Auto Transsmission Shelhadary
Diunggah oleh
HR0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan62 halamandetailed explanation of automatic transmission
Judul Asli
Auto Transsmission Shelhadary
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inidetailed explanation of automatic transmission
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan62 halamanAuto Transsmission Shelhadary
Diunggah oleh
HRdetailed explanation of automatic transmission
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 62
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
Sherief El Hadary ID:567
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Torque Converter
Hydraulic Control Unit
Planetary Gear Unit
TORQUE CONVERTER -
PURPOSE
The purposes of the
torque converter are
to:
Transmit engine torque
into the transmission
Multiply engine torque
Dampen engine
pulsations
Provide flywheel mass
Torque converter
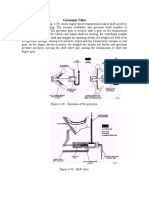
TORQUE CONVERTOR
CONSTRUCTION
TORQUE CONVERTOR
OPERATION
STATOR OPERATION
The purpose of the
stator is to re-direct
fluid flow to assist
engine rotation
during the
multiplication phase
The stator must not
interfere with the
fluid flow during the
coupling phase
ONE WAY CLUTCH
SPEED RATIO
Speed ratio is the comparison of pump
and impeller speeds expressed as a
percent.
Speed ratio = pump speedturbine speed X 100
TORQUE MULTIPLICATION
Torque multiplication occurs at speed
ratios lower than 90%
Torque multiplication is highest when
the torque converter is at STALL
STALL SPEED
The torque converter is at stall when:
The turbine is stationary
The pump is turning at maximum RPM
COUPLING POINT
The coupling point occurs at a speed
ratio of approximately 90%
Torque multiplication is no longer provided
VORTEX FLOW
Vortex flow is a
spiraling or rolling
flow of fluid in a
torque converter
when the speed
ratio is very low
(during torque
multiplication)
ROTARY FLOW
Rotary flow
occurs in a torque
converter at high
speed ratios the
fluid is simply
carried along with
the pump and
turbine vanes
LOCK UP TORQUE
CONVERTERS
In order to
increase efficiency
a hydraulically
applied clutch
locks the turbine
to the pump case
under certain
conditions to
remove slipping
PLANETARY GEARS -
PURPOSE
The planetary gear
unit provides:
A path for engine
power to get to the
drive shaft / final
drive
A way of changing
torque, speed, and
direction of the
engine power
Planetary Gear Unit
GEAR RATIO
Gear ratio is the comparison of input
gear revolutions to achieve one output
revolution
Driven gear teeth / Drive gear teeth
GEAR REDUCTION
Gear reduction provides greater output
torque at reduced output speed
Gear reduction is achieved by having a
small gear drive a large gear
DIRECT DRIVE
Direct drive is a gear ratio which results
in transmission of input torque and
speed to the output shaft without
affecting the torque and speed
Direct drive is achieved with two
equally sized gears
OVERDRIVE
Overdrive is a gear ratio which provides
reduced output torque at a greater
output speed
Overdrive is achieved by having a
larger gear driving a smaller gear
PLANETARY GEAR SETS
Planetary gear sets are used to
provide:
Park & Neutral
Gear reduction
Direct drive
Overdrive
Reverse
PLANETARY GEARS
PLANETARY OPERATION
In order for the planetary gear set to
transmit power, each of the three
members of the planetary gear set must
be perform one of three jobs:
Input
Output
Reaction
JOB DESCRIPTION
INPUT:
The input gear receives the engine power
OUTPUT
The output gear provides drive force to the
drive shaft or final drive
REACTION
The reaction member must be HELD and
prevented from moving
PARK / NEUTRAL
Park and neutral can be achieved by:
Disconnecting the input member
Disconnecting the reaction member
GEAR REDUCTION - #1
In this case:
The smallest gear
drives
The middle sized
gear is held
The largest gear (the
carrier) is driven
Result: Maximum
gear reduction
GEAR REDUCTION - #2
In this case:
The middle sized
gear drives
The smallest gear is
held
The largest gear is
driven
RESULT:
Gear reduction
DIRECT DRIVE
If any two members
are locked together
(both providing
input) direct drive
occurs.
OVERDRIVE
When the carrier
drives either other
gear OVERDRIVE
occurs
REVERSE
Reverse will only
occur if the carrier is
held
The sun gear drives
The ring gear is
driven
REVERSE OVERDRIVE
If the ring gear was to drive the sun
gear while holding the carrier, reverse
would occur in an overdrive ratio
SIMPSON GEAR SETS
Simpson gear sets
use a common sun,
two carriers, and
two ring gears
The sun, ring, and
pinions are the same
size
RAVIGNEAU GEAR SETS
Ravigneau gear sets
use:
Two sun gears
(different sizes)
Two sets of pinion
gears
One ring gear
RAVIGNEAU GEAR SETS
ACTUATORS
Actuators are used to connect members
of the planetary gear set to the:
Input shaft
Output shaft
Transmission case
ACTUATOR TYPES
The actuators used in automatic
transmissions can be:
Driving devices
Brake devices
DRIVE DEVICES
Driving devices are multiple disc wet
clutch packs
Attach input shafts to planetary gear
set members
CLUTCH PACKS
HOLDING DEVICES
Holding devices are used to control the
reaction member of a planetary gear set
Holding devices can be:
Multiple disc wet clutches
Brake bands
One way clutches
Roller
Sprag
CLUTCHES AS BRAKES
Clutches used as
brakes are identical
in construction to
clutches used as
driving devices
except the steels are
splined to the
transmission
housing or case
BRAKE BANDS
Band brakes use a servo piston to
apply the band around the outside of a
drum
BRAKE BAND
BRAKE BAND TYPES
Brake bands may be:
Single wrap
Double wrap
Double Wrap
Single Wrap (light)
Single Wrap (heavy)
HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT
The hydraulic control
section of the
transmission uses
hydraulic pressures to
control and perform
shifting of the
transmission gears Hydraulic Control Unit
PUMP TYPES
Transmission pumps may be:
Gear and crescent
Vane
Variable displacement vane
GEAR
VANE
VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT
VALVES
There are two main types of valves
used in automatic transmissions:
Pressure regulating or modulating valves
Relay valves
PRESSURE REGULATION
Pressure regulation is used to:
Limit the oil pressure in the transmission
Control shifting
In addition to primary regulation, some
transmissions use a blow off valve to
prevent overpressure
MAIN LINE PRESSURE
The first pressure developed in the
transmission is called MAIN LINE
PRESSURE
It is controlled by the opening point of the
pressure regulator valve
All other transmission pressures are
derived from main line pressure
All hydraulic devices are operated on main
line pressure
MAIN LINE REGULATION
BOOST PRESSURE
Under certain circumstances, mainline
pressure must be increased to increase
the holding pressure of the hydraulic
devices
High torque
Reverse
Low gear
High load
Heavy throttle demand
DECISION PRESSURE
In order to decide
what gear to be in
the transmission
must look at road
speed and engine
load just like the
driver of a manual
transmission
ROAD
SPEED
ENGINE
LOAD
ENGINE LOAD
Engine load can be determined by
either:
Throttle Pressure
Modulator Pressure
THROTTLE PRESSURE
Throttle pressure is:
A common means of indicating engine load
and driver demands
Derived from main line pressure
Controlled by the throttle valve, which is
directly linked to the throttle plate (engine
intake)
THROTTLE VALVE
GOVERNOR PRESSURE
Governor pressure is:
Used as an indication or road speed
Developed from main line pressure
Controlled by the governor valve
GOVERNOR VALVE TYPES
The three main types of governor
valves are:
Spool valve
Ball bearing
Shaft mounted
SPOOL GOVERNORS
BALL GOVERNORS
ACCUMULATORS
The purpose of accumulators is to
cushion the shift feel to increase
customer satisfaction
ACCUMULATOR TYPES
Accumulators can be:
Independent
Integral
Valve type
Restrictions (fixed orifices) can also be
used to increase shift feel
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Toyota Steering BasicsDokumen20 halamanToyota Steering BasicsWilliam Kibbe100% (2)
- Automatic Transmission Basics GuideDokumen87 halamanAutomatic Transmission Basics GuideHartatispdBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Transmission BasicsDokumen238 halamanAutomatic Transmission BasicsSílvio Santos100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Automatic TransmissionsDokumen220 halamanFundamentals of Automatic TransmissionsAndrés Arias100% (7)
- 3red Class Automotive Technology Chapter 3Dokumen15 halaman3red Class Automotive Technology Chapter 3abasBelum ada peringkat
- The Operation of Hydraulic Coupling and Torque ConverterDokumen10 halamanThe Operation of Hydraulic Coupling and Torque Convertergold pornBelum ada peringkat
- Sistemas de Operacion ElectricosDokumen78 halamanSistemas de Operacion ElectricosFrancisco Wilson Bezerra FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Clutch ServiceDokumen44 halamanClutch ServiceTanmayBelum ada peringkat
- Diesel Locomotive EngineDokumen21 halamanDiesel Locomotive Enginesinghnisha006482100% (1)
- 10 Automatic Transaxle SystemDokumen35 halaman10 Automatic Transaxle SystemYun ZhenBelum ada peringkat
- Manual TransmissionDokumen60 halamanManual Transmissionʞǝǝs Uǝ ƎpıɥBelum ada peringkat
- TRWDokumen143 halamanTRWFederico GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Parts/Components of Manual Transmission 1. Clutch 2. Clutch Pedal 3. Gearbox 4. Shift Fork 5. Shift Rod 6. Hydraulic SystemDokumen7 halamanParts/Components of Manual Transmission 1. Clutch 2. Clutch Pedal 3. Gearbox 4. Shift Fork 5. Shift Rod 6. Hydraulic SystemVJ CarbonellBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Transmission Basics PDFDokumen34 halamanAutomatic Transmission Basics PDFtambache69100% (1)
- Automatic Transmission SystemDokumen34 halamanAutomatic Transmission SystemGurpreet Singh AnttalBelum ada peringkat
- Bma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Dokumen36 halamanBma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Fu HongBelum ada peringkat
- On SteeringDokumen25 halamanOn SteeringKuldeep RajputBelum ada peringkat
- Maintain Optimal Engine Speed with Woodward GovernorDokumen42 halamanMaintain Optimal Engine Speed with Woodward Governorsantosh sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Vehicle Transmission ComponentsDokumen21 halamanIntroduction to Vehicle Transmission ComponentsManohara ErlaBelum ada peringkat
- Governor Valve Controls Automatic Transmission ShiftingDokumen17 halamanGovernor Valve Controls Automatic Transmission ShiftingAleksandar StevanovicBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic GearboxDokumen8 halamanAutomatic Gearboxmasterash02Belum ada peringkat
- Automatic Transmission ComponentsDokumen14 halamanAutomatic Transmission ComponentsAbdul Salam ASBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On Power Steering: by Sahaj Harnal 07AU626Dokumen32 halamanPresentation On Power Steering: by Sahaj Harnal 07AU626yomansahajBelum ada peringkat
- Caja de Cambios EATON FS6209Dokumen145 halamanCaja de Cambios EATON FS62097sergio950% (2)
- Automatic Transmission ComponentsDokumen12 halamanAutomatic Transmission ComponentsRizqy Fadry LazimBelum ada peringkat
- Rack and Pinion Steering Mechanism: ND WrenchDokumen9 halamanRack and Pinion Steering Mechanism: ND WrenchPankaj AmbereBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission PDFDokumen21 halamanTransmission PDFMohanish ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic TransmissionDokumen10 halamanAutomatic TransmissionSoumik Das100% (2)
- Automatict RansmissionDokumen34 halamanAutomatict RansmissionGanapati HegdeBelum ada peringkat
- Group 1: Canoy - Lacson - Mabaga - Mariano - Sedilla - SilvaDokumen51 halamanGroup 1: Canoy - Lacson - Mabaga - Mariano - Sedilla - SilvaEngr MechaBelum ada peringkat
- Automotive (2) Lab: EXP4: Automatic Transmissions and TransaxlesDokumen6 halamanAutomotive (2) Lab: EXP4: Automatic Transmissions and TransaxlesMohammad YahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Nandi Vishwavidyalaya Engine Technology GuideDokumen33 halamanNandi Vishwavidyalaya Engine Technology GuidePrasannaBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Transmission 1Dokumen6 halamanAutomatic Transmission 1boudy04Belum ada peringkat
- 01V Auto Trans SSPDokumen66 halaman01V Auto Trans SSPGolub MarkoBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Transmission: Presented by Shiv Raj Khoja Mechanical Iv YearDokumen28 halamanAutomatic Transmission: Presented by Shiv Raj Khoja Mechanical Iv YearShiv Raj Khoja100% (1)
- OPEL INSIGNIA 2013 Automatic Transmission - 6T70 (M7U M7W) - Description and OperationDokumen76 halamanOPEL INSIGNIA 2013 Automatic Transmission - 6T70 (M7U M7W) - Description and OperationGedas GvildysBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 17 - 02 - Starting & ManoeuvringDokumen16 halamanUnit 17 - 02 - Starting & ManoeuvringAisha ZaheerBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic TransmissionDokumen36 halamanAutomatic TransmissionIfeanyi IgwegbeBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Transmission GuideDokumen34 halamanAutomatic Transmission GuideAsad Khan100% (3)
- AUTO TRANSMISSION SYSTEMDokumen35 halamanAUTO TRANSMISSION SYSTEMAalekh PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic TransmissionDokumen82 halamanAutomatic Transmissionhongsun9309Belum ada peringkat
- 8 - Valve Body Circuits PDFDokumen49 halaman8 - Valve Body Circuits PDFhenok80% (5)
- Final ProjectDokumen35 halamanFinal ProjectAnsh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Transaxle System OverviewDokumen9 halamanAutomatic Transaxle System OverviewWiterMarcosBelum ada peringkat
- Group 8 TransmissionDokumen7 halamanGroup 8 TransmissionGiapy Phuc TranBelum ada peringkat
- Hardish TrivediDokumen56 halamanHardish Trivedihardish_trivedi7005Belum ada peringkat
- INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION SYSTEM AdityaDokumen20 halamanINTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION SYSTEM Adityavideo songBelum ada peringkat
- Rack and Pinion Steering System ExplainedDokumen20 halamanRack and Pinion Steering System ExplainedYogeshGargBelum ada peringkat
- Advancements of Automatic Gear Transmission SystemsDokumen21 halamanAdvancements of Automatic Gear Transmission SystemsKavindu UmayangaBelum ada peringkat
- ClutchesDokumen60 halamanClutchesRoopesh BhatBelum ada peringkat
- CLUTCHES AND COUPLINGS: PNEUMATIC, MECHANICAL, AND FLEXIBLE TYPESDokumen11 halamanCLUTCHES AND COUPLINGS: PNEUMATIC, MECHANICAL, AND FLEXIBLE TYPESSangharsh RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- OPEL INSIGNIA 2013 Automatic Transmission - 6T40 (MH8 MHH) - Description and OperationDokumen53 halamanOPEL INSIGNIA 2013 Automatic Transmission - 6T40 (MH8 MHH) - Description and OperationGedas GvildysBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumatic Auto Gear ChangerDokumen2 halamanPneumatic Auto Gear ChangerVijay GanapathyBelum ada peringkat
- Motorcycle, Solo (Harley-Davidson Model WLA)Dari EverandMotorcycle, Solo (Harley-Davidson Model WLA)Belum ada peringkat
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiDari EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiBelum ada peringkat
- Essex Terraplane Six 1933 Owner's Manual of InformationDari EverandEssex Terraplane Six 1933 Owner's Manual of InformationBelum ada peringkat
- Donny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionDari EverandDonny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- MR Bean Study CaseDokumen2 halamanMR Bean Study CaseHRBelum ada peringkat
- The Low Cost Airline: Airasia A Study of Opportunities, Challenges and Critical Success FactorsDokumen13 halamanThe Low Cost Airline: Airasia A Study of Opportunities, Challenges and Critical Success FactorsSam All YmnBelum ada peringkat
- 41 Undirected GraphsDokumen78 halaman41 Undirected GraphsHRBelum ada peringkat
- 021014Dokumen8 halaman021014HRBelum ada peringkat
- Testing Testing 123Dokumen1 halamanTesting Testing 123HRBelum ada peringkat
- A.Poet Part 1Dokumen1 halamanA.Poet Part 1HRBelum ada peringkat
- Catia MechanismDokumen36 halamanCatia MechanismPRASANTH G KRISHNAN100% (1)
- Exam 1 NotesDokumen8 halamanExam 1 NotesHRBelum ada peringkat
- Fireware XTM Basics v11 5 2Dokumen264 halamanFireware XTM Basics v11 5 2Himanshu SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics HW Solutions+studyDokumen3 halamanDynamics HW Solutions+studyHRBelum ada peringkat
- Seeding Sites Maps GoogledDokumen1 halamanSeeding Sites Maps GoogledHRBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Notes 3-18Dokumen6 halamanAdditional Notes 3-18HRBelum ada peringkat
- Items Supplied Application(s) : 23801 E. La Palma Ave., Yorba Linda, Ca 92887 Ph. 714.692.8180 Fax. 714.692.5016Dokumen3 halamanItems Supplied Application(s) : 23801 E. La Palma Ave., Yorba Linda, Ca 92887 Ph. 714.692.8180 Fax. 714.692.5016HRBelum ada peringkat
- Nclex RNDokumen36 halamanNclex RNHR100% (13)
- CompTIA A (220-802) ObjectivesDokumen22 halamanCompTIA A (220-802) ObjectivesRengescu Amalia100% (1)
- Edward J Romar Off TargetDokumen8 halamanEdward J Romar Off TargetHRBelum ada peringkat
- R-Tree Project: Albert-Jan YzelmanDokumen39 halamanR-Tree Project: Albert-Jan YzelmanHRBelum ada peringkat
- Bitcoin Manifesto - Satoshi NakamotoDokumen9 halamanBitcoin Manifesto - Satoshi NakamotoJessica Vu100% (1)
- BF05 Amortization Schedules PDFDokumen5 halamanBF05 Amortization Schedules PDFHRBelum ada peringkat
- Items Supplied Application(s) : 23801 E. La Palma Ave., Yorba Linda, Ca 92887 Ph. 714.692.8180 Fax. 714.692.5016Dokumen3 halamanItems Supplied Application(s) : 23801 E. La Palma Ave., Yorba Linda, Ca 92887 Ph. 714.692.8180 Fax. 714.692.5016HRBelum ada peringkat
- Aging and Creative Productivity: Key Findings, Criticisms and Complicating FactorsDokumen58 halamanAging and Creative Productivity: Key Findings, Criticisms and Complicating FactorsHRBelum ada peringkat
- Items Supplied Application(s) : 23801 E. La Palma Ave., Yorba Linda, Ca 92887 Ph. 714.692.8180 Fax. 714.692.5016Dokumen3 halamanItems Supplied Application(s) : 23801 E. La Palma Ave., Yorba Linda, Ca 92887 Ph. 714.692.8180 Fax. 714.692.5016HRBelum ada peringkat
- Week14.Biol1210 Review SlidesDokumen33 halamanWeek14.Biol1210 Review SlidesHRBelum ada peringkat
- Altro Coating3 MLDokumen1 halamanAltro Coating3 MLHRBelum ada peringkat
- Veloz Tech TestDokumen4 halamanVeloz Tech TestHRBelum ada peringkat
- 暑假想选*560;525park;510;: Code Course Title UnitsDokumen2 halaman暑假想选*560;525park;510;: Code Course Title UnitsMichael FordBelum ada peringkat
- Dimdim Installation GuideDokumen16 halamanDimdim Installation Guidencegrupoweb100% (4)
- Hello To PeopleDokumen1 halamanHello To PeopleMichael FordBelum ada peringkat
- Ch01 Show Rev 1Dokumen38 halamanCh01 Show Rev 1Will LiuBelum ada peringkat
- Hello To PeopleDokumen1 halamanHello To PeopleMichael FordBelum ada peringkat
- Looking For Heavy Cleaning But Without The Weight: GM 80P LCDokumen2 halamanLooking For Heavy Cleaning But Without The Weight: GM 80P LCBento BoxBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Relays and Different Types of Relays - All InstrumentationDokumen10 halamanBasics of Relays and Different Types of Relays - All InstrumentationAlex DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Foton Operation and Miantenance Manuai For View Series Light BusDokumen279 halamanFoton Operation and Miantenance Manuai For View Series Light BusHarlinton descalzi82% (17)
- Toxics in Massachusetts: A Town-By-Town ProfileDokumen38 halamanToxics in Massachusetts: A Town-By-Town ProfileWGBH NewsBelum ada peringkat
- USM 32X Operating Manual PDFDokumen188 halamanUSM 32X Operating Manual PDFcorey jacobsBelum ada peringkat
- Astor: Test TransformerDokumen1 halamanAstor: Test TransformermominzadahBelum ada peringkat
- Drying LectureDokumen85 halamanDrying LectureHaroon RahimBelum ada peringkat
- TriScroll 300 Series Dry Scroll Vacuum Pump PDFDokumen106 halamanTriScroll 300 Series Dry Scroll Vacuum Pump PDFWilliamRiveraBelum ada peringkat
- CIVIL ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS ASSIGNMENTDokumen4 halamanCIVIL ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS ASSIGNMENTjiwa remajaBelum ada peringkat
- Siemens Mobilett XP Products Safety Information Performing The Checks in Accordance With Iec 62353Dokumen34 halamanSiemens Mobilett XP Products Safety Information Performing The Checks in Accordance With Iec 62353Félix Enríquez0% (1)
- Caie As Level Geography 9696 Core Model Answers v1Dokumen31 halamanCaie As Level Geography 9696 Core Model Answers v1kgethilwemakgotsoBelum ada peringkat
- Request For Information: 8 June 2020Dokumen11 halamanRequest For Information: 8 June 2020Mhae PotBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Thermal EngineeringDokumen11 halamanApplied Thermal EngineeringFabrizio RinaldiBelum ada peringkat
- FM400 8X4 Tipper With Rock Body Specs & DetailsDokumen4 halamanFM400 8X4 Tipper With Rock Body Specs & DetailsHaneefa ChBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Kama - Kde 6500 TWDokumen2 halaman4 - Kama - Kde 6500 TWJavadBelum ada peringkat
- Dental Polymers GuideDokumen117 halamanDental Polymers GuideLalit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Monarch 3-Ph Catalogue MONCI-082012Dokumen12 halamanMonarch 3-Ph Catalogue MONCI-082012Chia PeterBelum ada peringkat
- Chaudhry2021 Does Culture Affect Energy PovertyDokumen16 halamanChaudhry2021 Does Culture Affect Energy PovertyRaul MJBelum ada peringkat
- PTK MateriDokumen101 halamanPTK MateriAnnisah MardiyyahBelum ada peringkat
- Aermec WRL 026-161HDokumen6 halamanAermec WRL 026-161HMilan PizdunBelum ada peringkat
- Servo Lubricants GreaseDokumen62 halamanServo Lubricants GreasenagbabuiBelum ada peringkat
- SNP Tanker ReportDokumen3 halamanSNP Tanker ReportfikrifadzalBelum ada peringkat
- Mock Trial 2Dokumen23 halamanMock Trial 2Azreen IzetBelum ada peringkat
- Ezstim Ii: Operator'S ManualDokumen29 halamanEzstim Ii: Operator'S ManualBabajee NavirajBelum ada peringkat
- Pump Curve For Beginners & Non-Pump Personnel: Compiled byDokumen10 halamanPump Curve For Beginners & Non-Pump Personnel: Compiled byCaner KibarBelum ada peringkat
- Research PaperDokumen5 halamanResearch PaperHoney AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- 3adw000078r0301 Dcs5 Software Descr e CDokumen228 halaman3adw000078r0301 Dcs5 Software Descr e Caninda_dBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies ProblemsDokumen10 halamanDynamics of Rigid Bodies ProblemsJohn Michael SalasBelum ada peringkat
- Welding HandbookDokumen729 halamanWelding HandbookIvan Dario BenitezBelum ada peringkat
- Fluent Combustion AnalysisDokumen31 halamanFluent Combustion AnalysisVignesh SambanBelum ada peringkat