11.jejas Dan Adaptasi
Diunggah oleh
AgaipJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
11.jejas Dan Adaptasi
Diunggah oleh
AgaipHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
INJURY AND ADAPTATION
PROCESSES
Department of Anatomic Pathology
Fac. of Medicine Gadjah Mada University
DEFINITION
Pathology is a discipline bridging clinical practice
and basic sciences
Identify changes in cells and tissues morphology
diagnoses and therapy
Focus of pathology:
etiology ( cause )
pathogenesis
pathways by which morphologic changes occurs
DEFINISI
Patologi adalah menjembatani disiplin praktek klinis dan
ilmu dasar
Identifikasi perubahan dalam jaringan sel dan morfologi -
diagnosis dan terapi
Fokus patologi:
etiologi (penyebab)
patogenesis
jalur dimana terjadi perubahan morfologi
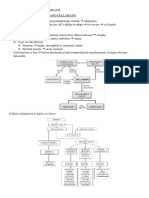
CELLULAR RESPONSES AGAINST INJURY
Cells
Cellular adaptations
Physiologic stresses/ pathologic stimuli
Adaptive responses:
atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia
Cellular injury
Adaptive capability is exceeded
Reversible injury
Irreversible injury
Dies: apoptosis and necrosis
Causes of cellular injury :
Hypoxia
Physical agents
Chemicals and drugs
Microbiologic agents
Immunologic agents
Genetic defects
Nutritional imbalances
Aging
Hipoksia
Agen fisik
Bahan kimia dan obat-obatan
Microbiologic agen
Kekebalan agen
Cacat genetik
Ketidakseimbangan gizi
Penuaan
Hypoxia
Diminish/ loss of blood supply
Constriction/ obstruction of blood vessel
Diminish of oxygen supply
Cardio-respiration failure
Heart failure
Lung diseases
Diminish / loss of oxygen carrying capacity
CO stable HbCO
Effect: depend on the grade of the stress
Hipoksia
Menghilangkan / kehilangan suplai darah
Penyempitan / penyumbatan pembuluh darah
Mengurangi pasokan oksigen
Kegagalan respirasi cardio -
Jantung
Penyakit paru-paru
Berkurang / hilangnya daya oksigen
HbCO stabil CO
Efek: tergantung pada derajat stres
DRUGS AND CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES
Toxic agent cellular death tissue death
Non toxic agent: glucosa high osmotic pressure
cellular injury
Specific target of chemical substance:
absorption, transportation, metabolism, excretion
- barbiturat liver damage due to degradation/
metabolism process
- mercurichlorida stomach (absorption), colon
and kidney ( excretion)
NARKOBA DAN KIMIA ZAT
Beracun agen jaringan seluler mati-
mati
Non toxic agent: glucosa - tekanan
osmotik tinggi cedera selular
Sasaran spesifik zat kimia:
penyerapan, transportasi,
metabolisme, ekskresi
- Barbiturat kerusakan hati akibat
degradasi / proses metabolisme
- mercurichlorida perut
(penyerapan), kolon dan ginjal
(ekskresi)
Microbiologic agents
Virus:
Cytolytic/cytophatic cellular death
Oncogenic ->>> proliferation -- neoplasm
Bacterie
Exotoxin
Endotoxin
Lecitinase damage of cell membrane
Hemolysin -> hemolysis
Fungi
actinomycosis
- Parasite
- Amoeba, malaria, toxoplasm
Worm
Filaria dll
Microbiologic agen
Virus:
Cytolytic / cytophatic kematian sel
Onkogenik ->>> proliferasi - neoplasma
Bacterie
Eksotoksin
Endotoksin
Lecitinase kerusakan membran sel
Hemolysin -> hemolisis
Jamur
actinomycosis
Parasit
Amuba, malaria, toxoplasm
Cacing
Filaria dll
Physical agent:
Cold
vasoconstriction blood supply << , intravascular
coagulation Crystalisasion of intravascular
substances
Hot
Hypermetabolism --- necroses due to burning
process
_ athmospher Caisson disease
_ electric -> burn ulcer cardiac arytmia
Fisik agen
Dingin
vasokonstriksi aliran darah <<, koagulasi
intravaskular - Crystalisasion dari zat
intravaskular
Panas
Hypermetabolism --- necroses akibat proses
pembakaran
Athmospher _ Caisson penyakit
_ Listrik -> membakar borok-jantung arytmia
Immunologic reaction
anaphylactic reaction
Genetic defects
Defect congenital
Hemoglobin S of sickle cell anemia
Nutritional imbalances
Protein calorie insufficiency, obesity
Atherosclerosis
Aging
acumulation of subletal injury -> decreased of
cellular responses
Reaksi kekebalan
reaksi anafilaksis
Cacat genetik
Cacat bawaan
Hemoglobin S dari anemia sel sabit
Ketidakseimbangan gizi
Kekurangan kalori protein, obesitas
Aterosklerosis
Penuaan
acumulation dari cedera subletal -> penurunan
dari tanggapan selular
Mechanisms of cell injury
Most forms of cell injury to ultimate cell death have
proved difficult to dissect, because:
* not all of injuries invariably fatal
* it is difficult to distinguish the primary target of
injury from any secondary ripple effects
* no precise cut-off point to establish cause and effect
Sebagian besar bentuk cedera sel utama
kematian sel memiliki
terbukti sulit untuk membedah, karena:
* Tidak semua luka selalu fatal
* Sulit untuk membedakan target utama
cedera dari setiap sekunder efek riak
* Tidak tepat cut-off point untuk menentukan
sebab dan akibat
There are a number of generalizations
The cellular responses to injurious depends on the type
of injury, its duration, and its severity
The consequences of injury are also dependent on the
type of cell, its current status, and its adaptability
Four intracellular systems are vulnerable:
1. cell membrane integrity
2. aerobic respiration
3. protein synthesis
4. the integrity of genetic aparatus
. Oxygen , oxygen derived free radicals and failure of
intracellular calcium homeostasis
Tanggapan selular untuk merugikan tergantung pada
jenis cedera, dengan durasi, dan tingkat keparahan
Konsekuensi dari cedera juga tergantung pada jenis sel,
status saat ini, dan kemampuan beradaptasi
Empat sistem intraselular yang rentan:
1. integritas membran sel
2. respirasi aerobik
3. sintesis protein
4. integritas aparatus genetik
. Oksigen, oksigen radikal bebas yang berasal dan
kegagalan homeostasis kalsium intraselular
Irreversible cell injury
Mechanisms of irreversible injury:
Inability to reverse mitochondrial dysfunction causing
marked ATP depletion
Development of profound disturbances in membrane
function
Several biochemical mechanisms may contribute to
membrane damage:
1. Loss of membrane phospholipids
2. Mitochondrial dysfunction
3. Cytoskeleton abnormalities
4. reactive oxygen species
5. Lipid breakdown products
6. Loss of intracellular amino acids
Mekanisme dari cedera ireversibel:
Ketidakmampuan untuk membalikkan disfungsi
mitokondria menyebabkan ATP ditandai penipisan
Pengembangan mendalam gangguan dalam fungsi
membran
Beberapa mekanisme biokimia dapat menyebabkan
kerusakan membran:
1. Hilangnya fosfolipid membran
2. Disfungsi mitokondria
3. Sitoskeleton kelainan
4. spesies oksigen reaktif
5. Produk pemecahan lipid
6. Kehilangan asam amino intraselular
Oxygen free radicals:
Superokside : O
2
-
Hidrogenperoksida : H
2
O
2
Ion hidroksil : OH *
Hydrogen peroxide
O
2
-
+ O
2
-
+ 2 H
+
SOD
H
2
O
2
+ O
2
Superoksid { O
2
-
} + enzym ( xanthine oxidase,
cytochrome P-450, dll )
Hidroksil [OH *]
- water hydrolysis due to ion radiation
H
2
O H
*
+ OH
*
- Fenton reaction:
Fe
++
+ H
2
O
2 ---
Fe
+++
+ OH * + OH
- Haber-Weiss reaction:
H
2
O
2
+ O
2
- ---
OH * + OH
+ O
2
Free radical injuced cell injury
Chemicals injury
Mercuri chloride + sulfidril of cellular membrane
Cyanide --- destruction of mitochondria
CCl
4 --
CCL
3
--- ( lipid peroxydase) fatty changes
Acetaminophen [ tylenol ) : toxic metabolite to the
liver
Chemicals cedera
Mercuri klorida + sulfidril dari membran
selular
--- Penghancuran sianida mitokondria
CCl4 - CCL3 --- (lipid peroxydase) - lemak
perubahan
Acetaminophen [Tylenol): metabolit
beracun ke hati
Sub-lethal injury [ reversible injury ]
Hydropic change = cellular swelling , hydropic change
Cellular edema : pale , vacuolated and edema of
cytoplasms
Causa: toxic agent, hypoxia
Reversible
irreversible, in a persistent causa ( mola hidatidosa,
adamantinoma )
Microscopic
membrane = blebbing, blunting
ME :
mikrovilli = distortion
mitokondria = fosfolipid amrof mass , clumping
RE = dilatation, disagregation of polisom
nuclear= disintegration of fibriler element
Sub-mematikan cedera [dibalik cedera]
Hidropik perubahan = selular pembengkakan, perubahan hidropik
Seluler edema: pucat, edema vacuolated dan cytoplasms
Causa: beracun agen, hipoksia
Reversibel
ireversibel, dalam sebuah gigih causa (mola hidatidosa,
adamantinoma)
Mikroskopis
membran = blebbing, menumpulkan
ME:
mikrovilli = distorsi
mitokondria = fosfolipid amrof massa, penggumpalan
RE = dilatasi, disagregation dari polisom
nuklir = disintegrasi fibriler elemen
Hydropic change
Hydropic change in liver tissue
Hydropic change in hydatid mole
Musin degeneration / accumulation
Hialin degeneration of the uterus tumor
Intracell accumulations :
Accumulation of normal cellular materials:
water, lipid, protein dan charbohydrat
Accumulation of abnormal materials:
exogenous and endogenous materials ---
Mineral , metabolism metabolite
Pigmen
Intracell akumulasi:
Akumulasi bahan seluler normal:
air, lemak, protein dan charbohydrat
Akumulasi bahan abnormal:
eksogen dan endogen bahan ---
Mineral, metabolisme metabolit
Pigmen
Fatty accumulation, Fatty change :
Fatty drops accumulation
due to abnormal of ribosomes function
>> liver
Causa : Hypoxia, alcohol
Microscopic:
Fatty drops - vacuola nuclear expanded to
the one side of the cell
Reversible : mild- moderate grade
Irreversible : severe grade
Lemak akumulasi, perubahan Fatty:
Tetes akumulasi lemak
karena abnormal fungsi ribosom
>> Hati
Causa: Hipoksia, alkohol
Mikroskopis:
Lemak tetes - vacuola - nuklir diperluas ke satu sisi sel
Reversibel: ringan-sedang kelas
Ireversibel: kelas berat
Fatty changes
Fatty accumulation of the liver normal liver tissue
Liver, Mallory hialin, alcoholism
Hemosiderin pigmen ( HE stain ) Prusian blue stain
Pigment carbon in the lung tissue
Lung tissue
Skin tissue Melanin pigment in the skin tissue
Bilirubin pigment in the skin and sclera of the eye
Lipofuchsin pigmen ( wear tear pigmen )
Calcification
Calsium accumulation in the organ/ tissues
Dhystrophic calcification :
Locally Calcification in nonviable/ dying tissue
Lithopedion, arteriosclerosis, calcification in
neoplastic processes, necrosis
- metastatic calcification :
Calcification in disturbance of calcium metabolism
Hyper parathyroid hormone, destruction of bone
tissue ( plasmacytoma ), vit. D related disorder, renal
failure
Pengapuran
Calsium akumulasi pada organ / jaringan
Dhystrophic kalsifikasi:
Pengapuran lokal di nonviable / sekarat jaringan
Lithopedion, arteriosclerosis, kalsifikasi dalam proses
neoplastik, nekrosis
- Kalsifikasi metastatik:
Pengapuran dalam gangguan metabolisme kalsium
Hyper paratiroid hormon, kerusakan jaringan tulang
(plasmacytoma), vit. D terkait disorder, gagal ginjal
Disthropic calcification
Calcification in breast cancer
Necrosis :
Morphological changes in the cellular death
Type of necrosis:
enzymatic dygestion liquifaction necrosis
protein denaturation coagulative necrosis
Microscopic : nuclear picnosis, caryorexis, cariolysis
Necrosis:
Morfologis perubahan dalam kematian
selular
Jenis Nekrosis:
dygestion enzimatik liquifaction nekrosis
denaturasi protein nekrosis coagulative
Mikroskopis: picnosis nuklir, caryorexis,
cariolysis
Necrotic tissue
Necrosis:
Coagulative necrosis
Liquefaction necrosis
Caseous necrosis
fat necrosis
Fibrinoid necrosis
gangrenous necrosis
Liquefaction necrosis coagulative necrosis
Coagulative necrosis liquefaction necrosis
Fat necrosis
Fibrinoid necrosis
Caseous necrosis
Gangrenous necrosis
Apoptosis :
Programmed cell death
- Destruction of cells during embriogenesis:
implantation, organogenesis
- homeostasis mechanism: normal cells
population
- Protection : immunologic reaction
- Ageing processes
Apoptosis:
Kematian sel terprogram
- Penghancuran sel selama
embriogenesis: implantasi, organogenesis
- Mekanisme homeostasis: populasi sel-
sel normal
- Perlindungan: reaksi kekebalan
- Penuaan proses
Regulation of cell death
Morphology of apoptosis:
Cellular shrinkage , denses organella
Condensation of chromatin, chromatin
aggregation, nuclear fragmented
apoptotic bodies
Phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies by
macrophages / cellular nearby
Morfologi apoptosis:
Cellular penyusutan, denses organella
Kondensasi kromatin, kromatin agregasi,
terfragmentasi nuklir
apoptotic tubuh
Apoptotic fagositosis dari badan oleh
makrofag / seluler di dekatnya
Adaptation processes:
Hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
Atrophy
Metaplsi
Dysplasi
Morfologi apoptosis:
Cellular penyusutan, denses organella
Kondensasi kromatin, kromatin agregasi,
terfragmentasi nuklir
apoptotic tubuh
Apoptotic fagositosis dari badan oleh
makrofag / seluler di dekatnya
Hyperplasia
Increase of cells number in an organ/ tissue
In an active DNA-synthesizing cells or cells mitoses
Physiologic hyperplasi
hormonal hyperplasi:
Glandular breast proliferation ( puberty,
pregnancy)
Uterus in pregnancy
Compensatoir hyperplasi
Partial hepatectomy
Pathologic hyperplasi:
Endometrial hyperplasi ( hormonal )
growth factor effect on target cells
Peningkatan jumlah sel dalam suatu organ / jaringan
Dalam aktif sintesis DNA sel atau mitosis sel
Fisiologis hyperplasi
hormon hyperplasi:
Kelenjar payudara proliferasi (pubertas, kehamilan)
Kehamilan rahim
Compensatoir hyperplasi
Partial hepatectomy
Patologis hyperplasi:
Endometrium hyperplasi (hormonal)
efek faktor pertumbuhan sel-sel sasaran
Endometrial hyperplasi
endometrium
miometrium
Hypertrophy
Increase in the size of cells - increase in the size of
tissue / organ
No new cells
Increase of cellular syntesis ( not edema )
Hypertrophy :
physiologic: uterus / breast during pregnancy ( hormonal
stimulation )
pathologic : muscular enlargement of the heart / sceletal
muscle ( >>> functional demand )
Peningkatan ukuran sel - peningkatan
ukuran jaringan / organ
Tidak ada sel-sel baru
Kenaikan syntesis selular (tidak edema)
Hipertrofi:
fisiologis: rahim / payudara selama
kehamilan (hormon stimulasi)
patologis: pembesaran otot jantung /
sceletal otot (>>> fungsional permintaan)
Hyperthropy of the heart
Atrophy
Shrinkage in the size of cells by loss of substances
Physiologic atrophy:
- embryogenic structure: thyroglossal duct
- decreased of uterus/ breast size after parturition
Pathologic atrophy:
1. Decreased workload / disuse atrophy
2. loss of inervation
3. diminished blood suply
4. inadequate nutrition
5. loss of endocrine stimulation
6. ageing process
7. pressure
Penyusutan dalam ukuran sel oleh hilangnya zat
Fisiologis atrofi:
- Embryogenic struktur: thyroglossal saluran
- Penurunan dari rahim / ukuran payudara setelah
kelahiran
Patologis atrofi:
1. Penurunan beban kerja / tidak digunakan atrofi
2. kehilangan inervation
3. SUPLY darah berkurang
4. nutrisi yang tidak mencukupi
5. hilangnya stimulasi endokrin
6. proses penuaan
7. tekanan
Testis atrophy Kidney atrophy
Metaplasi
Reversible changes in which one adult cell
type is replaced by another adult cell type
Exp: - columner epithel squamous epithel
( heavy smoker , chronic cervicitis)
- Squamous ep --- columner ep
( Barrets esophagus )
- columner ep --- apocrine ep
( fibrocystic changes of the breast )
- connective tissue metaplasia
Reversibel perubahan di mana satu tipe
sel dewasa digantikan oleh jenis sel
dewasa lain
Exp: - columner epithel - epithel squamous
(Perokok berat, cervicitis kronis)
- Skuamosa ep ep --- columner
(Barrets kerongkongan)
- Apokrin --- columner ep ep
(fibrokistik perubahan dari payudara)
- Metaplasia jaringan ikat
Barets esophagus ( squamous cell --- glandular cells )
Apocrine metaplasia of the breast
Dysplasi
mild moderate severe
Basal cell pro 1/3 2/3- all
liferation
Maturity yes / no yes / no no
Mitosis no/ mild moderate many
Cells atypi mild moderate severe
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cellular Injury and NecrosisDokumen68 halamanCellular Injury and NecrosisAl-Rejab JabdhirahBelum ada peringkat
- Jejas Sel, Kematian Sel Dan Adaptasi SelDokumen33 halamanJejas Sel, Kematian Sel Dan Adaptasi SelSantiFaridKalukuBelum ada peringkat
- PBL - Tropis: MalariaDokumen11 halamanPBL - Tropis: MalariaArifin Ayob0% (1)
- Gangguan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitDokumen77 halamanGangguan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitPutri Santri100% (2)
- Apoptosis & Nekrosis: Monita Sugianto Dosen Pengampu: Edhyana K. Sahiratmadja, DR., PHDDokumen34 halamanApoptosis & Nekrosis: Monita Sugianto Dosen Pengampu: Edhyana K. Sahiratmadja, DR., PHDmonitamiftahBelum ada peringkat
- OsteoporosisDokumen2 halamanOsteoporosisJuanitoCabatañaLimIIIBelum ada peringkat
- CNS Structure and Function: Brain and Spinal Cord AnatomyDokumen90 halamanCNS Structure and Function: Brain and Spinal Cord AnatomyhardianBelum ada peringkat
- Cough Variant AsthmaDokumen27 halamanCough Variant AsthmaSaikat BUTEX-40thBelum ada peringkat
- Askep StrokeDokumen24 halamanAskep StrokeRosita Debby IrawanBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotic Evaluation in CAP Therapy at Budi Asih HospitalDokumen5 halamanAntibiotic Evaluation in CAP Therapy at Budi Asih HospitalKoko NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- DHF Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDokumen23 halamanDHF Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengue Hemorrhagic FevermiraBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Pengaruh Kukusan Labu Terhadap Tekanan DarahDokumen13 halamanJurnal Pengaruh Kukusan Labu Terhadap Tekanan DarahAyudiah UprianingsihBelum ada peringkat
- Penyakit-Penyakit Jantung Kongenital.: M.S.GanesanDokumen63 halamanPenyakit-Penyakit Jantung Kongenital.: M.S.GanesanSyukri SamsudinBelum ada peringkat
- Code Stroke Emergency ResponseDokumen35 halamanCode Stroke Emergency Responsedewi wijayantiBelum ada peringkat
- Slide Happy Hypoxia Covid-19 DR ErlinaDokumen30 halamanSlide Happy Hypoxia Covid-19 DR ErlinaSuci Aryanti Nasir100% (1)
- Gangguan Dan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitDokumen37 halamanGangguan Dan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitFyana PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Lung CancerDokumen15 halamanLung CancerO.r. CadzBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal CairanDokumen9 halamanJurnal Cairanapriyani ikaBelum ada peringkat
- Kardio Kel.2Dokumen84 halamanKardio Kel.2Senja FajarBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotik Golongan Dan Nama Generik DagangDokumen2 halamanAntibiotik Golongan Dan Nama Generik DagangTimothy OlsonBelum ada peringkat
- Bhasa InggrisDokumen23 halamanBhasa InggrisrinaBelum ada peringkat
- Klasifikasi, Influenza InternetDokumen33 halamanKlasifikasi, Influenza InternetWinda RamadaniBelum ada peringkat
- Relationship Between Nurse Response Time and Risk of Hypovolemic ShockDokumen82 halamanRelationship Between Nurse Response Time and Risk of Hypovolemic ShockSafitryBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Injury 2023Dokumen135 halamanCell Injury 2023Dexcel concepcionBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Injury MechanismsDokumen87 halamanCell Injury MechanismsYashaswi SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Early Cell Injury and Homeostasis Leading To Point of No Return Causes of Cellular InjuryDokumen17 halamanEarly Cell Injury and Homeostasis Leading To Point of No Return Causes of Cellular InjurysridharBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Injury: Yodit Getahun, MDDokumen26 halamanCell Injury: Yodit Getahun, MDWolderufaelBelum ada peringkat
- 3.cell Injury NecrosisDokumen82 halaman3.cell Injury NecrosisRyan ColeBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Adaptation and Injury ReviewDokumen137 halamanCell Adaptation and Injury ReviewBabak Barghy100% (1)
- Intracellular AccumulationDokumen38 halamanIntracellular AccumulationElena PoriazovaBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanisms of Cell InjuryDokumen21 halamanMechanisms of Cell Injuryبراءة أحمد السلاماتBelum ada peringkat
- SHS 301 Lect-3Dokumen45 halamanSHS 301 Lect-3AAZEEN ALIBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology Introduction Cell Injury & AdoptationDokumen123 halamanPathology Introduction Cell Injury & Adoptationchicagoboy23Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Pathology: Cell InjuryDokumen5 halamanIntroduction To Pathology: Cell InjuryMara ZnagoveanuBelum ada peringkat
- Mod Cl1 Cell Injury and DeathDokumen9 halamanMod Cl1 Cell Injury and DeathWong Jian CongBelum ada peringkat
- Kematian Sel Dan ApoptosisDokumen85 halamanKematian Sel Dan ApoptosismayaBelum ada peringkat
- (MDP) Dr. Syamsu Rijal - Jejas Kematian Sel Last PDFDokumen64 halaman(MDP) Dr. Syamsu Rijal - Jejas Kematian Sel Last PDFAqma SabrinaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell InjuryDokumen30 halamanCell InjuryBlen AsmeromBelum ada peringkat
- ETIOLOGY of Cell InjuryDokumen77 halamanETIOLOGY of Cell InjurybesthachakrapaniBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death MechanismsDokumen30 halamanCell Injury, Adaptation and Death Mechanismsleksis09Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 - The Cell and Reaction To Injury - 2 Sep 2006Dokumen19 halamanLecture 3 - The Cell and Reaction To Injury - 2 Sep 2006api-3703352Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter One Introduction To Pathology Chapter One Introduction To PathologyDokumen26 halamanChapter One Introduction To Pathology Chapter One Introduction To PathologySivanarayana JayavaramBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Responses To Stress and Toxic InsultsDokumen53 halamanCellular Responses To Stress and Toxic InsultsAnastasiaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2 Cell Injury and Inflammation (1)Dokumen69 halamanLecture 2 Cell Injury and Inflammation (1)tangroBelum ada peringkat
- Cell InjuryDokumen118 halamanCell InjuryShanzayBelum ada peringkat
- 4-2020, Mechanisms of Cell InjuryDokumen34 halaman4-2020, Mechanisms of Cell InjuryAiza AnwarBelum ada peringkat
- 6.cell Membrane DiseasesDokumen40 halaman6.cell Membrane DiseasesStanley ChikoveBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Cell InjuryDokumen69 halaman1 Cell InjuryOsama OsamaBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Cell InjuryDokumen72 halaman03 Cell InjuryLunaLure100% (1)
- Pengantar Patologi AnatomiDokumen47 halamanPengantar Patologi AnatomiChristian V. H. TambaBelum ada peringkat
- PDF Document 6Dokumen56 halamanPDF Document 6Kendrix FlorendoBelum ada peringkat
- Class 2Dokumen65 halamanClass 2hari dharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Injury, Adaptations, and DeathDokumen34 halamanCellular Injury, Adaptations, and Deathkalyancv74Belum ada peringkat
- Cellular Responses To Stress and Toxic Insults: Adaptation, Injury, and DeathDokumen26 halamanCellular Responses To Stress and Toxic Insults: Adaptation, Injury, and DeathHusam ShawaqfehBelum ada peringkat
- Combine Class Cellular Injury, Adaptation and Cellular DeathDokumen92 halamanCombine Class Cellular Injury, Adaptation and Cellular DeathSuleiman KikulweBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Final 1Dokumen162 halamanPathophysiology Final 1Yeshaa Mirani100% (1)
- Pathology01 CellDeath Inflammation RepairDokumen140 halamanPathology01 CellDeath Inflammation RepairMiguel AranaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Pathology: Dr. MishaalDokumen69 halamanBasic Pathology: Dr. Mishaalaimi BatrisyiaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology 1 Cell Injury Adaptaions and DeathDokumen71 halamanPathology 1 Cell Injury Adaptaions and Deathm-18506Belum ada peringkat
- Cell PathophysiologyDokumen11 halamanCell PathophysiologyDURJOYBelum ada peringkat
- Who Reccomendation MalnutritionDokumen123 halamanWho Reccomendation MalnutritionAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Jpr-7-125 Postherptic Neuralgia Primary Care ProviderDokumen8 halamanJpr-7-125 Postherptic Neuralgia Primary Care ProviderAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Factors For Chronic and Recurrent Otitis Media-A Meta-AnalysisDokumen9 halamanRisk Factors For Chronic and Recurrent Otitis Media-A Meta-AnalysisNadhira Puspita AyuningtyasBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal 3Dokumen14 halamanJurnal 3AgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Herpes Zoster Dan PHNDokumen6 halamanHerpes Zoster Dan PHNAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Tinea Infection DX and Management BMJ 7 2012Dokumen10 halamanTinea Infection DX and Management BMJ 7 2012AgaipBelum ada peringkat
- 358 - Perubahan Status Kelembagaan SPBU DODO, CODO & CODO LiteDokumen1 halaman358 - Perubahan Status Kelembagaan SPBU DODO, CODO & CODO LiteAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Prescription of Antiviral Therapy After Herpes Zoster in General PracticeDokumen7 halamanPrescription of Antiviral Therapy After Herpes Zoster in General PracticeAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- ZJM 3750Dokumen6 halamanZJM 3750Hervi LaksariBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines Therapy CLMDokumen6 halamanGuidelines Therapy CLMAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- TutorialDokumen2 halamanTutorialAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines Therapy CLMDokumen6 halamanGuidelines Therapy CLMAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Top Penumonia 1385.fullDokumen5 halamanTop Penumonia 1385.fullSidgi BadjriBelum ada peringkat
- Stroke GuidelineDokumen15 halamanStroke GuidelinePetrik Aqrasvawinata FsBelum ada peringkat
- Prescription of Antiviral Therapy After Herpes Zoster in General PracticeDokumen7 halamanPrescription of Antiviral Therapy After Herpes Zoster in General PracticeAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Zac 1610Dokumen7 halamanZac 1610AgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Ch8 PsychiatryDokumen11 halamanCh8 PsychiatryAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines Therapy CLMDokumen6 halamanGuidelines Therapy CLMAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- PT InrDokumen3 halamanPT InrJeniah Lerios OcsioBelum ada peringkat
- Avaskular NekrosisDokumen27 halamanAvaskular NekrosisAgaip100% (1)
- Tropmed 86 843Dokumen3 halamanTropmed 86 843AgaipBelum ada peringkat
- 7.cell TransportDokumen48 halaman7.cell TransportAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Acute CVDDokumen8 halamanAcute CVDAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- SE Guidelines NCS 0412Dokumen21 halamanSE Guidelines NCS 0412inung_cahayaBelum ada peringkat
- ADEM FactsheetDokumen6 halamanADEM FactsheetayubahriBelum ada peringkat
- 6145 18385 1 PBDokumen6 halaman6145 18385 1 PBAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Management in HealthcareDokumen25 halamanFinancial Management in HealthcareAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- PsikiatriDokumen17 halamanPsikiatriAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Pedoman DiagnosisDokumen97 halamanPedoman DiagnosisAgaipBelum ada peringkat
- Rectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyDokumen28 halamanRectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyRaíla SoaresBelum ada peringkat
- ShaylaDokumen3 halamanShaylaapi-530728661Belum ada peringkat
- Case Study On Observation and Newborn CareDokumen38 halamanCase Study On Observation and Newborn CarePiyush Dutta100% (2)
- American River Cycling Club: W M H R ?Dokumen1 halamanAmerican River Cycling Club: W M H R ?Jotaro KujoBelum ada peringkat
- IBD MedicationDokumen19 halamanIBD MedicationTheghanBelum ada peringkat
- U BDokumen7 halamanU Bapi-3809387Belum ada peringkat
- Krok 2 - 2021 - 26 JulyDokumen19 halamanKrok 2 - 2021 - 26 JulyNicole VinnikBelum ada peringkat
- Weapons of Mass DestructionDokumen42 halamanWeapons of Mass DestructionstarkBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical For PracticalDokumen72 halamanClinical For PracticalYogendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Downer Cow and HypoMgDokumen13 halaman2-Downer Cow and HypoMgY.rajuBelum ada peringkat
- ADR UzbekistanDokumen80 halamanADR UzbekistanJose Juan Velazquez GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Hipospadia, PPT Blok 3.1 (English)Dokumen11 halamanHipospadia, PPT Blok 3.1 (English)weniBelum ada peringkat
- Choosing the Right PaediatricianDokumen263 halamanChoosing the Right PaediatricianSuneethaVangala100% (1)
- Unit - 10 - General Characters and Classification of Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadaliaDokumen38 halamanUnit - 10 - General Characters and Classification of Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadalianucleophilicmishraBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Nursing Mastery Test Part 2Dokumen16 halamanPsychiatric Nursing Mastery Test Part 2Rika MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Osha - Ergonomics - The Study of WorkDokumen14 halamanOsha - Ergonomics - The Study of Workhj100% (2)
- Basic Haematology Exercise 1 (MKEB2403)Dokumen10 halamanBasic Haematology Exercise 1 (MKEB2403)kiedd_04100% (8)
- Irritablebowelsyndrome: What Treatments Really WorkDokumen16 halamanIrritablebowelsyndrome: What Treatments Really WorkTeodora RaindropBelum ada peringkat
- The Promise of Energy Medicine (1984)Dokumen2 halamanThe Promise of Energy Medicine (1984)Regular BookshelfBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Microvascular SurgeryDokumen33 halamanBasics of Microvascular SurgeryPratikshya KothiaBelum ada peringkat
- Berger 1986Dokumen3 halamanBerger 1986kameliasitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Management of The Medically Compromised Dental PatientDokumen40 halamanManagement of The Medically Compromised Dental PatientabodyzizoBelum ada peringkat
- AIPG Paper CorrectedDokumen42 halamanAIPG Paper CorrectedbrihaspathiacademyBelum ada peringkat
- SwatiDokumen97 halamanSwatiswati malikBelum ada peringkat
- Word Parts Dictionary, Prefixes, Suffixes, Roots and Combining FormsDokumen237 halamanWord Parts Dictionary, Prefixes, Suffixes, Roots and Combining Formslaukings100% (9)
- International Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsDokumen5 halamanInternational Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsLilian Rahma AnandaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 12 Health Management Information SystemDokumen14 halamanLecture 12 Health Management Information SystemKamran SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- IV Push MedicationsDokumen67 halamanIV Push Medicationsbtalera100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Respiratory Diseases: Obstructed AlveoliDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Respiratory Diseases: Obstructed AlveoliApril Dianne ParungaoBelum ada peringkat
- Health Promotion and Primary Health CareDokumen51 halamanHealth Promotion and Primary Health CareBhawna JoshiBelum ada peringkat