Chapter 6 - Receiving and Checking Money
Diunggah oleh
shemida100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
303 tayangan19 halamanCAT T1
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniCAT T1
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
303 tayangan19 halamanChapter 6 - Receiving and Checking Money
Diunggah oleh
shemidaCAT T1
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 19
CHAPTER 6
Receiving and checking
Contents
Control over receipts
Remittance advices
Receipts given to customers
Ways in which customers pay
Cash: physical security considerations
Cheques
Receipt of cheque payments
Receipt of card payments
EFTPOS
Other receipts
Control over receipts
Ensure a good cash flow
Banking (performed promptly and correctly)
Security (avoiding loss or theft)
Documentation (remittance advice)
Remittance advices
Trade customers
usually send a
remittance advice with
their payment
A remittance advice
shows which invoices
a payment covers
Receipts given to customers
Till receipts Cash Register
Issuedby a cash operation
registers or 'tills‘ Store price info on
all stocks
Written receipts Record the value of
Ortyped may be the sale of each
used if no cash item and total
register is used Calculate the
required change to
customer
Issue a till receipt
showing the entire
transaction
Evidence of payment other
than in cash
Receipt from customers
Main types Other types
Cash Standing order
Cheque Direct debit
Credit or debit card Mail transfer and
telegraphic
transfer
Automated credit
services
Cash: physical security
Problem How to deal
Forgery Ø Careful
Theft examination
Ø Cash register
security, Safes
Ø Protective glass
('bandit screen')
Ø Frequent banking
Ø Never be sent by
Cheques
Definition New related words
A cheque is 'an Dishonored
unconditional order in Cheque guarantee
writing addressed by cards
a person to a bank,
signed by the person
giving it, requiring the
bank to pay on
demand a sum
certain in money to or
to the order of a
specified person or
Cheque: procedures
1. Ensure details are correct (date, payee,
amount)
2. Signature: on the cheque vs. guarantee
card
3. Check the details on the cheque
guarantee card.
'Expires end' date
Amount of the guarantee
Name agrees with that on the cheque
Other details
Cheques: physical security
Customers are asked to keep cheque
books and cards separate
The number of cheques in a book is
kept to a minimum.
Plastic card
Most retail
outlets which
accept PLASTIC
cards now use
an electronic
system known
in the UK as
EFTPOS
(Electronic
Funds Transfer
at Point of
Sale).
CREDIT vs.
DEBIT cards
Credit cards
Credit card payment involves 3
transactions
Debit card vs. Credit card
EFTPOS
Electronic Funds Transfer at Point of Sale:
makes possible the automatic transfer
of funds from a customer's bank
account to a retail organization at the
point in time when the customer
purchases goods (or services) from it.
The EFTPOS terminal
Other receipts
Standing orders and direct
Banker’s draft
debits
Method of Regular payments
payment available Standing order can
from banks for a only be changed
fee by the payer
Direct debit can be
When a customer
changed by the
needs a guarantee
receiver at will
that the payment
cannot be
dishonoured
Discussion
Business: electricity company
'I am a domestic customer, and receive a bill from you
each quarter. I want to continue to pay quarterly, but I
don't want to go the trouble of writing out a cheque or
making a special trip (for example to a bank or your
office) to pay the bill. However, I do need to know how
much the bill is going to be before I am due to pay it.
What method of payment would you suggest?‘
'You can pay by quarterly direct debit. You need to
complete a direct debit mandate form which
authorises us to debit amounts from your bank
account. We will send you a bill in the usual way each
quarter, and the amount due will be debited from your
account 14 days after the date of the bill, so you'll
know how much is to be debited well in advance. If an
error is made, either the bank or ourselves must put it
right.'
Business: mail order company
'I want to place an order with you. I don't
have a bank account, building society
account or a credit card, so I suppose that
I'll need to send you the amount due by
cash through the post. Is that OK?‘
'We do not advise you to send cash
through the post, as we cannot accept
responsibility if it is lost. We suggest that
you pay by postal order, obtained
from your post office. The post office
will charge a fee for this service.'
Business: DIY retailer
'I want to call in to your store to buy something costing
$34 for a friend. I understand that you accept cheques
supported by a cheque guarantee card. My friend has
made out and signed the cheque and given me her
cheque guarantee card. I'd like to bring the cheque and
card in when I collect the goods.‘
'In order to pay by a cheque supported by a banker's
card, it is necessary for the person whose
signature appears on the card to sign and date the
cheque in the presence of the payee – in other words,
in our store. This rule is a standard rule of all of the
banks. Please therefore ask your friend to call in to
make the payment herself, unless you wish to pay by
some other means, such as cash.’
Quiz
What is the function of a remittance advice?
Shows which invoices a payment covers
Should cash be sent through the post in 'an
emergency'?
No. Never!
Is it safe to send a cheque through the post?
Yes.
A cheque can be 'stopped' if it goes astray,
and 'traced' if deposited by an unauthorised
person.
A banker's draft cannot be dishonoured. True
or false?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Statement of Change in Financial Position-5Dokumen32 halamanStatement of Change in Financial Position-5Amit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Private Wealth Asia Hong Kong Forum AgendaDokumen15 halamanPrivate Wealth Asia Hong Kong Forum AgendaScarlett TaiBelum ada peringkat
- Final AccountsDokumen65 halamanFinal AccountsAmit Mishra100% (1)
- F8 - AcronymsDokumen2 halamanF8 - AcronymsMezbah Uddin Ahmed50% (2)
- Dating 101: Your Guide To Happiness in LifeDokumen25 halamanDating 101: Your Guide To Happiness in LifeFanny Sylvia C.100% (2)
- Basic Accounting Process PDFDokumen317 halamanBasic Accounting Process PDFObey SitholeBelum ada peringkat
- Osborne-Adsy TZ Ass 2 QuestionsDokumen16 halamanOsborne-Adsy TZ Ass 2 QuestionsAravinthan INSAF SmartClass100% (3)
- Asset Classes and Financial Instruments: Bodie, Kane, and Marcus Eleventh EditionDokumen48 halamanAsset Classes and Financial Instruments: Bodie, Kane, and Marcus Eleventh EditionFederico PortaleBelum ada peringkat
- ACCA Financial Management: Topic Area: - Investment Appraisal - Part 1 - Supplementary Notes - Practice QuestionsDokumen24 halamanACCA Financial Management: Topic Area: - Investment Appraisal - Part 1 - Supplementary Notes - Practice QuestionsTaariq Abdul-MajeedBelum ada peringkat
- Bank of America Matter Banking ConceptsDokumen8 halamanBank of America Matter Banking ConceptsJithendar ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- IB4B Statement Data Files GuideDokumen28 halamanIB4B Statement Data Files GuiderpillzBelum ada peringkat
- ACCA F3 Integrated Financial Accounting Course Companion, BPP PublishingDokumen44 halamanACCA F3 Integrated Financial Accounting Course Companion, BPP Publishingsmy890Belum ada peringkat
- Mortgage-Backed SecuritiesDokumen18 halamanMortgage-Backed SecuritiesAbid faisal AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Xero: A Comprehensive Guide for Accountants and BookkeepersDari EverandXero: A Comprehensive Guide for Accountants and BookkeepersBelum ada peringkat
- Special Client Onboarding TasksDokumen11 halamanSpecial Client Onboarding TasksRichard Rhamil Carganillo Garcia Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Ch. 2 Test Bank - InsuranceDokumen8 halamanCh. 2 Test Bank - InsuranceAhmed NaserBelum ada peringkat
- Crowe Proposal Audit 2021Dokumen7 halamanCrowe Proposal Audit 2021Hikhman Dwi RBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 - Maintaining Petty Cash RecordsDokumen28 halamanChapter 11 - Maintaining Petty Cash Recordsshemida100% (3)
- Chapter 11 - Maintaining Petty Cash RecordsDokumen28 halamanChapter 11 - Maintaining Petty Cash Recordsshemida100% (3)
- F6 ACCA BPP Smart Notes UKDokumen42 halamanF6 ACCA BPP Smart Notes UKSadi Seyidov100% (1)
- ACCA F3 China Slidesv2Dokumen129 halamanACCA F3 China Slidesv2JoeFSabater50% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Business Transactions and DocumentationDokumen40 halamanChapter 1 - Business Transactions and Documentationshemida86% (7)
- Interest & DiscountDokumen44 halamanInterest & DiscountJunior Noel0% (1)
- F1 ACCOUNTING FOR BUSINESS CHAPTERDokumen33 halamanF1 ACCOUNTING FOR BUSINESS CHAPTERWahaj A Khan67% (3)
- Internal Control and Accounting Systems: Student NotesDokumen40 halamanInternal Control and Accounting Systems: Student NotesLegogie Moses AnoghenaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 (Cansingnment Account)Dokumen24 halamanChapter 1 (Cansingnment Account)Bravish GowardhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 18 - Recording Payroll TransactionsDokumen64 halamanChapter 18 - Recording Payroll Transactionsshemida100% (2)
- Chapter 9 - Authorizing and Making PaymentsDokumen26 halamanChapter 9 - Authorizing and Making Paymentsshemida100% (2)
- UKGAAP in Your Pocket - A Guide To FRS 102Dokumen112 halamanUKGAAP in Your Pocket - A Guide To FRS 102Raouf ChBelum ada peringkat
- QB - Transportation and Trucking - Chart of AccountsDokumen1 halamanQB - Transportation and Trucking - Chart of AccountsMaryvic DomendenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Assets Liablities and The Accounting EquationDokumen51 halamanChapter 2 - Assets Liablities and The Accounting Equationshemida100% (7)
- Chapter 12 - Bank ReconciliationDokumen29 halamanChapter 12 - Bank Reconciliationshemida100% (7)
- 12 Month Cash Flow StatementDokumen1 halaman12 Month Cash Flow StatementMircea TeodorescuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 - Banking Monies RevceivedDokumen21 halamanChapter 7 - Banking Monies Revceivedshemida100% (3)
- Chapter 14 - The Receivables LedgerDokumen34 halamanChapter 14 - The Receivables Ledgershemida100% (2)
- Chapter 15 - Purchase and Purchase Returns Day BooksDokumen13 halamanChapter 15 - Purchase and Purchase Returns Day Booksshemida100% (2)
- Chapter 16 - The Payables LedgerDokumen31 halamanChapter 16 - The Payables Ledgershemida100% (3)
- Accounting concepts guide recordingDokumen8 halamanAccounting concepts guide recordingDeepu LuvesBelum ada peringkat
- On The Job Training Log Book: Faculty of CommerceDokumen12 halamanOn The Job Training Log Book: Faculty of CommerceAnonymous Hig1tC2hBelum ada peringkat
- CPA Examination Regulations: What You Need To KnowDokumen24 halamanCPA Examination Regulations: What You Need To KnowGeeti Grover AroraBelum ada peringkat
- PF CMA NotesDokumen19 halamanPF CMA NotesvigneshanantharajanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 17 - Control AccountsDokumen17 halamanChapter 17 - Control Accountsshemida75% (4)
- Aat Level 3 Fapr 1-2Dokumen29 halamanAat Level 3 Fapr 1-2Ira CașuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 - Completing Ledger AccountsDokumen36 halamanChapter 5 - Completing Ledger Accountsshemida100% (2)
- f2 Acca Lesson6 (Labour)Dokumen10 halamanf2 Acca Lesson6 (Labour)Mikhail Banhan100% (1)
- ACCA F2 SyllabusDokumen2 halamanACCA F2 SyllabussairambabailoveyouBelum ada peringkat
- Branch AccountsDokumen42 halamanBranch AccountsJafari SelemaniBelum ada peringkat
- BVN FaqDokumen15 halamanBVN FaqSalako A. SundayBelum ada peringkat
- CMA (USA) - Recorded Lectures Details V2Dokumen15 halamanCMA (USA) - Recorded Lectures Details V2frostyfusioncreameryBelum ada peringkat
- Latest Subsidiary BooksDokumen12 halamanLatest Subsidiary BooksRaghuBelum ada peringkat
- Fia Maintaining Financial Records Fa2 Study Text - AqgmzukDokumen2 halamanFia Maintaining Financial Records Fa2 Study Text - AqgmzukFahad Usmani0% (1)
- Acca f7Dokumen20 halamanAcca f7Sam MahBelum ada peringkat
- Signature Track Guidebook overviewDokumen7 halamanSignature Track Guidebook overviewAndre LuizBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionDokumen29 halamanQuestionMichael Johnson0% (1)
- 1.pilot Paper 1Dokumen21 halaman1.pilot Paper 1Eugene MischenkoBelum ada peringkat
- Basic, Savings and Checking Account Guidance: for Teens and Young AdultsDari EverandBasic, Savings and Checking Account Guidance: for Teens and Young AdultsBelum ada peringkat
- Canadian Taxation Notes 3Dokumen23 halamanCanadian Taxation Notes 3spiotrowskiBelum ada peringkat
- MnemonicsDokumen4 halamanMnemonicsgrindmastah100% (1)
- BSBFIA402 Report On Financial ActivityDokumen64 halamanBSBFIA402 Report On Financial ActivityAlexDrive100% (1)
- Paper f5 Mnemonics Sample Download v2Dokumen54 halamanPaper f5 Mnemonics Sample Download v2jkjiwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Recording and Summarizing TransactionsDokumen56 halamanChapter 4 - Recording and Summarizing Transactionsshemida60% (5)
- 15 Tax Deductions You Should Know - E-Filing GuidanceDokumen32 halaman15 Tax Deductions You Should Know - E-Filing GuidanceErin LamBelum ada peringkat
- Acca f5 SampleDokumen11 halamanAcca f5 Samplejasimuddin92Belum ada peringkat
- ACCA F3 2012 NotesDokumen20 halamanACCA F3 2012 NotesThe ExP GroupBelum ada peringkat
- Namma Kalvi Accountancy Unit 3 Sura English Medium GuideDokumen14 halamanNamma Kalvi Accountancy Unit 3 Sura English Medium GuideAakaash C.K.80% (5)
- Introduction To EmailDokumen20 halamanIntroduction To EmailCarlo BibalBelum ada peringkat
- William WongDokumen3 halamanWilliam WongKashif Mehmood0% (1)
- Different Methods of PaymentDokumen23 halamanDifferent Methods of Paymentcimr33Belum ada peringkat
- 5 Receiving and Checking MoneyDokumen25 halaman5 Receiving and Checking MoneyLucio Indiana WalazaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 6 Methods of Payment 6.1 Settlement of Bills:-: 1. Currency NotesDokumen5 halamanChapter - 6 Methods of Payment 6.1 Settlement of Bills:-: 1. Currency Notesmadhu anvekarBelum ada peringkat
- Lose Weight PlanDokumen3 halamanLose Weight PlanshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Pas - Abraham Charles Benny Hinn in India Adventures in God by John G. LakeDokumen6 halamanPas - Abraham Charles Benny Hinn in India Adventures in God by John G. LakeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Baba RobeDokumen2 halamanBaba RobeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Starter Resume TemplateDokumen3 halamanStarter Resume TemplateshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2. - Activity Based Costing PPT Dec 2011Dokumen5 halamanChapter 2. - Activity Based Costing PPT Dec 2011shemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Writing A Good Title and DescriptionDokumen4 halamanWriting A Good Title and DescriptionshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Baba RobeDokumen2 halamanBaba RobeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- KichdiDokumen1 halamanKichdishemidaBelum ada peringkat
- KichdiDokumen1 halamanKichdishemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Baba RobeDokumen2 halamanBaba RobeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- 06 June 2011 Letter of AbsenceDokumen1 halaman06 June 2011 Letter of AbsenceshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Baba RobeDokumen2 halamanBaba RobeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Recursion (Computer Science) : "Base Case" Redirects Here. For The Bass Solo By, SeeDokumen22 halamanRecursion (Computer Science) : "Base Case" Redirects Here. For The Bass Solo By, SeeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Recursion (Computer Science) : "Base Case" Redirects Here. For The Bass Solo By, SeeDokumen22 halamanRecursion (Computer Science) : "Base Case" Redirects Here. For The Bass Solo By, SeeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 - Statement of Financial Position and Income StatementDokumen28 halamanChapter 3 - Statement of Financial Position and Income Statementshemida75% (4)
- Gulab Jamun RecipeDokumen1 halamanGulab Jamun RecipeshemidaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Recording and Summarizing TransactionsDokumen56 halamanChapter 4 - Recording and Summarizing Transactionsshemida60% (5)
- Chapter 5 - Completing Ledger AccountsDokumen36 halamanChapter 5 - Completing Ledger Accountsshemida100% (2)
- Chapter 10 - Recording PaymentsDokumen19 halamanChapter 10 - Recording Paymentsshemida100% (2)
- Chapter 8 - Recording Monies ReceivedDokumen13 halamanChapter 8 - Recording Monies Receivedshemida100% (2)
- Chapter 13 - Sales and Sales Returns Day BooksDokumen26 halamanChapter 13 - Sales and Sales Returns Day Booksshemida100% (3)
- Reinsurance Industry Results 15Dokumen14 halamanReinsurance Industry Results 15Philip SandaBelum ada peringkat
- PAMI Asia Balanced Fund Product Primer v3 Intro TextDokumen1 halamanPAMI Asia Balanced Fund Product Primer v3 Intro Textgenie1970Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter-6 Data Analysis and InterpretationDokumen25 halamanChapter-6 Data Analysis and InterpretationMubeenBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 - Consolidated Financial Statements (Part 3)Dokumen41 halamanChapter 6 - Consolidated Financial Statements (Part 3)Rena Jocelle NalzaroBelum ada peringkat
- Cash Flow Statement 2019 HL Question Worked SolutionDokumen5 halamanCash Flow Statement 2019 HL Question Worked SolutionConor MurphyBelum ada peringkat
- Acc406 - Aug 2021 - QDokumen12 halamanAcc406 - Aug 2021 - Qtengku rilBelum ada peringkat
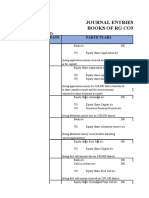
- Journal Entries in The Books of RG Company: Date ParticularsDokumen6 halamanJournal Entries in The Books of RG Company: Date ParticularsRohit GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- AGTL - 2009 Al Ghazi Tractors Limited OpenDoors - PKDokumen30 halamanAGTL - 2009 Al Ghazi Tractors Limited OpenDoors - PKMubashar TBelum ada peringkat
- Tariq Ali 1Dokumen62 halamanTariq Ali 1Hafeezullah ShareefBelum ada peringkat
- Statement-2020-08-11 4Dokumen1 halamanStatement-2020-08-11 4BrendaBelum ada peringkat
- Why I'm No Longer A QuantDokumen11 halamanWhy I'm No Longer A QuantshibusabrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Questions and Answers in AccounDokumen100 halamanPractice Questions and Answers in Accounwalidabdo274Belum ada peringkat
- Tax Invoice for 1oz Gold Coin 2021 Kangaroo PurchaseDokumen1 halamanTax Invoice for 1oz Gold Coin 2021 Kangaroo PurchaseGoran KovacevicBelum ada peringkat
- OpTransactionHistory21 01 2016Dokumen3 halamanOpTransactionHistory21 01 2016venkatesanjsBelum ada peringkat
- DJ BANK LTD. BALANCE SHEET AS ON 31-03-2018Dokumen7 halamanDJ BANK LTD. BALANCE SHEET AS ON 31-03-2018jaimin vasaniBelum ada peringkat
- CH 10 Multifactor Models of Risk and ReturnDokumen23 halamanCH 10 Multifactor Models of Risk and ReturnShantanu ChoudhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Hausi Sky Enterprise Financial ForecastDokumen14 halamanHausi Sky Enterprise Financial ForecastPutri NickenBelum ada peringkat
- Hamim Al Mukit - General Banking of Pubali Bank LTDDokumen42 halamanHamim Al Mukit - General Banking of Pubali Bank LTDHamim Al MukitBelum ada peringkat
- 9th Class MathsDokumen23 halaman9th Class MathsSrinu SehwagBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding invoices and statementsDokumen12 halamanUnderstanding invoices and statementsRonainda AritonangBelum ada peringkat
- RDInstallment Report 01!06!2023Dokumen1 halamanRDInstallment Report 01!06!2023PRADEEP KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- To The of .: Exceptions Principle IndemnityDokumen1 halamanTo The of .: Exceptions Principle IndemnityNKOYOYO HANNINGTONBelum ada peringkat
- Customers Views on Home LoansDokumen14 halamanCustomers Views on Home LoansGaurav KhetiaBelum ada peringkat
- Morgan Stanley CEO On Asian Market DifferentiationDokumen2 halamanMorgan Stanley CEO On Asian Market DifferentiationWorldwide finance newsBelum ada peringkat