Simple Past Present Perfect
Diunggah oleh
captainofseaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Simple Past Present Perfect
Diunggah oleh
captainofseaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
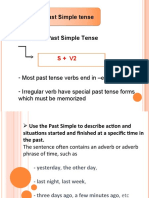
Past simple and present perfect
Time expressions that refer to the present, such as this morning, this month and today, can be used with either past simple or present perfect verbs. If we think of this morning (etc.) as a past, completed time period, then we use the past simple if we think of this morning (etc.) as a time period which includes the present moment, then we use the present perfect.
I didn't shave this morning. (= the morning is over and I didn't shave) I haven't shaved this morning. (= it is still the morning and I might shave later)
In news reports, you will often read about or hear recent events introduced with the present perfect, and then the past simple or other past tenses are used to give details: The film star Jim Cooper has died of cancer. He was 68 and lived in Texas... A teacher from Oslo has become the first woman to cross the Antarctic alone. It took her 42 days to make the crossing with her dog team. The US space shuttle Atlantis has returned safely to earth. It landed in Florida this morning...
With time clauses introduced by after, when, until, as soon as, once, by the time and the time expressions the minute/second/moment the past simple refers to past, completed events and the present perfect refers to future events. After she left hospital (past), she had a long holiday. After Dominic has left school (future), he will be spending six months in India The minute I got the news about Sue (past) I telephoned my parents. I'll contact you the minute I've got my exam results. (future)
In a sentence which includes a time clause with since, we generally prefer a past simple verb in the time clause and a present perfect verb in the main clause. The time clause refers to a particular point in the past: Since Mr. Hassan became president, both taxes and unemployment have increased. (rather than has become...) She hasn't been able to play tennis since she broke her arm. (rather than has broken...) Notice, however, that we use the present perfect in the time clause if the two situations described in the main clause and time clause extend until the present: Have you met any of your neighbours since you've lived here? (not ...you lived...)
PRACTICE Choose a verb to complete the sentence. have go oversleep read spend wear - I . a lot this week, but I have to get the book completely finished by this weekend. -A: Shall I make us some dinner? It's already 8 o'clock. B: No thanks. I to the dentist this afternoon and my mouth hurts too much to ear anything. -I three lectures today and I still have two more later this afternoon. - It was so hot today that I shorts and a T-shirt at work. -We ...... 200 on food this month and there's another week to go before I get paid. - A: Do you want a lift home? 13: No, I .......... ........ this morning because my alarm clock didn't go off, so I need to work late.
Complete the sentences with these pairs of verbs be able / feel happen /speak improve / be not want / fall rescue / be work / not have 1 Maria to go swimming since she ... in the river. 2 Since she .at the company she .a day off through illness. 3 Since he. the girl from the frozen pond, he .. on TV almost every day. 4 A lot . since I last .. to you. 5 Since I..... to drive I............ much more independent 6 Robert's reading. enormously since ..he at school.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- TENSES AND VERB FORMSDokumen7 halamanTENSES AND VERB FORMSMohammed ShahabBelum ada peringkat
- JWJWJWDokumen26 halamanJWJWJWShankSoham MohantyBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present TenseDokumen25 halamanSimple Present Tensebangkit99Belum ada peringkat
- ADDTNL CLASS Important Topics of GrammarDokumen48 halamanADDTNL CLASS Important Topics of GrammarArynda Dimas SadewoBelum ada peringkat
- A. Unit 1 Grammar - Perfect Aspect - TheoryDokumen11 halamanA. Unit 1 Grammar - Perfect Aspect - TheoryVerónica Pérez MadrigalBelum ada peringkat
- Guru PembimbingDokumen6 halamanGuru PembimbingRita SangidahBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen12 halamanTensesTanti AsihBelum ada peringkat
- Future Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureDokumen8 halamanFuture Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureEnrique Gomez OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Units 16 19 Grammar ExercisesDokumen5 halamanUnits 16 19 Grammar ExercisescabricaBelum ada peringkat
- English TensesDokumen25 halamanEnglish TensesShreeya GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- VB2 Grammar Lesson2 ExtraDokumen20 halamanVB2 Grammar Lesson2 ExtraOanh Nguyễn100% (1)
- CLASS PERIOD 12 PRESENT PERFECTDokumen4 halamanCLASS PERIOD 12 PRESENT PERFECTMaiHuongBelum ada peringkat
- Past Simple and Present Tense Verbs GuideDokumen6 halamanPast Simple and Present Tense Verbs GuideTruong NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- The Future Tense - Exercises 4 StsDokumen6 halamanThe Future Tense - Exercises 4 StsNoelia FogarBelum ada peringkat
- Present PerfectDokumen16 halamanPresent PerfectAnonymous cqoc4Mrk5PBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen7 halamanTensesdharoorBelum ada peringkat
- English Grammar Tenses and Speech GuideDokumen16 halamanEnglish Grammar Tenses and Speech GuideSandeep Goud KalalBelum ada peringkat
- Tenses of The Verb (Compiled)Dokumen5 halamanTenses of The Verb (Compiled)Kwing KweenBelum ada peringkat
- Cấu trúc câu bị động theo các thìDokumen13 halamanCấu trúc câu bị động theo các thìHà Trang NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Term Paper Revision XI 1st SemesterDokumen5 halamanTerm Paper Revision XI 1st SemesterCristina StoianBelum ada peringkat
- Future PDFDokumen5 halamanFuture PDFLazhar OuazaniBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar: A/ The Past SimpleDokumen4 halamanGrammar: A/ The Past Simpletran hoang minh 9a222Belum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect Continuous or Past Perfect Continuous RezolvateDokumen7 halamanPresent Perfect Continuous or Past Perfect Continuous RezolvateRadu ConstantinBelum ada peringkat
- Bài 1:mai and Lan Met Each Other Ten Years Ago When They Were Both Sixteen Years OldDokumen8 halamanBài 1:mai and Lan Met Each Other Ten Years Ago When They Were Both Sixteen Years OldĐặng HươngBelum ada peringkat
- Licence 1 English GrammarDokumen28 halamanLicence 1 English GrammarAïda KouabenanBelum ada peringkat
- Remaining TensesDokumen4 halamanRemaining Tensessaigbogun099Belum ada peringkat
- N I Dung 12.3.2023Dokumen5 halamanN I Dung 12.3.2023Bảo Ngọc Nguyễn VũBelum ada peringkat
- AnswerkeyDokumen23 halamanAnswerkeyBiruk TeshomeBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation1 1Dokumen37 halamanPresentation1 1RitaBelum ada peringkat
- Luyện Chuyên Sâu Anh 12 Thí Từ Vựng Và Ngữ Pháp Unit 4 - THE MASS MEDIADokumen9 halamanLuyện Chuyên Sâu Anh 12 Thí Từ Vựng Và Ngữ Pháp Unit 4 - THE MASS MEDIAhavi272006Belum ada peringkat
- Test 17.12Dokumen5 halamanTest 17.12somethingforlifeBelum ada peringkat
- Future Perfect Tense & Future Perfect Continous TenseDokumen6 halamanFuture Perfect Tense & Future Perfect Continous TenseKintan Budi Kresnanda100% (1)
- Advanced Grammar in A Nutshell PDFDokumen50 halamanAdvanced Grammar in A Nutshell PDFOssas OneBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present Tense (Subj + Verb I/+s or Es)Dokumen25 halamanSimple Present Tense (Subj + Verb I/+s or Es)Darius GanBelum ada peringkat
- Level 12Dokumen4 halamanLevel 12MohanedtaBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalsDokumen11 halamanConditionalsCătălina NadiaBelum ada peringkat
- Formation of Simple Present TenseDokumen20 halamanFormation of Simple Present TenseLeo ZerpaBelum ada peringkat
- Common Errors Final 2Dokumen16 halamanCommon Errors Final 2charu1302100% (1)
- CBR IngDokumen8 halamanCBR IngHany VarenciaBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen12 halamanTensesLucian VizireanuBelum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect Simple - P Perfect ContDokumen6 halamanPresent Perfect Simple - P Perfect ContAntonia AntoBelum ada peringkat
- English For Communication: Dana Camelia DiaconuDokumen35 halamanEnglish For Communication: Dana Camelia DiaconuAdela PanaitBelum ada peringkat
- Past Perfect Tense Simplu - Exprimă o Acţiune Trecută Care A Avut Loc Înaintea AlteiDokumen4 halamanPast Perfect Tense Simplu - Exprimă o Acţiune Trecută Care A Avut Loc Înaintea AlteiNicu CojocaruBelum ada peringkat
- Future TenseDokumen31 halamanFuture TenseFitarani0% (1)
- Present Perfect Tense Simple and ContinuousDokumen2 halamanPresent Perfect Tense Simple and ContinuousLiviu ChifaneBelum ada peringkat
- Reported SpeechDokumen21 halamanReported SpeechDana Mindrila80% (10)
- Part 1: Tenses.: Grammar ExercisesDokumen9 halamanPart 1: Tenses.: Grammar ExercisesThiết NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Participles and Relative ClausesDokumen5 halamanParticiples and Relative ClausesMaJu GaleanoBelum ada peringkat
- Cau Tuong Thuat - Co To ThuyDokumen5 halamanCau Tuong Thuat - Co To ThuyVân Hà Nguyễn NgọcBelum ada peringkat
- Future Perfect TenseDokumen13 halamanFuture Perfect TenseFitrianul Imamah Ambar100% (1)
- Grammar and Structure For Ielts: Unit 1: Present TenseDokumen59 halamanGrammar and Structure For Ielts: Unit 1: Present TensePingol PhamBelum ada peringkat
- There Are 12 Tenses in EnglishDokumen6 halamanThere Are 12 Tenses in EnglishyrynukaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Perfect Tenses and AspectDokumen5 halamanPerfect Tenses and Aspectaquiles borgonovoBelum ada peringkat
- Tenses: 1. Simple Present TenseDokumen8 halamanTenses: 1. Simple Present TensePriti guptaBelum ada peringkat
- VerbsDokumen48 halamanVerbsRyla TangahuBelum ada peringkat
- Past Simple TenseDokumen36 halamanPast Simple TenseRosary QuilingBelum ada peringkat
- I, Match The Column On The Left To The Column On The RightDokumen4 halamanI, Match The Column On The Left To The Column On The RightHoang HuyBelum ada peringkat
- Past Perfect Continuous UsesDokumen3 halamanPast Perfect Continuous UsesSHAHRIZ AZILLA BINTI MOHD SABRI MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect AdvancedDokumen4 halamanPresent Perfect Advanceddiala_aliBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Choose The Correct Alternative. Copy The Entire Paragraph in Your NotebookDokumen2 halaman1-Choose The Correct Alternative. Copy The Entire Paragraph in Your NotebookcaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen10 halamanTensescaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Women and NutritionDokumen3 halamanWomen and NutritioncaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Sharks Fco I Cond ConnDokumen4 halamanSharks Fco I Cond ConncaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- GBHMA10090004 Text - Great Fire of LondonDokumen2 halamanGBHMA10090004 Text - Great Fire of LondoncaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Spelling Test - WeatherDokumen1 halamanSpelling Test - WeatherLiterature92Belum ada peringkat
- Weather PT 2Dokumen1 halamanWeather PT 2captainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- I Like Questions : - You/ Be/to ParisDokumen8 halamanI Like Questions : - You/ Be/to PariscaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Using Passive VoiceDokumen1 halamanUsing Passive VoicecaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Passive VoiceDokumen7 halamanPassive VoicecaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Phrasal VerbsDokumen1 halamanPhrasal VerbscaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Phrasal and IdiomsDokumen1 halamanPhrasal and IdiomscaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Smart - Acute (Sight) - Enthusiastic, Eager - Very Strong (Sense of Duty)Dokumen1 halamanSmart - Acute (Sight) - Enthusiastic, Eager - Very Strong (Sense of Duty)captainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Fco I 2nd ConditionalDokumen3 halamanFco I 2nd ConditionalcaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Find Out More!: Teaching English To Young LearnersDokumen4 halamanFind Out More!: Teaching English To Young LearnersmbmjvnsBelum ada peringkat
- Franco Simple Past 1Dokumen1 halamanFranco Simple Past 1captainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Already, Still, YetDokumen1 halamanAlready, Still, YetcaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present Present Progressive/Continuous Affirmative SentencesDokumen6 halamanSimple Present Present Progressive/Continuous Affirmative SentencescaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- AdjectivesDokumen7 halamanAdjectivescaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- AdjectivesDokumen7 halamanAdjectivescaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Catholics Elect First Latin American Pope FrancisDokumen1 halamanCatholics Elect First Latin American Pope FranciscaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Passive VoiceDokumen7 halamanPassive VoicecaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- As A Modal Verb It Doesn't Change Its Tense and Doesn't Add '-S' For The Third Person SingularDokumen4 halamanAs A Modal Verb It Doesn't Change Its Tense and Doesn't Add '-S' For The Third Person SingularcaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Does Billy Sing A Funny Song?Dokumen2 halamanDoes Billy Sing A Funny Song?captainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Quantifiers With Countable NounsDokumen6 halamanQuantifiers With Countable NounsMaria GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Choose The MedalDokumen5 halamanChoose The MedalcaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- Quite RatherDokumen9 halamanQuite RatherMaria GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- As A Modal Verb It Doesn't Change Its Tense and Doesn't Add '-S' For The Third Person SingularDokumen4 halamanAs A Modal Verb It Doesn't Change Its Tense and Doesn't Add '-S' For The Third Person SingularcaptainofseaBelum ada peringkat
- The Canterville GhostDokumen4 halamanThe Canterville Ghostcaptainofsea0% (1)
- Eepc Foreign TradeDokumen3 halamanEepc Foreign Tradepeerspot.me3Belum ada peringkat
- The Revenue CycleDokumen8 halamanThe Revenue CycleLy LyBelum ada peringkat
- Barangay Hearing NoticeDokumen2 halamanBarangay Hearing NoticeSto Niño PagadianBelum ada peringkat
- Resume SureshDokumen2 halamanResume SureshSiva BandiBelum ada peringkat
- 18th SCM New Points 1 JohxDokumen55 halaman18th SCM New Points 1 JohxAnujit Shweta KulshresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Property LawDokumen10 halamanProperty LawVaalu MuthuBelum ada peringkat
- Patrice Jean - Communism Unmasked PDFDokumen280 halamanPatrice Jean - Communism Unmasked PDFPablo100% (1)
- DENR V DENR Region 12 EmployeesDokumen2 halamanDENR V DENR Region 12 EmployeesKara RichardsonBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Power in The United KingdomDokumen188 halamanNuclear Power in The United KingdomRita CahillBelum ada peringkat
- Amalgmation, Absorbtion, External ReconstructionDokumen9 halamanAmalgmation, Absorbtion, External Reconstructionpijiyo78Belum ada peringkat
- Tar Ge T 100: JS AccountancyDokumen33 halamanTar Ge T 100: JS Accountancyvishal joshiBelum ada peringkat
- Shakespeare and The Middle Ages 2009 PDFDokumen310 halamanShakespeare and The Middle Ages 2009 PDFgianiBelum ada peringkat
- J Alexander Kueng Cameras in CourtDokumen3 halamanJ Alexander Kueng Cameras in CourtLaw&CrimeBelum ada peringkat
- PenaltiesDokumen143 halamanPenaltiesRexenne MarieBelum ada peringkat
- R PosDokumen4 halamanR PosBirendra EkkaBelum ada peringkat
- The East India CompanyDokumen7 halamanThe East India CompanyArman HbibBelum ada peringkat
- JOIN OUR BATCH FOR AMUEEE PREPARATIONDokumen16 halamanJOIN OUR BATCH FOR AMUEEE PREPARATIONDRAG-E-SPORT100% (1)
- Kerala rules on dangerous and offensive trade licensesDokumen3 halamanKerala rules on dangerous and offensive trade licensesPranav Narayan GovindBelum ada peringkat
- 3059 10-5 TenderBulletinDokumen56 halaman3059 10-5 TenderBulletinFadyBelum ada peringkat
- The Magnificent-Equity ValuationDokumen70 halamanThe Magnificent-Equity ValuationMohit TewaryBelum ada peringkat
- Canada Application SummaryDokumen6 halamanCanada Application SummaryCarlos FdezBelum ada peringkat
- Blaw 1000 ReviewerDokumen10 halamanBlaw 1000 ReviewerKyla FacunlaBelum ada peringkat
- (7-3) Meco Manning vs. CuyosDokumen7 halaman(7-3) Meco Manning vs. CuyosJan Carlo SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Dumonde v. Federal Prison Camp, Maxwell AFB Et Al (INMATE 2) - Document No. 3Dokumen4 halamanDumonde v. Federal Prison Camp, Maxwell AFB Et Al (INMATE 2) - Document No. 3Justia.comBelum ada peringkat
- Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Latin American History: CloseDokumen21 halamanOxford Research Encyclopedia of Latin American History: CloseemiroheBelum ada peringkat
- Banga V Bello DigestDokumen2 halamanBanga V Bello DigestNylaBelum ada peringkat
- Capital Budget Project OverviewDokumen2 halamanCapital Budget Project OverviewddBelum ada peringkat
- MBA Internship Report FINALDokumen82 halamanMBA Internship Report FINALPratyaksha AgnihotriBelum ada peringkat
- Work Without Your Laptop.: Samsung Dex ProductivityDokumen2 halamanWork Without Your Laptop.: Samsung Dex ProductivityBtakeshi1Belum ada peringkat
- Class 32 Infill Exemption CriteriaDokumen3 halamanClass 32 Infill Exemption CriteriaDaniel JimenezBelum ada peringkat