Principles For Teaching Listening
Diunggah oleh
Grace NgJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Principles For Teaching Listening
Diunggah oleh
Grace NgHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
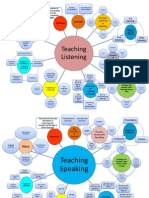
Principles for teaching listening
Integrate listening into the course Appeal to students personal goals
Use authentic language and contexts
Consider how students will respond
Teach listening strategies
Include both bottom-up AND top-down listening
Principles for teaching listening
Make sure pupils understand clearly what they are expected to do before they start on any activity Provide a context for listening Set them some straightforward questions when pupils listen to input for the first time.
Prepare your pupils for the main listening task by doing plenty of pre-listening tasks which will help them succeed in whatever kind of listening task they are required to do
Set tasks that are appropriate for the level of proficiency of the student and type of text.
Use formats that require minimum writing
Do not ask questions in the order in which the answers appear on the tape.
Arrange the questions in the order in which the answers appear on the tape.
Give students a chance to read through the questions before they listen to tape.
Many listening comprehension exercises concentrate almost entirely on comprehension of facts.
Decide on the number of times the students would be able to listen to listening input.
Help the pupils to gain confidence by encouraging them to ignore the bits they do not understand so long as they understand enough to do the task required of them.
Check all recorded material before you get the pupils to listen to it.
Ensure that the quality of your tape is excellent, exactly the way you want.
Choose a period that is suitable for a listening lesson.
Do your best to find listening input and listening tasks that pupils enjoy doing and make sure that there is a very high likelihood that most.
Principles for Teaching Speaking
Focus on fluency and accuracy (depending on objective)
Use intrinsically motivating techniques
Use authentic language in meaningful contexts
Provide appropriate feedback and correction
Optimize the natural link between listening and speaking (and other skills)
Give students the opportunity to initiate oral communication.
Develop speaking strategies.
Take account of the Be sensitive , sympathetic and encouraging. student as a Select material that is motivating person.
and within the ability of students
Reduce anxiety by moving from easy to more difficult Maintain a careful balance between accuracy and fluency
Taking short turns Provide a familiar, private environment The speaker has information that the listener does not have Information you expect the students to communicate is within their experience and understanding
Accuracy production of a range of correct and appropriate words and structures as well as correct use of phonological features like pronunciation, stress, intonation, rhythm Fluency ability to produce speech that has normal flow Maintaining a careful balance between accuracy-building and fluency-building
Provide a good model for students to imitate
Provide appropriate stimuli for eliciting speech
Learning to speak English in an acceptable way Using the target rhythms, stress patterns, words over and over again Consciously teaching students correct pronunciation, intonation
Proportion of the total time allocated What oral skill will they learn? Will they get enough practice in the target skill? Ratio between teacher talking time and student talking time Familiarity of content of stimulus Does the stimulus give too much of the language the student is supposed to use?
Vary interaction
Pair beside Pair opposite Group
Give clear instructions
Monitor student activity
Make sure you have made adequate preparation for your class
Handle errors sensitively and effectively
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Basic Sentence Structure: Parts of Sentences: Subject, Predicate, Object, Indirect Object, ComplementDokumen5 halamanBasic Sentence Structure: Parts of Sentences: Subject, Predicate, Object, Indirect Object, Complementbrakah maghrabyBelum ada peringkat
- TCT 201 Instructional TechnologyDokumen93 halamanTCT 201 Instructional Technologyjudith musyokiBelum ada peringkat
- Testing English As A Second Language CompressDokumen163 halamanTesting English As A Second Language CompressMurtuza MuftiBelum ada peringkat
- Procedural Text Lesson SequenceDokumen4 halamanProcedural Text Lesson Sequenceapi-238051278100% (1)
- Flipped Classroom Lesson Plan 331Dokumen6 halamanFlipped Classroom Lesson Plan 331api-279511284Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd Speaker TemplateDokumen4 halaman3rd Speaker TemplateKinAnggun SaengtyasaBelum ada peringkat
- Important Lesson Planning For The Teacher and The Learners: InteractiveDokumen19 halamanImportant Lesson Planning For The Teacher and The Learners: InteractivejosephkondoBelum ada peringkat
- Component A: Acquisition OF KnowledgeDokumen26 halamanComponent A: Acquisition OF KnowledgepersonwithheartBelum ada peringkat
- Delivery PlanDokumen3 halamanDelivery Planapi-734710904Belum ada peringkat
- Background Paper On Teaching ListeningDokumen12 halamanBackground Paper On Teaching ListeningSaman NaseemBelum ada peringkat
- MulticulturalDokumen14 halamanMulticulturalblessie delcoBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching MethodsDokumen25 halamanTeaching Methodslittle large2100% (1)
- Principles For Teaching Speaking SkillsDokumen2 halamanPrinciples For Teaching Speaking SkillsSymr MhzzbBelum ada peringkat
- Techniques For Teaching Listening and Speaking SkillsDokumen9 halamanTechniques For Teaching Listening and Speaking SkillsElfera Adriana100% (1)
- TSL3105 Teaching Listening and Speaking in The Primary ClassroomDokumen10 halamanTSL3105 Teaching Listening and Speaking in The Primary ClassroomNanthini SubramaniamBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching ListeningDokumen28 halamanTeaching ListeningMisis Krung P100% (4)
- 7 Listening TechniquesDokumen25 halaman7 Listening TechniquesThomas SembodoBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching English to Speakers of Other LanguagesDari EverandTeaching English to Speakers of Other LanguagesPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Teaching Listening NCLRCDokumen11 halamanTeaching Listening NCLRCJESS CrazyshoesBelum ada peringkat
- TESOLDokumen25 halamanTESOLshahzadBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching ListeningDokumen9 halamanTeaching Listeningsofija manaievaBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Reading: Welcome, Students!Dokumen40 halamanTeaching Reading: Welcome, Students!jade tagabBelum ada peringkat
- 875 Boyer Plan Assessing For LearningDokumen6 halaman875 Boyer Plan Assessing For Learningapi-548359274Belum ada peringkat
- Topic 3: Selection and Adaptation of Materials and ActivitiesDokumen14 halamanTopic 3: Selection and Adaptation of Materials and ActivitiesAisha FatimahBelum ada peringkat
- Routines One-Pager 6-16-14Dokumen2 halamanRoutines One-Pager 6-16-14api-277412077Belum ada peringkat
- p22-25 Teaching TipsDokumen4 halamanp22-25 Teaching TipsSilvia KalamenovaBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching ListeningDokumen24 halamanTeaching ListeningCesarGuerreroBelum ada peringkat
- The Five Key Components of Reading: - Phonemic Awareness - Phonics - Fluency - Vocabulary - ComprehensionDokumen62 halamanThe Five Key Components of Reading: - Phonemic Awareness - Phonics - Fluency - Vocabulary - Comprehensionkenneth martinBelum ada peringkat
- Six Components of ReadingDokumen62 halamanSix Components of ReadingKathleen Kay Rodriguez Cruz100% (1)
- BrochureDokumen2 halamanBrochureapi-278538540Belum ada peringkat
- Listening and SpeakingDokumen9 halamanListening and SpeakingRuslana KuchmaBelum ada peringkat
- ESOL Strategies Matrix A. Listening A1. LEA (Language Experience Approach)Dokumen17 halamanESOL Strategies Matrix A. Listening A1. LEA (Language Experience Approach)attar8Belum ada peringkat
- Mastering CELPIP Speaking: Strategies, Tips, and Practice for SuccessDari EverandMastering CELPIP Speaking: Strategies, Tips, and Practice for SuccessBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Concepts of Language Learning Materials: by Porntip BodeepongseDokumen36 halamanBasic Concepts of Language Learning Materials: by Porntip BodeepongsePorntip Bodeepongse รักในหลวง100% (4)
- Presentacion Nº9 Strategies For Listening PracticeDokumen17 halamanPresentacion Nº9 Strategies For Listening Practicerodrigo gonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Listening SkillsDokumen21 halamanTeaching Listening SkillsVansh RatheeBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Listening: Teaching English As A Foreign LanguageDokumen10 halamanTeaching Listening: Teaching English As A Foreign LanguageRoy Lustre AgbonBelum ada peringkat
- Build FluencyDokumen2 halamanBuild FluencyKatherin Rodriguez ZavaletaBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Listening SkillsDokumen21 halamanTeaching Listening SkillsManal EzzBelum ada peringkat
- Heidi M. Ladignon-Comprehension-based ApproachDokumen14 halamanHeidi M. Ladignon-Comprehension-based ApproachHeidi100% (1)
- Developing Independent Learning StrategiesDokumen2 halamanDeveloping Independent Learning StrategiestesolBelum ada peringkat
- Handout TeachingGoalsandMethodsDokumen14 halamanHandout TeachingGoalsandMethodsSharon B. JamesBelum ada peringkat
- Răspunsuri Metodică - FormatatDokumen24 halamanRăspunsuri Metodică - FormatatMagda GherasimBelum ada peringkat
- Techniques - Curr. ReportDokumen3 halamanTechniques - Curr. ReportRodel Bryan Coronejo ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Goals and Syllabus: Dewanti Dian Apriliani Efi Rokhayanti Novida Fatma Dewita Priskila Shendy HartantiDokumen30 halamanGoals and Syllabus: Dewanti Dian Apriliani Efi Rokhayanti Novida Fatma Dewita Priskila Shendy HartantiPriskila Shendy HartantiBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3: Selection and Adaptation of Materials and Activities Abohs, Fizi, SyafiqDokumen14 halamanTopic 3: Selection and Adaptation of Materials and Activities Abohs, Fizi, SyafiqYasseerRajBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching ListeningDokumen7 halamanTeaching ListeningMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- 41 Practical Work 1Dokumen13 halaman41 Practical Work 1мирослава ТурукBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Strategies For The Development of Literacy SkillsDokumen16 halamanTeaching Strategies For The Development of Literacy Skillsdany mosby100% (5)
- Teaching ReadingDokumen40 halamanTeaching ReadingJeruel PronBelum ada peringkat
- Delivery Plan Ela Teks 3Dokumen4 halamanDelivery Plan Ela Teks 3api-703164243Belum ada peringkat
- Oral Presentation Rubric RECIPEDokumen1 halamanOral Presentation Rubric RECIPEvaleska86100% (4)
- EN8F-Id-3: Deliver A Self-Composed Informative SpeechDokumen2 halamanEN8F-Id-3: Deliver A Self-Composed Informative SpeechEra Darren NacenoBelum ada peringkat
- The Silent WayDokumen11 halamanThe Silent WayDewi Ratnah100% (3)
- Teaching SpeakingDokumen7 halamanTeaching SpeakingGeorgio DarmanyBelum ada peringkat
- Mastering The Four SkillsDokumen47 halamanMastering The Four SkillsBukelwa MabuyaBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching of The Macro SkillsDokumen30 halamanTeaching of The Macro SkillsNiño Naldoza100% (1)
- Artifact #3: Unit Plan Project: Why Did You Include This Artifact?Dokumen36 halamanArtifact #3: Unit Plan Project: Why Did You Include This Artifact?api-288966220Belum ada peringkat
- Strategies for Teaching English Language, Literature, and ContentDari EverandStrategies for Teaching English Language, Literature, and ContentPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Tutorial 4Dokumen4 halamanTutorial 4Grace NgBelum ada peringkat
- An Introductory Part WhichDokumen2 halamanAn Introductory Part WhichGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- PLCDokumen5 halamanPLCGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- PLCDokumen5 halamanPLCGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Enacted CurriculumDokumen2 halamanEnacted CurriculumGrace Ng84% (19)
- ChantDokumen7 halamanChantGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- ColourDokumen1 halamanColourGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- TSL3113 ProFormaDokumen5 halamanTSL3113 ProFormaYi Jing LoiBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum StudiesDokumen30 halamanCurriculum StudiesSamantha Ong Pei ShanBelum ada peringkat
- Toilet Library Year 3 Classroom Year 2 Classroom Year 1 Classroom CanteenDokumen3 halamanToilet Library Year 3 Classroom Year 2 Classroom Year 1 Classroom CanteenGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Persatuan Kelab Kembara: Semester 6Dokumen1 halamanPersatuan Kelab Kembara: Semester 6Grace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Simulated Teaching Activity: Information Gap: Prepared byDokumen5 halamanSimulated Teaching Activity: Information Gap: Prepared byGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- The Writing Center Presents:: ProofreadingDokumen75 halamanThe Writing Center Presents:: ProofreadingGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Topic2 Role and Purposes of Assessment in Teaching and LearningDokumen29 halamanTopic2 Role and Purposes of Assessment in Teaching and LearningAemo LoveaBelum ada peringkat
- Table of ContentsDokumen1 halamanTable of ContentsGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- AskmebuyDokumen1 halamanAskmebuyGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan On ReadingDokumen7 halamanLesson Plan On ReadingGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly Scheme of Work BsDokumen2 halamanWeekly Scheme of Work BsGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- SyllabusDokumen4 halamanSyllabusGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Discuss The Importance of Authenticity in TestingDokumen2 halamanDiscuss The Importance of Authenticity in TestingGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- The ZooDokumen1 halamanThe ZooGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson PlanclotDokumen5 halamanDaily Lesson PlanclotGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- English Year 1 KSSR Yearly PlanDokumen19 halamanEnglish Year 1 KSSR Yearly Planrehnzz100% (1)
- Written Feedback of Peer ObservationDokumen4 halamanWritten Feedback of Peer ObservationGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Englishyearlyschemeofworkyear6 121230113931 Phpapp01Dokumen20 halamanEnglishyearlyschemeofworkyear6 121230113931 Phpapp01Grace NgBelum ada peringkat
- ContohDokumen37 halamanContohmaydoniBelum ada peringkat
- SyllabusDokumen4 halamanSyllabusGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Task 1Dokumen8 halamanTutorial Task 1Grace NgBelum ada peringkat
- SyllabusDokumen4 halamanSyllabusGrace NgBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Win-Win Performance Review (Position Agreement)Dokumen7 halamanSample Win-Win Performance Review (Position Agreement)JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Implementing The CurriculumDokumen14 halamanChapter 3 Implementing The Curriculumbonifacio gianga jr100% (1)
- Preliminaries OJT PortfolioDokumen8 halamanPreliminaries OJT PortfolioRoland IrojoBelum ada peringkat
- Explicit Instruction Smart Goals - Braden PellyDokumen4 halamanExplicit Instruction Smart Goals - Braden Pellyapi-430800269Belum ada peringkat
- Global Assessment FunctioningDokumen8 halamanGlobal Assessment Functioningalin67100% (1)
- Nursing AssessmentDokumen2 halamanNursing AssessmentCarmena IngenteBelum ada peringkat
- RRLDokumen2 halamanRRLKenneth NuñezBelum ada peringkat
- Magsaysay Memorial College: Christian Modelling)Dokumen2 halamanMagsaysay Memorial College: Christian Modelling)Jian Carlo RelanizaBelum ada peringkat
- Design Your Employee ExperienceDokumen8 halamanDesign Your Employee ExperienceDimple GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen3 halamanDaftar PustakaFikrah IslamiBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Attainment ModelDokumen1 halamanConcept Attainment Modelapi-242205744Belum ada peringkat
- Activity On Circulatory SystemDokumen2 halamanActivity On Circulatory SystemChin CustodioBelum ada peringkat
- Criminal Profiling FBIDokumen34 halamanCriminal Profiling FBIRoberto GodoyBelum ada peringkat
- Behavioural Interview PDFDokumen33 halamanBehavioural Interview PDFDeepthi VasanthakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Baseline Assessment Form 1Dokumen5 halamanBaseline Assessment Form 1api-541869781Belum ada peringkat
- (1954) Bell - The Relationship Between Leadership and EmpathyDokumen2 halaman(1954) Bell - The Relationship Between Leadership and EmpathyDavid Lourenço FilhoBelum ada peringkat
- PE Peer Teaching Lesson PlanDokumen2 halamanPE Peer Teaching Lesson PlansillyaiBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Guide: Chapter Seven-Behavioral Learning Theory: Operant ConditioningDokumen4 halamanLearning Guide: Chapter Seven-Behavioral Learning Theory: Operant ConditioningXzandria WellsBelum ada peringkat
- Apendices: Appendix IDokumen6 halamanApendices: Appendix IAytenewBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Abnormality Definitions and ModelsDokumen8 halamanEvaluation of Abnormality Definitions and ModelsKhadija JawedBelum ada peringkat
- Tpe 3Dokumen8 halamanTpe 3api-547598526100% (1)
- m8 Sdaie Lesson Plan - FinalDokumen3 halamanm8 Sdaie Lesson Plan - Finalapi-438185362Belum ada peringkat
- DLP FormatDokumen2 halamanDLP Formatrudy rex mangubat0% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 DinzDokumen9 halamanCHAPTER 2 DinzDinz Guanzon TayactacBelum ada peringkat
- The Ultimate Eu Test Book: Administrator (Ad) Edition 2013Dokumen2 halamanThe Ultimate Eu Test Book: Administrator (Ad) Edition 2013Porrosberla0% (1)
- Module 1 Writing AssignmentDokumen5 halamanModule 1 Writing Assignmentapi-279202840Belum ada peringkat
- Reflection Paper of Ron Clark StoryDokumen2 halamanReflection Paper of Ron Clark StoryLucky50% (2)
- Contemp 4Dokumen4 halamanContemp 4Dario Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Research IntroductionDokumen20 halamanSample Research IntroductionSaphire DelBelum ada peringkat
- Alejandro-Chapter 4-Reflection PaperDokumen3 halamanAlejandro-Chapter 4-Reflection PaperAngelica AlejandroBelum ada peringkat