quality of the products to get normal profits, and leads to deterioration in quality of their produced goods. 7)Hording of Essential Goods: The inflation leads to hoarding of the essential goods by the traders as well as the consumers both in order to make betterness in the future . 8)Loss of Confidence : The inflation has an adverse impact on the confidence of the people towards their home currency and towards their wealth or assets.
Effects on Distribution : As always unjust to the poor inflation has the following effects on various groups of the society 1) Debtors are the gainers as they repay less in real terms and the creditors are the losers as they receive less in real terms. 2)Wages and Salary Earners :During the inflation the wage and salary earners are the losers because their purchasing power do not rise in the proportion of rise in their cost of livings. 3)Fixed Income Groups :During the inflation the fixed income groups are worst losers since their money income remains fixed against increase in the prices of goods . 4)Entreprenurs :During the inflation the entrepreneurs (manufacturers, merchants, or business) are the gainers as the gainers as the production costs do not rise as the prices of products rtises rapidly. 5)Investors :During the inflation, the investors investing in the equity shares are the gainers and the investors investing in bonds and debentures are the losers due to a certain fixed interest on them. 6)Farmers:During the inflation ,the farmers are the gainers as they are debtors and they pay to their creditors to their creditors to possess marketable surplus.
Effects on Socio political stability: As dangerous to development of a society ,the inflation has the following non economic effects 1)Class-conflict: Socially, inflation is unjust as it redistributes the income and wealth in favour of the rich and therefore it leads to class conflict in the society. 2)Political Instability :Politically , the instability exists in the economy of the corruption and consequences of suffered morality of the people . In brief ,inflation is unfavourable for the poor unjustifiable for the society and dangerous for the economy of a particular country. b) Fiscal Measures: 1)Government Expenditure :As an important instrument to control inflation the Government has to reduce its own expenditure. 2)Taxation: The Government increases the rates of existing taxes and imposes additional taxes to reduce the purchasing power of the public. 3)Public Borrowing :As government issues bonds to borrow money from public the private savings of the households and business houses is absorbed . 4)Debt Management :The existing public debt should be so managed as to reduce the supply of money and further expansion of credit by commercial banks . 5)Over-Valuation: Over-Valuation discourages exports and leads to increase domestic availability of products . c) Miscellaneous Measures 1)Expansionof Output : The government adopts liberal import policy to kept down the prices of the essential consumer goods through expansion of output. 2)Wages Policy :In order to control the inflation the trade unions oppose but the government consider a cut in wage rates to decrease the incom es of the workers. 3)Price control and rationing : For controlling the prices of the 3essential goods the governmet undertakes price control and rationing .
MEASURES TO CONTROY INFLATION: a) Monetary Measures : 1)Bank Rate : Bank rate is the official rate of interest of the Central Bank (Reserve Bank of India) .An increase in bank rate discourages borrowing by the businessmen and the consumers resulting in fall in inflation . 2)Sale of Government Securities :The Central Bank sells the Government Securities to the public, in the open markets, to withdraw the purchasing power and to control money supply of the households and businesshouse. 3)Cash Reserve Ratio: Cash Reserve Ratio is the ratio pf cash to total deposit liability of banks held with the central bank. A rise in CRR means lesser available of credit through the banking system to restrict purchase powers.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Statement - 271185814 - Juan Camilo Cardenas AguirreDokumen12 halamanStatement - 271185814 - Juan Camilo Cardenas AguirrePedro Ant. Núñez UlloaBelum ada peringkat
- Financing Disbursement Master Roll: B0685 Malapatan RegularDokumen18 halamanFinancing Disbursement Master Roll: B0685 Malapatan RegularAsa Ph MalapatanBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Accounting NotesDokumen25 halamanFinancial Accounting NotesNamish GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- BSN Giro Account Statement for Alister MaribenDokumen4 halamanBSN Giro Account Statement for Alister MaribenAlister MaribenBelum ada peringkat
- FINALREPORTBANKNEW Converted 95201213Dokumen58 halamanFINALREPORTBANKNEW Converted 95201213dinjoBelum ada peringkat
- Interest Rates: Type Interest Rate Savings AccountDokumen16 halamanInterest Rates: Type Interest Rate Savings Accountrohanfyaz00Belum ada peringkat
- NPA ManagementDokumen18 halamanNPA ManagementVincy LuthraBelum ada peringkat
- 57b2e7d35a4d40b8b460abe4914d711a.docxDokumen6 halaman57b2e7d35a4d40b8b460abe4914d711a.docxZohaib HajizubairBelum ada peringkat
- CW 13 LTF Key 1Dokumen6 halamanCW 13 LTF Key 1Jedidiah ManglicmotBelum ada peringkat
- Final Draft Philippines Case StudyDokumen43 halamanFinal Draft Philippines Case StudyDarwin SolanoyBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Statement 2014Dokumen9 halamanFinancial Statement 2014shahid2opuBelum ada peringkat
- SHF Order FormDokumen2 halamanSHF Order FormFernando PlansBelum ada peringkat
- Working Capital ManagementDokumen39 halamanWorking Capital ManagementRebelliousRascalBelum ada peringkat
- Subprime Mortgage CrisisDokumen50 halamanSubprime Mortgage CrisisAli HabibBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Income Tax Return SummaryDokumen8 halamanIndian Income Tax Return Summarybhashkar yadavBelum ada peringkat
- Pledge-Contract Act: Simar MakkarDokumen8 halamanPledge-Contract Act: Simar MakkarPearl LalwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Irr (Presentation)Dokumen19 halamanIrr (Presentation)shaidi198971% (17)
- Fisher EquationDokumen2 halamanFisher Equationtimothy454Belum ada peringkat
- Final Work On BarclaysDokumen5 halamanFinal Work On BarclaysKurstina RamsamyBelum ada peringkat
- Final Accounts Without AdjustmentsDokumen22 halamanFinal Accounts Without AdjustmentsFaizan MisbahuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Guideline On Classification of NPL and Provision For Substandard, Bad and Doubtful Debts (BNM-GP3)Dokumen20 halamanGuideline On Classification of NPL and Provision For Substandard, Bad and Doubtful Debts (BNM-GP3)Shaa DidiBelum ada peringkat
- Price Target Research - GBDC - Revision - Golub Capital BDC Inc - 10 PagesDokumen10 halamanPrice Target Research - GBDC - Revision - Golub Capital BDC Inc - 10 PagesSagar PatelBelum ada peringkat
- For Student - Animation - Environment and MarketDokumen69 halamanFor Student - Animation - Environment and MarketJaylord MagpantayBelum ada peringkat
- Sepa GuideDokumen5 halamanSepa GuideSantosh Poojari0% (1)
- International Business Finance FINS3616: By: Mishal Manzoor M.manzoor@unsw - Edu.auDokumen48 halamanInternational Business Finance FINS3616: By: Mishal Manzoor M.manzoor@unsw - Edu.auKelvin ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Course OutlineDokumen8 halamanCourse OutlineLaxman KeshavBelum ada peringkat
- Statements 7344Dokumen4 halamanStatements 7344Валентина ШвечиковаBelum ada peringkat
- CSI OverviewDokumen27 halamanCSI OverviewAmit Namdeo88% (8)
- TT06 - QuesDokumen3 halamanTT06 - QuesLe Tuong MinhBelum ada peringkat
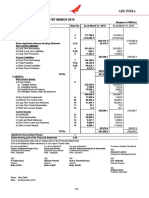
- Balance Sheet As at 31st March 2015Dokumen1 halamanBalance Sheet As at 31st March 2015Mrigul UppalBelum ada peringkat