Presentation 1
Diunggah oleh
PeNgHoOiDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Presentation 1
Diunggah oleh
PeNgHoOiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
As density is the ratio of mass to volume, increment in mass outweigh increase in volume.
Thus, density increases going down the group. Boiling point decreases down the group as the electrical attractive forces between the immobile ions in the metal lattice and the free mobile delocalised electrons decreases due to increment in atomic radii.
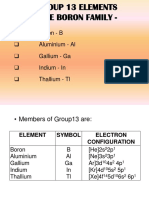
atomic atomic mass number (amu) Metalloid valence electron configuration melting point/boiling point (C)
Atomic radius increases down the group as an extra inner shell of electrons is added per period.
density (g/cm3) at 25C
most common atomic oxidation electrone radius (pm) state gativity
Metallic character increases down the group as ionization energies decreases.
Boron Metal Aluminium Gallium Indium Thallium
10.81
2s22p1
2075/4000
2.34
87
13 31 49 81
26.98 69.72 114.82 204.38
3s23p1 4s24p1 5s25p1 6s26p1
660/2519 29.7/2204 156.6/2072 304/1473
2.7 5.91 7.31 11.8
118 136 156 156
3 3 3 1
1.6 1.8 1.8 1.8
Diagonal relationship
Refers to pairs of diagonally adjacent elements in the second and third periods of the periodic table. Results in similarity among atomic size, electronegativity and properties of compounds.
Group 13 elements generally have +3 oxidation state. However, lower oxidation state is getting more stable descending the group. Eg. Tl+ has a +1 oxidation state.
ns2np1(p block)
General Features of Group 13
Aluminium third most abundant element (after oxygen and silicon)
Melting point Boiling point Density 660 C 2520C 2.70gcm-3
metallic ( except boron , which is a solid metalloid ) chemically reactive at moderate temperature ( except boron ) scarce in nature ( except aluminium , which is the most abundant metallic element ) High charge density leads to high polarising power. This gives rise to the significant of covalent characteristics among group 13 compounds.
Major factor : charge density among the pairs are relatively similar. Proof: boron and silicon are both semiconductors, forming halides that are hydrolysed in water and have acidic oxides. Both Be 2+ and Al 3+ are hydrated to produce [Be(H20)4]2+ and [Al(H2O)6]3+ respectively. Another similarity between aluminum and beryllium is that they are amphoteric. Both metals also react with oxygen to produce an oxide coating that protects other metals from corrosion. Both metals can also react with halides that can act as Lewis acids.
Reactivity and metallic characteristics
They have three electrons in their outermost shell (a full S orbital and one electron in the P orbital) with the valence electron configuration: ns2np1. The Boron Family has oxidation states +3 or +1. The +3 oxidation states are favorable except for the heavier elements, such as Tl, which prefers +1 oxidation state due to its stability. This is known as the inert pair effect. Electrode potential increases going down the group (reactivity decreases as going down group) Ionization Energy decreases going down the group (since the electrons are farther from the core and due to screening effect, therefore are easier to remove). *Tl
does not follow normal trends
Electronegativi 1.6 ty (pauling scale) Crystal structure Facecentered cubic
Thallium -Common uses of Thallium include rat poison, insecticide, and treatment of skin infections
Aluminium -Impure Al2O3 are found as gemstones such as ruby and sapphire. -Recycling aluminium saves 95% of energy required to produce new aluminium. -Aluminium is somehow might cause Alzheimers Disease based on recent research.
versatile => ductile and malleable generally, Al forms ionic compounds with covalent characteristics due to high charge density which makes it polarize the electron cloud of an anion. Thus, Al is a strong reducing agent. Example: aluminium oxide 2050C strong ionic bond between Al3+ and O2- with significant covalent characteristics >> amphoteric. Al2O3(s) + 6HCl (aq) 2AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2O(l) Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH (aq) +3 H2O 2NaAl(OH)4 (aq) Al2O3 catalyst in cracking of alcohol & dehydration of alkene, stationary phase in column or thin layer chromatography, refractory furnace bricks. Aluminium as alloy Aluminium is added in duralumin and magnalium for manufacture of body of aircraft and engine block. Interesting facts: A) When 2 molecules of AlCl3 meets, dimerisation will occur. One of the lone pair of one of the Cl atom of each AlCl3 will form dative bond with empty 3d orbital of the other Al atom, forming a dimer, Al2Cl6. B) Aluminium wire is used in overhead high tension cables, replacing old copper wire due to lighter weight and conductivity of aluminium. C) Acidic property of Al3+ ion In aqueous solution, Al3+ ions able to attract 6 water molecules to form 6 dative bonds, forming hexaaquaaluminium(III) ion. Due to high charge density of Al3+ ion it withdraws the electron density from the O-H bonds in the water molecules, thus weakening the bonds. As a result, water molecule of the hexaaquaaluminium(III) ion acts as Bronsted-Lowry acid and donates H+ ions. D) Despite aluminium is reactive, Al is resistant against oxidation. Why? When Al exposed to air, it forms a thin, non-porous and impenetrable oxide layer of Al2O3 on the surface which protects the aluminium from further attack by oxygen or dilute acid.
0CCURANCE
Do not occur elementally in nature due to their high reactivity in its elemental state. B - Na2 [B4O5(OH)4]8H2O (borax), H3BO3 (boric acid) Al - bauxite (Al2O3), cryolite (Na3AlF6) << to reduce the melting point of bauxite Ga - byproduct of aluminum refining In - byproduct of lead refining Ti - byproduct of lead refining Boron -Boron produces a green flame. -Boron is present in laboratory glass wares. It has low thermal expansion. -Research indicates Boron may be beneficial for the treatment of arthritis.
Indium -A thin layer of indium tin oxide can be found on LCD displays, such as through the monitor in which you are reading this.
Boron
Only semi-metal of this group. Electron deficient compound, make it a strong Lewis acid. Due to its lack of a complete octet Boron is a Lewis acid, so it forms hydrides and the simplest boron hydride found is diborane, B2H6. Eg. Widely used in synthesis of organic compounds. Essential nutrients for plants. Boron (B) deficiency is the most widespread micronutrient deficiency around the world and causes large losses in crop production both quantitatively and qualitatively. Boron deficiency affects vegetative and reproductive growth of plants resulting in inhibition of cell expansion, death of meristem and reduced fertility.
References
1. Ralph H. Petrucci, F. Geoffrey Herring, Jeffry D. Madura, Carey Bissonnette. General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications, 10th ed. Canada, Toronto, Ontario: Pearson Canada; 2010. 2. Author unknown. Ruby. http://gem5.com/stone/100/ruby/#sthash.aJBQohkf.dpuf (accessed 13 Dec 2013). 3. Author unknown. Alzheimer's Again Linked To Aluminum. http://www.rense.com/general37/alum.htm (accessed 13 Dec 2013). 4. Shriver & Atkins. Inorganic Chemistry, Forth Edition ed. The United Kingdom: Oxford University Press; 2006. 5. Author unknown. Boron. http://www.webelements.com/boron/chemistry.html (accessed 14 Dec 2013). 6. Author unknown. The Element of Group 13. http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/principles-ofgeneral-chemistry-v1.0/s26-01-the-elements-of-group-13.html (accessed 16 Dec 2013). 7. Author unknown. Group 13. http://www.rsc.org/chemsoc/visualelements/pages/data/intro_groupiii_data.html (accessed 1 Jan 2014).
Gallium -Due to it's melting point, gallium melts in your hands.
Group members: Lee Peng Hooi (BP0913034147), Chen Wei Yin ( BP0913034069), Nur Farah (BP0913034089), Siti Khadijah (BP0913034202), Yue Lee Kuan (BP0913034222), Denise Wong (BP0913034229), Kok Chee Leng (BP0913034242), Tang Kar Foong (BP0913034296), Yeap Wei Leng (BP091303430), Lim Kai Xin (BP0913034303), Cheng Huei Sze (BP0913034308)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Chemistry of Chromium, Molybdenum and Tungsten: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesDari EverandThe Chemistry of Chromium, Molybdenum and Tungsten: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- INFO-Sheet Fumis ALPHADokumen2 halamanINFO-Sheet Fumis ALPHAAnthony GilmoreBelum ada peringkat
- P BlockDokumen29 halamanP BlockVishal SBelum ada peringkat
- ThepblockelementsDokumen56 halamanThepblockelementsAshutosh Ganesan92% (13)
- Group 13 The Boron FamilyDokumen130 halamanGroup 13 The Boron Familystella jovita0% (1)
- Group 13 AluminiumDokumen48 halamanGroup 13 AluminiumLooi Chui Yean100% (1)
- 13,14 Group TheoryDokumen29 halaman13,14 Group TheoryAlkaChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Group IIIA: The Chemistry of AluminumDokumen12 halamanGroup IIIA: The Chemistry of AluminumEvgeni GenevBelum ada peringkat
- The P-Block ElementsDokumen20 halamanThe P-Block ElementsNabiha KaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Earth MetalsDokumen27 halamanEarth MetalsAmanda PachecoBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 - The P-Block ElementsDokumen44 halamanRevision Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 - The P-Block ElementsDevashree NaikBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium and Its Compound A. BackgroundDokumen8 halamanAluminium and Its Compound A. BackgroundNur Ayu Pertiwi HasmanBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium MetallurgyDokumen3 halamanAluminium MetallurgyShubham ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminum CorrosionDokumen1 halamanAluminum CorrosionthanhnguyenhhvnBelum ada peringkat
- AluminiumDokumen20 halamanAluminiummradu1Belum ada peringkat
- 5 Electricity and Chemistry: ElectrolysisDokumen12 halaman5 Electricity and Chemistry: Electrolysistotatote034Belum ada peringkat
- Universidad Nacional de San Antonio Abad Del Cusco: Facultad de Ing. Geológica Y GeográficaDokumen24 halamanUniversidad Nacional de San Antonio Abad Del Cusco: Facultad de Ing. Geológica Y Geográfica321fuego321Belum ada peringkat
- Grupo IIIDokumen22 halamanGrupo IIIAbril ArteagaBelum ada peringkat
- Discussion of RustingDokumen15 halamanDiscussion of RustingShamil Azha Ibrahim0% (1)
- Laporan Unit 1 Anorganik Mutia Salsabila PDFDokumen47 halamanLaporan Unit 1 Anorganik Mutia Salsabila PDFMutia SalsabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chemistry: Group 13 AluminiumDokumen38 halamanInorganic Chemistry: Group 13 AluminiumLooi Chui Yean0% (1)
- Lec 5Dokumen18 halamanLec 5Khaled AbeedBelum ada peringkat
- Alum ExptDokumen10 halamanAlum ExptRivy Valen PabesakBelum ada peringkat
- Le 4Dokumen37 halamanLe 4alaialiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter # 4 Chemistry Class - XII P-Block ElementsDokumen10 halamanChapter # 4 Chemistry Class - XII P-Block ElementsSharoon JohnBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance and Negative Impact of Electrochemical IndustriesDokumen4 halamanThe Importance and Negative Impact of Electrochemical IndustriesSally ChewBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment I Aluminium and Its Compound 1.1 ObjectivesDokumen9 halamanExperiment I Aluminium and Its Compound 1.1 ObjectivesAhlish Rahma AlfianaBelum ada peringkat
- AluminiumDokumen19 halamanAluminiumAnkur Jain100% (1)
- The Extration of The Versitile AluminiumDokumen36 halamanThe Extration of The Versitile Aluminiumvishnu_c_singhBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Copper Complex II Coordination NumberDokumen18 halamanDetermination of Copper Complex II Coordination NumberHasrilia BeskaraBelum ada peringkat
- The P-Block Elements - Shobhit NirwanDokumen20 halamanThe P-Block Elements - Shobhit NirwanAadarsh PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Tarnish & CorrosionDokumen18 halamanTarnish & CorrosionPreeti AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium Oxide - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen7 halamanAluminium Oxide - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dBelum ada peringkat
- The P-Block ElementsDokumen14 halamanThe P-Block ElementsAbhay100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Question and AnswerDokumen53 halamanOrganic Chemistry Question and Answergoi_pin100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Question and AnswerDokumen53 halamanOrganic Chemistry Question and AnswerApex InstituteBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Unit 1Dokumen5 halamanLaporan Unit 1Muliati TatiBelum ada peringkat
- Tarnish and Corrosion: DefinitionsDokumen3 halamanTarnish and Corrosion: DefinitionsangelrasBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Notes Pt. 2Dokumen124 halamanChemistry Notes Pt. 2Blohsh KeenenBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminum - Oxide Production ProcessDokumen1 halamanAluminum - Oxide Production ProcessAbdur Rahim WaseemBelum ada peringkat
- P Block Group 13,14 TheoryDokumen29 halamanP Block Group 13,14 TheoryShreyansh RaiBelum ada peringkat
- Golongan Iiia and Iva Elements: Na B O ODokumen2 halamanGolongan Iiia and Iva Elements: Na B O OWanda Nafisah HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Group 13Dokumen4 halamanGroup 13Surisetti Jyothsna LathaBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Metals & Non TheoryDokumen60 halaman8 Metals & Non TheorySARANGMUMBAIBelum ada peringkat
- Rusting of IrDokumen14 halamanRusting of IrRohit MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 2 Q4 Week 8.d F With QA v.1 BETADokumen15 halamanGen Chem 2 Q4 Week 8.d F With QA v.1 BETAAllona Jane BrionesBelum ada peringkat
- Delhi Public School: Rusting of Iron (Chemistry Project File) BY: Snigdha Monu MishraDokumen10 halamanDelhi Public School: Rusting of Iron (Chemistry Project File) BY: Snigdha Monu MishraSnigdha MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Anoganik Unit 1Dokumen14 halamanAnoganik Unit 1Nur Ayu Pertiwi HasmanBelum ada peringkat
- Ee DraftDokumen10 halamanEe DraftHarshavarthini AnanthasayananBelum ada peringkat
- Boron Family TKCHDokumen17 halamanBoron Family TKCHPrasanna NadkarniBelum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry of MetalsDokumen8 halamanThe Chemistry of MetalsPatrick Joshua GregorioBelum ada peringkat
- AluminumDokumen18 halamanAluminumAkniet RysbekovaBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry Part II 5 6Dokumen109 halamanGeneral Chemistry Part II 5 6LUH EKA YANTHIBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Group 13Dokumen11 halaman2 - Group 13Mahin ChandwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksDari EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksBelum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry of Carbon: Organometallic ChemistryDari EverandThe Chemistry of Carbon: Organometallic ChemistryPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Extractive Metallurgy 1: Basic Thermodynamics and KineticsDari EverandExtractive Metallurgy 1: Basic Thermodynamics and KineticsBelum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry of Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic ChemistryDari EverandThe Chemistry of Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic ChemistryBelum ada peringkat
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesDari EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- A Closer Look at Silicon - Chemistry Book for Elementary | Children's Chemistry BooksDari EverandA Closer Look at Silicon - Chemistry Book for Elementary | Children's Chemistry BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Document Trafag PD3.4Dokumen7 halamanDocument Trafag PD3.4Rick Van den BosBelum ada peringkat
- MillDokumen51 halamanMillsenaBelum ada peringkat
- The Multiple Directions of Antiferromagnetic Spintronics Nature Physics PDFDokumen4 halamanThe Multiple Directions of Antiferromagnetic Spintronics Nature Physics PDFLog LouBelum ada peringkat
- Appendix B Laplace Transform: Time Domain, E.G. If We Have A Voltage V Which Is ADokumen6 halamanAppendix B Laplace Transform: Time Domain, E.G. If We Have A Voltage V Which Is AulaganathanBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Evaluation of Sustained Release Microcapsules Containing Diclofenac SodiumDokumen4 halamanDesign and Evaluation of Sustained Release Microcapsules Containing Diclofenac SodiumLia Amalia UlfahBelum ada peringkat
- Ibraim Overview Influence of Pozzolanic Materials PDFDokumen12 halamanIbraim Overview Influence of Pozzolanic Materials PDFrobertsj21Belum ada peringkat
- Sample 7613Dokumen11 halamanSample 7613VikashKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Coprime FactorisationDokumen20 halamanCoprime FactorisationasgharBelum ada peringkat
- Shaft Locking DeviceDokumen24 halamanShaft Locking DevicechienhamthepBelum ada peringkat
- Leica ICD Brochure enDokumen4 halamanLeica ICD Brochure enCsaba GibártiBelum ada peringkat
- GATE 2014 Examination CE: Civil Engineering: Read The Following Instructions CarefullyDokumen33 halamanGATE 2014 Examination CE: Civil Engineering: Read The Following Instructions CarefullySai KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Binders: 1. Compaction Behaviour of Organic Binders in Alumina Ceramics (PVA & PEG) General FactsDokumen13 halamanBinders: 1. Compaction Behaviour of Organic Binders in Alumina Ceramics (PVA & PEG) General FactsPranav KumarBelum ada peringkat
- BlastingDokumen138 halamanBlastingcklconBelum ada peringkat
- User Guide: Elcometer 147Dokumen4 halamanUser Guide: Elcometer 147sergioBelum ada peringkat
- Pushing The Boundaries of Steel Machining.: ISO Insert Series For Steel TurningDokumen24 halamanPushing The Boundaries of Steel Machining.: ISO Insert Series For Steel TurningAlexandre SouzaBelum ada peringkat
- Sieve Analysis of Soil: By: Muhammad Firdaus, ST, MTDokumen12 halamanSieve Analysis of Soil: By: Muhammad Firdaus, ST, MTdaus_parisi100% (1)
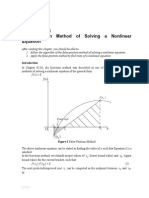
- False-Position Method of Solving A Nonlinear Equation: Exact RootDokumen6 halamanFalse-Position Method of Solving A Nonlinear Equation: Exact Rootmacynthia26Belum ada peringkat
- 3 IntroductionDokumen5 halaman3 IntroductionKhamvanh PhengnaoneBelum ada peringkat
- Nonlinear Analysis Methods For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Shear WallsDokumen8 halamanNonlinear Analysis Methods For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Shear Wallsakif-benzer-6764Belum ada peringkat
- Conclusion and Recommendations HTDokumen1 halamanConclusion and Recommendations HTAdiel AdrieBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2Dokumen5 halamanLab 2Adeem Hassan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- LNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Dokumen24 halamanLNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Ram Charan Konidela100% (1)
- Constant Effort SupportsDokumen31 halamanConstant Effort SupportsKen SidhartaBelum ada peringkat
- Pyrobel Brochure 2012Dokumen24 halamanPyrobel Brochure 2012PegaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical and Electronic Measurements and InstrumentationDokumen12 halamanElectrical and Electronic Measurements and InstrumentationKarthik VBelum ada peringkat
- Week11 Turton - Cost of ManufacturingDokumen32 halamanWeek11 Turton - Cost of ManufacturingNrl Nbl Rmln100% (1)
- Quality Assurance Plan For Civil4mDokumen3 halamanQuality Assurance Plan For Civil4mMohammed Abdul BaseerBelum ada peringkat
- Set Theory For The Working Mathematician - Krzysztof Ciesielski - 1997Dokumen244 halamanSet Theory For The Working Mathematician - Krzysztof Ciesielski - 1997Jack Bullets100% (3)