Hormones
Diunggah oleh
Dontu MariaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hormones
Diunggah oleh
Dontu MariaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
AP Biology 2006-2007
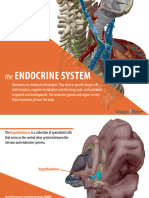
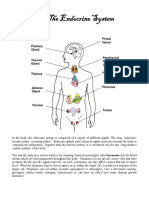
Endocrine System
Hormones
AP Biology
Regulation
Why are hormones needed?
chemical messages from one
body part to another
communication needed to
coordinate whole body
homeostasis & regulation
metabolism
growth
development
maturation
reproduction
growth hormones
AP Biology
Regulation & Communication
Animals rely on 2 systems for regulation
endocrine system
ductless gland which secrete
chemical signals directly into blood
chemical travels to target tissue
slow, long-lasting response
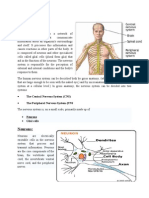
nervous system
system of neurons, central
nerve system
transmits electrical signal to
target tissue
fast, short-lasting response
AP Biology
Regulation by chemical messengers
Axon
Neurotransmitter
Endocrine gland
Receptor proteins
Hormone carried
by blood
Target cell
Neurotransmitters released by neurons
Hormones release by endocrine glands
Receptor proteins
AP Biology
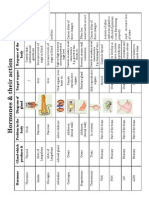
Classes of Hormones
Protein-based hormones
polypeptides
small proteins: insulin, ADH
glycoproteins
large proteins + carbohydrate: FSH, LH
amines
modified amino acids: epinephrine, melatonin
Lipid-based hormones
steroids
modified cholesterol: sex hormones, aldosterone
AP Biology
How do hormones act on target cells
Lipid-based hormones
hydrophobic & lipid-soluble
diffuse across membrane & enter cells
bind to receptor proteins in cytoplasm & nucleus
bind to DNA as transcription factors
Protein-based hormones
hydrophilic & not lipid soluble
cant diffuse across membrane
trigger secondary messenger pathway
activate cellular response
enzyme action, uptake or secretion of molecules
AP Biology
nucleus
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
DNA
mRNA
protein
steroid hormone
blood
protein
carrier
2
3
5
4
S
S
S
1
S
Action of lipid (steroid) hormones
receptor protein
AP Biology
Action of protein hormones
3
4
GTP
activates
enzyme
activates
enzyme
activates
enzyme
Receptor
protein
cAMP
Protein
hormone
ATP
1
2
cytoplasm
Produces an action
protein
messenger
cascade
G protein
AP Biology
adrenal gland
Action of epinephrine (adrenalin)
3
4
GTP
activates
protein kinase-A
activates
phosphorylase
activates
adenylyl cyclase
receptor
protein
cAMP
epinephrine
ATP
1
2
cytoplasm
G protein
liver cell
glucose glycogen
released
to blood
AP Biology
Benefits of a 2 messenger system
Amplification!
Signal molecule
Receptor protein Activated adenylyl cyclase
Amplification
Amplification
Amplification
Amplification
GTP G protein
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
Enzymatic product
Enzyme
Protein kinase
cAMP
Not yet
activated
AP Biology 2005-2006
Negative Feedback Model
high
low
hormone 1
lowers
body condition
hormone 2
gland
specific body condition
raises
body condition
gland
AP Biology 2005-2006
Body Temperature
high
low
nerve signals
sweat
nerve signals
brain
body temperature
shiver
brain
dilates surface
blood vessels
constricts surface
blood vessels
Feedback
Nervous System Control
AP Biology 2005-2006
liver
pancreas
liver
Blood Sugar
blood sugar level
insulin
body
cells take
up sugar
from blood
liver stores
sugar
reduces
appetite
glucagon
pancreas
liver
releases
sugar
triggers
hunger
high
low
Feedback
Endocrine System Control
AP Biology 2005-2006
nephron
low
Blood Osmolarity
blood osmolarity
blood pressure
ADH
increased
water
reabsorption
increase
thirst
renin
increased
water & salt
reabsorption
high
Feedback
Endocrine System Control
pituitary
angiotensinogen
angiotensin
nephron
adrenal
gland
aldosterone
AP Biology
Endocrine & Nervous system links
Hypothalamus = master control center
nervous system
receives information from nerves around body
about internal conditions
regulates release of hormones from pituitary
Pituitary gland = master gland
endocrine system
secretes broad range
of hormones
regulating other
glands
AP Biology
Thyroid gland
Hypothalamus
Anterior
pituitary
Gonadotropic
hormones:
Follicle-
stimulating
hormone (FSH)
& luteinizing
hormone (LH)
Mammary
glands
in mammals
Muscles
of uterus
Kidney
tubules
Posterior
pituitary
Thyroid-stimulating
Hormone
(TSH)
Antidiuretic
hormone
(ADH)
Adrenal
cortex
Bone
and muscle Testis
Ovary
Melanocyte
in amphibian
AP Biology
Homology in hormones
prolactin
mammals
milk
production
birds
fat
metabolism
amphibians
metamorphosis
& maturation
fish
salt &
water
balance
growth
& development
What does this tell you about these hormones?
growth
hormone
same gene family
AP Biology
Regulating metabolism
Hypothalamus
TRH = TSH-releasing hormone
Anterior Pituitary
TSH = thyroid stimulating hormone
Thyroid
produces thyroxine hormones
metabolism & development
bone growth
mental development
metabolic use of energy
blood pressure & heart rate
muscle tone
digestion
reproduction
tyrosine
iodine
thyroxine
AP Biology
Goiter
Iodine deficiency
causes thyroid to
enlarge as it tries to
produce thyroxine
AP Biology
Regulating blood calcium levels
Increased blood Ca
++
Thyroid
Parathyroids
Low blood Ca
++
Parathyroid
hormone (PTH)
Increased absorption
of Ca
++
from intestine
due to PTH activation
of Vitamin D
Reabsorption of Ca
++
&
excretion of PO
4
Osteoclasts
dissolve CaPO
4
crystals in
bone, releasing
Ca
++
Negative
feedback
AP Biology 2005-2006
corpus
luteum
ovary
Female reproductive cycle
pregnancy
maintains
uterus lining
no
yes
Feedback
estrogen
egg
matures &
is released
(ovulation)
builds up
uterus lining
FSH & LH
progesterone
progesterone
fertilized egg
(zygote)
HCG
corpus luteum breaks down
progesterone drops
menstruation
corpus
luteum
maintains
uterus lining
GnRH
pituitary
gland
hypothalamus
AP Biology 2005-2006
Any Questions??
AP Biology 2005-2006
Animal Reproduction
&
Development
AP Biology 2005-2006
Oogenesis
Meiosis 1 completed
during egg maturation
Meiosis 2 completed
triggered by fertilization
ovulation
What is the advantage
of this development
system?
AP Biology 2005-2006
Fertilization
AP Biology 2005-2006
Fertilization
Joining of sperm & egg
sperm head enters egg
AP Biology 2005-2006
Cleavage
Repeated mitotic divisions of zygote
1st step to becoming multicellular
unequal divisions establishes body plan
different cells receive different portions of egg
cytoplasm & therefore different regulatory signals
AP Biology 2005-2006
Cleavage
zygote morula blastula
establishes future development
AP Biology 2005-2006
Gastrulation
Establish 3 cell layers
ectoderm
outer body tissues
skin, nails, teeth, nerves
mesoderm
blood, bone & muscle
endoderm
inner lining
digestive system
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
protostome vs. deuterostome
gastrulation in
primitive chordates
AP Biology 2005-2006
Neurulation
1st organ to form is notochord &
nerve chord
develop into nervous system
Neural groove
Notochord
Neural tube
AP Biology 2005-2006
Organogenesis
Umbilical blood vessels
Chorion
Amnion
Yolk
sac
Allantois
Fetal blood vessels
Maternal blood vessels
Bird embryo
Mammalian embryo
Placenta
AP Biology 2005-2006
Placenta
Materials exchange across membranes
AP Biology 2005-2006
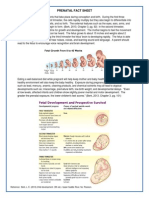
Human fetal development
7 weeks 4 weeks
AP Biology 2005-2006
Sex determination
XY
XX
Testes
Y
Sperm Zygote
Zygote
Ovum
Sperm
Ovum
X
X
X
Indifferent
gonads
SRY
No SRY
Ovaries
(Follicles do not
develop until
third trimester)
Seminiferous
tubules
Develop in
early
embryo
Leydig cells
AP Biology 2005-2006
Human fetal development
10 weeks
AP Biology 2005-2006
Human fetal development
12 weeks 20 weeks
AP Biology 2005-2006
Human fetal development
The fetus just spends much of the 2
nd
&
3
rd
trimesters just growing
and doing various flip-turns & kicks
inside amniotic fluid
Week 20
AP Biology 2005-2006
Human fetal development
24 weeks (6 months; 2nd trimester)
fetus is covered
with fine, downy
hair called
lanugo. Its skin
is protected by
a waxy material
called vernix
AP Biology 2005-2006
Human fetal development
30 weeks (7.5 months)
umbilical cord
AP Biology 2005-2006
Getting crowded in there!!
32 weeks (8 months)
The fetus
sleeps 90-95%
of the day &
sometimes
experiences
REM sleep, an
indication of
dreaming
AP Biology 2005-2006
Birth
positive feedback
AP Biology 2005-2006
Intestine
Placenta
Umbilical
cord
Wall of
uterus
Vagina
Cervix
Birth (36 weeks)
Bladder
AP Biology 2005-2006
The end of the journey!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Principles of HomeostasisDokumen31 halamanPrinciples of Homeostasisleeminhoangrybird100% (1)
- Nervous System FunctionsDokumen234 halamanNervous System Functionsalyssa_marie_keBelum ada peringkat
- Hormones:: Signaling MoleculesDokumen20 halamanHormones:: Signaling MoleculesSangeeta DwivediBelum ada peringkat
- Hormones and Endocrine SystemsDokumen26 halamanHormones and Endocrine SystemsNikko Adhitama100% (4)
- HormonesDokumen31 halamanHormonestuvvacBelum ada peringkat
- VisibleBody Endocrine SystemDokumen15 halamanVisibleBody Endocrine Systemcascavelette0% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous System AnatomyDokumen10 halamanAutonomic Nervous System AnatomyghalyBelum ada peringkat
- NeurologyDokumen42 halamanNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- Pre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyDokumen5 halamanPre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyGlenice Joy SenocBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Structure and FunctionsDokumen46 halamanNervous System Structure and FunctionssureshdassBelum ada peringkat
- The Digestive SystemDokumen38 halamanThe Digestive SystemrabiaBelum ada peringkat
- Prenatal Fact SheetDokumen2 halamanPrenatal Fact Sheetapi-276693463Belum ada peringkat
- Maintaining Balance: Homeostasis in the Human BodyDokumen16 halamanMaintaining Balance: Homeostasis in the Human Bodyloulou612100% (1)
- The Nervous System: Neurons, Supporting Cells, and Key ConceptsDokumen37 halamanThe Nervous System: Neurons, Supporting Cells, and Key ConceptsShriram100% (2)
- HormonesDokumen1 halamanHormonesTang Tiong Min 郑中铭100% (1)
- Endocrine System and Major Disorders: A Concise GuideDokumen153 halamanEndocrine System and Major Disorders: A Concise GuideAnthony Riggs100% (1)
- Reflex PhysiologyDokumen46 halamanReflex Physiologysharmaine_ting100% (1)
- Practical PhysiologyDokumen436 halamanPractical Physiologyaastha212002100% (1)
- Nervous System LecDokumen26 halamanNervous System LecLuningning Nobleza100% (3)
- Digestive System in HumanDokumen20 halamanDigestive System in Humanapi-400692183Belum ada peringkat
- Enzymes and MetabolismDokumen26 halamanEnzymes and Metabolismzorbax100% (3)
- Respiratory SystemDokumen9 halamanRespiratory Systemtheglobalnursing89% (9)
- Female Reproductive SystemDokumen42 halamanFemale Reproductive SystemDoki NatsuBelum ada peringkat
- Gastric Juice RegulationDokumen22 halamanGastric Juice Regulationjanuian75% (4)
- Epigenetics PDFDokumen50 halamanEpigenetics PDFReham Ibrahim75% (4)
- Endocrine System GlandsDokumen40 halamanEndocrine System GlandsSolita PorteriaBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of HomeostasisDokumen17 halamanPhysiology of HomeostasisRamadan PhysiologyBelum ada peringkat
- Week12 13 RENAL PhysiologyDokumen41 halamanWeek12 13 RENAL Physiologyirwan kastellaBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry of Hormones 1Dokumen21 halamanBiochemistry of Hormones 1Hazel Grace BellenBelum ada peringkat
- HD 201 E1 20140127 Histology of The Male Reproductive SystemDokumen7 halamanHD 201 E1 20140127 Histology of The Male Reproductive SystemMaxine Alba100% (1)
- Neuron Notes NewDokumen35 halamanNeuron Notes NewBiologie Profesor100% (1)
- Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors: ExteroreceptorsDokumen10 halamanSensory Receptors Sensory Receptors: ExteroreceptorsMikhail CarvalhoBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine SystemDokumen20 halamanThe Endocrine SystemJonathan TabbunBelum ada peringkat
- Reflexes by CKDokumen19 halamanReflexes by CKChaman Lal KarotiaBelum ada peringkat
- Female HormonesDokumen28 halamanFemale Hormonesİlbey Kayra Özçelik100% (1)
- Endocrine Disruptors and Hormonal CancerDokumen8 halamanEndocrine Disruptors and Hormonal CancerPol MaliaBelum ada peringkat
- GENETICS Reviewer PDFDokumen6 halamanGENETICS Reviewer PDFMargarita RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen26 halamanNervous Systemhanimunch0% (1)
- Modes of InheritanceDokumen47 halamanModes of Inheritancesudhir_narang_3Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 34 The Endocrine SystemDokumen39 halamanChapter 34 The Endocrine SystemCarl Agape Davis100% (3)
- Neuron Communication LectureDokumen31 halamanNeuron Communication LectureJennifer Isom Schmidtke, Ph.D.100% (1)
- The nervous system in 40 charactersDokumen12 halamanThe nervous system in 40 charactersLol lol100% (2)
- HormonesDokumen29 halamanHormonesCandy Chieng67% (3)
- Tissue RepairDokumen9 halamanTissue RepairSakidu LegionBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninDokumen4 halamanEndocrine System (Lab Notes) Pineal Gland:: MelatoninHazel Mae Tapia100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDokumen41 halamanCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisCarissa MarchanBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen30 halamanNervous SystemkenBelum ada peringkat
- Limbic System (Behaviour and Emotion)Dokumen19 halamanLimbic System (Behaviour and Emotion)Patterson MachariaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervou S System:: NeuronsDokumen16 halamanNervou S System:: NeuronsFizzah100% (4)
- Endocrine SystemDokumen11 halamanEndocrine SystemDayledaniel SorvetoBelum ada peringkat
- Human Body SystemsDokumen4 halamanHuman Body Systemsoiu7hjjs100% (15)
- Digestive SystemDokumen3 halamanDigestive Systemcymon estrada100% (1)
- The Endocrine System: Hormones and DiseasesDokumen24 halamanThe Endocrine System: Hormones and DiseasesMd Nasir Uddin Mahmood100% (2)
- Epigenetic Regulation of Gene Expression in CancerDokumen36 halamanEpigenetic Regulation of Gene Expression in CancerSusi Rutmalem100% (2)
- The Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSDokumen73 halamanThe Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSlady ann jimenez100% (3)
- Summary of Muscular System 4Dokumen4 halamanSummary of Muscular System 4api-253866502100% (1)
- An Introduction To Biomedical EngineeringDokumen56 halamanAn Introduction To Biomedical Engineeringjose_mario1128100% (1)
- Parts and functions of the human respiratory systemDokumen43 halamanParts and functions of the human respiratory systemBuuvee BeBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System Study GuideDokumen4 halamanThe Endocrine System Study Guideapi-2776680980% (1)
- The Fragmentation of Being PDFDokumen333 halamanThe Fragmentation of Being PDFDontu Maria100% (2)
- Fertility2018 Del Brochure Final PDFDokumen8 halamanFertility2018 Del Brochure Final PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- APChemistry StudyGuide PDFDokumen53 halamanAPChemistry StudyGuide PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- German Chapter One v2Dokumen231 halamanGerman Chapter One v2Jasmin ĆosićBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicalChemistry Course GuideBook PDFDokumen56 halamanPhysicalChemistry Course GuideBook PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Learning and Judgement in Higher Education PDFDokumen237 halamanAssessment Learning and Judgement in Higher Education PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- A General Framework For Reasoning On InconsistencyDokumen51 halamanA General Framework For Reasoning On InconsistencyDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- FecundatiaDokumen48 halamanFecundatiaDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Thinking PDFDokumen212 halamanCritical Thinking PDFDontu Maria100% (7)
- Numerical Quantum DynamicsDokumen281 halamanNumerical Quantum DynamicsDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Bounded Rationality The Adaptive Toolbox PDFDokumen371 halamanBounded Rationality The Adaptive Toolbox PDFDontu Maria100% (2)
- A Rationality Principle PDFDokumen1 halamanA Rationality Principle PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Emergent Knowledge Strategies Strategic Thinking in Knowledge Management PDFDokumen214 halamanEmergent Knowledge Strategies Strategic Thinking in Knowledge Management PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Internet of Things - CERP-2009Dokumen50 halamanInternet of Things - CERP-2009Guilherme De VasconcelosBelum ada peringkat
- Becoming A Successful Scientist Strategic Thinking For Scientific Discovery PDFDokumen259 halamanBecoming A Successful Scientist Strategic Thinking For Scientific Discovery PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Emergent Knowledge Strategies Strategic Thinking in Knowledge Management PDFDokumen214 halamanEmergent Knowledge Strategies Strategic Thinking in Knowledge Management PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Insight in Three CirclesDokumen4 halamanStrategic Insight in Three CirclesDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Icsi Perform PDFDokumen11 halamanIcsi Perform PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Essentials SteinbergDokumen442 halamanEssentials SteinbergDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Fertility Society AustraliaDokumen27 halamanFertility Society AustraliaDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology of The Cell: Aisling AhlströmDokumen39 halamanBiology of The Cell: Aisling AhlströmDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Ferti Liz AreDokumen13 halamanFerti Liz AreDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Sperm Safe Prep PDFDokumen106 halamanSperm Safe Prep PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Depletion On Meiotic Maturation, Cumulus Expansion, and Early Cleavage, But Did Not RescueDokumen11 halaman1 Depletion On Meiotic Maturation, Cumulus Expansion, and Early Cleavage, But Did Not RescueDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Oocyte Grading PDFDokumen6 halamanOocyte Grading PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum AustralianDokumen27 halamanCurriculum AustralianDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Sperm Pattern PDFDokumen5 halamanSperm Pattern PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Early Cleavage Embryo PDFDokumen6 halamanEarly Cleavage Embryo PDFDontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Asa Handbook2010Dokumen204 halamanAsa Handbook2010Dontu MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Lose Last 5kgDokumen122 halamanLose Last 5kgchaninators100% (2)
- 12G Lab3 GARCIADokumen3 halaman12G Lab3 GARCIARuthangela GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Robin's DIY FMD Menu and RecipesDokumen8 halamanRobin's DIY FMD Menu and RecipesmBelum ada peringkat
- BIOCHEMISTRY CARBOHYDRATESDokumen100 halamanBIOCHEMISTRY CARBOHYDRATESJiezl Abellano AfinidadBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition and Keeping FitDokumen4 halamanNutrition and Keeping FiteltisiBelum ada peringkat
- Fcs 359 Lesson Plan 2Dokumen2 halamanFcs 359 Lesson Plan 2api-384129594Belum ada peringkat
- Food Chemistry: Andre Mu Ller, Hans SteinhartDokumen9 halamanFood Chemistry: Andre Mu Ller, Hans SteinhartAlfredo CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Lipid AnalysisDokumen59 halamanLipid AnalysisM Luqman HakimBelum ada peringkat
- Dengue Discharge PlanDokumen1 halamanDengue Discharge PlanChris Denver BancaleBelum ada peringkat
- Canadian Infantry AOFP - Validity of Crossfit TestedDokumen4 halamanCanadian Infantry AOFP - Validity of Crossfit TestedJesseKentBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrients, digestion, absorption and metabolism quizDokumen12 halamanNutrients, digestion, absorption and metabolism quizAnchal Singh100% (3)
- Collagen Types 1Dokumen24 halamanCollagen Types 1hayiwadaBelum ada peringkat
- Business PlanningDokumen51 halamanBusiness PlanningJustine MadambaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Experimental Results FinalDokumen15 halaman4 Experimental Results FinalMohit AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly Meal Planning and Selection and For Special OccasionDokumen6 halamanWeekly Meal Planning and Selection and For Special OccasionNhet Nhet Mercado100% (2)
- OLEODokumen9 halamanOLEOfatien zakariaBelum ada peringkat
- Goat Farming 2004Dokumen154 halamanGoat Farming 2004Jahn Symon RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Lesser Known Facts About Tryptophan Side Effects: What Are The Problems With Tryptophan?Dokumen26 halamanLesser Known Facts About Tryptophan Side Effects: What Are The Problems With Tryptophan?stambicaBelum ada peringkat
- Influence of Jackfruit Pulp On The Quality and Shelf Life of Jackfruit CakeDokumen6 halamanInfluence of Jackfruit Pulp On The Quality and Shelf Life of Jackfruit Cakeokta misro'iBelum ada peringkat
- Portmafia GroupDokumen27 halamanPortmafia Groupalvinlarano11Belum ada peringkat
- Top Notch 2 UNIT 4 - 5 - 6 VocabularyDokumen18 halamanTop Notch 2 UNIT 4 - 5 - 6 VocabularyRikardoBelum ada peringkat
- Hospitality Studies Memo Nov 2008 Eng MemoDokumen14 halamanHospitality Studies Memo Nov 2008 Eng MemoqanaqBelum ada peringkat
- Taller de InglesDokumen2 halamanTaller de InglesAndresBelum ada peringkat
- NeuroergonomicDokumen19 halamanNeuroergonomicrifqi_udinBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Ramadan Fat Loss PDFDokumen4 halamanNatural Ramadan Fat Loss PDFAhmed KabeerBelum ada peringkat
- Mind Reset Guide: Unlock the Secrets to Permanent Weight LossDokumen17 halamanMind Reset Guide: Unlock the Secrets to Permanent Weight LossOkoli VivianBelum ada peringkat
- Lucca 1994Dokumen8 halamanLucca 1994dhea giftBelum ada peringkat
- Konjac NutritionDokumen54 halamanKonjac NutritionMathilda PasaribuBelum ada peringkat
- Anthony Ditillo Training RoutinesDokumen5 halamanAnthony Ditillo Training RoutinesWarhammer1367% (3)
- 18 Amazing Health Benefits From Honey and CinnamonDokumen4 halaman18 Amazing Health Benefits From Honey and Cinnamongladiola1100% (1)