Introduction To Sets: Whole Numbers
Diunggah oleh
Gigi G. BullandayDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Introduction To Sets: Whole Numbers
Diunggah oleh
Gigi G. BullandayHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
INTRODUCTION TO
SETS
Whole Numbers
Pre-requisite
Concept:
Objectives:
You are expected to
describe and illustrate
a well-defined set;
determine subsets of
a given set;
define/describe a
universal set, null set,
finite, infinite, equal,
equivalent sets;
find the cardinality of
sets
Key Words
SET
UNIVERSAL SET
SUBSET
NULL SET
FINITE AND
INFINITE SETS
EQUAL SETS
EQUIVALENT SETS
CARDINALITY OF
SETS
SETS
A set is a well-defined group of objects called
elements that share a common
characteristics.
For example: 3 and 5 form the set of prime
numbers greater than 2 but less than 7.
We use the symbol to show that something is a
member of a set you read it as is an element
of or is a member of
The symbol means the opposite you read it as
is not an element of or is not a member of
Sets are usually named by capital letters. The
elements of the set are enclosed in .
A = {3, 5}
The universal set denoted by the symbol , is the
set of all objects under consideration.
Example 1:
Given that set B ={a,b,2,3} determine whether each
of the following statement is TRUE or FALSE.
1. a B
2. 3 B
3. b B
4. 4 B
Guided Practice
Given set C = {m,3,4,n } determine whether
each of the following statement is TRUE or
FALSE.
1. n C
2. 3 C
3. 5 C
4. 4 C
Empty Set
An empty set or Null set has no elements. It is
denoted by { } or .
Subsets
A subset is a set whose elements are also
contained in another set. The symbol means
is a subset of.
A B A is a subset of B
All elements of A are in B
A B A is a proper subset of B
Not all elements of A are in B.
Note that:
Any set is a subset of itself.
The empty set is a subset of itself.
Example 2:
Let B = { x/ x is an even number} RULE
METHOD
B = { 0,2,4,6,8,} LISTING
METHOD/ROSTER
METHOD
D = {8,10,12,14 }
Is D a subset of B?
Example 3:
Let A = {0,2,4}
Determine the subsets of A.
Guided Practice
Let A ={1,3,5,d,e,f}
B= {2,3,e,g }
5. Explain whether B A.
6. List all subsets of B.
Let C = {x/x is a prime number greater than 5
but less than 17}
7. List set C and all its subsets.
Equality of Sets
Two sets are equal if they have all of the same
elements in them.
So if A = {1,2,a,b } and
B = {b,a,2,1 } then A and B are equal
Note that empty sets are equal because they are
exactly the same.
Two sets are equivalent if they have exactly
the same number of elements, even if their
elements are not the same.
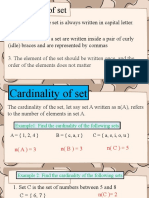
Cardinality of Sets
Finite Set is a set that has a finite number of
elements. For example {2,4,6,8,10} is a finite
set with 5 elements. The number of elements
of a finite set is called the Cardinality of the
set.
A set that is not finite is called infinite. For
example {1,2,3,4, } the set of positive
integers.
Independent Practice
1. Determine set A whose elements are all
multiples of both 3 and 4 that are greater than
9 but less than 30.
2. Let U = {all letters of the alphabet}
Determine set C whose elements are the
vowels.
3. Write down G = {all prime numbers greater
than 5 but less than 7 }
For Exercises 4 and 5
Let C = { all odd numbers }
D = {1,3,5,7}
4. Explain whether D C.
5. List all the subsets of D.
For Exercises 6 and 7
Let E = {q,r,s,8,9}
F = {q,7,8,r }
6. Explain whether F E.
7. List all subsets of F.
8. Let A = {2,4,6,8}
B = {all even numbers greater than 0 but
less than 10}
Explain whether A = B.
9.What is the cardinality of A?
10. Give an example of a finite set and infinite
set.
Lesson Quiz
1-3
1. Write down A = {all prime numbers between
30 and 40 }
2. Find n(A)
3. List all subsets of A
4 -5
Given B = {m,n,p,6,7} , C = { p, 6} , D= {a,b,c,3,5}
4. Is C B ? Explain.
5. Is D equivalent to B? Explain.
Lesson Quiz
6. Given G = {all multiples of 3} . Is G finite or
infinite? Explain
7.Give an example of a well-defined set.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Sets and SubsetsDokumen11 halamanSets and Subsetsyaoi yuriBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Plan About SetsDokumen4 halamanUnit Plan About Setsmykee zephanie ybanezBelum ada peringkat
- Math8 q4 w5 Studentsversion v1Dokumen10 halamanMath8 q4 w5 Studentsversion v1cade ytBelum ada peringkat
- V. Justification: VII. Possible ExtensionsDokumen2 halamanV. Justification: VII. Possible ExtensionsIsabel ClementeBelum ada peringkat
- M7 Q1L2.1 Operations On Sets (Union and Intersection of Sets)Dokumen3 halamanM7 Q1L2.1 Operations On Sets (Union and Intersection of Sets)Caitlin Joy MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Decilesfor Grouped DataDokumen9 halamanDecilesfor Grouped DataJinky TabigneBelum ada peringkat
- Cot 1Dokumen27 halamanCot 1JOCELYN PARAGOSOBelum ada peringkat
- Math 103Dokumen58 halamanMath 103Jandee CayaBelum ada peringkat
- Venn Diagram: Learning OutcomesDokumen9 halamanVenn Diagram: Learning OutcomesRosemarie GoBelum ada peringkat
- Probability 7.1.1 Sample Space and Events: H E B A TDokumen14 halamanProbability 7.1.1 Sample Space and Events: H E B A TbenjoeBelum ada peringkat
- Infinity and Its CardinalitiesDokumen88 halamanInfinity and Its CardinalitiesMohammed RazikBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 10 I. Weekly Objectives: Lets ROLL ItDokumen10 halamanLesson Plan in Mathematics 10 I. Weekly Objectives: Lets ROLL ItMark Kevin GeraldezBelum ada peringkat
- Number Operations and IntegersDokumen9 halamanNumber Operations and IntegersJessa Mae BanquirigBelum ada peringkat
- Measure of Central Tendency Grouped DataDokumen10 halamanMeasure of Central Tendency Grouped DataErika BenitezBelum ada peringkat
- (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-1) (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-2) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 1Dokumen9 halaman(Stem - Pc11T-Iia-1) (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-2) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 1Naddy RetxedBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean Theorem and The Distance FormulaDokumen15 halamanPythagorean Theorem and The Distance FormulaEvelyn MaligayaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 7 Math Lesson 2.1. Union and Intersection of Sets Teaching GuideDokumen8 halamanGrade 7 Math Lesson 2.1. Union and Intersection of Sets Teaching GuideReshel LadioBelum ada peringkat
- Relationship of Areas of Two Quadrilaterals When The Midpoints of Sides of Arbitrary Quadrilaterals Are The Vertices of Inner QuadrilateralsDokumen7 halamanRelationship of Areas of Two Quadrilaterals When The Midpoints of Sides of Arbitrary Quadrilaterals Are The Vertices of Inner QuadrilateralsChynna Grace MaderaBelum ada peringkat
- SArasin Decilesfor Grouped DataDokumen9 halamanSArasin Decilesfor Grouped DataMaress SosobanBelum ada peringkat
- Divisibility RulesDokumen13 halamanDivisibility RulesJeffrey Catacutan FloresBelum ada peringkat
- I. Multiple Choice Direction: Read Carefully Each Item and Choose The Letter Corresponding To The Correct AnswerDokumen6 halamanI. Multiple Choice Direction: Read Carefully Each Item and Choose The Letter Corresponding To The Correct AnswerKiesha AltheaBelum ada peringkat
- M2L1 - Laws of ExponentsDokumen4 halamanM2L1 - Laws of Exponentsdorris09Belum ada peringkat
- Union and Intersection Part 2Dokumen14 halamanUnion and Intersection Part 2glaizaBelum ada peringkat
- Detail Lesson PlanDokumen14 halamanDetail Lesson Planmaffy fernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Summative Assessment Q4Dokumen10 halaman2nd Summative Assessment Q4Marchell PaqueraBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Math 12Dokumen6 halamanLesson Plan Math 12Louis Fetilo FabunanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter8 Probability PDFDokumen13 halamanChapter8 Probability PDFAriston EtormaBelum ada peringkat
- IPLANDokumen6 halamanIPLAN19 Juvelyn OmpocBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Infinite SequencesDokumen14 halaman3.1 Infinite SequencesShiru AllanBelum ada peringkat
- Factoring Trinomials: Trial and Error and The AC-MethodDokumen7 halamanFactoring Trinomials: Trial and Error and The AC-MethodmomathtchrBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics 7: First Quarter: Week 1 Learners Activity SheetsDokumen16 halamanMathematics 7: First Quarter: Week 1 Learners Activity SheetsJaymar SarvidaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Set and Set OperationsDokumen82 halaman1.1 Set and Set OperationsRaymart LeysonBelum ada peringkat
- Parallel Lines Cut by A Transversal ActivityDokumen5 halamanParallel Lines Cut by A Transversal Activityapi-534095936Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1718 RelationDokumen62 halamanLecture 1718 RelationSamratBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 10: I. ObjectiveDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan in Mathematics 10: I. ObjectiveRachelle EstrelladoBelum ada peringkat
- Lessonplaninmathematics10permutations 1Dokumen2 halamanLessonplaninmathematics10permutations 1Edwin SartinBelum ada peringkat
- Multiplying and Dividing Rational ExpressionsDokumen24 halamanMultiplying and Dividing Rational ExpressionsClark Keith A. GatdulaBelum ada peringkat
- Sets An IntroductionDokumen2 halamanSets An IntroductionJean Marie Ga LacsonBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Xi Fourth Quarter FEBRUARY 26, 2019Dokumen5 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Xi Fourth Quarter FEBRUARY 26, 2019dionesio lanuriasBelum ada peringkat
- DemonstrationDokumen11 halamanDemonstrationRalph GimonBelum ada peringkat
- 'DETAILED-LESSON-PLAN-IN-MATHEMATICS2-1' With YouDokumen4 halaman'DETAILED-LESSON-PLAN-IN-MATHEMATICS2-1' With YouRanema GarayBelum ada peringkat
- Quartiles of Grouped DataDokumen17 halamanQuartiles of Grouped DataLoaf DoggoBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 11 I. Objectives: KN CF F IDokumen4 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 11 I. Objectives: KN CF F ILouis Fetilo FabunanBelum ada peringkat
- Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications: Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsDokumen61 halamanDiscrete Mathematics and Its Applications: Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsBijori khanBelum ada peringkat
- Abstract Algebra MIDTERMDokumen2 halamanAbstract Algebra MIDTERMJun Francis MaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Trigo - Midterm Special ExamDokumen3 halamanTrigo - Midterm Special ExamLeonald OseraBelum ada peringkat
- 20170321120320chapter 3 - Isomorphism and HomomorphismDokumen29 halaman20170321120320chapter 3 - Isomorphism and HomomorphismNashz ChanceBelum ada peringkat
- 48.3 Events and The Union and Intersection of Events#Dokumen4 halaman48.3 Events and The Union and Intersection of Events#Paulo EsguerraBelum ada peringkat
- DLLmath PermutationDokumen9 halamanDLLmath PermutationErwin DiosoBelum ada peringkat
- Permutation DLLDokumen4 halamanPermutation DLLIncroyable InangBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test On MatricesDokumen10 halamanPractice Test On MatricesowaisBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Part 1 PDFDokumen17 halamanChapter 1 - Part 1 PDFأحمد الرقبBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Omer Baktir 1Dokumen10 halamanLesson Plan Omer Baktir 1api-501227468Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 SET THEORYDokumen11 halamanChapter 2 SET THEORYLee Anne DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Operations On Sets: By: Teacher MYRA CONCEPCIONDokumen22 halamanOperations On Sets: By: Teacher MYRA CONCEPCIONInahing Mameng100% (1)
- Lesson 5 - Remainder and Factor TheoremDokumen7 halamanLesson 5 - Remainder and Factor TheoremAmmar RizwanBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter 1 Week 1: Language of SetsDokumen38 halamanQuarter 1 Week 1: Language of Setsggvgrrr75% (4)
- MMW Report - UpdatedDokumen46 halamanMMW Report - UpdatedVence EscoteBelum ada peringkat
- Cardinality and Types of SetsDokumen15 halamanCardinality and Types of SetsJakielyn MangampatBelum ada peringkat
- Math 7 Lesson 1.2 Set RelationsDokumen41 halamanMath 7 Lesson 1.2 Set RelationsRose ArceoBelum ada peringkat
- Pte Lastest QuestionsDokumen202 halamanPte Lastest QuestionsIelts Guru ReviewBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-Communication & NetworkingDokumen70 halamanChapter-Communication & NetworkingAfsar AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Pit Viper 351Dokumen6 halamanPit Viper 351Sebastian Robles100% (2)
- The Impact of Teaching PracticeDokumen14 halamanThe Impact of Teaching PracticemubarakBelum ada peringkat
- A. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Dokumen5 halamanA. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Aakriti SanjelBelum ada peringkat
- Webinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018Dokumen62 halamanWebinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018AlexBelum ada peringkat
- Social and Professional Issues Pf2Dokumen4 halamanSocial and Professional Issues Pf2DominicOrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Y2V7 Full With SSDokumen294 halamanY2V7 Full With SSAyanokoji KyotakaBelum ada peringkat
- Genie Awp SpecsDokumen4 halamanGenie Awp SpecsIngrid Janet GuardadoBelum ada peringkat
- Dede - (2010) - Comparing Frameworks For 21st Century Skills PDFDokumen16 halamanDede - (2010) - Comparing Frameworks For 21st Century Skills PDFNaing Lynn HtunBelum ada peringkat
- SalivaDokumen42 halamanSalivaAtharva KambleBelum ada peringkat
- TA35 & TA40 Articulated Dumptruck Maintenance Manual: Click Here For Table ofDokumen488 halamanTA35 & TA40 Articulated Dumptruck Maintenance Manual: Click Here For Table ofKot878100% (2)
- Parkinson Hoehn and Yahr ScaleDokumen3 halamanParkinson Hoehn and Yahr ScaleCarol Artigas GómezBelum ada peringkat
- C3H Hawaii (Polynesian Islands) (Native Food in Hawaii)Dokumen19 halamanC3H Hawaii (Polynesian Islands) (Native Food in Hawaii)Yoon Yati ShinBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDokumen5 halamanAcid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 Scienceclashhunting123123Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignDokumen7 halamanApplication of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Sections PDFDokumen36 halamanSteel Sections PDFTonderai RusereBelum ada peringkat
- Raw:/storage/emulated/0/download/1623980378472 - 1623980347729 - PE 4 Module 2Dokumen11 halamanRaw:/storage/emulated/0/download/1623980378472 - 1623980347729 - PE 4 Module 2Marvin Espenocilla EspeñoBelum ada peringkat
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Dokumen49 halamanCpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Jasmine LimBelum ada peringkat
- Jesoc5 1 PDFDokumen15 halamanJesoc5 1 PDFfaisal3096Belum ada peringkat
- Authority To TravelDokumen39 halamanAuthority To TraveljoraldBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Year. PunctuationDokumen14 halaman3rd Year. PunctuationmawarBelum ada peringkat
- English Paper 1 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Lower Secondary Sample Test For Use With Curriculum Published in September 2020Dokumen11 halamanEnglish Paper 1 Mark Scheme: Cambridge Lower Secondary Sample Test For Use With Curriculum Published in September 2020ABEER RATHIBelum ada peringkat
- R820T Datasheet-Non R-20111130 UnlockedDokumen26 halamanR820T Datasheet-Non R-20111130 UnlockedKonstantinos GoniadisBelum ada peringkat
- 310 311 320 321 Toilet Warranty Codes PDFDokumen11 halaman310 311 320 321 Toilet Warranty Codes PDFTerri MartinBelum ada peringkat
- RHEL 9.0 - Configuring Device Mapper MultipathDokumen59 halamanRHEL 9.0 - Configuring Device Mapper MultipathITTeamBelum ada peringkat
- Betty Blue Eyes Kotta PDFDokumen306 halamanBetty Blue Eyes Kotta PDFCsóka Anita83% (6)
- Level 2 Online BPDokumen98 halamanLevel 2 Online BProbertduvallBelum ada peringkat
- EvoFox Katana-X Mechanical Gaming Keyboard With Outemu Blue Switches Vivid Rainbow Lighting With 13 Preset Effects DedicatedDokumen1 halamanEvoFox Katana-X Mechanical Gaming Keyboard With Outemu Blue Switches Vivid Rainbow Lighting With 13 Preset Effects Dedicatedsaqibdar7051236186Belum ada peringkat
- Smartpilot s1 s1g Service ManualDokumen30 halamanSmartpilot s1 s1g Service Manualmalte winbaldBelum ada peringkat