The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Diunggah oleh
arunprasadvr0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
99 tayangan25 halamanChapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making. Determining the organizational vision precedes all other management decisions. Organization's strengths should help shape the vision.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
ch01
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniChapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making. Determining the organizational vision precedes all other management decisions. Organization's strengths should help shape the vision.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
99 tayangan25 halamanThe Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Diunggah oleh
arunprasadvrChapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making. Determining the organizational vision precedes all other management decisions. Organization's strengths should help shape the vision.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 25
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 1
Cost Management
Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating Performance
Prepared by
Gail Kaciuba
Midwestern State University
Chapter 1
The Role of Accounting Information in
Management Decision Making
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 2
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in
Management Decision Making
Learning objectives
Q1: What types of decisions do managers make for an
organization?
Q2: What is the role of accounting information in
management decision making?
Q3: How do uncertainties and biases affect the quality of
decisions?
Q4: How can managers make higher-quality decisions?
Q5: What information is relevant for decision making?
Q6: What is ethical decision making and why is it
important?
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 3
Q1: Organizational Vision and Core Competencies
The organizational vision is the core purpose and
ideology of the organization.
Determining the organizational vision precedes all
other management decision making.
Management must also isolate the organizations
core competencies its strengths relative to
competitors.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 4
Q1: Organizational Vision and Core Competencies
Organizational
Vision
Core
Competencies
The organizational vision and the
core competencies are closely
related.
The organizations strengths
should help shape the vision.
The vision should help locate the
organizations strengths.
If you were starting an accounting practice, what would be your
organizational vision?
What do you think would be your core competencies?
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 5
Q1: Organizational Strategies
Organizational
Vision & Core
Competencies
OrganizationalS
trategies
Organizational strategies are the tactics
that managers use to work toward the
organizational vision while taking
advantage of the core competencies.
These strategies are long-term in nature.
Examples include organization structure,
financial structure, and long-term
resource allocation strategies.
If you were starting an accounting practice, what would be some of your
organizational strategies?
How do these work toward your organizational vision?
How do they take advantage of your core competencies?
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 6
Q1: Operating Plans
Organizational
Strategies
Operating
Plans
Operating plans are the short-term
implementations of the organizational
strategies.
Operating plans usually include
budgeted goals for revenues and
expenses.
Examples include schedules for
employees and procedures for daily
relationship management decisions
with suppliers.
If you were starting an accounting practice, what would be some of your
operating plans?
How do these relate to your organizational strategies?
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 7
Q1: Actual Operations
Operating
Plans
Actual
Operations
Actual operations are the actions
taken and the results achieved.
The organizations information
system measures the results of
actual operations.
Examples include number of units
sold, advertising expense, and the
wage expense for the period.
If you had an accounting practice, what would information would you
want to collect about the results of your actual operations?
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 8
Q2: Monitoring and Motivating Performance
Organizational
Vision & Core
Competencies
Actual
Operations
Managers use the results of actual
operations to monitor performance and
ensure that it is in line with the
organizational vision.
Managers may find that the results of
actual operations make them re-think the
organizational vision or their view of the
organizations core competencies.
If you had an accounting practice, can you think of an example of a
measure of actual operations and how you would use it to motivate
performance?
Can you think of an example of a measure of actual operations that
might make you redefine your organizational vision or your view of your
core competencies?
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 9
Q2: Financial, Managerial, and Cost Accounting
Financial accounting
prepares reports most
frequently used by decision
makers external to the
organization.
Managerial accounting
prepares reports most
frequently used by decision
makers internal to the
organization.
Cost accounting is a method for measuring the cost of a
project, process, or thing*. It includes both financial and
nonfinancial information and is used for both financial and
managerial accounting.
*This is the definition of cost accounting from the Institute of Management Accountants
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 10
Q2: Strategic Cost Management
and the Balanced Scorecard
Strategic cost management is an approach to
reducing costs while strengthening the
organizations strategic position.
The balanced scorecard can be used to formalize
strategic cost management efforts by detailing
financial and nonfinancial benchmarks for all
segments of the organization.
Examples of such benchmarks include:
Personnel can reduce costs by completing all hiring within 20
days of initial interview.
Production can reduce costs and improve quality if Engineering
can reduce the number of processes in the production process.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 11
Q3: Uncertainties, Biases, and Decision Quality
Uncertainties are issues and information about
which there is doubt.
Biases are preconceived notions adopted without
careful thought.
Both uncertainty and bias reduce decision quality.
Decision quality refers to the characteristics of a
decision that affect the likelihood of achieving a
positive outcome.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 12
Q3: Uncertainties and Biases in Information
Uncertainties come from many sources and can be
exogenous or endogenous.
Biases can come from many sources.
The future is always uncertain.
Managers may be uncertain that the right information
was captured in a report.
The decision maker may be biased towards or against a
particular alternative.
The methods used to collect information could have
introduced bias.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 13
Q3: Uncertainties, Biases, and Decision Quality
Lori loves to sew and has always made her own clothes. People often
tell her that she is the best-dressed person theyve ever met. She can
design and sew a lovely outfit in under 2 days. She is considering
opening a store that could sell her home-made fashions. Then she could
combine her work with her hobby.
Can you identify some of the uncertainties Lori faces? Can you think of
any way she can reduce some of these uncertainties?
Can you identify any possible personal biases that Lori may have? How
could these affect her decision making process?
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 14
Q4: Characteristics of Higher-Quality Decisions
Higher quality decisions come from a
higher quality decision making process.
Such a process is thorough, unbiased,
focused, strategic, creative, and visionary.
This process requires reports that are
relevant, understandable, and available.
These reports must contain information
that is more certain, complete, relevant,
timely and valuable.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 15
Q4: Steps for
Better Thinking
Source: (c) 2002. C. L. Lynch, S. K. Wolcott, and G. E. Huber, Steps for Better Thinking: A
Developmental Problem-Solving Process (August 5, 2002).
Steps for Better
Thinking is a
process to help
address open-
ended questions.
Open-ended
questions have no
single correct
solution; managers
must seek the best
solution.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 16
Q4: Steps for Better Thinking Foundation (Knowing)
Foundation level skills include a knowledge of the
terminology and basic concepts that are relevant
to the decision at hand.
An individual with Foundation level skills can:
perform calculations to arrive at correct answer
define terms in his/her own words
describe a concept
list the elements contained in a concept or
process
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 17
Q4: Steps for Better Thinking - Identifying
Step 1 skills include the ability to identify relevant
information and uncertainties.
An individual with Step 1 skills can:
create a list of issues related to the decision
sort information that is relevant
identify the reasons for the underlying
uncertainties
perform research to obtain input into the
decision
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 18
Q4: Steps for Better Thinking - Exploring
Step 2 skills include the ability to explore
interpretations of the information and connections
between alternative solutions approaches.
An individual with Step 2 skills can:
recognize and control for his/her own biases
articulate assumptions and reasoning
associated with alternative points of view
organize information in meaningful ways to
encompass problem complexities
compare and contrast different approaches to
a problems solutions
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 19
Q4: Steps for Better Thinking - Prioritizing
Step 3 skills include the ability to prioritize
alternatives, come to a decision, and implement
the decision.
An individual with Step 3 skills can:
develop guidelines for prioritizing alternatives
prioritize alternatives after objective analysis
communicate findings in a manner appropriate
to the audience
describe how the solution or decision might
change if priorities change
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 20
Q4: Steps for Better Thinking - Envisioning
Step 4 skills include the ability to monitor the
decision and innovate new strategies to modify
the decision when circumstances change.
An individual with Step 4 skills can:
explain the limitations of the decision made
establish a plan for monitoring the performance
of the decision
explain how conditions may change in the
future and how this may change the decision
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 21
Q5: What Information is Relevant
for Decision Making?
Information is relevant if:
it concerns the future, and
it varies across the alternatives.
Avoidable cash flows are future cash flows that
differ across the alternatives.
also called incremental cash flows
also called relevant cash flows
Unavoidable cash flows are non-incremental and
are therefore also called irrelevant cash flows.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 22
Q5: What Information is Relevant
for Decision Making?
You have a small computer repair company and are deciding whether to
replace your old copy machine or repair it. In the list of information
below, identify which data are relevant to this decision and which are
irrelevant.
The purchase price of the copy machine was $1200.
The repair costs are $320.
The copy machine can make 20 copies per minute.
If you repair it, the machine will use less toner than it does now.
You make approximately 1000 copies per month.
The repair wont fix the broken stapler.
The repair carries a one-year warranty.
The copy machine was a gift from your spouse.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 23
Q6: Components of Ethical Decision Making
Identify ethical problems as they arise.
Consider the well-being of others and society
when exploring alternatives.
Clarify and apply your ethical values when
choosing a course of action.
Continuously improve your personal ethics and
those of your organization.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 24
Q6: The IMAs Code of Ethics
The Institute of Management Accountants (IMA)
has a Code of Ethics that states that IMA
members have a responsibility to:
maintain an appropriate level of professional competence
and perform their professional duties in accordance with
laws, regulations, and standards;
refrain from disclosing confidential information (unless
legally obligated), or using (or even appearing to use)
confidential information to illegal advantage;
avoid actual and apparent conflicts of interest; and
communicate information fairly and objectively, and disclose
all relevant information to decision makers.
John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Chapter 1: The Role of Accounting Information in Management Decision Making
Eldenburg & Wolcotts Cost Management, 1e Slide # 25
Q6: Ethical Decision Making
Suppose you work for the Lee K. Fawcett Plumbing Company as Mr.
Fawcetts administrative assistant. Recently Mr. Fawcett asked you to
type some financial statements from his hand-written notes so that he
can take them to the bank as part of a loan application.
This exercise seems odd to you because the companys CPA recently
delivered the monthly financial statements that she prepares.
While typing the financial statements you notice that the building the
company rents is listed as an asset. Also, you write checks each month
for the monthly payments on two car loans, and these are not listed as
liabilities.
Do you have an ethical dilemma? Discuss your approach to handling
this situation.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Essentials of Business Ethics: Creating an Organization of High Integrity and Superior PerformanceDari EverandEssentials of Business Ethics: Creating an Organization of High Integrity and Superior PerformanceBelum ada peringkat
- Decision Quality: Value Creation from Better Business DecisionsDari EverandDecision Quality: Value Creation from Better Business DecisionsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- The Handbook of Global Corporate TreasuryDari EverandThe Handbook of Global Corporate TreasuryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Performance Evaluation and CompensationDokumen34 halamanPerformance Evaluation and CompensationarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Management and Organization AssessmentsDokumen10 halamanPrinciples of Management and Organization Assessmentsbmaria krizzaBelum ada peringkat
- Key Performance Indicators for Government and Non Profit Agencies: Implementing Winning KPIsDari EverandKey Performance Indicators for Government and Non Profit Agencies: Implementing Winning KPIsPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Managing Performance in Turbulent Times: Analytics and InsightDari EverandManaging Performance in Turbulent Times: Analytics and InsightPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Basic Construction Management: The Superintendent's JobDari EverandBasic Construction Management: The Superintendent's JobPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Performance Improvement: Optimizing Results through People, Process, and OrganizationsDari EverandFundamentals of Performance Improvement: Optimizing Results through People, Process, and OrganizationsBelum ada peringkat
- The Traits of Today's CFO: A Handbook for Excelling in an Evolving RoleDari EverandThe Traits of Today's CFO: A Handbook for Excelling in an Evolving RoleBelum ada peringkat
- Rti 1Dokumen22 halamanRti 1REG.B/0620103018/LUQMAN AHMADBelum ada peringkat
- The Government Manager's Guide to Earned Value ManagementDari EverandThe Government Manager's Guide to Earned Value ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 Content PDFDokumen4 halamanWeek 1 Content PDFRosarie JenkinsBelum ada peringkat
- FIFO And LIFO Accounting A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandFIFO And LIFO Accounting A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Data Conversion: Calculating the Monetary BenefitsDari EverandData Conversion: Calculating the Monetary BenefitsBelum ada peringkat
- Executive's Guide to Project Management: Organizational Processes and Practices for Supporting Complex ProjectsDari EverandExecutive's Guide to Project Management: Organizational Processes and Practices for Supporting Complex ProjectsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- IT Investment Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandIT Investment Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- The Space Between Strategy and Execution: 8 Pillars of Successful Business TransformationDari EverandThe Space Between Strategy and Execution: 8 Pillars of Successful Business TransformationBelum ada peringkat
- Implementing Beyond Budgeting: Unlocking the Performance PotentialDari EverandImplementing Beyond Budgeting: Unlocking the Performance PotentialPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Social Return On Investment A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandSocial Return On Investment A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Make It Work or Make It Go Away: A Handbook for Dod Program ManagersDari EverandMake It Work or Make It Go Away: A Handbook for Dod Program ManagersBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Due Diligence A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandFinancial Due Diligence A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Outperform with Expectations-Based Management: A State-of-the-Art Approach to Creating and Enhancing Shareholder ValueDari EverandOutperform with Expectations-Based Management: A State-of-the-Art Approach to Creating and Enhancing Shareholder ValueBelum ada peringkat
- The New One-Page Project Manager: Communicate and Manage Any Project With A Single Sheet of PaperDari EverandThe New One-Page Project Manager: Communicate and Manage Any Project With A Single Sheet of PaperPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (16)
- Chief Financial Officer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandChief Financial Officer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Management Essentials You Always Wanted To Know (Second Edition)Dari EverandPrinciples of Management Essentials You Always Wanted To Know (Second Edition)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Objectives and Key Results: Driving Focus, Alignment, and Engagement with OKRsDari EverandObjectives and Key Results: Driving Focus, Alignment, and Engagement with OKRsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- Becoming Lean: Practical Steps to Build CompetitivenessDari EverandBecoming Lean: Practical Steps to Build CompetitivenessPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Leadership Shift: How to Lead Successful Transformations in the New NormalDari EverandThe Leadership Shift: How to Lead Successful Transformations in the New NormalBelum ada peringkat
- Chief Revenue Officer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandChief Revenue Officer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- IT107 HandOut 007Dokumen5 halamanIT107 HandOut 007jin_adrianBelum ada peringkat
- Balance Sheet And The Income Statement A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandBalance Sheet And The Income Statement A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- 20221217195544D6181 Kimmel Accounting 8e PPT Ch22 Budgetary-Planning WithNarrationDokumen102 halaman20221217195544D6181 Kimmel Accounting 8e PPT Ch22 Budgetary-Planning WithNarrationpipityesni13Belum ada peringkat
- Benefits Management: How to Increase the Business Value of Your IT ProjectsDari EverandBenefits Management: How to Increase the Business Value of Your IT ProjectsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Chapter 1 TVTDokumen14 halamanChapter 1 TVTtemedebereBelum ada peringkat
- Making Technology Investments Profitable: ROI Road Map from Business Case to Value RealizationDari EverandMaking Technology Investments Profitable: ROI Road Map from Business Case to Value RealizationPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- CH 1Dokumen27 halamanCH 1Anique buttBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Management For IT Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandFinancial Management For IT Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 - Introduction To MADokumen18 halamanWeek 1 - Introduction To MABambang HasmaraningtyasBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Of Information A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandEconomics Of Information A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- IT Portfolio Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandIT Portfolio Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Chief Investment Officer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandChief Investment Officer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Market Structure ComparisonDokumen1 halamanMarket Structure ComparisonNadeem AftabBelum ada peringkat
- Preparing Future Transportation Automated Vehicle 30Dokumen80 halamanPreparing Future Transportation Automated Vehicle 30ahawkins8223Belum ada peringkat
- E-Auction Notice - Canara MineralsDokumen6 halamanE-Auction Notice - Canara MineralsarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- CSCP Book1Dokumen216 halamanCSCP Book1busy_andrey90% (10)
- GitaManagement PDFDokumen4 halamanGitaManagement PDFParminder Singh RaiBelum ada peringkat
- Action To Be Taken For IntermediaryDokumen1 halamanAction To Be Taken For IntermediaryarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing The Future MckinseyDokumen184 halamanManufacturing The Future MckinseyDaneyal MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- PFA in Hospital PDFDokumen5 halamanPFA in Hospital PDFarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Abc FSN HMLDokumen7 halamanAbc FSN HMLarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing The Future MckinseyDokumen184 halamanManufacturing The Future MckinseyDaneyal MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- Course ListDokumen1 halamanCourse ListarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Process Costing: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen50 halamanProcess Costing: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- A Decision Support System For Inventory Management: Siddharth ParekhDokumen10 halamanA Decision Support System For Inventory Management: Siddharth Parekhd_rcBelum ada peringkat
- Discriminant 1Dokumen7 halamanDiscriminant 1arunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Product and By-Product Costing: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen24 halamanJoint Product and By-Product Costing: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Performance Measurement: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen21 halamanStrategic Performance Measurement: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Costs and Variance Analysis: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen43 halamanStandard Costs and Variance Analysis: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Investment Decisions: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen36 halamanStrategic Investment Decisions: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Management of Revenues and Costs: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen20 halamanJoint Management of Revenues and Costs: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring and Assigning Support Department CostsDokumen36 halamanMeasuring and Assigning Support Department Costsarunprasadvr100% (1)
- Activity-Based Costing and Management: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen25 halamanActivity-Based Costing and Management: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Static and Flexible Budgets: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen29 halamanStatic and Flexible Budgets: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring and Assigning Costs For Income StatementsDokumen19 halamanMeasuring and Assigning Costs For Income StatementsarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Job Costing: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen35 halamanJob Costing: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Relevant Costs For Nonroutine Operating Decisions: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen58 halamanRelevant Costs For Nonroutine Operating Decisions: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen33 halamanCost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- GRE ETS Snapshot AroundynamicsDokumen38 halamanGRE ETS Snapshot AroundynamicsarunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- The Cost Function: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformanceDokumen49 halamanThe Cost Function: Measuring, Monitoring, and Motivating PerformancearunprasadvrBelum ada peringkat
- Brown Resume-WPS OfficeDokumen1 halamanBrown Resume-WPS OfficeTech 4 TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Admission ST James Naman& AnshuDokumen7 halamanAdmission ST James Naman& AnshuDaleep SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Calyptra: Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Universitas Surabaya Vol.2 No.2 (2013)Dokumen16 halamanCalyptra: Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Universitas Surabaya Vol.2 No.2 (2013)shidqi amartyaBelum ada peringkat
- DundalkpcDokumen26 halamanDundalkpcthestorydotieBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio Analysis MCQs - Accounting Ratio MCQsDokumen9 halamanRatio Analysis MCQs - Accounting Ratio MCQsPavan ChinnikattiBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting For Provisions and Contingent LiabilitiesDokumen8 halamanAccounting For Provisions and Contingent LiabilitiesHenry Lister100% (1)
- Intermediate Accounting 3 - January 24, 2023, F2F DiscussionDokumen8 halamanIntermediate Accounting 3 - January 24, 2023, F2F DiscussionZhaira Kim CantosBelum ada peringkat
- 08 Identifying & Assessing The Risks of Material MisstatementDokumen5 halaman08 Identifying & Assessing The Risks of Material Misstatementrandomlungs121223Belum ada peringkat
- Acca Ethics and Professionalism.Dokumen22 halamanAcca Ethics and Professionalism.abirking50% (2)
- Sabari Inn DRHPDokumen283 halamanSabari Inn DRHPArpan Mehta SameerBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9 ValuationDokumen85 halamanChapter 9 ValuationSaravanaaRajendran100% (1)
- Accountancy ImpQ CH04 Admission of A Partner 01Dokumen18 halamanAccountancy ImpQ CH04 Admission of A Partner 01praveentyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Future-Student-Guide ANUDokumen28 halamanFuture-Student-Guide ANUCynthia RaniBelum ada peringkat
- TM 6 - Tugas CGDokumen2 halamanTM 6 - Tugas CGauliaBelum ada peringkat
- Final Examination Slip SEMESTER 1, 2021/2022 SESSION: Remarks No Category Credit Course Name Course Code GroupDokumen2 halamanFinal Examination Slip SEMESTER 1, 2021/2022 SESSION: Remarks No Category Credit Course Name Course Code Groupzarif zakwanBelum ada peringkat
- Commerce 2004Dokumen50 halamanCommerce 2004shtasneemBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 2 - METODOSDokumen19 halamanTarea 2 - METODOSROGER GONZALES BECERRABelum ada peringkat
- 01 x01 Basic ConceptsDokumen10 halaman01 x01 Basic ConceptsXandae MempinBelum ada peringkat
- SBMF Examinations June 2010Dokumen50 halamanSBMF Examinations June 2010van Dana kam'sBelum ada peringkat
- SS Topic 6Dokumen8 halamanSS Topic 6ibrahimkingpubg7Belum ada peringkat
- Q 4 Results Intimation 240522Dokumen29 halamanQ 4 Results Intimation 240522kumar sunnyBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting 102 TermsDokumen3 halamanAccounting 102 TermsAlfred MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokumen10 halamanIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionErwin Labayog MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- How To Prepare Balance SheetDokumen5 halamanHow To Prepare Balance SheetSIddharth CHoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- ICAI Directory Final16-17 PDFDokumen212 halamanICAI Directory Final16-17 PDFArmaan ChhaprooBelum ada peringkat
- CH 1 Auditing and Internal ControlDokumen20 halamanCH 1 Auditing and Internal Controlangelica valenzuelaBelum ada peringkat
- Statement of Financial PositionDokumen88 halamanStatement of Financial PositionSAMSON ALBERT SALAS100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Conceptual Framework and Theoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and ReportingDokumen11 halamanChapter 2 Conceptual Framework and Theoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and ReportingMARIABelum ada peringkat
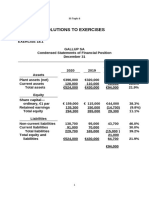
- Solution Manual03Dokumen68 halamanSolution Manual03yellowberries100% (2)