Roling Analisa Mekanika
Diunggah oleh
Izzuddin SiregarHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Roling Analisa Mekanika
Diunggah oleh
Izzuddin SiregarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
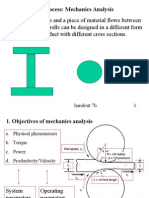
Rolling Process: Mechanics Analysis Two opposite rolls and a piece of material flows between them.
. The shape of rolls can be designed in a different form to construct the product with different cross sections.
handout 7b
1. Objectives of mechanics analysis
a. Physical phenomenon
b. Torque c. Power
d. Productivity/Velocity
System parameters
Operating parameters
handout 7b 2
2. Physical phenomenon Spreading: mass conservation
w
t 0 w0 v 0 t f w f v f
Volume before rolling = the volume after rolling
v0 v f
handout 7b
t 0 w0 L0 t f w f L f
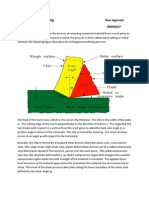
Vo < Vr < Vf Friction causes the velocity of work piece to increase its velocity Inertia causes the velocity of work piece to decrease its velocity
No-slip point
handout 7b
It is the friction between the work and the roll that drives the workflow between two rolls. The friction force is developed based on coefficient of the friction and roll force due to the contact curve.
The pressure varies along the contact length
handout 7b
3. Condition to roll
draft, d = |tf-t0|: dmax
d m ax R
2
Friction coefficient
Radius of the roll
The (actual) draft should be less than d max
handout 7b 6
4. Contact length
L R(t 0 t f )
5. Contact force
F w pdL
0
F Y f wL
N: rotation speed of the roll, rev / min
7
6. Torque
7. Power
T 0.5FL
P 2NFL
handout 7b
For the rolling process, the true strain is:
t0 ln tf
The average flow stress is the same expression, i.e.
Yf
( Y f d )
0
k 1 n
n
8
handout 7b
Example 1 (21.2): A 2.0-in. thick slab is 10.0 in. wide and 12.0 ft long. Thickness is to be reduced in three steps in a hot rolling operation. Each step will reduce the slab to 75% of its previous thickness. It is expected that for this metal reduction of the slab will widen by 3% in each step. If the entry speed of the slab in the first step is 40 ft/min, and roll speed is the same for the three steps, determine (a)
length and (b) exit velocity of the slab after the final
reduction
handout 7b 9
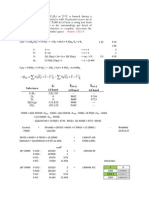
Solution for example 1 (given in the classroom) Diketahui : Tebal = 2 in 75% = 0,5 in
Lebar = 10 in + 3% x 3 step
Panjang = 12 ft
Ditanya : a) Lf = ?
b) Vf = ?
handout 7b
10
Example 2: A 10-in. wide, 1.0-in thick plate is to be reduced in a single pass in a two-high rolling mill to a thickness of 0.8 in. The roll has a radius = 20 in., and its speed = 50 ft/min. The work material has a strength coefficient = 35.000 lb/in.2 and a strain hardening exponent = 0.2. Determine (a) roll force, (b) roll torque, and (c) power
required to accomplish this operation.
handout 7b 11
Solution for example 2 Lebar 10, tebal 1 (given in the classroom)
Diketahui : Lebar =10 in
Tebal = 1 in
Rroll = 20 in
Vo = 50 ft/min Miu = 35.000 lb/in2 E = 0.2 Ditanya : a) F=? b) T=? c) P=?
handout 7b 12
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Solution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionDari EverandSolution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionBelum ada peringkat
- PHY180 Formal Lab Report - Newton's Third LawDokumen4 halamanPHY180 Formal Lab Report - Newton's Third LawAfiq Asri100% (3)
- 3 End of Chapter3 Problems BULKDokumen6 halaman3 End of Chapter3 Problems BULKqusayBelum ada peringkat
- Ieee 80 Grounding Design SystemDokumen103 halamanIeee 80 Grounding Design SystemReynanteBelum ada peringkat
- PE-II Numerical Assignment 2Dokumen3 halamanPE-II Numerical Assignment 2Waqas Ud-din0% (1)
- TutorialDokumen5 halamanTutorialAbdul Razak RahmatBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of Wire DrawingDokumen27 halamanTheory of Wire Drawinggamini ranaweera80% (5)
- 2017 Simulation of Three-Phase Transformerless Online UPS Using MATLAB-SIMULINK-IJAERDV04I0569640 PDFDokumen7 halaman2017 Simulation of Three-Phase Transformerless Online UPS Using MATLAB-SIMULINK-IJAERDV04I0569640 PDFTài Nguyễn Minh NhậtBelum ada peringkat
- Roling Analisa MekanikaDokumen12 halamanRoling Analisa MekanikaanjanandaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1Dokumen1 halamanAssignment 1Abdul RafayBelum ada peringkat
- Problemas LaminaciónDokumen10 halamanProblemas LaminaciónYosmar Emmanuel Vargas TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDokumen96 halamanAbrasive Jet MachiningAbdulaziz FarhanBelum ada peringkat
- N0174147G Manufacturing ProcessesDokumen10 halamanN0174147G Manufacturing Processesphillip chirongweBelum ada peringkat
- Description of Sample Problems: To Features in LS-DYNADokumen30 halamanDescription of Sample Problems: To Features in LS-DYNAmech118Belum ada peringkat
- Bulk Problems PDFDokumen5 halamanBulk Problems PDFSatyasankar LgBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 3 - Procesos de Conformado MasivoDokumen3 halamanTarea 3 - Procesos de Conformado MasivoYuliana Montserrat SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Problems: Problem 1 Problem 2Dokumen2 halamanProblems: Problem 1 Problem 2Lily Margareth ArrietaBelum ada peringkat
- TE 1997 and 2003 Course Oct 2009Dokumen492 halamanTE 1997 and 2003 Course Oct 2009Ajay Solate0% (1)
- Pressure Drop and Velocity Simulations in Non-Stochastic Lattice Structure For Filter Applications Fabricated Using Additive ManufacturingDokumen8 halamanPressure Drop and Velocity Simulations in Non-Stochastic Lattice Structure For Filter Applications Fabricated Using Additive ManufacturingEduardo Leal SalgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Description of Sample Problems: Ls-DynaDokumen29 halamanDescription of Sample Problems: Ls-DynaraviBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 1 2.008 Design and Manufacturing II: SolutionDokumen12 halamanQuiz 1 2.008 Design and Manufacturing II: SolutionLa Casita de TonyBelum ada peringkat
- Angle of DepressionDokumen9 halamanAngle of DepressionNiko ChavezBelum ada peringkat
- Solution: (a) N = v/πD = 70,000 mm/80 = 279 rev/minDokumen11 halamanSolution: (a) N = v/πD = 70,000 mm/80 = 279 rev/minwoihoBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank (PPII)Dokumen7 halamanQuestion Bank (PPII)Udaiyar BarathadhithyaBelum ada peringkat
- HW Solutions 1,2,3,4Dokumen3 halamanHW Solutions 1,2,3,4iyouezra100% (4)
- Assignment3forming Solutions 121213110849 Phpapp02Dokumen4 halamanAssignment3forming Solutions 121213110849 Phpapp02Renaldi Khaesar KumaraBelum ada peringkat
- r7210202 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen1 halamanr7210202 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- PHD Admissions - Sample Question Paper: Y (X) X DX X Dy XDokumen2 halamanPHD Admissions - Sample Question Paper: Y (X) X DX X Dy XabBelum ada peringkat
- CVEN9806 Major Assignment - 2016Dokumen2 halamanCVEN9806 Major Assignment - 2016321daiqiBelum ada peringkat
- Solving Session 1 Mech422Dokumen2 halamanSolving Session 1 Mech422Ismail Abou ZeidBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Key AnswerDokumen6 halamanFinal Exam Key Answergirma worku100% (1)
- Training Mixed TopixDokumen117 halamanTraining Mixed TopixSigue Ramel HinayasBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Sheet Metal Machining and Cutting Conditions 2016Dokumen3 halamanProblem Sheet Metal Machining and Cutting Conditions 2016Muhammad imranBelum ada peringkat
- Nr220301-Mechanics of FluidsDokumen8 halamanNr220301-Mechanics of FluidsSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- 03 Section 2 Example Bridge (E)Dokumen11 halaman03 Section 2 Example Bridge (E)Diego Benavides KBelum ada peringkat
- FMA3601 Assignment 2 MemoDokumen6 halamanFMA3601 Assignment 2 MemoDaniel MabengoBelum ada peringkat
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Dokumen9 halamanJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2saiteja1234Belum ada peringkat
- R7 210304 Mechanics of SolidsDokumen2 halamanR7 210304 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Dokumen9 halamanJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2nvemanBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Materials For Civil and Construction Engineers 3rd Edition by MamloukDokumen13 halamanSolution Manual For Materials For Civil and Construction Engineers 3rd Edition by Mamloukdawkexhume0ixeh6100% (28)
- Dynamics of Machinery r10 May-2016Dokumen20 halamanDynamics of Machinery r10 May-2016Srimanthula SrikanthBelum ada peringkat
- CH304Dokumen2 halamanCH304Watch DogsBelum ada peringkat
- Abrasive Water Jet MachineDokumen12 halamanAbrasive Water Jet MachineRav VenkateshBelum ada peringkat
- CM 801 A Process Piping Design Jun 2020Dokumen2 halamanCM 801 A Process Piping Design Jun 2020RAHUL MATHURBelum ada peringkat
- FlowLabEOC2e CH02Dokumen3 halamanFlowLabEOC2e CH02tomekzawistowskiBelum ada peringkat
- Case 1 (A) : Single Spindle Drill BitDokumen30 halamanCase 1 (A) : Single Spindle Drill BitNeocent DesignsBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 2Dokumen2 halamanTutorial 2Zaid ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4-Bulk Deformation ProcessesDokumen38 halamanChapter 4-Bulk Deformation ProcessesG. Dancer GhBelum ada peringkat
- Drilling PPDokumen26 halamanDrilling PPAnonymous T32l1R100% (1)
- Chapter 4Dokumen11 halamanChapter 4omar mareiBelum ada peringkat
- Cutting Force Thrust ForceDokumen1 halamanCutting Force Thrust ForcepmagrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Question PapersDokumen89 halamanQuestion PapersDreamer ChavanBelum ada peringkat
- FMHM 8Dokumen8 halamanFMHM 829viswa12Belum ada peringkat
- 414 TutorialsDokumen2 halaman414 TutorialsAMOS SIFUNABelum ada peringkat
- Orthogonal Machining - Mechanical ExperimentDokumen4 halamanOrthogonal Machining - Mechanical ExperimentRavi AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationDari EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionDari EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Borehole Analytics: Annular Flow, Hole Cleaning, and Pressure ControlDari EverandModern Borehole Analytics: Annular Flow, Hole Cleaning, and Pressure ControlBelum ada peringkat
- Discrete-continuum Coupling Method to Simulate Highly Dynamic Multi-scale Problems: Simulation of Laser-induced Damage in Silica Glass, Volume 2Dari EverandDiscrete-continuum Coupling Method to Simulate Highly Dynamic Multi-scale Problems: Simulation of Laser-induced Damage in Silica Glass, Volume 2Belum ada peringkat
- Vibrating Screen MachineDokumen2 halamanVibrating Screen MachineIzzuddin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Spherical Roller Bearings-22312Dokumen2 halamanSpherical Roller Bearings-22312Izzuddin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Radial Shaft Seals For General Industrial Applications-40x52x7 HMSA10 RG PDFDokumen1 halamanRadial Shaft Seals For General Industrial Applications-40x52x7 HMSA10 RG PDFIzzuddin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Tugas MKE Fuel and CombutionDokumen10 halamanContoh Tugas MKE Fuel and CombutionIzzuddin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Speedy Instan (Update April 2014)Dokumen1 halamanSpeedy Instan (Update April 2014)Izzuddin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Air PropertiesDokumen1 halamanAir PropertiesIzzuddin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Gambar Teori DasarDokumen2 halamanGambar Teori DasarIzzuddin SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Movie StudioDokumen20 halamanMovie StudioIlkham Navi AdiBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2 DynamicsDokumen2 halamanProblem Set 2 DynamicsKent Edve Neil Rabe0% (2)
- Basics of VibrationsDokumen45 halamanBasics of Vibrationsravimech_862750Belum ada peringkat
- Transline Part 2Dokumen97 halamanTransline Part 2Haw-ChyunBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Data - HVR International - Resistors For Compact CircuitryDokumen2 halamanTechnical Data - HVR International - Resistors For Compact CircuitryNuma LumaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - ANSYS Mechanical Prepost-SolverVol2Dokumen1.011 halaman1 - ANSYS Mechanical Prepost-SolverVol2Rama BaruvaBelum ada peringkat
- Friction Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanFriction Lesson PlanmichelleBelum ada peringkat
- Final ExamDokumen8 halamanFinal ExamykBelum ada peringkat
- Cracking Bgcse PhysicsDokumen96 halamanCracking Bgcse Physicstmoatshe96Belum ada peringkat
- MCC and Panels Maintenance ProcedureDokumen15 halamanMCC and Panels Maintenance ProcedureÁlvaro Manterola Lazcano100% (19)
- Additive and Subtractive Polarity - An Electrician's Guide To Single Phase TransformersDokumen4 halamanAdditive and Subtractive Polarity - An Electrician's Guide To Single Phase TransformersDeoudrafBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulics: Prepared by Ajesh Kumar.T Si/FireDokumen18 halamanHydraulics: Prepared by Ajesh Kumar.T Si/FireSuriya Das100% (2)
- Nichrome Wire Heating Element Design Basics PDFDokumen7 halamanNichrome Wire Heating Element Design Basics PDFInfant RajBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Formual and Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Moving Charges and MagnetrismDokumen13 halamanPhysics Formual and Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Moving Charges and MagnetrismKhushraj Jain100% (1)
- Structural Dynamics Exam - 2008Dokumen5 halamanStructural Dynamics Exam - 2008yusufhargeyBelum ada peringkat
- WIRE ROPE HAULAGE WordDokumen16 halamanWIRE ROPE HAULAGE WordAnshul yadavBelum ada peringkat
- High Altitude, Aviation & Space PhysiologyDokumen51 halamanHigh Altitude, Aviation & Space PhysiologyMelissa Salayog100% (2)
- Acti9 RCCB Katalog Indonesia PDFDokumen3 halamanActi9 RCCB Katalog Indonesia PDFarnosyBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual - EEE 402 - Exp01 July2014Dokumen7 halamanLab Manual - EEE 402 - Exp01 July2014AhammadSifatBelum ada peringkat
- Extensive Review On Laminated Bus Bar For Low and High Power ApplDokumen7 halamanExtensive Review On Laminated Bus Bar For Low and High Power ApplMANGAL KUMAR MOHAPATRABelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Sensors and TransducersDokumen22 halamanChapter 7 Sensors and TransducersAbu ZinnirahBelum ada peringkat
- Pea Grid Code (Eng)Dokumen18 halamanPea Grid Code (Eng)Thanasate PrasongsookBelum ada peringkat
- FileDokumen9 halamanFilegobichand7Belum ada peringkat
- Fresnel Diffraction PDFDokumen31 halamanFresnel Diffraction PDFassefaBelum ada peringkat
- Harmonics in Industrial NetworksDokumen24 halamanHarmonics in Industrial NetworksbonifaciusBelum ada peringkat
- LLG FaultDokumen8 halamanLLG Faultranjish_007Belum ada peringkat
- Airbus. Test EquipmentDokumen14 halamanAirbus. Test EquipmentСергей НиколаевBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid LabDokumen19 halamanFluid LabFu HongBelum ada peringkat