Cell as the Basic Unit of Life
Diunggah oleh
adi8641Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cell as the Basic Unit of Life
Diunggah oleh
adi8641Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
BM Version
Forward
Exit
Chapter 2 : Cell as a Unit of Life
2.1 What is a Cell? What is a cell? Parts of microscope Functions of part on a microscope General structure of animal cells and plant cells The functions of cell structures 2.2 Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Unicellular organisms Multicellular organisms
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
Chapter 2 : Cell as a Unit of Life
2.3 Cell Organisation in the Human Body The types and functions of human cells Organisation of cells The system of the human body and their functions 2.4 The Human Being a Complex Organism The human being a complex organism
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
2.1 What is a Cell?
A cell is the basic unit of life Its function is to carry out life processes Its size too small and can only be seen with the help of a microscope
Cell
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
2.1 What is a Cell?
Eyepiece Body tube Arm Coarse focus knob Fine focus knob Objective lens Stage Clip Diaphragm Mirror Part of a microscope
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
Base
Functions of parts on a microscope
Parts of a microscope Function Magnify the specimen by 10 For holding the microscope
2.1 What is a Cell?
Eyepiece
Arm
Coarse focus knob Change the position of the objective lens when focusing with low-powered objective lens Fine focus knob Stage Base
Continue
Change the position of the objective lens slightly for fine focusing Place the glass slide Stabilize the microscope
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
2.1 What is a Cell?
Functions of parts on a microscope
Part of microscope Mirror Function
Reflects light up through an opening in the stage to illuminate the specimen
Control the amount of light entering objective lens Hold the slide on the stage Align the position of the eyepiece with the objective lens Magnify the size of a specimen by 4, 10 or 40
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
Diaphragm Clip Body tube Objective lens
2.1 What is a Cell?
General structure of animal cells and plant cells
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Nucleus Cytoplasm
Vacuole
Chloroplast
Animal cell Plant cell
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
2.1 What is a Cell?
The functions of cell structures
Structures Cell membranes Cell wall Functions Controls the movement of substances into or out of the cell Supports and gives the cell a regular shape
Cytoplasm
Nucleus Vacuole
The place where chemical processes take place Controls all activities of the cell
Salt solution and sugar solution are stored here Carries out photosynthesis
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
Chloroplast
2.2 Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Unicellular organisms
Organisms that consist of only one cell Very tiny Only be seen under a microscope Live in wet places such as the sea, ponds and drains
BM Version
Have different body shapes Examples are Euglena, Chlamydomonas, Paramecium, Amoeba, Pleurococcus and yeast cell
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
2.2 Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms
Multicellular organisms
Organisms that consist of many cell Examples Hydra, Mucor and Spirogyra
Hydra
Mucor
BM Version
Spirogyra
Previous Forward Menu Exit
2.3 Cell Organisation in the Human Body
The types and functions of human cells
Types of cells Functions
Muscle cell
Human sperm cell White blood cell Human egg cell Nerve cell Fat cell Red blood cell Bone cell
Enables movement
Male reproductive cell Protects the body against disease Female reproductive cell Sends nerve impulses Stores fat Carries oxygen to every part of body Forms bones
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
2.3 Cell Organisation in the Human Body
Organisation of cells
Tissue Cell There are 200 types of cells in our body System Different organs working together to carry out a certain function form a system Cells of the same type that carry out the same function form a tissue
Organ Different tissues working together to carry out a certain function form an organ Organism Different system make up the whole organism
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
2.3 Cell Organisation in the Human Body
The system of the human body and their functions
System Digestive system Functions To digest food so that it can be easily absorbed and used by the body Reproductive system To produce reproductive cells Nervous system Respiratory system To help the body respond to changes inside and outside the body To enable gaseous exchange to take place To carry oxygen and food to all parts of the body and waste substances to the kidneys
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
Blood circulatory system
Continue
2.3 Cell Organisation in the Human Body
Systems of the human body and their functions
System
Skeletal system Excretory system Muscular system Lymphatic system Endocrine system
Functions
To support the weight of the body and protect soft organs To remove toxic substances from the body To help the body to move To defend the body against disease with the help of lymphocytes To produce hormones to control the bodys activities and development
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
2.4 The Human Being ! A Complex Organism
A human being is a complex organism because human cells are organised into tissues, organs and systems Human cells are specialised. Cell specialisation helps divide body functions among the different types of cells Without the organisation of the cells, life processes cannot be carried out effectively
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
The end
Versi BI
Keluar
Bab 2 : Sel Sebagai Unit Benda Hidup
2.1 Apakah itu Sel? Apakah itu sel? Bahagian mikroskop Fungsi bahagian pada mikroskop Struktur sel haiwan dan sel tumbuhan Fungsi struktur sel 2.2 Organisma Unisel dan Multisel Organisma unisel Organisma multisel
Versi BI Keluar
Bab 2 : Sel Sebagai Unit Benda Hidup
2.3 Organisasi Sel dalam Badan Manusia Jenis-jenis dan fungsi sel manusia Organisasi sel Sistem badan manusia dan fungsinya 2.4 Manusia Organisma Kompleks Manusia organisma kompleks
Versi BI
Keluar
2.1 Apakah itu Sel?
Sel adalah unit asas benda hidup Fungsinya adalah untuk menjalankan proses kehidupan Saiznya adalah kecil dan boleh dilihat dengan bantuan mikroskop
Sel
Versi BI Keluar
2.1 Apakah itu Sel?
Kanta mata Tiub badan Gagang Pelaras kasar Pelaras halus Kanta objek
Pentas
Klip Diafragma Cermin Bahagian mikroskop
Versi BI Keluar
Tapak
Fungsi bahagian pada mikroskop
Bahagian mikroskop
2.1 Apakah itu Sel?
Fungsi
Kanta mata
Gagang Pelaras kasar
Membesarkan spesimen 10
Memegang mikroskop Mengubah kedudukan kanta objek apabila mengfokus dengan kanta objek berkuasa rendah Mengubah kedudukan kanta objek bagi mendapatkan imej yang jelas Tempat letak slaid kaca Menstabilkan mikroskop
Versi BI Keluar
Pelaras halus
Pentas
Tapak
2.1 Apakah itu Sel?
Fungsi bahagian pada mikroskop
Bahagian mikroskop Cermin Fungsi Memantulkan cahaya ke arah kanta objek Mengawal jumlah cahaya yang memasuki kanta objek Memegang slaid pada pentas Melaraskan kedudukan kanta mata dengan kanta objek Membesarkan saiz specimen 4, 10 atau 40
Versi BI Keluar
Diafragma Klip Tiub badan Kanta objek
2.1 Apakah itu Sel?
Struktur sel haiwan dan sel tumbuhan
Dinding sel Membran sel
Nukleus Sitoplasma
Vakuol
Kloroplas
Sel haiwan Sel tumbuhan
Versi BI Keluar
2.1 Apakah itu Sel?
Fungsi struktur sel
Struktur Membran sel Fungsi Mengawal pergerakan bahan yang masuk dan keluar dari sel Menyokong dan memberi bentuk yang tetap Tempat di mana proses kimia mengambil alih Mengawal semua aktiviti sel Larutan garam dan gula disimpan di sini Menjalankan fotosintesis
Versi BI Keluar
Dinding sel
Sitoplasma Nukleus Vakuol Kloroplas
2.2 Organisma Unisel dan Multisel
Organisma unisel
Organisma yang Mempunyai bentuk yang berbeza mengandungi satu sel sahaja Contohnya Euglena, Klamidomonas, Sangat halus Paramesium, Ameba, Hanya boleh dilihat Pleurokokus and yis dengan mikroskop Tinggal di tempat yang lembap seperti laut, kolam dan longkang
Versi BI Keluar
2.2 Organisma Unisel dan Multisel
Organisma multisel
Organisma yang mengandungi banyak sel Contoh Hidra, Mukor and Spirogira
Hidra
Mukor
Spirogira
Versi BI Keluar
2.3 Organisasi Sel dalam Badan Manusia
Jenis-jenis dan fungsi sel manusia Jenis-jenis sel Sel otot Fungsi Membolehkan pergerakan
Sel sperma manusia Sel pembiakan lelaki Sel darah putih Sel telur manusia Sel saraf Melindungi badan melawan penyakit Sel pembiakan perempuan Menghantar impuls saraf
Sel lemak
Sel darah merah Sel tulang
Menyimpan lemak
Membawa oksigen ke setiap bahagian badan Membentuk tulang
Versi BI Keluar
2.3 Organisasi Sel dalam Badan Manusia
Organisasi sel
Sel Tisu Sel sama jenis yang menjalankan fungsi yang sama dinamakan tisu
Terdapat 200 jenis sel dalam badan kita
Sistem Kumpulan organ yang bersamasama menjalankan fungsi tertentu dinamakan sistem
Organ Kumpulan tisu yang bersama-sama menjalankan fungsi tertentu dinamakan organ
Organisma Sistem yang berbeza-beza membentuk suatu organisma
Versi BI Keluar
2.3 Organisasi Sel dalam Badan Manusia
Sistem dalam badan manusia dan fungsinya
Sistem Sistem pencernaan Fungsi Mencerna makanan supaya mudah diserap dan digunakan oleh badan Menghasilkan sel pembiakan Membantu badan merangsang perubahan di dalam dan d luar badan Membolehkan pertukaran gas Membawa oksigen dan makanan ke semua bahagian badan dan bahan buangan ke ginjal
Versi BI Keluar
Sistem pembiakan
Sistem saraf Sistem pernafasan Sistem peredaran darah
2.3 Organisasi Sel dalam Badan Manusia
Sistem dalam badan manusia dan fungsinya
Sistem
Sistem rangka Sistem perkumuhuan Sistem otot Sistem limfa Sistem endokrin
Fungsi
Menyokong berat badan dan melindungi organ yang lembut Menyingkirkan bahan kumuh daripada badan Membantu badan bergerak Mempertahankan badan melawan penyakit Menghasilkan hormon untuk mengawal aktiviti badan dan pembangunan
Versi BI Keluar
2.4 Manusia ! Organisma Komples
Manusia merupakan organisma kompleks kerana sel manusia tersusun kepada tisu, organ dan sistem Sel manusia adalah istimewa. Keisitmewaan sel ini membantu fungsi badan dalam kalangan pelbagai jenis sel Tanpa organisasi sel, proses kehidupan tidak akan berkesan
Versi BI
Keluar
tamat
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- f1 Chapter 2Dokumen36 halamanf1 Chapter 2mexfloziaBelum ada peringkat
- BM Version: Exit ForwardDokumen34 halamanBM Version: Exit ForwardSY ChowBelum ada peringkat
- Animal and Plant Cell Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Part of A Microscope and Their Function Cell OrganisationDokumen21 halamanAnimal and Plant Cell Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Part of A Microscope and Their Function Cell OrganisationNor Hafiza AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokumen11 halamanCell Structure and FunctionTang Szu ChingBelum ada peringkat
- Hapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeDokumen29 halamanHapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeShu85Belum ada peringkat
- CellDokumen12 halamanCellMasTura MdZinBelum ada peringkat
- PMR Science Form 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDokumen8 halamanPMR Science Form 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDavid AntonitoBelum ada peringkat
- 1) Lecture1Dokumen69 halaman1) Lecture1gurunathnkulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDari EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell Is The Unit of LifeDokumen25 halamanScience Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell Is The Unit of LifeMuhammad Shazni Daud100% (1)
- Animal Cell - Definition, Structure, Parts, FunctioDokumen39 halamanAnimal Cell - Definition, Structure, Parts, FunctioKolade YousuffBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 03 - Cell Structure and FunctionDokumen32 halamanChapter 03 - Cell Structure and FunctionKhadija PrescottBelum ada peringkat
- What is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeDokumen6 halamanWhat is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeWaleed Bin KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Cells Unit Powerpoint 2Dokumen110 halamanCells Unit Powerpoint 2.....Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Biology: by Dr. Navaid SiddiquiDokumen114 halamanIntroduction To Biology: by Dr. Navaid SiddiquiSyeda Warisha AmirBelum ada peringkat
- BIOCHEM-LAB ACTIVITY 1 (Caminos, Keen Jude)Dokumen3 halamanBIOCHEM-LAB ACTIVITY 1 (Caminos, Keen Jude)Keen Jude CaminosBelum ada peringkat
- CH 10Dokumen32 halamanCH 10api-238589602Belum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 2Dokumen20 halamanScience Form 1 - Chapter 2Beevy GB85% (39)
- Form 1 C2 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganizationDokumen1 halamanForm 1 C2 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganizationYuhannBelum ada peringkat
- Organization and Maintenance of Organism: Delhi Public School Bangalore EastDokumen39 halamanOrganization and Maintenance of Organism: Delhi Public School Bangalore EastTania MBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2Dokumen60 halamanScience Form 1 Chapter 2Anie EntalaiBelum ada peringkat
- 02 - Cells PowerpointDokumen24 halaman02 - Cells PowerpointMisbah FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and Function Semi Detailed LPDokumen8 halamanCell Structure and Function Semi Detailed LPCJ Perito75% (4)
- Cells as the building blocks of lifeDokumen26 halamanCells as the building blocks of lifeAmz Abd AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Science Chapter 2 Form 1Dokumen23 halamanScience Chapter 2 Form 1Kelvin0% (1)
- 2 BioenergeticsDokumen27 halaman2 BioenergeticshanniemaelimonBelum ada peringkat
- Bio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesDokumen18 halamanBio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesMuhammad Mahi Nurul IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Pastel Yellow Simple Illustrative English Word Choice and Connotations PresentationDokumen15 halamanPastel Yellow Simple Illustrative English Word Choice and Connotations PresentationKeerthi SureshBelum ada peringkat
- Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDokumen16 halamanCell - The Basic Unit of LifeTHARISHINI A/P THANABALASINGAM A18KT0305Belum ada peringkat
- BW1 CellsDokumen13 halamanBW1 CellsMichael KavanaghBelum ada peringkat
- MAKALAH. Struktur Dan Fungsi Sel, Jaringan Dan Sistem Tubuh ManusiaDokumen23 halamanMAKALAH. Struktur Dan Fungsi Sel, Jaringan Dan Sistem Tubuh ManusiadediBelum ada peringkat
- Cell - Structure, Function and OrganizationDokumen1 halamanCell - Structure, Function and Organization- adlina -100% (1)
- BoichemistryDokumen20 halamanBoichemistrynishwa RajpootBelum ada peringkat
- Cells Summary NotesDokumen5 halamanCells Summary NotesThanusha DhanarajBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Basis of LifeDokumen4 halamanCellular Basis of LifeFerlyn Comon-VillalonBelum ada peringkat
- General Biology Modules 1 3Dokumen36 halamanGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarBelum ada peringkat
- BIOLOGYDokumen27 halamanBIOLOGYElijah AtudilloBelum ada peringkat
- Year 11 Biology Module 1 2023 NotesDokumen55 halamanYear 11 Biology Module 1 2023 NotesLBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Dan FungsiDokumen24 halamanCell Dan FungsinindyastomoBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 5 Livings BeingsDokumen8 halamanUNIT 5 Livings BeingsAlba etceteraBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Notes Chpter 2Dokumen10 halamanBiology Notes Chpter 2Wan HasliraBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDokumen48 halamanCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDeneshwaran RajBelum ada peringkat
- Cells: The Basic Units of LifeDokumen31 halamanCells: The Basic Units of LifeJuliet ZeinBelum ada peringkat
- The Cellular Basis of LifeDokumen50 halamanThe Cellular Basis of LifeSteve EstebanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell As A Basic Unit of LifeDokumen33 halamanCell As A Basic Unit of LifeadhamklBelum ada peringkat
- WEEK 1 - Theory - WorksheetDokumen9 halamanWEEK 1 - Theory - WorksheetRajal PratapBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Buffers 2021Dokumen13 halamanIntroduction and Buffers 2021Kipchirchir AbednegoBelum ada peringkat
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDokumen18 halamanCell As A Unit of LifeMohamad Abdul WahabBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDokumen54 halamanCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Cytology Study GuideDokumen4 halamanCytology Study Guidenaruto710@wuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDokumen64 halamanChapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationMohd Haidil100% (1)
- GCSE Biology Notes: Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes, Cell Structure and MicroscopyDokumen78 halamanGCSE Biology Notes: Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes, Cell Structure and MicroscopyLix FNBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokumen27 halamanCell Structure and Functiontssandoval100% (1)
- U-1 Introducing Cells-1Dokumen41 halamanU-1 Introducing Cells-1SHANBelum ada peringkat
- CG - Y9 - 02-03 Levels of Organisation & Cell StructureDokumen39 halamanCG - Y9 - 02-03 Levels of Organisation & Cell StructureCharlotte BurkeBelum ada peringkat
- Biology F4 Teaching ModuleDokumen13 halamanBiology F4 Teaching ModuleNurfatin Jamaludin100% (1)
- Matematik - Tingkatan 1Dokumen35 halamanMatematik - Tingkatan 1Sekolah Portal96% (52)
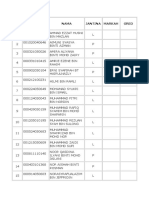
- NOKP / BIL NO. SIJIL NAMA JANTINA MARKAH GREDDokumen2 halamanNOKP / BIL NO. SIJIL NAMA JANTINA MARKAH GREDadi8641Belum ada peringkat
- Taman Kenawar - Feb 2017Dokumen1 halamanTaman Kenawar - Feb 2017adi8641Belum ada peringkat
- Jadual Orientasi 2017Dokumen1 halamanJadual Orientasi 2017adi8641Belum ada peringkat
- Soalan No.4Dokumen2 halamanSoalan No.4adi8641Belum ada peringkat
- Logo RotisDokumen1 halamanLogo Rotisadi8641Belum ada peringkat
- NOKP / BIL NO. SIJIL NAMA JANTINA MARKAH GREDDokumen2 halamanNOKP / BIL NO. SIJIL NAMA JANTINA MARKAH GREDadi8641Belum ada peringkat
- Sma Gemas: Sekolah Menengah Agama Gemas 73400 Gemas, Negeri Sembilan Darul Khusus TEL / FAX: 07-9482031 EmailDokumen1 halamanSma Gemas: Sekolah Menengah Agama Gemas 73400 Gemas, Negeri Sembilan Darul Khusus TEL / FAX: 07-9482031 Emailadi8641Belum ada peringkat
- Test GGHGGGGDokumen1 halamanTest GGHGGGGadi8641Belum ada peringkat
- StationeryDokumen1 halamanStationeryadi8641Belum ada peringkat
- Trial Negeri Sembilan English Pra SPM 2013 SET 1 K1 - K2 - Question - SchemeDokumen0 halamanTrial Negeri Sembilan English Pra SPM 2013 SET 1 K1 - K2 - Question - SchemeCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Trial Negeri Sembilan English Pra SPM 2013 SET 1 K1 - K2 - Question - SchemeDokumen0 halamanTrial Negeri Sembilan English Pra SPM 2013 SET 1 K1 - K2 - Question - SchemeCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Sleep With Buteyko - Physician D - McKeown, PatrickDokumen137 halamanSleep With Buteyko - Physician D - McKeown, PatrickLuis Oneto RothBelum ada peringkat
- Extended Definition RevisedDokumen6 halamanExtended Definition Revisedapi-491301139Belum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiografia BasicaDokumen49 halamanElectrocardiografia BasicaENRIQUEVERSAGBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Physical MobilityDokumen2 halamanImpaired Physical MobilityNicole Genevie MallariBelum ada peringkat
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDokumen8 halamanHow Cells Harvest EnergyDJ ISAACS25% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Congenital Heart Diseases PDFDokumen8 halamanPathophysiology of Congenital Heart Diseases PDFdramitjainBelum ada peringkat
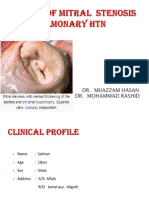
- A Case of Mitral StenosisDokumen29 halamanA Case of Mitral StenosisShadab KamalBelum ada peringkat
- First AId Notes - UpdatedDokumen54 halamanFirst AId Notes - UpdatedewawireBelum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource Was: Patient InformationDokumen1 halamanThis Study Resource Was: Patient InformationissaiahnicolleBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology 2 HistologyDokumen2 halamanPhysiology 2 HistologyFahim Khan100% (2)
- Basics of Mechanical Ventilation For Dogs and Cats PDFDokumen15 halamanBasics of Mechanical Ventilation For Dogs and Cats PDFFelipe GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Cardaic Emergency Drugs.Dokumen13 halamanCardaic Emergency Drugs.Alma SusanBelum ada peringkat
- Maintaining Normal PH Through BuffersDokumen40 halamanMaintaining Normal PH Through BuffersRJ Noor JanBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Base BalanceDokumen27 halamanAcid Base BalanceKamran Khan KhalilBelum ada peringkat
- Health Examination Form: Instruction For FilingDokumen3 halamanHealth Examination Form: Instruction For FilingJonathanBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Organisation of Plant TissueDokumen5 halaman1.1 Organisation of Plant TissueADMIN SUKMABelum ada peringkat
- Patofisiologi CHFDokumen7 halamanPatofisiologi CHFHafiz Idul FitranulBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDokumen7 halamanAcute Coronary SyndromesAiman ArifinBelum ada peringkat
- When Is The Best Time of Day To Work OutDokumen5 halamanWhen Is The Best Time of Day To Work OutsiesmannBelum ada peringkat
- Study Notes Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen2 halamanStudy Notes Anatomy and Physiologyapi-434852691Belum ada peringkat
- Brainbee Challenge CrosswordDokumen2 halamanBrainbee Challenge Crosswordyudrea88Belum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of ThrombophlebitisDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of ThrombophlebitisJennifer ArdeBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 202 Essay #4 - Rio SaladoDokumen2 halamanBIO 202 Essay #4 - Rio SaladoAllison ScottBelum ada peringkat
- Davao Doctors College nursing program drug study for ranitidineDokumen4 halamanDavao Doctors College nursing program drug study for ranitidinePao LaurenteBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Imspq 2015Dokumen9 halamanSoal Imspq 2015AgungBudiPamungkasBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Dyspnea-Harrison SummaryDokumen5 halamanChapter 2 Dyspnea-Harrison SummaryLeang KarichakBelum ada peringkat
- CardiomyopathyDokumen23 halamanCardiomyopathyDefyna Dwi LestariBelum ada peringkat
- Sensory Motor IntegrationDokumen8 halamanSensory Motor IntegrationAdelinaPanaetBelum ada peringkat
- DarahDokumen14 halamanDarahChristantya VitaBelum ada peringkat
- PhysioEx Exercise 2 Activity 1Dokumen5 halamanPhysioEx Exercise 2 Activity 1PatriBelum ada peringkat