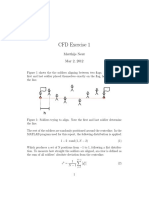
02 Regresi Linier Sederhana
Diunggah oleh
Dede Firmansyah AlbanjaryHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
02 Regresi Linier Sederhana
Diunggah oleh
Dede Firmansyah AlbanjaryHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
presented by:
Regresi Linier Sederhana
(RLS)
Dudi Barmana, M.Si.
2
Agenda
Persamaan RLS & asumsi yg mendasari
model
Pendugaan (titik & interval) parameter model
Pengujian parameter model dg Uji-t dan Uji-F
(Anova), serta penafsirannya
Korelasi dalam RLS: Koefisien korelasi linier
()
Ukuran penilaian kemampuan/kesesuaian
model
Prediksi menggunakan model
Today Quote
Jika seseorang merasa bahwa mereka tidak pernah
melakukan kesalahan selama hidupnya, maka
sebenarnya mereka tidak pernah mencoba hal-hal baru
dalam hidupnya
---Einstein---
Persamaan RLS dan
Asumsi yg mendasari model
Simple Linear Regression Model
y
i
= |
0
+ |
1
x
i
+ c
i
x
i
: regressor variable
y
i
: response variable
|
0
: the intercept, unknown
|
1
: the slope, unknown
c
i
: error with E(c
i
) = 0 and Var(c
i
) = o
2
(unknown)
The errors are uncorrelated sehingga cov(c
i
,c
j
)
= 0; i j
5
Given x,
E(y|x) = E(|
0
+ |
1
x + c) = |
0
+ |
1
x
Var(y|x) = Var(|
0
+ |
1
x + c) = o
2
Responses are also uncorrelated.
Regression coefficients: |
0
, |
1
|
1
: the change of E(y|x) by a unit change in
x
|
0
: E(y|x=0)
6
Pendugaan parameter model
(titik & interval)
Pendugaan Titik
Least-squares Estimation of the Parameters
Estimation of |
0
and |
1
n pairs: (y
i
, x
i
), i = 1, , n
Method of least squares: Minimize
8
=
+ =
n
i
i i
x y S
1
2
1 0 1 0
)] ( [ ) , ( | | | |
Least-squares normal equations:
9
10
The least-squares estimator:
11
The fitted simple regression model:
A point estimate of the mean of y for a
particular x
Residual:
An important role in investigating the
adequacy of the fitted regression model and
in detecting departures from the underlying
assumption!
12
Properties of the Least-Squares Estimators
and the Fitted Regression Model
are linear combinations of y
i
are unbiased estimators.
0 1
and
| |
xx i i
n
i
i i
S x x c y c / ) ( ,
1
1
= =
=
|
x y
1 0
| | =
0 1
and
| |
13
0 1 1 0 1 0
1 1 0
1
1
)
( )
(
) (
) ( ) ( )
(
| | | | | |
| | |
|
= + = =
= + =
= =
=
x x x y E E
x c
y E c y c E E
i
i i
i
i i
n
i
i i
= = =
= =
i
xx
i
i
xx
i
i
i i
i
i i
S
x x
S
c
y Var c y c Var Var
2
2
2
2
2 2
2
1
) (
) ( ) ( )
(
o o
o
|
)
1
( )
(
2
2
0
xx
S
x
n
Var + =o |
14
Some useful properties:
The sum of the residuals in any regression
model that contains an intercept |
0
is always 0,
i.e.
Regression line always passes through the
centroid point of data,
= = =
i
i i
i
i i
i
i
x x y y y y e 0 )) (
( ) (
1
|
=
i i
i i
y y
) , ( y x
= =
i
i i i
i
i i
x x y y x e x 0 )) (
(
1
|
= + =
i i
i i i i i
x x y y x x y e y 0 )) (
) ))(( (
(
1 1
| |
15
Estimator of o
2
Residual sum of squares:
xy T
xy
i
i
i
i
i
i
i i
i
i
S SS
S y y
x x y y
y y e SS
1
1
2
2
1
2
2
s Re
) (
)) (
(
)
(
|
|
|
=
=
=
= =
16
Since ,
the unbiased estimator of o
2
is
MS
E
is called the residual mean square.
This estimate is model-dependent.
2
) 2 ( ) ( o = n SS E
E
E
E
MS
n
SS
s =
= =
2
2 2
o
Pendugaan Interval
Assume that
i
are normally and
independently distributed
( )
2
0
0 0
~
se
n
t
|
| |
( )
2
1
1 1
~
se
n
t
|
| |
Parameter
0
Pendugaan interval sebesar (1-) 100 %
0 :
X Y
1 0
| |
=
( )
s
X X n
X
t
n
i
i
n
i
i
n
2
1
1
2
1
2
2
1 , 2
0
(
(
(
(
=
=
o
|
( )
( )
=
=
=
n
i
i
n
i
i
X X n
X
s
1
2
1
2
0
se |
Parameter
1
Pendugaan interval sebesar (1-) 100 %
1 :
( )( )
( )
2
1
=
X X
Y Y X X
i
i i
|
( )
=
=
n
i
i
X X
s
1
2
1
) ( se |
( )
( )
n
i
i
, n
X X
s
1
2
2
1 2
1
t |
20
Confidence interval for o
2
:
Pengujian parameter model
dg Uji-t dan Uji-F (Anova), serta
penafsirannya
Hypothesis Testing on the Slope and
Intercept
22
Assume
i
are normally distributed
y
i
~ N(|
0
+ |
1
x
i
, o
2
)
Use of t-Tests
Test on slope:
H
0
: |
1
= |
10
v.s. H
1
: |
1
|
10
) / , ( ~
2
1 1 xx
S N o | |
23
If o
2
is known, under null hypothesis,
(n-2) MS
E
/ o
2
follows a _
2
n-2
If o
2
is unknown,
Reject H
0
if |t
0
| > t
o/2, n-2
) 1 , 0 ( ~
/
2
10 1
0
N
S
Z
xx
o
| |
=
2
1
10 1 10 1
0
~
)
=
n
xx E
t
se S MS
t
|
| | | |
24
Test on intercept:
H
0
: |
0
= |
00
v.s. H
1
: |
0
|
00
If o
2
is unknown
Reject H
0
if |t
0
| > t
o/2, n-2
2
0
00 0
2
00 0
0
~
)
) / / 1 (
=
+
=
n
xx E
t
se
S x n MS
t
|
| | | |
25
Testing Significance of Regression
H
0
: |
1
= 0 v.s. H
1
: |
1
0
Accept H
0
: there is no linear relationship
between x and y.
26
Reject H
0
: x is of value in explaining the
variability in y.
Reject H
0
if |t
0
| > t
o/2, n-2
2
1
1
0
~
)
=
n
t
se
t
|
|
27
The Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
Use an analysis of variance approach to test
significance of regression
28
SS
T
: the corrected sum of squares of the
observations. It measures the total variability in
the observations.
SS
Res
: the residual or error sum of squares
The residual variation left unexplained by the
regression line.
SS
R
: the regression or model sum of
squares
The amount of variability in the observations
accounted for by the regression line
SS
T
= SS
R
+ SS
Res
+ =
i
i i
i
i i
y y y y y y
2 2 2
)
( )
( ) (
29
The degree-of-freedom:
df
T
= n-1
df
R
= 1
df
Res
= n-2
df
T
= df
R
+ df
Res
Test significance regression by ANOVA
SS
Res
= (n-2) MS
Res
~ _
2
n-2
SS
R
= MS
R
~ _
2
1
SS
R
and SS
Res
are independent
xy R
S SS
1
| =
2 , 1
Re Re
0
~
) 2 /(
1 /
=
n
s
R
s
R
F
MS
MS
n SS
SS
F
30
E(MS
Res
) = o
2
E(MS
R
) = o
2
+ |
1
2
S
xx
Reject H
0
if F
0
> F
o/2,1, n-2
If |
1
0, F
0
follows a noncentral F with 1 and n-
2 degree of freedom and a noncentrality
parameter
2
2
1
o
|
xx
S
=
31
More About the t Test
The square of a t random variable with f degree
of freedom is a F random variable with 1 and f
degree of freedom.
xx s
S MS se
t
/
Re
1
1
1
0
|
|
|
= =
0
Re Re
1
Re
2
1 2
0
F
MS
MS
MS
S
MS
S
t
s
R
s
xy
s
xx
= = = =
|
|
Korelasi dalam RLS:
Koefisien korelasi linier ()
33
The estimator of
34
Test on
100(1-o)% C.I. for
Ukuran penilaian
kemampuan/kesesuaian model
Coefficient of Determination
36
The coefficient of determination:
The proportion of variation explained by the
regressor x
0 R
2
1
Example, R
2
= 0.9018. It means that 90.18%
of the variability in strength is accounted for
by the regression model.
T T
R
SS
SS
SS
SS
R
s Re
2
1 = =
37
R
2
can be increased by adding terms to the
model.
For a simple regression model,
E(R
2
) increases (decreases) as S
xx
increases
(decreases)
R
2
does not measure the magnitude of the
slope of the regression line. A large value of
R
2
imply a steep slope.
R
2
does not measure the appropriateness of
the linear model.
2 2
1
2
1 2
) (
o |
|
+
~
xx
xx
S
S
R E
Prediksi menggunakan model
Prediction of New Observations
39
is the point estimate of the new
value of the response
follows a normal distribution with mean 0
and variance:
0 1 0 0
x y | | + =
0
y
0 0
y y =
]
) ( 1
1 [ )
( ) (
0 2
0 0
xx
S
x x
n
y y Var Var
+ + = = o
40
The 100(1-o)% confidence interval on a future
observation at x
0
(a prediction interval for
the future observation y
0
)
41
pertanyaan
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Sunk CostDokumen35 halamanSunk CostAhmedSaad647Belum ada peringkat
- CFD Online FLUENT Moisture ModelingDokumen3 halamanCFD Online FLUENT Moisture Modelingkulov1592Belum ada peringkat
- Ring Programming Language Book - Part 56 of 84Dokumen10 halamanRing Programming Language Book - Part 56 of 84Mahmoud Samir FayedBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of MachinesDokumen8 halamanMechanics of MachinesSachi MensiBelum ada peringkat
- Literature ReviewDokumen11 halamanLiterature Reviewfayyazmodi50% (2)
- AWS90 Ch05 ModalDokumen24 halamanAWS90 Ch05 ModalCinitha ABelum ada peringkat
- Performance of Levee Underseepage Controls: A Critical ReviewDokumen52 halamanPerformance of Levee Underseepage Controls: A Critical ReviewLuiz AlvesBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0020722506000942 MainDokumen13 halaman1 s2.0 S0020722506000942 MainAyushmanSrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class XII Mathematics - Vector Algebra Assignment 4Dokumen3 halamanCBSE Class XII Mathematics - Vector Algebra Assignment 4Gauri ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- Access Modifiers in JavaDokumen6 halamanAccess Modifiers in Javaimjd2Belum ada peringkat
- Cambridge Primary Resource List, Mathematics Stages 1,2,3Dokumen8 halamanCambridge Primary Resource List, Mathematics Stages 1,2,3Shahid Hameed100% (1)
- HelloDokumen53 halamanHelloDaniel WertinBelum ada peringkat
- Lectures On Kinetic Theory of Gases and Statistical Physics: Alexander A. SchekochihinDokumen157 halamanLectures On Kinetic Theory of Gases and Statistical Physics: Alexander A. Schekochihinjk bhaiiiBelum ada peringkat
- Learning To Script With AutoIt V3 (Last Updated 17 Feb 2010)Dokumen106 halamanLearning To Script With AutoIt V3 (Last Updated 17 Feb 2010)Chew Ting LiangBelum ada peringkat
- Books: Mathemagician's Guide To Lightning Calculation and Amazing Math Tricks. New YorkDokumen4 halamanBooks: Mathemagician's Guide To Lightning Calculation and Amazing Math Tricks. New Yorkdbrizzolara191Belum ada peringkat
- Graphing Calculator by Mathlab: User ManualDokumen119 halamanGraphing Calculator by Mathlab: User ManualddBelum ada peringkat
- CFD Ex1 ResultsDokumen4 halamanCFD Ex1 ResultsMattBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra 2 Summer Student Enrichment PacketDokumen26 halamanAlgebra 2 Summer Student Enrichment PacketAna ChicasBelum ada peringkat
- SQL ReferenceDokumen1.167 halamanSQL ReferenceTanooj ChowdaryBelum ada peringkat
- Aroon IndicatorDokumen15 halamanAroon IndicatorChiranjib ParialBelum ada peringkat
- Shear Strength & Mohr Circle ProblemsDokumen24 halamanShear Strength & Mohr Circle ProblemsNIKHIL BANDWALBelum ada peringkat
- TAU - DLR Deutsh Software Flow Aero SolverDokumen7 halamanTAU - DLR Deutsh Software Flow Aero SolverilyesingenieurBelum ada peringkat
- BRFplus KT 2013 Day1Dokumen35 halamanBRFplus KT 2013 Day1javedsarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Kant HusserlDokumen257 halamanKant Husserlaseman1389100% (5)
- Cost Volume Profit (CVP) AnalysisDokumen40 halamanCost Volume Profit (CVP) AnalysisAnne PrestosaBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Control II Hover V7Dokumen22 halamanAutomatic Control II Hover V7Arsalan AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- 9700 s12 GTDokumen2 halaman9700 s12 GTBilal AyubBelum ada peringkat
- PhysyllDokumen48 halamanPhysyllThanviomBelum ada peringkat
- SMDM ProjectDokumen19 halamanSMDM Projectnishant100% (1)
- Physics MYP Questions 3Dokumen14 halamanPhysics MYP Questions 3shikhaBelum ada peringkat