Unit 5 Substructure Design Foundations Compressed
Diunggah oleh
HundeejireenyaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Unit 5 Substructure Design Foundations Compressed
Diunggah oleh
HundeejireenyaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN FOUNDATIONS
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
In any building the superstructure the substructure (foundations) the supporting soil act together to give the building structural stability
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Foundations are the vital link between the superstructure and the ground. The criteria for a successful foundation are: it should be at a minimum depth and size, without exceeding the allowable bearing capacity of any soil layer below the foundation. it should have settlement consistent with the supporting structure it should be able to withstand natural ground movements from frost, moisture and heat regard is given to buildability it should be economical
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
The principles of foundations. The basic function of a foundation is to intercept the load exerted by a building structure and transfer this load to the supporting soil in such a way that the building will not sink into the ground (subside) Structural stability is normally achieved in either of two ways, or indeed a combination of both. Spread the load exerted by the building over a sufficiently wide area to prevent the supporting ground being overstressed Divert or transfer the load to a strata, deep in the ground, which is capable of supporting the imposed load without failure
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
When a building is placed on the ground it exerts a force on the soil. Safe foundations place that load such that the soil is not overloaded. The ability of the ground or soil to bear a load varies with types of soil and ground depth
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Typical subsoil bearing capacities Type of subsoil Rocks, granites and chalk Non-cohesive soils Compact sands Loose uniform sands Cohesive soils Hard clays Soft clays and silts Peats and made-up ground Bearing Capacity (kN/M2) 600 10000 100 - 600
0 600
To be determined by investigation
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
To achieve this basic function the foundation must be:
Be constructed of materials that will not be degraded by chemicals found in the soil around the foundation. Normally foundations are composed of concrete and when conditions demand, the specification of the concrete will need to be altered to avoid corrosive elements in the soil. Able to withstand the effect of frost (also applies to services buried in ground)
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
TYPES OF SOIL Rock The hardest rock is igneous e.g. granite and basalt. Normally they have a high safe bearing capacity, 2-3 times that of sedimentary rocks and 25-30 times that of clays and sands. Generally bedrock is an excellent base to build on but unfortunately the cost of levelling and the cost of excavating service trenches outweighs the initial advantage of a good natural base. Course grained non-cohesive soils Gravels and sands come under this heading. When loaded they shear if unconfined. The particles slide over each other at an angle known as the angle of internal friction . Fine grained cohesive soils These include clays and silts. The major problem with these types of soil is that their nature changes with the level of moisture in the soil. When the soil drys out they shrink, but when the moisture content is increased the soil swells. When water trapped in the soil freezes it can cause vertical heave
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Types of soil Organic soils These include peat, loam and mud. Generally unsuitable for building on. Normally 150-200 mm thick. Such soil (top soil) is usually removed before building begins. Made up soil As the stock of quality building land diminishes, poorer ground is often used. Today made up ground is being utilised. Extreme care should be taken to ensure that such land is properly investigated.
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Working out imposed loads
A
6.000
6.000
6.000
6.000
6.000
C1 B1 B1
C4 B1 B1
C4 B1
C4 B1 B1
C4 B1 B1
C1
B1
B1
B3 B3 B1 B3 B3 B3
SD1
B3 B3 B1 B3 B3 B3
SD1
B3 B3 B1 B3 B3 B3
SD1
B3 B3 B1 B3 B3 B3
SD1
B3 B3 B1 B3 B3 B3
SD1
6.000
C2
C5
C5
C5
C5
C2
SD1
SD1
SD1
SD1
SD1 9.000
B2
B2
B2
B2
C6
B3 B1
C3
B3 B1
C3
B3 B1
C3
B3 B1
C3
B3 B1
C6
B2
B2
B1 B2 B3
= = =
406 x 130 x 39 Universal Beam 457 x 152 x 74 Universal Beam 305 x 127 x 37 Universal Beam
C1 C2 C3 C4
= 254 x 254 x 71 Universal Column = 305 x 305 x 88 Universal Column = 305 x 305 x 149 Universal Column = 305 x 305 x 79 Universal Column = 305 x 305 x 186 Universal Column = 254 x 254 x 85 Universal Column
Note that this building has 3 storeys above ground level + a concrete roof having the same construction as the floors. The ground floor slab is ground supported and is to be disregarded in foundation assessments.
SD1
Structural Concrete Composite Floor using Corus ComFlor 80 Composite Floor Decking- depth of slab = 150mm. Load imposed by ComFloor Deck = 0.75kN/m2
C5 C6
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
QUESTION FOR DISCUSSION IN CLASS The loads exerted by the building vary according to the size, use and form of construction used. What loads are exerted by a building on to the ground below the building? As discussed in unit 2, the building is exposed to both dead and live loads Permanent or dead loads: the weight of the structure, cladding and fixed equipment Temporary or live loads : imposed loads people furniture, nonfixed equipment. environmental or dynamic loads - snow or wind. thermal loads temperature changes causing load on structure
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
To achieve this basic function the foundation must be:
Strong enough to prevent downward vertical loads shearing through the foundation
Capable of withstanding the opposing forces, the weight of the building and the resistance of the soil, such that the foundation will not bend
Stable so that it will not overturn .Whenever possible loads on foundations should be placed centrically.
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
To achieve this basic function the foundation must be:
Capable of withstanding changing conditions in the ground if they occur, e.g. movement caused by shrinking and swelling, water pressure, etc.
Accommodate initial settlement of the structure. It is especially important that uneven settlement does not occur. That the installation of foundations does not overstress the ground such that adjacent existing foundations and services are damaged. It should be noted that the installation of new ground based services can undermine existing foundations. It should also be noted that where services pass under or adjacent to foundations the load exerted on them by the foundations may cause failure. In such situations, such as a sewer collapse this may in turn undermine the foundation.
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
BUILDING NEAR TREES The combination of shrinkable soils and trees, hedgerows or shrubs represents a hazard to structures that requires special consideration. Trees, hedgerows and shrubs take moisture from the ground and, in cohesive soils such as clay, this can cause significant volume changes resulting in ground movement. This has the potential to affect foundations and damage the supported structure. In order to minimise this risk, foundations should be designed to accommodate the movement or be taken to a depth where the likelihood of damaging movement is low.
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Water requirements for different types of trees
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Main types of foundations
Near Surface Foundations - spread foundations Strip Foundations Pad Foundations Continuous Column Founds Balanced Footings Rafts: Plain Slabs Stiffened Edge Downstand Raft Upstand Raft Cellular Raft Buoyancy tanks Deep Foundations Piled Foundations Bored Piles Driven Piles
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Main types of foundations
Spread foundations
Piled foundations
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
SPREAD FOUNDATIONS
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Simplest form of foundation is the strip foundation, used to support a load bearing wall Main types of strip foundations
Conventional strip
Deep strip
Wide strip
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
CONVENTIONAL STRIP FOUNDATIONS Spread the load exerted by the building over a sufficiently wide area to prevent the supporting ground being overstressed
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
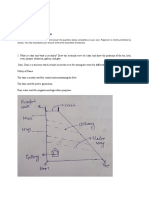
A good quality freehand sketch of a simple strip foundation
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Deep strip foundations Tend to be used at depths greater than 1.2 m deep
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
A good quality freehand sketch of a deep strip or trench fill foundation
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Pad foundation
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
GROUND BEAMS
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
RAFT FOUNDATIONS Spread the load over a wider area
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
RAFT FOUNDATIONS Spread the load over a wider area
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Raft foundation
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
PILE FOUNDATIONS
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Pile Foundations Divert or transfer the load to a strata, deep in the ground, which is capable of supporting the imposed load without failure
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Pile foundations
Two main types displacement & replacement
Typical displacement or driven pile
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Displacement or percussive piles being installed
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Typical replacement or bored pile
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Pile cap
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
BASEMENTS
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
What type of foundation would you use in the assignment? Where would you locate the foundations? Is there a role for a basement?
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
School of the Built Environment Construction Technology D19SC
Unit 3 SUBSTRUCTURE DESIGN - FOUNDATIONS
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Construction Tech AssignmentDokumen13 halamanConstruction Tech AssignmentHashan PereraBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Components of A StructureDokumen12 halamanBasic Components of A StructureBasmaI73% (11)
- Assignment 9.3 - DamsDokumen6 halamanAssignment 9.3 - DamsJurel GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Underwater-Construction RDDokumen28 halamanUnderwater-Construction RDKarthik UBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 1 Control StructuresDokumen20 halamanLec 1 Control Structuresamin alzuraikiBelum ada peringkat
- Headworks Explained: Types, Components and Failure CausesDokumen63 halamanHeadworks Explained: Types, Components and Failure CausesNikhil PhulBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Diversion Headworks WeirsDokumen14 halamanTypes of Diversion Headworks WeirsRAKESH KUMAR 061Belum ada peringkat
- Irrigation Channels Design and AlignmentDokumen88 halamanIrrigation Channels Design and AlignmentDeepankumar AthiyannanBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation Engineering: Meaning and Types of FoundationDokumen29 halamanFoundation Engineering: Meaning and Types of FoundationNasr UllahBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation 131210020404 Phpapp01Dokumen49 halamanFoundation 131210020404 Phpapp01jitBelum ada peringkat
- CH 5 Cross DrinageDokumen40 halamanCH 5 Cross DrinageAbuye HDBelum ada peringkat
- Pitched Roofs..Dokumen78 halamanPitched Roofs..nawin1234Belum ada peringkat
- Types of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Dokumen14 halamanTypes of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Rahul Kumawat100% (1)
- Introduction To Pavment and Types of PavmentsDokumen24 halamanIntroduction To Pavment and Types of PavmentsMehroz BalochBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Design of RockfilldamsDokumen20 halamanPrinciples of Design of Rockfilldamsumairfarooq2Belum ada peringkat
- Construction Technology WallsDokumen24 halamanConstruction Technology WallsAsish Seeboo100% (1)
- Cross Drainage Works - 29052016Dokumen30 halamanCross Drainage Works - 29052016Md Raihan Ali100% (1)
- Lecturenote 2080083980CH-1Dokumen60 halamanLecturenote 2080083980CH-1Kena Qale100% (1)
- Basic Building MaterialsDokumen7 halamanBasic Building MaterialsNatnael AndargeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-5.2 Floor SystemDokumen68 halamanChapter-5.2 Floor SystemFikaduKitessa67% (3)
- Principles of Dam Design Notes 1 - Design of Earth DamsDokumen2 halamanPrinciples of Dam Design Notes 1 - Design of Earth Damsscelo butheleziBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Cofferdams for Foundation ExcavationDokumen5 halamanTypes of Cofferdams for Foundation ExcavationCristiana FelicianoBelum ada peringkat
- BasementsDokumen15 halamanBasementsMeshari FahimBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture No.1 CEDDokumen34 halamanLecture No.1 CEDekhtisham ul haqBelum ada peringkat
- Pin ContentDokumen20 halamanPin ContentSwetha100% (2)
- Pakistan Dams Types PartsDokumen22 halamanPakistan Dams Types PartsEnigmatic Yousafzai100% (1)
- History and Development of Irrigation SystemsDokumen32 halamanHistory and Development of Irrigation SystemsArjelyBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Components of Small Earth DamsDokumen6 halamanDesign and Components of Small Earth DamsErnst OtienoBelum ada peringkat
- Diversion Head Work: Prof. M.B Chougule DKTE' YCP IchalkaranjiDokumen63 halamanDiversion Head Work: Prof. M.B Chougule DKTE' YCP Ichalkaranjishamsu100% (1)
- Hydraulic Structure 1Dokumen211 halamanHydraulic Structure 1tazebBelum ada peringkat
- Irrigation TutorialsDokumen6 halamanIrrigation TutorialsPratik SolankiBelum ada peringkat
- CENG 6606 HSII - 2 Diversion Head WorksDokumen29 halamanCENG 6606 HSII - 2 Diversion Head WorksKenenisa BultiBelum ada peringkat
- FoundationsDokumen10 halamanFoundationsian.kelly4937100% (7)
- 3 - Spring Water TappingDokumen39 halaman3 - Spring Water Tappingمهندس ابينBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Chapter 2 Substructure BFC21002Dokumen116 halaman03 Chapter 2 Substructure BFC21002Claudius IdusBelum ada peringkat
- Road Drainage SystemDokumen10 halamanRoad Drainage SystemE5 Sec - DW & CE [Army]Belum ada peringkat
- Storm Drain System GuideDokumen21 halamanStorm Drain System GuideRojayneBelum ada peringkat
- Selection of FoundationDokumen16 halamanSelection of FoundationroshanBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Water Supply in BuildingsDokumen6 halaman04 Water Supply in BuildingsAshwin NayanarBelum ada peringkat
- Embankment Dams 1Dokumen7 halamanEmbankment Dams 1Schmooz ErBelum ada peringkat
- Components of DamsDokumen37 halamanComponents of DamsAmanuel AzemeteBelum ada peringkat
- Diversion WorksDokumen16 halamanDiversion Worksmoha_yenus5333100% (2)
- Hydraulic Structure I - CENG 3161: Design Principle of DamsDokumen144 halamanHydraulic Structure I - CENG 3161: Design Principle of DamsAbduljebar HussienBelum ada peringkat
- Components & Elements of Built StructureDokumen42 halamanComponents & Elements of Built StructurepurvaBelum ada peringkat
- Earthened DamsDokumen16 halamanEarthened Damsgopisrt100% (1)
- Compensated FoundationDokumen12 halamanCompensated FoundationekaciptaBelum ada peringkat
- Shallow Foundations in SoilDokumen45 halamanShallow Foundations in SoilAizat HermanBelum ada peringkat
- Earthen DamDokumen25 halamanEarthen DamDeeksha DeekshuBelum ada peringkat
- Sub Structure & Super Structure PDFDokumen13 halamanSub Structure & Super Structure PDFInsan Pangestu100% (1)
- Building ServicesDokumen39 halamanBuilding ServicesSyeda SumayyaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Runoff: Key Factors, Process and Cycle SummaryDokumen32 halamanUnderstanding Runoff: Key Factors, Process and Cycle SummaryAafaque HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Ribbed SlabDokumen1 halamanRibbed SlabMohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Earth EN DAM: Title:-Design of Earthen Dam. IntroductionDokumen13 halamanEarth EN DAM: Title:-Design of Earthen Dam. IntroductionRenish Gadhiya100% (1)
- Lesson 7 Construction Dewatering and Ground FreezingDokumen17 halamanLesson 7 Construction Dewatering and Ground FreezingRsjBugtongBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhDokumen13 halamanPile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhAmey Deshmukh100% (1)
- Foundation Science1)Dokumen14 halamanFoundation Science1)Infinity Architectural design technologistBelum ada peringkat
- Construction TechnologyDokumen64 halamanConstruction TechnologySenarath Bandara100% (3)
- Foundations Engg, Lec 1, IntroductionDokumen29 halamanFoundations Engg, Lec 1, IntroductionLearners of Civil Engineering100% (1)
- Lecture No.8 - Bridge FoundationsDokumen40 halamanLecture No.8 - Bridge FoundationsGerald Maginga100% (1)
- DA2103 - FoundationsDokumen42 halamanDA2103 - FoundationsZULKEFLE ISMAILBelum ada peringkat
- Drainage and Irrigation Engineering CourseDokumen56 halamanDrainage and Irrigation Engineering CourseHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- IntroductinDokumen52 halamanIntroductinPrd Dighizqi100% (1)
- Irrigation Engineering Course OverviewDokumen17 halamanIrrigation Engineering Course OverviewHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- IntroductinDokumen52 halamanIntroductinPrd Dighizqi100% (1)
- Chapter Two: Basics in Irrigation EngineeringDokumen80 halamanChapter Two: Basics in Irrigation EngineeringHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Two: Basics in Irrigation EngineeringDokumen80 halamanChapter Two: Basics in Irrigation EngineeringHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Irrigation Engineering Course OverviewDokumen17 halamanIrrigation Engineering Course OverviewHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Irrigation Basics: R. Allen StrawDokumen44 halamanIrrigation Basics: R. Allen StrawHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Irrigation EngineeringDokumen9 halamanIntroduction To Irrigation EngineeringHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 Substructure Design Foundations CompressedDokumen53 halamanUnit 5 Substructure Design Foundations CompressedHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Irrigation Basics: R. Allen StrawDokumen44 halamanIrrigation Basics: R. Allen StrawHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Irrigation Engineering Course OverviewDokumen17 halamanIrrigation Engineering Course OverviewHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Drainage and Irrigation Engineering CourseDokumen56 halamanDrainage and Irrigation Engineering CourseHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan: Sub Code &name: Unit: I Branch: Civil Semester: VDokumen5 halamanLesson Plan: Sub Code &name: Unit: I Branch: Civil Semester: VHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Urban Design Module For Enginering-1Dokumen5 halamanUrban Design Module For Enginering-1HundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Irrigation EngineeringDokumen9 halamanIntroduction To Irrigation EngineeringHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Schedule - Ue: No - Date of Exam Year Course Title Course Code Exam Room Invigilator TimeDokumen1 halamanFinal Exam Schedule - Ue: No - Date of Exam Year Course Title Course Code Exam Room Invigilator TimeHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Guide To Trench ExcavationsDokumen43 halamanGuide To Trench ExcavationsmlakkissBelum ada peringkat
- BEARING CAPACITYDokumen35 halamanBEARING CAPACITYhact72100% (3)
- Excavations and Trenching: 29 CFR 1926 Subpart PDokumen119 halamanExcavations and Trenching: 29 CFR 1926 Subpart PHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit5 PNDokumen15 halamanUnit5 PNMilos KekicBelum ada peringkat
- Unit5 PNDokumen15 halamanUnit5 PNMilos KekicBelum ada peringkat
- Guide To Trench ExcavationsDokumen43 halamanGuide To Trench ExcavationsmlakkissBelum ada peringkat
- Excavations and Trenching: 29 CFR 1926 Subpart PDokumen119 halamanExcavations and Trenching: 29 CFR 1926 Subpart PHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures - HandoutsDokumen24 halamanSeismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures - HandoutsCHarlesghylonBelum ada peringkat
- Building Construction: Mr. Manjally NdowDokumen39 halamanBuilding Construction: Mr. Manjally NdowHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Clasificacion de SuelosDokumen23 halamanClasificacion de SuelosPilar Huancahuire TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Spread Footing Design For ColumnsDokumen19 halamanSpread Footing Design For ColumnsHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Guide RC Project Nagy-Gyorgy T 2013-04-09Dokumen69 halamanGuide RC Project Nagy-Gyorgy T 2013-04-09Bogdan BîngăBelum ada peringkat
- SNC 2p1 Course Overview 2015Dokumen2 halamanSNC 2p1 Course Overview 2015api-212901753Belum ada peringkat
- Alignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFDokumen18 halamanAlignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFAshutosh MauryaBelum ada peringkat
- H I ĐĂNG Assigment 3 1641Dokumen17 halamanH I ĐĂNG Assigment 3 1641Huynh Ngoc Hai Dang (FGW DN)Belum ada peringkat
- HSSC English Model PaperDokumen32 halamanHSSC English Model PaperMaryam Abdus SalamBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Service Exam Clerical Operations QuestionsDokumen5 halamanCivil Service Exam Clerical Operations QuestionsJeniGatelaGatillo100% (3)
- Copula and Multivariate Dependencies: Eric MarsdenDokumen48 halamanCopula and Multivariate Dependencies: Eric MarsdenJeampierr Jiménez CheroBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 Global Finance Business Management Analyst Program - IIMDokumen4 halaman2020 Global Finance Business Management Analyst Program - IIMrishabhaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Baobab MenuDokumen4 halamanBaobab Menuperseverence mahlamvanaBelum ada peringkat
- Template WFP-Expenditure Form 2024Dokumen22 halamanTemplate WFP-Expenditure Form 2024Joey Simba Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- WindSonic GPA Manual Issue 20Dokumen31 halamanWindSonic GPA Manual Issue 20stuartBelum ada peringkat
- British Universal Steel Columns and Beams PropertiesDokumen6 halamanBritish Universal Steel Columns and Beams PropertiesjagvishaBelum ada peringkat
- Staffing Process and Job AnalysisDokumen8 halamanStaffing Process and Job AnalysisRuben Rosendal De Asis100% (1)
- Worksheet 5 Communications and Privacy: Unit 6 CommunicationDokumen3 halamanWorksheet 5 Communications and Privacy: Unit 6 Communicationwh45w45hw54Belum ada peringkat
- Oxygen Cost and Energy Expenditure of RunningDokumen7 halamanOxygen Cost and Energy Expenditure of Runningnb22714Belum ada peringkat
- Open Far CasesDokumen8 halamanOpen Far CasesGDoony8553Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 Discussion Document - Batch 03Dokumen4 halamanTutorial 1 Discussion Document - Batch 03Anindya CostaBelum ada peringkat
- Command List-6Dokumen3 halamanCommand List-6Carlos ArbelaezBelum ada peringkat
- AtlasConcorde NashDokumen35 halamanAtlasConcorde NashMadalinaBelum ada peringkat
- Prasads Pine Perks - Gift CardsDokumen10 halamanPrasads Pine Perks - Gift CardsSusanth Kumar100% (1)
- 2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapDokumen15 halaman2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapDremie WorksBelum ada peringkat
- France Winckler Final Rev 1Dokumen14 halamanFrance Winckler Final Rev 1Luciano Junior100% (1)
- ALXSignature0230 0178aDokumen3 halamanALXSignature0230 0178aAlex MocanuBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Methodology Analysis: 360' Degree Feedback: Its Role in Employee DevelopmentDokumen3 halamanCritical Methodology Analysis: 360' Degree Feedback: Its Role in Employee DevelopmentJatin KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- Busbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersDokumen1 halamanBusbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersVikram SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Developing the cycle of maslahah based performance management system implementationDokumen27 halamanDeveloping the cycle of maslahah based performance management system implementationM Audito AlfansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Technical specifications for JR3 multi-axis force-torque sensor modelsDokumen1 halamanTechnical specifications for JR3 multi-axis force-torque sensor modelsSAN JUAN BAUTISTABelum ada peringkat
- Revit 2010 ESPAÑOLDokumen380 halamanRevit 2010 ESPAÑOLEmilio Castañon50% (2)
- Dolni VestoniceDokumen34 halamanDolni VestoniceOlha PodufalovaBelum ada peringkat
- Beauty ProductDokumen12 halamanBeauty ProductSrishti SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Dokumen12 halamanPaper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Hisham AlEnaiziBelum ada peringkat