Pemicu 3 Kelopmpok 7
Diunggah oleh
Daniel Hans Jaya0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan42 halamancase
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inicase
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan42 halamanPemicu 3 Kelopmpok 7
Diunggah oleh
Daniel Hans Jayacase
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 42
GROUP 7
Dr. Wiyarni Pambudi Sp.A
Name NIM
STEPHANIE WIBISONO 405070001
MEMBER
LISA WIBOWO 405070004
MEMBER
ANDI SURYA JAYA 405070010
MEMBER
CLAUDIO UDJAJA 405070011
LEADER
FAJAR PERMATA SARI 405070032
SCRIBER
JACKY TANZIL 405070061
MEMBER
CHASTINE FAUSTINA 405070070
MEMBER
DIAN WIJAYANTI 405070076
MEMBER
ELLEN ARISTIKA G. 405070083
MEMBER
RITCHIE SANTOSO 405070115
MEMBER
FERDY SANJAYA 405070118
MEMBER
HARI DARMAWAN LEE 405070155
SECRETARY
Learning Objective
Knowing the process of normal swallow
Knowing the problem of swallow
Knowing the process of digestion and
absorption
Knowing the process of hungry and and
satisfied
Knowing the nutrition for child
CASE 3B
Jacko, a one-month-old male baby is brought to your private practice by
his parents with a chief complain of constant irritability and regurgitation.
The 2.8 kg newborn baby of an uneventful full term pregnancy and delivery,
was discharged on the second day of life. He always seems to be hungry,
and since his mother is certain that she does not produce enough breast
milk, she gives milk formula after she breastfed him. That has already
happened for two weeks.
Jacko currently breastfeeds for 10 minutes, then consumes another 60 ml
by bottle. When left with grandparents, he will finish an entire 120 ml bottle
in 5-10 minutes and they reported that he will cry if they try to cut it off at
the recommended 60 ml. Vomiting generally occurs immediately after
feedings. It is not forceful, nor it is blood or biletinged. He fills 10 diapers
with urine daily, and lately he has had watery stools, which have further
worried his grandparents. Despite all this, he weighed 3.5 kg at the two
week checkup and he now weighs 4.3 kg.
Exam: VS are unremarkable. His physical examination is notable only for
fussiness when laid supine on the table, with resolution when held upright
or in the prone position. You witness effortless regurgitation of 2-5 ml of
curdled formula every few minutes during examination since his parents
topped him off with milk formula in your waiting room before the
appointment.
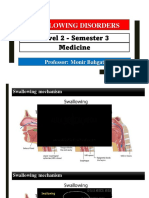
Process Of Swallowing
Picture : process of swallowing
Swallowing
The movement swallowed was followed with
the rise posterior the tongue in a sudden
push food/liquid to posterior pharynx
superior&anterior larynx move, epiglotis
position courage larynx airway, nasofarynx
closed by palatum molle and uvula
The posterior esophagus sphincter relaxation
with constrictor farynx muscle, push the food into
esophagus first peristaltic wave
Second peristaltic wavelocal distention that
played a role in the evacuation esofagus from
leftovers/the contents of gasterwave this
emptied esofagus with movement efforts
encouraged
Nervus
Nervus trigeminus
Nervus glosofaringeal
Nervus vagus
Regurgitation
Definition
Regurgitation was the rise in food from throat
or the side without being accompanied by the
feeling of nausea and the contraction of the
very strong stomach muscle.
Etiology
Regurgitasi often as a result of by acid that
rose from the side (refluk acid).
Regurgitasi could be also caused by the
constriction (striktur) or the throat
obstruction.
Symptom
Acid that came from the side caused
regurgitasi from materials that were felt acid
or bitter. The constriction or the throat
obstruction caused regurgitation the liquid
had phlegm that did not feel or food that was
not yet digested.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis refluks acid was maintained was
based on results of the inspection x-rayed, the
grating of the pressure and the throat acidity
and the other inspection. The diagnosis from
the constriction or the throat obstruction was
maintained was based on results of the
inspection x-rayed or endoscopy
GER
Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) or Reflux is the
medical term used to describe a condition in
which stomach contents - food and gastric
acid - frequently flow back up out of the
stomach into the esophagus
GERD
GERD stands for gastroesophageal reflux
disease or acid reflux disease. The problem
occurs when acid and other contents of the
stomach repeatedly flow back up into the
esophagus. This happens because the lower
esophageal sphincter (LES) either relaxes at
the wrong time, or it is weak, so it allows acid
and other stomach contents to flow back up
into the esophagus.
Etiology
The position sfingter in abdomen
the Corner insertio esofagus inside gaster
Pressure sfingter
The pressure sfingter spontan mechanism
main refluks
Refluks through sfingter that was weak
chronic often happen in esofagitis
Refluks with the pressure normal,terjadi if the
stomach pressure me (cough, cry,
defecation)
Etiology
Other lifestyle contributors to GERD may include the following :
being overweight
overeating
consuming certain foods, such as citrus, peppermint, chocolate,
fatty, and spicy foods
caffeine
alcohol
smoking
use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs) drugs such as
aspirin and ibuprofen
Other medical causes of heartburn may include the following:
gastritis - an inflammation of the stomach lining.
ulcer disease
Symptoms of GERD :
Vomit and slow gaster emptiness
Pneumonia aspiration
Chronic cough
Mengi
Relaps Pneumonia
Rumination
Failure to thrive
Symptoms of GERD :
Heartburn
Regurgitation
Difficulty swallowing
Water brash
Diagnosis
The mild case clinical value & response against therapy
Severe case
did esofagografi barium with the guidance fluoroscopy
Scintiscans show the aspirations of the contents of
gaster and show the refluks
Esofagoskopi evaluating reflux & severe strictur
Biopsy esofagus prove the existence reflux
Diagnosis
Roentgentgrafi with coventional Barium
- Exhibited the existence of the period that
disturbing in the lumen/exhibited reflux
gastroseofagus
Picture and video of esofagram
Knew the change in the pattern swallowing &
esofagus peristaltic movement
Manometri Esophagus
Evaluated the wave of the pressure in esophageal
& change in the pressure on low esophageal
sphincter
Scan radionuklid
Evaluated peristaltic efficiency in cleaned esofagus &
tested the existence refluks and aspirastion
pH in distal esophagus
Sensitive for the gaster acid refluks
Endoskopi fiberoptic
Carried out the biopsy and visualisation esofagus
without general anaesthesia , examination this to
detect and take the foreign object
Complications
include esophageal cancer, erosive
esophagitis, and Barrett's esophagus. GERD
also aggravates asthma and sleep apnea
Theraphy
Metoklopramid
Domperidone
Cisapride
Antasida
Anatgonis reseptor H2
PPI (Omeprazol)
Atresia esofagus (AE)
Esophageal atresia is a disorder of the
digestive system in which the esophagus does
not develop properly.
Variasi Atresia Esofagus
Gross of Boston :
Tipe A atresia esofagus without fistula or pure atresia esofagus (10%)
Tipe B atresia esofagus withTEF proksimal (<1%)
Tipe C atresia esofagus with TEF distal (85%)
Tipe D atresia esofagus with TEF proksimal and distal (<1%)
Tipe E TEF withoutatresia esofagus or fistula tipe H (4%)
Tipe F stenosis esofagus kongenital (<1%)
Causes
the upper esophagus ends blindly and does
not connect with the lower esophagus and
stomach
Diagnosed
blood tests
chest x-rays and other x-rays
a special chest x-ray that is done after a
nasogastric tube is put through the nose into
the esophagus to the point where the
esophagus stops
cinefluorography, a moving X-ray scan to
observe the function of the esophagus
ACHALASIA
The disturbance motility that was rare where
the relative obstruction in continuation
gastroesofagus to more badly,because the
nonexistence of the peristaltic wave in
esophageal
Symptomps
dysphagia
Regurgitation
cough
Failure to thrive
Retention in esophagusesophagitis
Diagnosis
Manometri esofagus find imperfect and the
nonexistence relaxation of lower esophagus
sphincter at the time of swallowing, dont
existence of the peristaltic wave at the time of
swallowing, no existence of the peristaltic
wave of the primary promoter / sekunder,
increase lower sphincter esophagus
Therapy
Nifedipin (channel of calsium duct)
Botulisme intrasfingter injection
Operation a gap of muscle fiber in
gastroesofagus be connected.
Balloon cateter and fluoroscopy
Hungry process
Nucleus lateral hypotalamus, as a center of
hungry
Nucleus ventromedial hypotalamus as a
center of satisfied
And sinergy with nucleus paraventrikular,
dorsomedial, dan arkuata
The Standard nutrition For Child
Kalori : 100 -120 / kg BB.
Example child with 8 kg : 8 x 100 /120 = 800/960 kkal
Protein : 1,5 - 2 g / kg BB
Example child with 8 kg : 8 x 1,5/2 = 12/16 : 4 = 3/4 gram
Karbohidrat : 50-60 % from the total calory
Lemak: 20 % from the total calory
CONCLUSIONS
Jacko maybe suffered GER (gastroesophageal
reflux) caused by overeating.
Watery stools occurs because of too much
consume milk so the digestion and absorbtion
is uncompletely
Suggestion
Give nutrition appropriate with the need and
age.
References
Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL,
Jameson JL, et all, editors. Harrisons principle of internal
medicine. 17
th
ed. USA: Mc Graw Hill medical, 2008.
Wyllie R. The digestive system. In Kliengman RM, berhman RE,
Jenson HB, stanton BF. Nelsons textbook of pediatrics. 18
th
ed. Philadelphia: WB saunders Co, 2007: 1521-645
Sondheimer JM, Sundaram S. Gastrointestinal tract. In Hay
WW, Levin MJ, Sondheimer JM, Deterding RR. Current
diagnosis & treatmentpediarics. 19
th
ed. New york: the
Mcgraw-Hill Co, 2009:557-608
Departemen Farmakologi dan Terapi. Farmakologi dan Terapi.
Edisi 5 Jakarta: Balai penerbit FKUI, 2007.
Sherwood L, Human phisiology. 5
th
ed. Belmont: Thomson
learning 2004.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Sick Sinus Syndrome in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionDokumen1 halamanSick Sinus Syndrome in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionDaniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Reading RadioDokumen20 halamanJurnal Reading RadioDaniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- Sick Sinus Syndrome in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionDokumen1 halamanSick Sinus Syndrome in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionDaniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- ChecklistDokumen1 halamanChecklistDaniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- Group 12 Case 2bDokumen52 halamanGroup 12 Case 2bDaniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- JNC 8 Guideline Algorithm for Treating HypertensionDokumen2 halamanJNC 8 Guideline Algorithm for Treating HypertensionTaradifaNurInsi0% (1)
- Grading of Angina PDFDokumen1 halamanGrading of Angina PDFndre_bocchaanBelum ada peringkat
- Studying for the Cardiology BoardsDokumen20 halamanStudying for the Cardiology BoardsDaniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- Get That Cow Milk Away From Me, Please... !!: Oleh: Kelompok 12 Fasilitator: Dr. Agus SapoetraDokumen60 halamanGet That Cow Milk Away From Me, Please... !!: Oleh: Kelompok 12 Fasilitator: Dr. Agus SapoetraDaniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacotherapy of AsthmaDokumen40 halamanPharmacotherapy of AsthmaThediDarmaWijayaBelum ada peringkat
- When "Warteg" Gives Him More: Group 7Dokumen46 halamanWhen "Warteg" Gives Him More: Group 7Daniel Hans JayaBelum ada peringkat
- Kerley B Lines Pulmonary EdemaDokumen7 halamanKerley B Lines Pulmonary EdemaDaniel Hans Jaya100% (1)
- Kerley B Lines Pulmonary EdemaDokumen7 halamanKerley B Lines Pulmonary EdemaDaniel Hans Jaya100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- General Surgery OME PDFDokumen25 halamanGeneral Surgery OME PDFNathan Korean KimBelum ada peringkat
- JCC ECCO Endoscopy Consensus 11 2013 FINAL PDFDokumen37 halamanJCC ECCO Endoscopy Consensus 11 2013 FINAL PDFTikejdit BoukhamBelum ada peringkat
- Naskah PublikasiDokumen12 halamanNaskah PublikasiMuhammad Abdul AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Gastritis 180122045533Dokumen16 halamanGastritis 180122045533Manish SapkotaBelum ada peringkat
- Swallowing Disorders 2022Dokumen29 halamanSwallowing Disorders 2022Mohammed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Dr. Evelyn Angie M. BiomedDokumen36 halamanInflammatory Bowel Diseases: Dr. Evelyn Angie M. BiomedAnnisBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Colonic Diverticulitis: Annals of Internal MedicineDokumen16 halamanAcute Colonic Diverticulitis: Annals of Internal MedicineOscar F RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Sigmoid Volvulus Journal ReadingDokumen7 halamanSigmoid Volvulus Journal ReadingLiza MPBelum ada peringkat
- Gastrointestinal Root WordsDokumen4 halamanGastrointestinal Root WordsPaula McAuliffeBelum ada peringkat
- DuodenitisDokumen3 halamanDuodenitisAhmad MaulanaBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Pancreatitis 1Dokumen21 halamanChronic Pancreatitis 1Bala DhanaBelum ada peringkat
- Skills Enema AdministrationDokumen16 halamanSkills Enema AdministrationFreida Michelle BonnitBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Pathology QuestionsDokumen19 halamanOral Pathology QuestionsBhoomikaBelum ada peringkat
- Kharkov National Medical University Course on Acute CholecystitisDokumen4 halamanKharkov National Medical University Course on Acute CholecystitisslyfoxkittyBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Intestinal Obstruction (01) PPTDokumen75 halamanLecture Intestinal Obstruction (01) PPTseptiandwirismianto88% (33)
- Effects of ginger aromatherapy on reducing nausea and vomiting in pregnant womenDokumen7 halamanEffects of ginger aromatherapy on reducing nausea and vomiting in pregnant womenLastri Khairin100% (1)
- Netter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 10Dokumen6 halamanNetter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 10Panagiotis SouldatosBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenterology: Diseases of The EsophagusDokumen18 halamanGastroenterology: Diseases of The EsophagusKayeshiana30Belum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Tuberculosis PDFDokumen54 halamanAbdominal Tuberculosis PDFNashif RayhanBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive Trans 2Dokumen30 halamanDigestive Trans 2Ericson CandelariaBelum ada peringkat
- Komplikasi Operasi HemorrhoidDokumen28 halamanKomplikasi Operasi HemorrhoidVelrones TampubolonBelum ada peringkat
- Tejas - Expert Ayurveda - Search - Feb 23Dokumen130 halamanTejas - Expert Ayurveda - Search - Feb 23Priya AswaniBelum ada peringkat
- Colon Resection Procedure and Post-Op GuidelinesDokumen10 halamanColon Resection Procedure and Post-Op GuidelinesAaramBelum ada peringkat
- Colon, Rectum & AnusDokumen6 halamanColon, Rectum & AnusLeikkaBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal LFTsDokumen2 halamanAbnormal LFTsRenu RosyBelum ada peringkat
- GERD – Definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology and diagnostic investigationsDokumen132 halamanGERD – Definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology and diagnostic investigationsSorana VasilescuBelum ada peringkat
- Osce AbdomenDokumen33 halamanOsce AbdomenistiBelum ada peringkat
- (2011) Prevalence of Crohns Disease in Endoscopic Unit RSCM PDFDokumen4 halaman(2011) Prevalence of Crohns Disease in Endoscopic Unit RSCM PDFfikriafisBelum ada peringkat
- Mouth and oral cavity conditionsDokumen5 halamanMouth and oral cavity conditionsFan EliBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan PasienDokumen248 halamanLaporan Pasiennasita kristianaBelum ada peringkat