A Case of Severe Statin Induced Ileus
Diunggah oleh
snipergirlDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A Case of Severe Statin Induced Ileus
Diunggah oleh
snipergirlHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Multiple Muscle Melt: severe atorvastatin-induced hepatitis associated with rhabdomyolysis and leiomyolysis
Authors
Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Monash Medical Centre, Clayton, Victoria, Australia
Discussion
Introduction Our patient also had an extremely aggressive form of
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) use progressive myositis involving not only axial muscles but
is becoming more and more common. also his muscles of respiration.
Similarly to liver impairment, factors that increase the
With an increasing breadth of indications, likelihood of myopathy include co-administration of
it has become the one of the top most drugs metabolised by subgroup CYP3A4 as well as
prescribed classes in developed fibrates.
From the experience in treating other myopathies,
countries. In Australia, atorvastatin is the steroids show normalisation of creatine kinase over
most commonly prescribed PBS- time, however efficacy is best shown in dermatomyositis
subsidised medication. Lipid lowering and polymyositis .
Myositis involving both skeletal and smooth muscle has
agents are the most commonly prescribed been documented in inflammatory myopathies
class. Hepatitis and myositis are both previously in several case studies. Smooth muscle
recognised side effects of statin therapy . myositis associated with statin therapy however is very
rare, with only a few case studies noted in the literature.
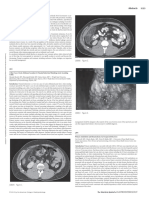
Severe hepatitis, however, is less MRI of thighs showing T2 hyperintensity These case studies suggest that it is associated with
common. Visceral myopathy is also a more severe hepatitis or rhabdomyolysis (figure 1). Our
very rare and perhaps under-recognised respiratory function tests suggested diaphragmatic
involvement which has not been previously described.
adverse event. Though no definitive histology was available, the severe
We present an unusual case of both ileus which culminated in bowel perforation was
paralytic ileus and urinary retention Within 24 hours of admission, he developed severe muscle weakness, suspected to have been caused by leiomyolysis. Bowel
with a pronounced proximal emphasis. Neck flexor and proximal arm function improved concomitantly with recovery of
associated with severe rhabdomyolysis muscles were weak at MRC Grade 3/5, and hip flexor, gluteal and skeletal muscle and liver function. There was no clinical
with diaphragmatic involvement and quadriceps groups had 2/5 weakness. A creatinine kinase (CK) done at evidence of peripheral or autonomic neuropathy. Other
hepatitis after an increase in dose of this time was found to be elevated at 9923IU/ml. reports of intestinal pseudo-obstruction are scarce. One
Atorvastatin was ceased, but weakness and CK increased over the case occurred after the addition of cerivastatin to
atorvastatin. next three days. He was bed-bound and unable to move his limbs, cyclosporine resulting in a paralytic ileus,
head or trunk against gravity. Vital capacity decreased. Two days after rhabdomyolysis and severe hepatitis. Another case
admission, he went into acute urinary retention of 831mL. MRI showed
Case Report T2 signal change in gluteal, thigh adductor and hamstring muscle
reports the addition of erythromycin to existing statin
therapy, with subsequent multi-organ failure and ileus .
A 51 year old man with known alcohol abuse was groups (Figure 1). A myositic screen was negative. Histopathological In both these cases, combination therapy was the
admitted with a 5 day history of jaundice without evaluation of a percutaneous vastus lateralis muscle biopsy revealed a precipitant. Our case illustrates that dose escalation
abdominal pain, fevers or rigors on a background diffuse toxic rhabdomyolysis affecting all muscle layers consistent with a can also be the trigger.
of generalised myalgia and lethargy, with no drug-related myositis . Urinary retention postulated to be due to bladder
Abdominal Xray on Day 8 of admission showing ileus
associated bladder or bowel dysfunction. It appeared he was starting to have diaphragmatic involvement and smooth muscle involvement has been described
His past history included alcoholic pancreatitis , oxygen saturations also decreased. Due to these concerns, he was previously. Our case, however, shows that this can
hypertension and hyperlipidaemia. commenced on empiric intravenous hydrocortisone (100mg IV qid) on occur along with severe skeletal and bowel myositis.
The myalgia corresponded to a change in dose of day 3. Whether urodynamics in the acute setting is helpful
atorvastatin from 20mg to 40mg daily. The patient 5 days after admission, he developed acute severe abdominal remains unclear.
was also taking rabeprazole 20mg twice daily, distension associated with nausea, vomiting and absolute constipation.
candesartan 16mg daily and thiamine 100mg daily. An abdominal X-ray revealed grossly dilated large and small bowel
Nil other substances including herbal supplements loops with no transition point (figure 3) and a gastrograffin follow- Conclusion
or illicit drugs were taken. through confirmed no mechanical no obstruction. On sigmoidoscopy an In the setting of a recently introduced or dose
Examination revealed jaundice, non-tender irregular, oedematous, congested mucosa was seen, however no cause escalated statin therapy, severe skeletal myositis
hepatomegaly, no evidence of decompensation or was found for this abnormality, nor any mass lesion. Ileus continued and
stigmata of chronic liver disease. Mild proximal should prompt the treating clinician to monitor
he once again underwent emergent decompression, this time with
muscle weakness limiting ambulation to 10m was respiratory status carefully, ideally with daily vital
colonoscopy which was aborted due to the high risk of perforation.
also noted. There were no other abnormal Unfortunately, he developed a transverse colon perforation post- capacities. Monitoring of bladder and bowel
neurological signs. His cardiorespiratory findings procedure and proceeded to laparotomy with formation of defunctioning function is also necessary to look for any smooth
were unremarkable. colostomy. muscle involvement and the use of steroids may
aid in both skeletal and smooth muscle recovery.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Drug Study - CaDokumen3 halamanDrug Study - Casaint_ronald8Belum ada peringkat
- Azithromycin, Cefixime, Paracetamol Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanAzithromycin, Cefixime, Paracetamol Drug StudyAzizah VillaminBelum ada peringkat
- Psoriasis: Which Therapy For Which Patient: Avalos Ampudia PamelaDokumen2 halamanPsoriasis: Which Therapy For Which Patient: Avalos Ampudia Pamelapamela avalosBelum ada peringkat
- Mitchel 1997Dokumen23 halamanMitchel 19976mqpjqh2vqBelum ada peringkat
- 36 FTPDokumen5 halaman36 FTPNovita Sri RahayuBelum ada peringkat
- DS MyastheniaGravisDokumen4 halamanDS MyastheniaGravisLETADA, HANNAH CLARICEBelum ada peringkat
- DISH TreatmentDokumen6 halamanDISH TreatmentBorsecBelum ada peringkat
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDokumen12 halamanGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraBelum ada peringkat
- ArthritistreatmentDokumen11 halamanArthritistreatmentVANIA MAYTE ELIZALDE VERGARABelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effect Nursing InterventionsDokumen2 halamanDrugs Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effect Nursing InterventionsKim RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Small Animal Massage TherapyDokumen7 halamanSmall Animal Massage TherapyShayne ShotBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDokumen5 halamanAcute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaernitaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology NSAIDs PDFDokumen13 halamanPharmacology NSAIDs PDFPrincess Pearl Infante GadianoBelum ada peringkat
- Palliative care constipation and nausea treatmentDokumen1 halamanPalliative care constipation and nausea treatmentTudor AlinBelum ada peringkat
- A Rare Case of Acute Abdomen Secondary To Omental.283Dokumen1 halamanA Rare Case of Acute Abdomen Secondary To Omental.283prabowoaji12Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study DexamethasoneDokumen4 halamanDrug Study Dexamethasoneamal abdulrahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Photobiomodulation - An Invaluable Tool For All Dental SpecialtiesDokumen8 halamanPhotobiomodulation - An Invaluable Tool For All Dental SpecialtiessillyazianBelum ada peringkat
- Molecules: Transdermal and Topical Drug Administration in The Treatment of PainDokumen16 halamanMolecules: Transdermal and Topical Drug Administration in The Treatment of PainAbraham GomezBelum ada peringkat
- 7 (6) - Karadag-2020-Management of Behcet's SyndromeDokumen10 halaman7 (6) - Karadag-2020-Management of Behcet's Syndromekueiying.suBelum ada peringkat
- High-Dose Thiamine and Essential Tremor: Antonio CostantiniDokumen4 halamanHigh-Dose Thiamine and Essential Tremor: Antonio CostantiniBrew-sam ABBelum ada peringkat
- Life 12 00206Dokumen28 halamanLife 12 00206Cesar Daniel IsmerioBelum ada peringkat
- Topical Action of Buriti Oil (Mauritia Flexuosa L.) in Myositis Induced in RatsDokumen8 halamanTopical Action of Buriti Oil (Mauritia Flexuosa L.) in Myositis Induced in RatsLeidy Yurani Villa GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Clin Experimental Derm - 2021 - PradhanDokumen6 halamanClin Experimental Derm - 2021 - PradhanfabianBelum ada peringkat
- Seminário 4.1-Principles of Chemotherapy and RadiotherapyDokumen7 halamanSeminário 4.1-Principles of Chemotherapy and RadiotherapyAngellique NiyiragiraBelum ada peringkat
- Task 1. Active Learning Template: Assessment Teamwork and CollaborationDokumen2 halamanTask 1. Active Learning Template: Assessment Teamwork and CollaborationAce FabrigasBelum ada peringkat
- Used in Combination Therapy For Thyroid Storm Treatment.: RationaleDokumen4 halamanUsed in Combination Therapy For Thyroid Storm Treatment.: RationaleMicah LatosaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Oxygen Therapy.6Dokumen3 halamanFundamentals of Oxygen Therapy.6Fitri Amelia RizkiBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Guide To Joint and Soft Tissue Injection TechniquesDokumen5 halamanPractical Guide To Joint and Soft Tissue Injection TechniquesHerry HendrayadiBelum ada peringkat
- Evangelista Drug-StudyDokumen15 halamanEvangelista Drug-Studydinglasanerica57Belum ada peringkat
- MeSo TherapyDokumen5 halamanMeSo TherapybillBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study orDokumen3 halamanDrug Study orJuvanni SantosBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDokumen12 halaman6 Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresJanah CalitBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Tab YheDokumen6 halamanDrug Tab YhegeejeiBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanDrug StudyLorence RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Prolotherapy For Knee PainDokumen6 halamanProlotherapy For Knee Painligagenix100% (3)
- Drug Study: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/ Adverse Effect Contraindication Nursing ConsiderationDokumen6 halamanDrug Study: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/ Adverse Effect Contraindication Nursing ConsiderationBoomPanessLamahangBelum ada peringkat
- Exploring Rheumatism Remedies Through The Lens of Homoeopathic Plant FamiliesDokumen3 halamanExploring Rheumatism Remedies Through The Lens of Homoeopathic Plant FamiliesDr Ananda Kumar PingaliBelum ada peringkat
- Os Efeitos Modulatorios Do Treinamento Com Exercicios Sobre As Disfuncoes Imunometabolicas Induzidas Pela ObesidadeDokumen26 halamanOs Efeitos Modulatorios Do Treinamento Com Exercicios Sobre As Disfuncoes Imunometabolicas Induzidas Pela ObesidadeAna Souza LimaBelum ada peringkat
- Acceleration of Dental Movement by PhotobiomodulationHow Does It HappenDokumen3 halamanAcceleration of Dental Movement by PhotobiomodulationHow Does It HappenJuan AndradeBelum ada peringkat
- Specific ActionDokumen3 halamanSpecific Actionmoritashinobu2011Belum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanDrug Studyw dBelum ada peringkat
- Graft Versus Host DiseaseDokumen1 halamanGraft Versus Host DiseaseIzhra MargateBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 The Use MTX in DermatologyDokumen18 halaman2012 The Use MTX in DermatologyChika SabaBelum ada peringkat
- DS ObDokumen7 halamanDS ObZheyrille A. ArevaloBelum ada peringkat
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanAzithromycin Drug StudySHEILA MAE SACLOTBelum ada peringkat
- Soft Tissue Injuries Simply Need Peace and LoveDokumen2 halamanSoft Tissue Injuries Simply Need Peace and LoveALEJANDRABelum ada peringkat
- Respuesta Metabolica Al Trauma Cap 1 FonsecaDokumen6 halamanRespuesta Metabolica Al Trauma Cap 1 FonsecaJulio Magaña QuiñonesBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanDrug StudyKathleen RagudoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study CeftriaxioneDokumen2 halamanDrug Study CeftriaxioneJulie LesmorasBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study OmeprazoleDokumen3 halamanDrug Study OmeprazoleSandeepBelum ada peringkat
- Dacanay Jungco Omeprazole DsDokumen2 halamanDacanay Jungco Omeprazole DsTRISHA JUNGCOBelum ada peringkat
- Combinatorial Drug Therapy For Cancer in The Post-Genomic EraDokumen13 halamanCombinatorial Drug Therapy For Cancer in The Post-Genomic EraBobBelum ada peringkat
- Reviews: Methotrexate and Its Mechanisms of Action in Inflammatory ArthritisDokumen10 halamanReviews: Methotrexate and Its Mechanisms of Action in Inflammatory ArthritisanitaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Pre Drug StudyDokumen22 halamanCase Pre Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacBelum ada peringkat
- Ampisul, Hydrocort, Salbu, Mupirocin DrugsDokumen4 halamanAmpisul, Hydrocort, Salbu, Mupirocin DrugsClarissa GuifayaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathogenesis of Obesity: Josanne VassalloDokumen4 halamanPathogenesis of Obesity: Josanne VassalloAdkhiatul MuslihatinBelum ada peringkat
- Rle (NCM 116) CasesDokumen12 halamanRle (NCM 116) CasesLaurence ZernaBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic enzyme therapy with Trypsin, Bromelain and Rutoside in post operative casesDokumen4 halamanSystemic enzyme therapy with Trypsin, Bromelain and Rutoside in post operative casesganesh.divekar7256Belum ada peringkat
- Gout Obat HosppharmDokumen8 halamanGout Obat HosppharmnandaBelum ada peringkat
- Logic and Its Metatheory: Instructor InformationDokumen6 halamanLogic and Its Metatheory: Instructor InformationMarco StoroniMazzolani Di MaioBelum ada peringkat
- Design Audit ToolDokumen7 halamanDesign Audit ToolThe Dementia Centre100% (1)
- GEY 102-Introduction To Geology 1-Lecture Slides - Prof. M.E. NtonDokumen44 halamanGEY 102-Introduction To Geology 1-Lecture Slides - Prof. M.E. Ntonabuabdmuqseet2001Belum ada peringkat
- NSTP 2 Modules Lesson on Community OrganizingDokumen14 halamanNSTP 2 Modules Lesson on Community OrganizingJestony Riray CagmatBelum ada peringkat
- Advocacy Plan Final Edec 435Dokumen11 halamanAdvocacy Plan Final Edec 435api-375034422Belum ada peringkat
- QP ScriptDokumen57 halamanQP ScriptRitesh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Initial Evaluation in The 11th Form B1 LevelDokumen2 halamanInitial Evaluation in The 11th Form B1 LevelDumitru GruscaBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 C R I M I N A L L A W 1 Reviewer Wordpresscom 5a237cee1723dd6eef7c227dDokumen15 halaman2012 C R I M I N A L L A W 1 Reviewer Wordpresscom 5a237cee1723dd6eef7c227dSan PedroBelum ada peringkat
- BuddhismDokumen49 halamanBuddhismFabio NegroniBelum ada peringkat
- Agganna Sutta - Theory of KingshipDokumen8 halamanAgganna Sutta - Theory of KingshipTanya ChopraBelum ada peringkat
- 03.KUNCI KODING 11 IPA-IPS SMT 2 K13 REVISI - TP 23-24 - B.InggrisDokumen2 halaman03.KUNCI KODING 11 IPA-IPS SMT 2 K13 REVISI - TP 23-24 - B.InggrisfencenbolonBelum ada peringkat
- Adolescent HealthDokumen19 halamanAdolescent Healthhou1212!67% (3)
- Balancing The Cybersecurity BattlefieldDokumen4 halamanBalancing The Cybersecurity BattlefieldLilminowBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Treadmill Based and Track Based Rockport 1 Mile Walk Test For Estimating Aerobic Capacity in Healthy Adults Ages 30-50 YearsDokumen4 halamanComparison of Treadmill Based and Track Based Rockport 1 Mile Walk Test For Estimating Aerobic Capacity in Healthy Adults Ages 30-50 Yearsmanjula dangeBelum ada peringkat
- Mayans.M.C.S05E03.720p.WEB .x265-MiNX - SRTDokumen44 halamanMayans.M.C.S05E03.720p.WEB .x265-MiNX - SRTmariabelisamarBelum ada peringkat
- Vaclav Havel - From 'Mistake'. SAGEDokumen9 halamanVaclav Havel - From 'Mistake'. SAGEADIELruleBelum ada peringkat
- O The Beat 1 - TBDokumen164 halamanO The Beat 1 - TBJulliana SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Fardapaper Community Based Corporate Social Responsibility Activities and Employee Job Satisfaction in The U.S. Hotel Industry An Explanatory StudyDokumen9 halamanFardapaper Community Based Corporate Social Responsibility Activities and Employee Job Satisfaction in The U.S. Hotel Industry An Explanatory StudyDavid Samuel MontojoBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan For KSSR Year 4 (SK)Dokumen4 halamanLesson Plan For KSSR Year 4 (SK)Mohamad Firdaus100% (3)
- Depository Receipts: Presented By-Vikash Sharma (51) Ruchi BangaDokumen12 halamanDepository Receipts: Presented By-Vikash Sharma (51) Ruchi Bangasuraj kumar0% (1)
- Mythical Origins of The Hungarian Medieval LegislationDokumen8 halamanMythical Origins of The Hungarian Medieval LegislationLucas LixaBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Training Program Proposal for StudentsDokumen2 halamanSAP Training Program Proposal for StudentsAjay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 15 Tips To Get Fair Skin Naturally PDFDokumen2 halaman15 Tips To Get Fair Skin Naturally PDFLatha SivakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 3 Vol XXXX No. 2 Dec 2010Dokumen11 halamanPaper 3 Vol XXXX No. 2 Dec 2010Mubi BaloliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Irish Blessings and PrayersDokumen17 halamanIrish Blessings and PrayersvivesurBelum ada peringkat
- NCLT Orders Relief To Home BuyersDokumen7 halamanNCLT Orders Relief To Home BuyersPGurusBelum ada peringkat
- PGW Spring SuitDokumen14 halamanPGW Spring Suitapi-3700386Belum ada peringkat
- 50 Sets of Puzzles and Seating Arrangement For IBPS PO Mains 2017 SolutionsDokumen23 halaman50 Sets of Puzzles and Seating Arrangement For IBPS PO Mains 2017 SolutionssaBelum ada peringkat
- TOS-GRADE-10 EnglishDokumen2 halamanTOS-GRADE-10 EnglishPRINCESS VILLASANTABelum ada peringkat
- Past PaperDokumen3 halamanPast PaperKyle CuschieriBelum ada peringkat