Thorax
Diunggah oleh
mr_davidHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Thorax
Diunggah oleh
mr_davidHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
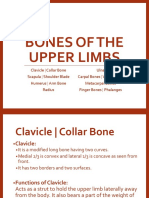
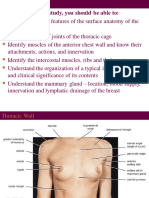
THORAX
Thorax or Chest
Osseo-cartilaginous cage
Function: containing & protecting
of the primary organ of respiratory
& circulation
Shape:
Conical broad below & narrow
above
Longer behind
Flatted from before backward
Boundaries
Posterior: 12 thoracic vertebrae &
posterior portion of the ribs
Anterior: sternum & coastal cartilage
Lateral: ribs
Upper: 1
st
TV, margin of the sternum &
ribs
Below: 12
th
TV & ribs, subcostal angle
Reniform: broader from side-side
Sternum
Flat, narrow bone find in the
medial part in the front of the
chest
3 parts:
Manubrium - handle part
Gladiolus body, biggest part; joins
manubrium at sternal angle
Ensiform or xiphoid appendix:
inferior piece, pointed part.
Manubrium
Surface
Smooth affords attachment
Anterior: convex from side to side,
concave from above downward
Posterior: concave
Border
superior border: the thickest part
Centrally: pre sternal notch
Side: oval articular surface
Inferior: oval and rough, cover w/
thin layer of cartilage
Lateral: depression of the 1
st
costal cartilage
Small facet: forms notch for the
reception of the 2
nd
costal
cartilage
Gladiolus
Surface
anterior surface: nearly flat; marked by
three transverse ridges
posterior surface: slightly concave, is also
marked by three transverse lines
Border
Superior: oval and articulates with the
manubrium sternal angle
Inferior: narrow, and articulates with the
xiphoid process
Lateral border
superior angle:
has a small facet - forms a cavity for the
cartilage of the 2
nd
rib
below this are four angular depressions
- receive the cartilages of the
3
rd
,4
th
,5
th
,6
th
ribs
Inferior angle
has a small facet- forms a notch for the
cartilage of the 7
th
rib.
Xiphoid Appendix
Surface: affords attachments
Anterior: anterior costoxiphoid
ligament & Rectus abdominis
Posterior: posterior costoxiphoid
ligament, fibers of the diaphragm
&Transversus thoracis
Lateral: aponeuroses of the
abdominal muscles
Ossified in the upper part
Ossification
Originally 2 bars on each side
6 centres: 1- manubrium, 4 - body, &1 -
xiphoid process
manubrium and first piece of the body,
during the sixth month of fetal life
second and third pieces of the body
during the seventh month of fetal life
fourth piece, during the first year after
birth;
xiphoid process, between the fifth and
eighteenth years.
Ribs
elastic arches of bone, which form a
large part of the thoracic skeleton
situated one below the other in such a
manner that spaces called intercostal
spaces are left between them
Normally, 12 pairs are present
7 true ribs
3 false ribs
2 floating ribs
Common Characteristics
Posterior extremity:
Head: marked by a kidney-shaped
articular surface
Neck: flattened portion which extends
lateralward from the head
2.5 cm. long
Anterior: flat and smooth
Posterior: rough for the attachment of the
ligament of the neck
Superior: rough crest (crista colli cost)
Inferior: rounded
Tubercle
Tubercle
Articular: oval surface for articulation
Non-articular: rough elevation, and affords
attachment to the ligament of the tubercle
more prominent in the upper than in the lower
ribs.
Body:
External surface is convex, smooth
Marked - a little in front of the tubercle, by a
prominent line, directed downward and
lateralward angle
Internal surface is concave, smooth
Directed a little upward behind the angle
Superior border is thick and rounded, is
marked by an external and an internal lip
Inferior border is thin, and has
attached to it an Intercostalis
externus.
Between Internal Surface and the
inferior border is a groove, the costal
groove, for the intercostal vessels
and nerve.
Anterior Extremity:
flattened, and presents a porous,
oval, concave depression, into which
the costal cartilage is received.
Peculiar Ribs
1
st
, 2
nd
, 10
th,
11
th
, 12
th
The first rib is the most curved and
usually the shortest of all the ribs.
Head-small, rounded, possesses only a
single articular facet
no angle
upper surface: 2 grooves - scalene
tubercle
under surface: smooth, and destitute of a
costal groove
anterior extremity is larger and thicker
2
nd
rib: much longer than the first, but has
a very similar curvature
non-articular portion - feebly marked
angle is slight
posterior part there is a short costal
groove
10
th
rib: single articular facet on its head
11
th
rib: single articular facet on the head
no necks or tubercles
slight angle and a shallow costal groove
12
th
rib: almost the same w/ 11
th
rib
has neither of angle and costal groove
shorter
Ossification
ossified from four centers
primary center for the body
three epiphysial centers
one for the head and one each for the articular
and non-articular parts of the tubercle
eleventh and twelfth ribs have each only
two centers
Angle toward end - second month of fetal
life
Seen first in the sixth and seventh ribs
The epiphyses for the head and tubercle-
b/n the sixteenth and twentieth years;
united to the body about the twenty-fifth
year.
Costal Cartilage
Bars of hyaline cartilage
Function:
prolong the ribs forward
contribute very materially to the
elasticity
first seven pairs are connected with
the sternum
next three articulated w/ the 7
th
cartilage
last two have pointed extremities
Surface
Anterior surface: convex, and looks forward
and upward
Posterior surface: concave, and directed
backward and downward
Border
superior is concave, the inferior convex
Extremities
lateral end: continuous with the osseous
tissue of the rib
medial end of the first is continuous with the
sternum
medial ends of the six succeeding ones are
received into shallow concavities of the
sternum
medial ends of the eighth, ninth, and tenth
are connected
eleventh and twelfth are pointed and free
Thank You
&
Have a Nice Day
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Bones and Joints of ThoraxDokumen57 halamanBones and Joints of ThoraxNunmoy HnialumBelum ada peringkat
- Thoracic ESDokumen237 halamanThoracic ESAbel Belete100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - AV - 2022Dokumen50 halamanLecture 1 - AV - 20222019190566Belum ada peringkat
- Appendiculars (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)Dokumen183 halamanAppendiculars (2015 - 06 - 09 20 - 43 - 48 Utc)DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Huesos y Art Miembro SupDokumen90 halamanHuesos y Art Miembro SupKarla QuinteroBelum ada peringkat
- Thoracic CageDokumen74 halamanThoracic Cagesharathb771Belum ada peringkat
- Sternum and RibsDokumen11 halamanSternum and RibsIshwarya paulrajBelum ada peringkat
- Thorax AllDokumen174 halamanThorax Allravindra sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- The Thoracic CageDokumen35 halamanThe Thoracic Cagehananabodeaf41Belum ada peringkat
- Respiratory System Anatomy For Other Health ScienceDokumen165 halamanRespiratory System Anatomy For Other Health Scienceahmedmustefa773Belum ada peringkat
- Vertebral ColumnDokumen64 halamanVertebral ColumnJavin BissoondyalBelum ada peringkat
- Human Skeleton: Harichanra Gawas 3 Yr B.SC. M.I.TDokumen76 halamanHuman Skeleton: Harichanra Gawas 3 Yr B.SC. M.I.TOmkar GaonkarBelum ada peringkat
- Osteology of Upper LimbDokumen63 halamanOsteology of Upper LimbAkomolede AbosedeBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Subaxial Cervical SpineDokumen70 halamanAnatomy of Subaxial Cervical SpinePrakash SelvamBelum ada peringkat
- THX Bones NDokumen8 halamanTHX Bones Naminshafihassan902Belum ada peringkat
- Thoracic Wall: by Professor NzarubaraDokumen76 halamanThoracic Wall: by Professor NzarubaraEsdras DountioBelum ada peringkat
- Bones of The Shoulder Girdle and ArmDokumen16 halamanBones of The Shoulder Girdle and ArmShimmering MoonBelum ada peringkat
- المحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانDokumen9 halamanالمحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانAbdullah TheBelum ada peringkat
- The Skeleton: Chapter 7 - Part BDokumen6 halamanThe Skeleton: Chapter 7 - Part BJonathan HigginbothamBelum ada peringkat
- Vertebrae and Appendicular ANAPHY AND PHYSIODokumen10 halamanVertebrae and Appendicular ANAPHY AND PHYSIOshannenmaehfajanilanBelum ada peringkat
- Bones of The Thorax.Dokumen18 halamanBones of The Thorax.maemowBelum ada peringkat
- ANAT 100 - Module 2 Summary NotesDokumen6 halamanANAT 100 - Module 2 Summary NotesRahul BhardwajBelum ada peringkat
- Thorax - Thoracic Wall ALLIED 2022Dokumen62 halamanThorax - Thoracic Wall ALLIED 2022Anania EmmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- SHIKHA SAGAR Thorax BonesDokumen30 halamanSHIKHA SAGAR Thorax BonesShikha SagarBelum ada peringkat
- Hafizah Binti Mohd Hoshni Musculoskeletal Anatomy Skeleton of The ThoraxDokumen28 halamanHafizah Binti Mohd Hoshni Musculoskeletal Anatomy Skeleton of The ThoraxhafizahhoshniBelum ada peringkat
- Back and Spinal CordDokumen16 halamanBack and Spinal CordCarlos CaCoBelum ada peringkat
- ANATOMY I 20.03.20 I Thoracic CageDokumen23 halamanANATOMY I 20.03.20 I Thoracic CageArianna RomanoBelum ada peringkat
- Pe01-Lesson 2Dokumen85 halamanPe01-Lesson 2Joan Mae YaoBelum ada peringkat
- ScapulaDokumen17 halamanScapulaMHKBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomical Terms Used in Description of BonesDokumen29 halamanAnatomical Terms Used in Description of Bonesapi-19916399Belum ada peringkat
- THEVERTEBRALCOLUMNDokumen29 halamanTHEVERTEBRALCOLUMNpreetam912002.22Belum ada peringkat
- Ribs, Cartilages and Thoracic VertebraDokumen28 halamanRibs, Cartilages and Thoracic VertebraEniola DaramolaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Week 3 NotesDokumen32 halamanAnatomy Week 3 NotesBasil AdeelBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4Dokumen138 halamanWeek 4Anne nicole P. CasemBelum ada peringkat
- Class III Lower LimbDokumen82 halamanClass III Lower LimbAyana UrmaleBelum ada peringkat
- Sternum OsteologyDokumen34 halamanSternum OsteologyRohit SahBelum ada peringkat
- Hyoid and Ribs: Presented By: Anupriya Sinha Bfs Vi Roll No.:-07 2017-2020Dokumen13 halamanHyoid and Ribs: Presented By: Anupriya Sinha Bfs Vi Roll No.:-07 2017-2020niteshBelum ada peringkat
- Thoracic Wall ShortDokumen11 halamanThoracic Wall ShortkiranBelum ada peringkat
- Ribs and Vertebra BonesDokumen97 halamanRibs and Vertebra BonesJerlyns OmondiBelum ada peringkat
- 1.thoracic CageDokumen23 halaman1.thoracic CageCharles SainzBelum ada peringkat
- Kines Anatomy Ch. 14-16Dokumen36 halamanKines Anatomy Ch. 14-16icedragon727Belum ada peringkat
- 3.bones of UpperlimbDokumen120 halaman3.bones of UpperlimbBlessed LoveBelum ada peringkat
- FemurDokumen2 halamanFemurMarzanul Islam AnikBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnDokumen60 halamanStructure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnJohn DoeBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Extremities Ortho SG3Dokumen119 halamanUpper Extremities Ortho SG3Nuhu Bankwhot100% (1)
- Anatomy Lab 1Dokumen31 halamanAnatomy Lab 1Spotify IraqBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomi 1.2 Skeleton AxialDokumen45 halamanAnatomi 1.2 Skeleton Axialaqilah15noveraBelum ada peringkat
- Share '1579792243522 - Lecture 2Dokumen21 halamanShare '1579792243522 - Lecture 2MOHAMMAD ALSWEITYBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy 1 - MSS (Upper Limb)Dokumen127 halamanAnatomy 1 - MSS (Upper Limb)Abdullah As'adBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Bones of The Upper LimbDokumen28 halaman1 Bones of The Upper LimbForwardBelum ada peringkat
- Thorax Back and SpineDokumen63 halamanThorax Back and SpineShiela ClementeBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Lac.1Dokumen43 halamanAnatomy Lac.1minayayoongi2004Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - Bones of The Upper LimbsDokumen38 halamanLecture 4 - Bones of The Upper LimbsTheLegendKiller337Belum ada peringkat
- 9. المحاضرة التاسعة - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىDokumen6 halaman9. المحاضرة التاسعة - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىAbdullah TheBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Femur, Patella and TibiaDokumen10 halaman2 Femur, Patella and Tibiaطه طارقBelum ada peringkat
- Thoracic Segment KpsDokumen77 halamanThoracic Segment Kpskrishna bptBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System Notes 2023Dokumen16 halamanSkeletal System Notes 2023shinamaejBelum ada peringkat
- Fractures Around The Elbow JointDokumen31 halamanFractures Around The Elbow Jointalimran MahmudBelum ada peringkat
- Chest Wall, Pelural Cavity, LungDokumen48 halamanChest Wall, Pelural Cavity, LungKizuna Hiki-kunBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Ways To Succeed With USMLE Step 1Dokumen19 halaman10 Ways To Succeed With USMLE Step 1Zunaira Abdul Ghaffar100% (2)
- Doctor-Patient Relationship: Hyacinth C. Manood, MD, FPPADokumen25 halamanDoctor-Patient Relationship: Hyacinth C. Manood, MD, FPPAmr_davidBelum ada peringkat
- Ophthalmology NotesDokumen81 halamanOphthalmology Notesmr_david50% (2)
- Shizophrenia Other Psychotic Disorders: Hyacinth C. Manood, MD, DPBPDokumen56 halamanShizophrenia Other Psychotic Disorders: Hyacinth C. Manood, MD, DPBPDani NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- Psychosis Due To Endocrine DISTURBANCESDokumen47 halamanPsychosis Due To Endocrine DISTURBANCESmr_davidBelum ada peringkat
- Predisposing and Precipitating Factors To Mental IllnessDokumen25 halamanPredisposing and Precipitating Factors To Mental Illnessmr_david100% (1)
- Test 4Dokumen8 halamanTest 4Phương AnhBelum ada peringkat
- SUMMATIVE Entrep Q1Dokumen2 halamanSUMMATIVE Entrep Q1ocsapwaketsBelum ada peringkat
- My Home Is My CastleDokumen9 halamanMy Home Is My CastleNur ZhanBelum ada peringkat
- Wed 0945-Avionics Modernization For LegacyDokumen38 halamanWed 0945-Avionics Modernization For LegacygasparferrerBelum ada peringkat
- A Door Into Hindi DevanagariDokumen8 halamanA Door Into Hindi DevanagariHoang NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Bell Atlantic Corp v. TwomblyDokumen4 halamanBell Atlantic Corp v. Twomblylfei1216Belum ada peringkat
- Ad3na0ab (COMBI NACCO-ing)Dokumen30 halamanAd3na0ab (COMBI NACCO-ing)Kaique MelloBelum ada peringkat
- A Natural Disaster Story: World Scout Environment BadgeDokumen4 halamanA Natural Disaster Story: World Scout Environment BadgeMurali Krishna TBelum ada peringkat
- Class ProgramsDokumen30 halamanClass Programsludivino escardaBelum ada peringkat
- CV TemplateDokumen4 halamanCV TemplateIri PopescuBelum ada peringkat
- Rhinitis Allergic: Elma Wiliandini G4A020043Dokumen10 halamanRhinitis Allergic: Elma Wiliandini G4A020043elma wiliandiniBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Three: The Topography of Ethiopia and The HornDokumen4 halamanChapter Three: The Topography of Ethiopia and The Horneyob astatke100% (1)
- Philosophers and The Mysteries - Jan N. Bremmer PDFDokumen28 halamanPhilosophers and The Mysteries - Jan N. Bremmer PDFPricopi VictorBelum ada peringkat
- International Business of Pizza HutDokumen13 halamanInternational Business of Pizza Hutpratikdotia9100% (2)
- HR Awards PPT 2020 12.09.2020 FinalDokumen64 halamanHR Awards PPT 2020 12.09.2020 FinalLolo OhwBelum ada peringkat
- Conflict of Laws by Sempio DiyDokumen81 halamanConflict of Laws by Sempio DiyAp Arc100% (10)
- C++ & Object Oriented Programming: Dr. Alekha Kumar MishraDokumen23 halamanC++ & Object Oriented Programming: Dr. Alekha Kumar MishraPriyanshu Kumar KeshriBelum ada peringkat
- Scholars' Letter On SCOTUS Ethics CodeDokumen2 halamanScholars' Letter On SCOTUS Ethics CodeConcerned citizen50% (2)
- Batangas Polytechnic College: The Morning After Case 7Dokumen4 halamanBatangas Polytechnic College: The Morning After Case 7Jonard Marco RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Interim Order in The Matter of Sukhchain Hire Purchase LimitedDokumen18 halamanInterim Order in The Matter of Sukhchain Hire Purchase LimitedShyam SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Salt Iodine WYD Iodine Checker Instruction ManualDokumen13 halamanSalt Iodine WYD Iodine Checker Instruction ManualCatherine LargaBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual Tosoh Aia360Dokumen4 halamanService Manual Tosoh Aia360OmerBelum ada peringkat
- Pablo Gualberto Vs Gualberto VDokumen2 halamanPablo Gualberto Vs Gualberto VNotaly Mae Paja BadtingBelum ada peringkat
- Family Law Outline RevisedDokumen11 halamanFamily Law Outline RevisedAdriana CarinanBelum ada peringkat
- Public Procurement Rules 2004Dokumen35 halamanPublic Procurement Rules 2004Mubashir SheheryarBelum ada peringkat
- Danamma Vs AmarDokumen13 halamanDanamma Vs AmarParthiban SekarBelum ada peringkat
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 125Dokumen17 halamanCoronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 125CityNewsTorontoBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Is Where You'Re Not LookingDokumen20 halamanRisk Is Where You'Re Not LookingJesse100% (5)
- Baywatch - Tower of PowerDokumen20 halamanBaywatch - Tower of Powerkazimkoroglu@hotmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- 750-366 Hawk 1000 07 13 PDFDokumen82 halaman750-366 Hawk 1000 07 13 PDFAlexis CruzBelum ada peringkat