CNS Anatomy Guide
Diunggah oleh
cndy310 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan19 halamancns
Judul Asli
08 Human Phys Central Nervous System
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inicns
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan19 halamanCNS Anatomy Guide
Diunggah oleh
cndy31cns
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 19
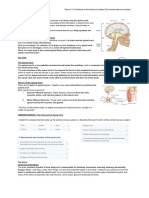
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Thing to be covered
Anatomy of the CNS
The Spinal Cord
The Brain
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Anatomy of the CNS
The Skull or Cranium (for brain)
The Vetebral Column (for spinal cord)
Meninges
Dura mater (outermost layer)
Arachnoid membrane ( middle layer)
Pia mater (innermost layer)
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Cranial vault - 1.4L; cells - 1.0L; blood - 0.1- 0.15L;
CSF - 0.2-0.3L
Colorless, salty solution
Continuously secreted from specialized cells
(ependymal cells) in the choroid plexus in ventricles
Ependyma actively transport Na
+
and solutes into
ventricles
Functions: Physical and chemical protection
Contains little protein and lower K
+
, Ca
++
, HCO
3
-
,
and glucose
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Path of CerebroSpinal Fluid
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Three-dimensional view of the ventricles of the
Brain
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
The Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Function - protection
Brain capillaries much less permeable than others
Protects the brain from blood composition
fluctuations
Can transport nutrients into the ISF
Exceptions - posterior pituitary and vomiting center
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
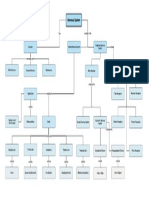
Divisions of the CNS
Gray matter
Nuclei
White matter
Tracts - ascending and descending
Spinal cord
Dorsal root (afferent, sensory)
Ventral root (efferent, motor)
Dorsal horns
Ventral horns
Dorsal root ganglion
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Organization of the grey matter of the spinal
cord
Major ascending and descending pathways
of the spinal cord
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
The Brain
Cerebrum
Brain stem
Cerebellum
Forebrain - cerebrum and diencephalon
Brain stem - midbrain, pons, medulla
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
The Brain Stem
Contains the third and fourth ventricles
9 cranial nerves emerge (know tables 9-1 & 2 )
Medulla oblongata contains vital centers
Pyramids
Midbrain or mesencephalon controls eye and ear
functions
Reticular formation - arousal and sleep
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
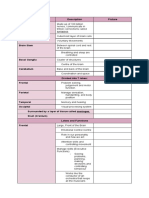
The Cranial Nerves (Know Table 9-1)
I Olfactory
II Optic
III Oculomotor
IV Trochlear
V Trigeminal
VI Abducens
VII Facial
VIII Vestibulocochlear
IX Glossopharyngeal
X Vagus
XI Accessory
XII Hypoglossal
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
The Cerebellum
Process sensory information
Coordinates muscle activity
Involves cordinating balance and equilibrium
The Diencephalon
Composed of thalamus and the hypothalamus
Also contains the pineal gland
Thalamus has several nuclei and is described as a
relay station for signals on their way to the cerebral
cortex
The hypothalamus contains centers for behaviorial
drives and homeostasis (See Table 9-2 for more info)
It controls both endocrine and autonomic functions
Receives information from various sources
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
The Cerebrum: Lobes and Fissures of the
Cerebral Hemispheres: Lateral Left
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
The Cerebrum: Lobes and Fissures of the
Cerebral Hemispheres: Medial surface
Lobes:
1. Frontal
2. Parietal
3. Occipital
4. Temporal
5. Limbic
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Major Regions of the Cerebral Hemipheres
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Functional Area of the Cerebrum
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Motor and Sensory Areas of the Cerebrum
Human Physiology
The Central Nervous System
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Central Nervous SystemDokumen19 halamanCentral Nervous SystemLorry PetreBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen48 halamanNervous SystemSuvalari Mimi JonathanBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDokumen26 halamanDisorders of The Nervous Systemshishiminaj100% (1)
- Stella Maris Polytechnic: The Nervous SystemDokumen50 halamanStella Maris Polytechnic: The Nervous SystemKalpana jestinaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology NOTES 4Dokumen38 halamanAnatomy and Physiology NOTES 4mike921goldBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroanatomy & PhysiologyDokumen44 halamanNeuroanatomy & PhysiologyKarina MawarnursaviraBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen18 halamanNervous SystemGwynth Mrgrtt GnzlsBelum ada peringkat
- DIENCEPHALON: (Thalamus and Hypothalamus) THALAMUS: P. 531 Many NucleiDokumen7 halamanDIENCEPHALON: (Thalamus and Hypothalamus) THALAMUS: P. 531 Many Nucleijael92Belum ada peringkat
- Brain Anatomy and FunctionsDokumen21 halamanBrain Anatomy and Functionsayat ullahBelum ada peringkat
- 8.2. EncephalonDokumen86 halaman8.2. EncephalonIxzuluzxi100% (2)
- SARAF PUSAT DAN OTONOMDokumen72 halamanSARAF PUSAT DAN OTONOMellaBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of Nervous System: Spinal Cord BrainDokumen38 halamanPhysiology of Nervous System: Spinal Cord Brainsam bossaBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Structures and their Functions ExplainedDokumen6 halamanBrain Structures and their Functions ExplainedUjjal Kumar Sarker100% (2)
- Nervous System Structure and FunctionsDokumen46 halamanNervous System Structure and FunctionssureshdassBelum ada peringkat
- CVD Case StudyDokumen12 halamanCVD Case StudySean MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Evidence-Based NursingDokumen9 halamanEvidence-Based NursingKate AbadBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System GuideDokumen59 halamanNervous System GuideDR Archana Agarwal100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Nervous SystemDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of the Nervous SystemnanatdaboyBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen8 halamanAnatomy and Physiologymhel03_chickmagnetBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Structure and FunctionDokumen61 halamanBrain Structure and FunctionBINITABelum ada peringkat
- CNS: Anatomy and Functions of the Central Nervous SystemDokumen70 halamanCNS: Anatomy and Functions of the Central Nervous SystemZyrick Laurence Eslao TimmangoBelum ada peringkat
- Frog Nervous System Anatomy and FunctionsDokumen38 halamanFrog Nervous System Anatomy and Functionsnone57% (7)
- Neuro Case PresentationDokumen52 halamanNeuro Case PresentationjisarafaelBelum ada peringkat
- Midbrain ("Mesencephalon")Dokumen56 halamanMidbrain ("Mesencephalon")Полина Бауэр100% (1)
- Endo All MergeDokumen586 halamanEndo All MergeShivani DurgeBelum ada peringkat
- Human BrainDokumen37 halamanHuman BrainjhoenlitBelum ada peringkat
- Brain FunctionDokumen68 halamanBrain FunctionIdzhamReezaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDokumen90 halamanNervous System and Endocrine SystemCeres LucenteBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Physiologyssairej06Belum ada peringkat
- Physiological Psy LectureDokumen125 halamanPhysiological Psy LectureKdrama SweetieBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 15: NERVOUS SYSTEM, Brain and Cranial Nerve: Embryology of The BrainDokumen3 halamanCHAPTER 15: NERVOUS SYSTEM, Brain and Cranial Nerve: Embryology of The BrainDyah Ayu Pratama SariBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System II: Essentials of Human AnatomyDokumen29 halamanNervous System II: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودBelum ada peringkat
- The Brain Stem: Location and Basic PhysiologyDokumen33 halamanThe Brain Stem: Location and Basic PhysiologyMohammad AliBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Syaraf PusatDokumen73 halamanSistem Syaraf PusatClaraAmeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanLecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemT-Bone02135Belum ada peringkat
- Zodiac Academy: Hari Krishna G L Academic CoordinatorDokumen94 halamanZodiac Academy: Hari Krishna G L Academic CoordinatorHARI KRISHNA G LBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Nervous SystemDokumen25 halaman3.1 Nervous SystemHARNOOR KAURBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System GuideDokumen16 halamanNervous System Guidexuxi dulBelum ada peringkat
- Central Nervous System: - BrainDokumen26 halamanCentral Nervous System: - BrainMonaBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Stem AnatomiDokumen55 halamanBrain Stem AnatomiNor Ubudiah SetiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to the Anatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemDokumen72 halamanIntroduction to the Anatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemTony Hermawan100% (1)
- 7 Nervous SystemDokumen32 halaman7 Nervous SystemGynewBelum ada peringkat
- Brain & Limbic SystemDokumen63 halamanBrain & Limbic Systemgopscharan100% (1)
- Brain and Behaviour 3Dokumen9 halamanBrain and Behaviour 3sonika parikhBelum ada peringkat
- BrainDokumen2 halamanBrainAngad SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To The Brain and Cranial NervesDokumen5 halamanChapter 14 - An Introduction To The Brain and Cranial Nervestomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayBelum ada peringkat
- (L3) - Neural Control and Coordination - Oct 21, 2019Dokumen37 halaman(L3) - Neural Control and Coordination - Oct 21, 2019Anamika SorengBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous System 001Dokumen35 halamanThe Nervous System 001gelisar3sBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial NervesDokumen57 halamanChapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nervesgabbs_123Belum ada peringkat
- Complexity of Connectivity and Branching/networksDokumen4 halamanComplexity of Connectivity and Branching/networksmuryumBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanNervous SystemNicah FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Patients Profile I. Biographic DataDokumen18 halamanPatients Profile I. Biographic DataEmJay BalansagBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Week 9 BioDokumen6 halaman3rd Week 9 BioTaze UtoroBelum ada peringkat
- MHNDokumen26 halamanMHNGopika SBelum ada peringkat
- CNS 1Dokumen13 halamanCNS 1Jeff ParkBelum ada peringkat
- CNS - Final ReviewDokumen14 halamanCNS - Final ReviewcoldfiresidhuBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Bee R1 P2Dokumen9 halamanBrain Bee R1 P2sarahsyedazakiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 NotesDokumen16 halamanChapter 2 NotesOfeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Anatomy and Physiology GuideDokumen36 halamanBrain Anatomy and Physiology GuideJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesBelum ada peringkat
- CDC Response GuideDokumen65 halamanCDC Response GuidePremaWahiniBelum ada peringkat
- Combinedimmunodeficiencies - Ding N MayDokumen38 halamanCombinedimmunodeficiencies - Ding N Maycndy31Belum ada peringkat
- CDC Response GuideDokumen65 halamanCDC Response GuidePremaWahiniBelum ada peringkat
- Eco 1Dokumen23 halamanEco 1cndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Emil Von Behring: Presented byDokumen9 halamanEmil Von Behring: Presented bycndy31Belum ada peringkat
- PlasmiddddDokumen4 halamanPlasmiddddcndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Emil Von Behring: Presented byDokumen9 halamanEmil Von Behring: Presented bycndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Combinedimmunodeficiencies - Ding N MayDokumen38 halamanCombinedimmunodeficiencies - Ding N Maycndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Emil Von Behring: Presented byDokumen9 halamanEmil Von Behring: Presented bycndy31Belum ada peringkat
- CDC Response GuideDokumen65 halamanCDC Response GuidePremaWahiniBelum ada peringkat
- VSO Activity BookDokumen127 halamanVSO Activity Bookcndy31100% (1)
- 3A Rush PVD V Surg PoV PresentationDokumen22 halaman3A Rush PVD V Surg PoV Presentationcndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Organ TransplantsDokumen18 halamanOrgan Transplantscndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Plasmid MicrobioDokumen8 halamanPlasmid Microbiocndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Basics of Organ Donation & Management of Brain Dead DonorDokumen38 halamanBasics of Organ Donation & Management of Brain Dead DonordrilakBelum ada peringkat
- Medicolegalaspectoforgantransplantationandbraindeath 140112204911 Phpapp01Dokumen47 halamanMedicolegalaspectoforgantransplantationandbraindeath 140112204911 Phpapp01cndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Cadaver Organ DonationDokumen83 halamanCadaver Organ Donationcndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Organ Donation SimpleDokumen46 halamanOrgan Donation Simplecndy31Belum ada peringkat
- 400080Dokumen88 halaman400080cndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Organ TransplantsDokumen18 halamanOrgan Transplantscndy31Belum ada peringkat
- 3600+ Review Questions Volume1-5eDokumen132 halaman3600+ Review Questions Volume1-5eEric TyBelum ada peringkat
- Plasmid MicrobioDokumen8 halamanPlasmid Microbiocndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Calicut 2000 2010Dokumen5 halamanAnatomy Calicut 2000 2010cndy31Belum ada peringkat
- EmbryologyDokumen102 halamanEmbryologycndy31100% (1)
- 1281 PDFDokumen64 halaman1281 PDFcndy31Belum ada peringkat
- Top Confucius Quotes on Learning, Respect and WisdomDokumen1 halamanTop Confucius Quotes on Learning, Respect and Wisdomcndy31Belum ada peringkat
- EmbryologyDokumen102 halamanEmbryologycndy31100% (1)
- Declension of Russian AdjectivesDokumen4 halamanDeclension of Russian Adjectivescndy31Belum ada peringkat
- The Russian Pronoun DeclensionsDokumen3 halamanThe Russian Pronoun Declensionscndy31Belum ada peringkat
- 12 rules for life by Dr. Jordan Peterson analyzedDokumen12 halaman12 rules for life by Dr. Jordan Peterson analyzedTamo Mujiri100% (1)
- Introduction to the Anatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemDokumen72 halamanIntroduction to the Anatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemTony Hermawan100% (1)
- Year 9 Chapter 8 Sense and Control Sample AnswersDokumen80 halamanYear 9 Chapter 8 Sense and Control Sample Answerskyle leeBelum ada peringkat
- 15 CortexDokumen87 halaman15 Cortexandreea_grama_11Belum ada peringkat
- C9apstudy GuideDokumen37 halamanC9apstudy GuidejqtdBelum ada peringkat
- General Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANDokumen7 halamanGeneral Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANMariel EfrenBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen2 halamanDaftar PustakaGilbert Sterling OctaviusBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Implications: Mr. Ibrahim Rawhi Ayasreh RN, MSN, AcnsDokumen15 halamanBiological Implications: Mr. Ibrahim Rawhi Ayasreh RN, MSN, AcnsIbrahim R. AyasrehBelum ada peringkat
- Biomaterials and Cells For Neural Tissue EngineeringDokumen60 halamanBiomaterials and Cells For Neural Tissue EngineeringYusser olguínBelum ada peringkat
- Coordination and Response - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Dokumen1 halamanCoordination and Response - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Misheel BatzorigBelum ada peringkat
- QUIZ DAY - MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM & BODY SYSTEMSDokumen37 halamanQUIZ DAY - MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM & BODY SYSTEMSCHUCKZ CAPARASBelum ada peringkat
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDokumen19 halamanBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanBelum ada peringkat
- BiologicalBasisBehavior Bluestone PDFDokumen30 halamanBiologicalBasisBehavior Bluestone PDFdaphnereezeBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition Ebook PDFDokumen61 halamanPrinciples of Human Physiology 6th Edition Ebook PDFbilly.sparks463100% (40)
- INTROPSY Reviewer (Book and Lecture Notes) Chapters 1 and 2Dokumen11 halamanINTROPSY Reviewer (Book and Lecture Notes) Chapters 1 and 2jonaxx enthusiastBelum ada peringkat
- TU (IOM) MBBS Curriculum (1st and 2nd Year)Dokumen40 halamanTU (IOM) MBBS Curriculum (1st and 2nd Year)Govind Mani BhattBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Education in The Tertiary LevelDokumen35 halamanPhysical Education in The Tertiary Levelhatsune mikuBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Brain AnatomyDokumen32 halamanIntroduction To Brain AnatomySasikala Mohan100% (1)
- Test Bank For Seeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Cinnamon Vanputte and Jennifer Regan and Andrew Russo DownloadDokumen48 halamanTest Bank For Seeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Cinnamon Vanputte and Jennifer Regan and Andrew Russo DownloadBenjaminWilsongaco100% (16)
- PT - Science 6 - Q2Dokumen10 halamanPT - Science 6 - Q2Seyr EdzBelum ada peringkat
- Cns InfectionDokumen379 halamanCns InfectionNio AlfaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3ADokumen28 halamanChapter 3AjBelum ada peringkat
- The Psychopath MagnetizedDokumen9 halamanThe Psychopath MagnetizedAvengingBrainBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Concept MapDokumen1 halamanNervous System Concept MapWild RiftBelum ada peringkat
- Albert Ellis-The Art and Science of LoveDokumen292 halamanAlbert Ellis-The Art and Science of Loveinnersensation100% (3)
- Ebook PDF Visualizing Human Biology 5th Edition PDFDokumen41 halamanEbook PDF Visualizing Human Biology 5th Edition PDFjerry.leverett380100% (34)
- Formative Test I (Plus Feedback) NBSS 2020-2021 - Attempt ReviewDokumen1 halamanFormative Test I (Plus Feedback) NBSS 2020-2021 - Attempt ReviewAlif YusufBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous System - PsychologyDokumen17 halamanThe Nervous System - Psychologyjanet100% (2)
- Chapter 17 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Dokumen36 halamanChapter 17 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Suffa Academy100% (3)
- UCSP - Parts of The Brain Q1Dokumen15 halamanUCSP - Parts of The Brain Q1harperBelum ada peringkat