Ecg Compression
Diunggah oleh
pawan_32Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ecg Compression
Diunggah oleh
pawan_32Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ECG Signal Delineation And
Compression
Chapters 6.2.6 6.3
18th November
T-61.181 Biomedical Signal Processing
Outline
I. ECG signal delineation
Definition (What)
Clinical and biophysical background (Why)
Delineation as a signal processing (How)
II. ECG signal compression
General approach to data compression
ECG signal compression
(Intrabeat/Interbeat/Interlead)
III. Summary
Part I.
EGC signal delineation
Delineation - Overview
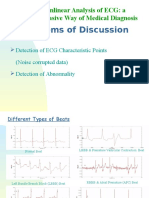
Aim Automatically decide/find onsets and
offsets for every wave (P, QRS, and T) from ECG
signal (PQRST-complex)
Note! Experts (Cardiologist) use manual/visual
approach
Why?
Why Clinically relevant parameters such
as time intervals between waves, duration of
each wave or composite wave forms, peak
amplitudes etc. can be derived
To understand this look how ECG signal is
generated
ECG Signal Generation
What Are We Measuring?
ECG gives (clinical) information from
generation and propagation of electric
signals in the heart.
Abnormalities related to generation
(arrhythmia) and propagation (ischemia,
infarct etc.) can be seen in ECG-signal
Also localization of abnormality is possible
(12 lead systems and BSM)
Clinically Relevant Parameters
PR interval
SA ventricles
QT interval
ventricular
fibrillation
ST segment
ischemia
QRS duration
Bundle brand block
depolarization
Signal Processing Approach to
Delineation (How)
Clinical importance should now be clear
Delineation can also be done manually by
experts (cardiologist) expensive and time
consuming. We want to do delineation
automatically (signal processing)
No analytical solution performance has
to be evaluated with annotated databases
Building Onset/Offset Detector
Many algorithms simulate cardiologist
manual delineation (ground truth) process:
Experts look 1) where the slope reduce to
flat line 2) respect maximum upward,
downward slope
Simulate this: define the boundary
according to relative slope reduction with
respect maximum slope LPD approach
Low-Pass Differentiated (LPD)
Signal is 1) low-pass filtered i.e. high
frequency noise is removed (attenuated) and
2) differentiated dv/dt
New signal is proportional to slope
Operations can be done using only one FIR
filter :
) ( * ) ( ) ( n h n x n y =
LPD cont.
Each wave has a unique frequency band
thus different low-pass (LP) filtering
(impulse) responses are needed for each
wave (P, QRS, and T)
Design cut-off frequencies using Power
Spectral Density (PSD)
Differentiation amplifies (high freq.) noise
and thus LP filtering is required
LPD cont..
Waves w={P,QRS,T} are segmented from
the i:th heart beat.
Using initial and final extreme points
thresholds for can be derived
+ =
=
oteherwise
W W n n y
yw
e i i
i
, 0
,...,
) (
0
u u
w K w y w
w K w y w
e
i
e
i
e
o
i
o
i
o
/
/
=
=
q
q
LPD cont...
Constants are control the boundary detection they
can be learnt from annotated database
Search backwards from initial extreme point.
When threshold is crossed onset has been
detected
Search forward from last extreme point and when
threshold is crossed offset is detected.
Part II.
EGC signal compression
General Data Compression
The idea is represent the signal/information
with fewer bits
Any signal that contains some redundancy
can be compressed
Types of compression: lossless and lossy
compression
In lossy compression preserve those
features which carry (clinical) information
ECG Data Compression
1) Amount of data is increasing: databases,
number of ECG leads, sampling rate,
amplitude resolution etc.
2) ECG signal transmission
3) Telemetry
ECG Data Compression
Redundancy in ECG data: 1) Intrabeat 2)
Interbeat, and 3) Interlead
Sampling rate, number of bits, signal
bandwidth, noise level and number of leads
influence the outcome of compression
Waveforms are clinically important
(preserve them) whereas isoelectric
segments are not (so) relevant
Intrabeat Lossless Compression
Not efficient has mainly historical value
Sample is predicted as a linear combination
of past samples and only prediction error is
stored (smaller magnitude):
) (
) (
) ( ... ) 1 ( ) (
1
n x n x e
p n x a n x a n x
p p
p p
=
+ + =
Intrabeat Lossy Compression
Direct Method
Basic idea: Subsample the signal using
parse sampling for flat segments and dense
sampling for waves:
(n,x(n)), n=0,...,N-1 (nk,x(nk)), k=0,...,K-1
Example AZTEC
Last sampled time point is in n0
Increment time (n) As long as signal in
within certain amplitude limits (flat)
)) ( ) ( (
2
1
) (
) ( ) (
)} ( , ), 1 ( ), ( max{ ) (
)} ( , ), 1 ( ), ( min{ ) (
max min
min max
0 0 max
0 0 min
k k k
n x n x n y
n x n x
n x n x n x n x
n x n x n x n x
+ =
<
+ =
+ =
c
Intrabeat Lossy Compression
Transform Based Methods
Signal is represented as an expansion of
basis functions:
Only coefficients need to be restored
Requirement: Partition of signal is needed
(QRS-detectors)
Method provides noise reduction
=
=
N
k
k k
w x
1
Interbeat Lossy Compression
Heart beats are almost identical (requires
QRS detection, fiducial point)
Subtract average beat and code residuals
(linear prediction or transform)
1 ,..., 0 ) (
) (
)
(
1
) (
1 ,..., 0 )
( ) (
1
= =
+ =
= + =
N n n s n x y
n x
L
n s
N n n X n x
i i i
j i
L
j
i
i i
u
u
Interlead Compression
Multilead (e.g. 12-lead) systems measure
same event from different angles
redundancy
Extend direct and transform based method
to multilead environment
Extended AZTEC
Transform concatenated signals
(
(
(
(
=
12
2
1
x
x
x
x
Summary - part I
Delineation = automatically detect waves
and their on- and offsets (What)
Clinically important parameters are
obtained (Why)
Design algorithm that looks relative slope
reduction (How)
LPD-method Differentiate low-pass
filtered signal
Summary - part II
Compression = remove redundancy:
intrabeat, interbeat, and interlead
Why Large amount of data, transmission
and telemetry
Lossless (historical) and lossy compression
Notice which features are lost (isoelectric
segments dont carry any clinical
information)
Summary - part II cont.
Intrabeat 1) direct and 2) transform based
methods
1) Subsample signal with non-uniform way
2) Use basis function (save only weights)
Interbeat subtract average beat and code residuals
(linear prediction or transform-coding)
Interlead extend intrabeat methods to multilead
environment
Thank you!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Problems of Discussion: Nonlinear Analysis of ECG: A Noninvasive Way of Medical DiagnosisDokumen48 halamanProblems of Discussion: Nonlinear Analysis of ECG: A Noninvasive Way of Medical DiagnosisNur HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Aveus Moniteur Surveillance PDFDokumen4 halamanAveus Moniteur Surveillance PDFayo_adekoyaBelum ada peringkat
- 1097Dokumen28 halaman1097scscsBelum ada peringkat
- E.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentDokumen36 halamanE.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentAch ThungBelum ada peringkat
- G60 Patient MonitorDokumen2 halamanG60 Patient MonitorSuhaimi RostiBelum ada peringkat
- Planar4 System CatalogDokumen194 halamanPlanar4 System CatalogMohamed OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Mr. Hamza Ratrout Revised By: Dr. Irene RocoDokumen28 halamanBasic Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Mr. Hamza Ratrout Revised By: Dr. Irene Rocoأبوأحمد الحكيمBelum ada peringkat
- Contemp. Prog. Safety SysDokumen43 halamanContemp. Prog. Safety SysCristina Bianca LeãoBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab Code EcgDokumen4 halamanMatlab Code Ecgmanik9000Belum ada peringkat
- 9 OverrideControlDokumen10 halaman9 OverrideControlsamiran21Belum ada peringkat
- Signal Processing in MATLABDokumen3 halamanSignal Processing in MATLABRadu VancaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 StudentsDokumen59 halamanModule 1 StudentsMahesh M P NairBelum ada peringkat
- ST-T Depression HannaDokumen11 halamanST-T Depression Hannadrimran570Belum ada peringkat
- Conditioning CircuitsDokumen57 halamanConditioning CircuitsakozyBelum ada peringkat
- ConverterDokumen17 halamanConverterJimmy TanBelum ada peringkat
- 'Signal Corrupted With Zero-Mean Random Noise' 'Time (Milliseconds) 'Dokumen3 halaman'Signal Corrupted With Zero-Mean Random Noise' 'Time (Milliseconds) 'jorge humbertoBelum ada peringkat
- Allen BradleyDokumen12 halamanAllen BradleyABVSAIBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateDokumen17 halamanECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateImja94Belum ada peringkat
- EKG Signal Processing An Algorithm To Detect and Align QRS ComplxDokumen33 halamanEKG Signal Processing An Algorithm To Detect and Align QRS ComplxaryakushalBelum ada peringkat
- Pneupac BrochureDokumen9 halamanPneupac BrochureahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Securing The Local Network Network: CCNA SecurityDokumen146 halamanSecuring The Local Network Network: CCNA SecurityGaston BouaounBelum ada peringkat
- Security&OpmarkDokumen19 halamanSecurity&Opmarksina20795Belum ada peringkat
- EEL 3123 Lab Manual - PDF LABDokumen79 halamanEEL 3123 Lab Manual - PDF LABkamalBelum ada peringkat
- Infant IncubatorDokumen29 halamanInfant IncubatorELI NAINABelum ada peringkat
- and 330425 Accelerometer Acceleration Transducers: DatasheetDokumen9 halamanand 330425 Accelerometer Acceleration Transducers: DatasheetJOSE MARIA DANIEL CANALESBelum ada peringkat
- Artificial IntelligenceDokumen22 halamanArtificial IntelligenceJubair Ahmed BarbhuiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Gsgmscd0601 01e Exaquantum Ara - UsDokumen11 halamanGsgmscd0601 01e Exaquantum Ara - Usbmw316Belum ada peringkat
- Design and Implementation of Low Cost ECG Monitoring System and Analysis Using Smart DeviceDokumen5 halamanDesign and Implementation of Low Cost ECG Monitoring System and Analysis Using Smart DeviceIJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- 002-MHIAC - PPT - Presentation IEC-61131 3 StandardDokumen47 halaman002-MHIAC - PPT - Presentation IEC-61131 3 StandardEder JuárezBelum ada peringkat
- 04 ECG NormalDokumen13 halaman04 ECG NormalJevisco LauBelum ada peringkat
- Fuzzy Logic Tutorial: What Is, Application & ExampleDokumen7 halamanFuzzy Logic Tutorial: What Is, Application & ExampleDe' LufiasBelum ada peringkat
- ECG MatlabDokumen4 halamanECG MatlabPavan PakkiBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg Matlab CodeDokumen2 halamanEcg Matlab CodemakBelum ada peringkat
- Basic ECG Interpretation: Cardiology and Vascular Department Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin UniversityDokumen61 halamanBasic ECG Interpretation: Cardiology and Vascular Department Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin UniversityHayat Hamzah DawiBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg 111029102429 Phpapp01Dokumen103 halamanEcg 111029102429 Phpapp01Vickry WahidjiBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation Patient MonitorDokumen17 halamanPresentation Patient MonitorMuh Iwan TaufikBelum ada peringkat
- Inductive SensorsDokumen96 halamanInductive SensorsMoustapha SeyeBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Project Report NewDokumen24 halamanECG Project Report NewdileepkinjarapuBelum ada peringkat
- Profibus EvolutionDokumen16 halamanProfibus EvolutionnourBelum ada peringkat
- The Heart As A PumpDokumen25 halamanThe Heart As A PumpBali PalBelum ada peringkat
- Conquering The ECGDokumen25 halamanConquering The ECGPankaj PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Basic: Fieldmate R1.02 For The SalespersonDokumen22 halamanBasic: Fieldmate R1.02 For The SalespersonNumanBelum ada peringkat
- Number Systems and Codes: Chapter ObjectivesDokumen14 halamanNumber Systems and Codes: Chapter ObjectivesozzaapriodedeBelum ada peringkat
- Chicken Pox SOAPDokumen8 halamanChicken Pox SOAPKevin NyasogoBelum ada peringkat
- Centum VP Maintenance PDFDokumen2 halamanCentum VP Maintenance PDFdaviqueirozdemedeirosBelum ada peringkat
- Firstaid ModuleDokumen143 halamanFirstaid Moduleretni wulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Exposure Calculator Noise Level (L DB) Exposure Duration (Hours)Dokumen2 halamanExposure Calculator Noise Level (L DB) Exposure Duration (Hours)Gustavo AlcântaraBelum ada peringkat
- PedekgDokumen42 halamanPedekgJojo JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab Code For EcgDokumen5 halamanMatlab Code For Ecgsriteja406Belum ada peringkat
- 02 - Project 2 Excercise Robotino Part A ExcercisesDokumen30 halaman02 - Project 2 Excercise Robotino Part A ExcercisesdedegressBelum ada peringkat
- Electric ShockDokumen4 halamanElectric ShockTamjid KabirBelum ada peringkat
- THE Electrocardiogram (Ecg / Ekg) : By: DR Yasir MansouriDokumen83 halamanTHE Electrocardiogram (Ecg / Ekg) : By: DR Yasir Mansourirofi modiBelum ada peringkat
- ECG ThesisDokumen40 halamanECG ThesisMirza MehranBelum ada peringkat
- Networks in Process AutomationDokumen24 halamanNetworks in Process AutomationRajeshBelum ada peringkat
- Minnesota Code - PrineasDokumen338 halamanMinnesota Code - Prineasrgmaguila1533Belum ada peringkat
- Electronics II NotesDokumen41 halamanElectronics II NotesactuatorBelum ada peringkat
- T00108 Configuring The Enterprise View WorkshopDokumen14 halamanT00108 Configuring The Enterprise View WorkshopLe Thanh HaiBelum ada peringkat
- Pattern Analysis of Different ECG SignalDokumen4 halamanPattern Analysis of Different ECG SignalngovantamcuteBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation of Algorithms For QRS Detection From ECG Signals UsingDokumen10 halamanImplementation of Algorithms For QRS Detection From ECG Signals UsingMuhsinBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Audio Processing Revisited: Juan P BelloDokumen29 halamanDigital Audio Processing Revisited: Juan P BellokoustubhthoratBelum ada peringkat
- NikeDokumen10 halamanNikepawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- Reguler Functions in SQLDokumen29 halamanReguler Functions in SQLpawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- Vision Mission EEDokumen1 halamanVision Mission EEpawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- The Good Teacher Is More Than A Lecturer - The Twelve Roles of The Teacher - MEDEV, School of Medical Sciences Education Development PDFDokumen5 halamanThe Good Teacher Is More Than A Lecturer - The Twelve Roles of The Teacher - MEDEV, School of Medical Sciences Education Development PDFpawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- Sample Question Paper Digital Communication SystemsDokumen4 halamanSample Question Paper Digital Communication Systemspawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- Organic Farming - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen35 halamanOrganic Farming - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediapawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- Intelligent Mobile Health Monitoring System (IMHMS)Dokumen16 halamanIntelligent Mobile Health Monitoring System (IMHMS)Anup KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Wireless Communication SystemsDokumen9 halamanIntroduction To Wireless Communication Systemspawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- Government Schemes For Urban Poor-EnglishDokumen107 halamanGovernment Schemes For Urban Poor-Englishpawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- Optional Installations: Installing A WAN Interface CardDokumen12 halamanOptional Installations: Installing A WAN Interface Cardpawan_32100% (1)
- Edc 1Dokumen1 halamanEdc 1pawan_32Belum ada peringkat
- HACCP Carbonated Soft DrinksDokumen9 halamanHACCP Carbonated Soft DrinksmubdiantiBelum ada peringkat
- Sat-Asatkaryavada in DiseaseDokumen7 halamanSat-Asatkaryavada in DiseaseSamhitha Ayurvedic ChennaiBelum ada peringkat
- FACTSHEET YouthSuicideRevisedSpring2010Dokumen10 halamanFACTSHEET YouthSuicideRevisedSpring2010Riyan SudrajadBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment and Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy - UpToDate PDFDokumen52 halamanTreatment and Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy - UpToDate PDFDerian Yamil Bustamante AngelBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Tumor Biology On Cancer Treatment and Multidisciplinary Strategies - M. Molls, Et Al., (Springer, 2009) WWDokumen363 halamanThe Impact of Tumor Biology On Cancer Treatment and Multidisciplinary Strategies - M. Molls, Et Al., (Springer, 2009) WWiuliBelum ada peringkat
- Ip Finall BillDokumen7 halamanIp Finall BillvijaykumarBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Troponin IDokumen1 halamanCardiac Troponin IPABRIK SEPULUHBelum ada peringkat
- National Health PolicyDokumen31 halamanNational Health PolicyGayathri R0% (1)
- Humidification in The Intensive Care UnitDokumen272 halamanHumidification in The Intensive Care UnitAbu HibbaanBelum ada peringkat
- Zantac Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanZantac Drug StudyCee Kaye Gee0% (1)
- Politeknik Ungku Omar: Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi MalaysiaDokumen9 halamanPoliteknik Ungku Omar: Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi Malaysiaazmir100% (3)
- 766ue 2019-01Dokumen101 halaman766ue 2019-01Angelita Kstro D SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- FcpsDokumen205 halamanFcpsSoniya DulalBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For Ineffective Airway Clearance.Dokumen2 halamanNCP For Ineffective Airway Clearance.Vanessa Joy Contreras100% (1)
- 2015 Coca-Cola MENA Scholarship ApplicationDokumen15 halaman2015 Coca-Cola MENA Scholarship ApplicationMehroze MunawarBelum ada peringkat
- #NephJC CTscan TranscriptDokumen22 halaman#NephJC CTscan TranscriptSatrio Budi WicaksonoBelum ada peringkat
- Essay SamplesDokumen10 halamanEssay SamplesJackie Vacalares100% (1)
- CestodesDokumen39 halamanCestodesNachiket Vijay PotdarBelum ada peringkat
- Ayurveda FitoterapiaDokumen112 halamanAyurveda FitoterapiaKerol Bomfim100% (2)
- New Report About Holyoke Soldiers' HomeDokumen10 halamanNew Report About Holyoke Soldiers' HomeMike PlaisanceBelum ada peringkat
- AntibioticsDokumen53 halamanAntibioticsMaheen IdreesBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Methodologies Chapter 4 9-1.2012 PDFDokumen26 halamanEndocrine Methodologies Chapter 4 9-1.2012 PDFLeora LiBelum ada peringkat
- Marathon Training BrochureDokumen16 halamanMarathon Training BrochurebrainiousBelum ada peringkat
- Cam4 6 1861Dokumen10 halamanCam4 6 1861Ćatke TkećaBelum ada peringkat
- GoniometryDokumen22 halamanGoniometryDuppala Sateesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- A Review Paper On Arjuna Terminalia Cardio Protective Potential in Ayush & Modern MedicineDokumen12 halamanA Review Paper On Arjuna Terminalia Cardio Protective Potential in Ayush & Modern MedicineDR MEENAKSHI SONIBelum ada peringkat
- Antimony: CharacteristicsDokumen21 halamanAntimony: CharacteristicsRaveendra MungaraBelum ada peringkat
- List of Abstract Presenters ISMPNP-2024 EMAILDokumen7 halamanList of Abstract Presenters ISMPNP-2024 EMAILasadalijanjua.0003Belum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Pas BingDokumen8 halamanContoh Soal Pas BingAnnisa AuliaBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines TAVI TAVRDokumen15 halamanGuidelines TAVI TAVRRossellaDisalvo100% (1)