THANATOLOGY - Study of Death
Diunggah oleh
Virendar Pal Singh50%(2)50% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
132 tayangan104 halamanThanatology is the branch of science that deals with the study of death. It examines the cessation of life through the permanent and irreversible failure of the nervous, circulatory, and respiratory systems. The diagnosis of death focuses on determining irreversible brain damage through tests demonstrating the absence of brain stem reflexes. Post-mortem changes that occur after death include algor mortis (cooling of the body), lividity (pooling of blood in the lower areas of the body), and rigor mortis (stiffening of muscles). These signs are important for medico-legal investigations to determine cause, manner, and time of death.
Deskripsi Asli:
Medicolegal aspects of death.
Judul Asli
Thanatology
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThanatology is the branch of science that deals with the study of death. It examines the cessation of life through the permanent and irreversible failure of the nervous, circulatory, and respiratory systems. The diagnosis of death focuses on determining irreversible brain damage through tests demonstrating the absence of brain stem reflexes. Post-mortem changes that occur after death include algor mortis (cooling of the body), lividity (pooling of blood in the lower areas of the body), and rigor mortis (stiffening of muscles). These signs are important for medico-legal investigations to determine cause, manner, and time of death.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
50%(2)50% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
132 tayangan104 halamanTHANATOLOGY - Study of Death
Diunggah oleh
Virendar Pal SinghThanatology is the branch of science that deals with the study of death. It examines the cessation of life through the permanent and irreversible failure of the nervous, circulatory, and respiratory systems. The diagnosis of death focuses on determining irreversible brain damage through tests demonstrating the absence of brain stem reflexes. Post-mortem changes that occur after death include algor mortis (cooling of the body), lividity (pooling of blood in the lower areas of the body), and rigor mortis (stiffening of muscles). These signs are important for medico-legal investigations to determine cause, manner, and time of death.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 104
THANATOLOGY
Thanatos = Death Logos = Science
Branch of Science that deals with Study of Death.
Death = Cessation of Life
Permanent & Irreversible cessation of 3 Vital Systems
Nervous,
Circulatory
Respiratory
If any of these 3 systems fail - other two also fail
Tripod of Life
Criteria for Declaration of Death - Brain Death
Resp. & circulation can be maintained artificially.
Irreversible brain damage occurs during the
period of transient stoppage of resp. /circulation.
Irreversible brain damage Body in Vegetative form
THANATOLOGY
Why Declaration of Death is important ?
Cremation
Organ Transplantation
BRAIN DEATH
Diagnosed by the following tests.
1. Absence of corneal reflex.
2. Dilated & Fixed Pupils - NOT reacting to light.
3. Absence of Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex.
4. Absence of Cranial Motor Nerve response to Pain
5. Absence of Cough Reflex.
6. Test withdrawal of ventilator results in Stoppage of resp.
Death may be divided into
1. Somatic Death
2. Molecular Death
SOMATIC / SYSTEMIC / CLINICAL DEATH
Death of the Body as a whole
Soma = Body
During Somatic death life is present at tissues & cells
When tissues & cells die, it is termed as Molecular /
Cellular death.
CELLULAR / MOLECULAR DEATH
Death at cellular level - Occurs in parts
Nervous tissue 5 mts,
Muscles about 3-4 hrs.
Organ which needs more blood supply during life
die early due to lack of circulation.
Death is a Process - Occur in stages
First somatic death
followed by
Molecular death
DIAGNOSIS OF SOMATIC DEATH IS DIFFICULT IN:
1. Soon after Death (body is warm).
2. Suspended Animation.
3. Coma due to Sedatives / Hypnotics.
4. Hypothermia.
5. Electrocution
6. Drowning.
MODES OF DEATH
Abnormal Physiological State at the time of death
1.Coma 2.Syncope 3. Asphyxia
Coma
Death due to irreversible damage of vital centers of brain
Coma may occur due to:
Raised Intra-cranial pressure.
Poisons (Opium, Alcohol).
Metabolic disorders (uremia)
SYNCOPE (MODE OF DEATH)
Failure of functions of heart.
It may occur due to:
Heart Disease.
Hemorrhage
Pathological condition of Blood.
Cadio-toxic Poisons (Digitalis, Aconite, Oleander)
ASPHYXIA (MODE OF DEATH)
Failure of Resp. System
It may occur due to:
Occlusion of Air passages.(hanging, strangulation)
Breathing of irrespirable gases.
Traumatic Asphyxia.
Disease of Resp. System (Pneumonia)
Paralysis of Resp. center (Opium poisoning)
Manner of
Death
UNNATURAL
Homicidal Suicidal Accidental
NATURAL
Related to
circumstances
at the site of
Death
SIGNS OF DEATH
Immediate Signs (Signs of Somatic death)
1. Insensibility & loss of EEG rhythm.
2. Cessation of CIRCULATION
3. Cessation of RESPIRTION
SIGNS OF DEATH
Early Signs (Signs of Molecular death)
(with in 12-24 hrs)
1. Cooling of Body - ALGOR MORTIS
2. Changes in the Eye.
3. Changes in the Skin.
4. Post mortem Lividity.
5. Changes in the Muscles.
SIGNS OF DEATH
Late Changes (Occurs about 24 hrs after death)
1. Decomposition
2. Modification
I. Adipocere/ Saponification
II. Mummification
IMMEDIATE SIGNS
1. Insensibility & Loss of EEG rhythm.
Loss of sensation - touch, pain, temp.
Loss of Voluntary power to move
Loss of Reflexes.
May occur due to Vagal Inhibition, Epilepsy, Drowning.
Become conclusive if Loss of EEG rhythm for 5 mts.
2. Cessation of CIRCULATION
Heart sounds - Not heard - for 5mts.
Flat ECG for 5mts.
Not Conclusive
of Death
IMMEDIATE SIGNS
3. Cessation of RESPIRATION
Absence of breath sounds continuously for 5mts.
Resp. may stop in a living person:
1.Voluntary act
2. Drowning
3. New Born Infant
Cooling of Body / Algor Mortis
Algor = Coldness Mortis = Death
After Death Heat Production - Stops
Heat Loss - Continues
THANTOMETER
Records temp. of Dead body
Chemical thermometer
25 cm long, marked 0-50C
Inserted in the Rectum 8-10 cm deep for 2-3 mts or
in to the Abdomen (under Liver) by making a slit.
ALGOR MORTIS
Iso-thermic Phase
After death - Body temp. remains Unchanged - For 45 mts
Takes some time for Temp. Gradient to be created
b/w Inner core & Body surface
SIGMOID / INVERTED S
B
o
d
y
T
e
m
p
.
Time Since Death
Rate of Cooling
In 1
st
2 hrs
Rate of Fall in temp = Half the difference b/w body temp
& the surrounding
In Next 2hrs temp falls at Half of the above rate.
Thereafter temp falls slowly till the equilibrium.
In Tropical countries (India) - Avg. heat loss 0.5-0.7C / hr
Body attains Env Temp in - About 16-20 hrs.
Time Since Death = Normal Body Temp Rectal temp
Avg. Rate of fall in Temp / hr
Normal body temp = 37.2 C
Avg. rate of fall of temp / hr = 0.6
Post Mortem Caloricity
Increase in Body Temp during first few hrs after death
Sun stroke, Pontine Hm (Heat regulation mechanism - Disturbed)
Tetanus & Strychnine poisoning
Acute Viral / Bacterial Infection: Lobar Pneumonia, Typhoid.
Rate of Cooling depends upon
Age-
Children, Adults of small stature - Cool rapidly (large body surface)
Condition of the body
Lean bodies - Cool rapidly ; Obese bodies - Cool slowly
Sex
Females - Cool slowly (more subcutaneous fat)
Mode of Death
Sudden death in Healthy person - Cools Slowly
Asphyxia, Lightning, CO poisoning Cools Slowly.
Wasting disease Cools rapidly.
Rate of Cooling depends upon
Surroundings
Well ventilated room- Body Cools rapidly
Under water - Body cools rapidly
Body covered with clothes / lying in bed - cools slowly
Env. Temp
Temp diff. b/w env & body is more - Body cools rapidly
Skin Changes
Pale, ashy white, loose translucency.
Postmortem Staining / Lividity / Hypostasis /
Suggilation / Vibices / Livor Mortis
Discoloration or Staining of skin & organs
Reason - Accumulation of bld in dependent body parts
distending the toneless capillaries & veinules
Starts - within an hour after death
Mottled patches on dependent parts within 1-3 hrs
Patches coalesce in about 3-6 hrs.
Fixation of PM Staining
Position of body changed - Lividity will not change
Stagnation of blood in Distended & Toneless capillaries
Inability of bld to flow from toneless capillaries
Staining of tissues due to diffusion of Hb
Rigor mortis in the surrounding muscles
NOT due to - Blood Coagulation
Distribution & Fixation of Lividity helps to determine:
Position of dead body
Time since death (more than 8 hrs)
Hanging - PM Staining on
Dependent Lower limbs
External Genitalia &
Lower part of Forearms & Hands.
Drowning - PM Staining on
Head & Upper parts of Body
(Body floats with face downwards)
If body is in moving water (river) Staining may not
develop
Areas of Contact Flattening
Lividity is absent
Pressure of the body occlude toneless capillaries.
Supine position - Areas of contact flattening
Back of shoulders
Gluteal region
Back of calves.
Skin underneath Tight clothes - Lividity absent.
Tight collar around Neck - White band
- mistaken as strangulation mark
Extent of Lividity depends on
- Vol. of blood in circulation
- duration for which blood remains liquid after death.
Excessive Bleeding - Lividity is limited in extent.
CCF - Blood vol. Increase - Lividity is marked
Color of Lividity depends on :-
Color of blood
Cause of death
Normal color of Lividity
initially Bluish Pink
afterwards Bluish Purple
Hemorrhage & Anemia- it is very faint.
Asphyxia - Lividity is prominent & purple
(bld is mainly Venous & do not clot Readily)
Lobar pneumonia - Lividity is less obvious.
(bld. Coagulates rapidly)
CO Poisoning, Burns, Hypothermia --Bright cherry Red
KCN---------------------Pink
Phosphorus-----------Dark Brown
HS----------------------Bluish Green
Nitrites-----------------Reddish Brown
Potassium Chlorate---Chocolate Brown
LIVIDITY
CONGESTION
Cause Capillary & Small Vein
distension with blood
Pathology in the
organ
Situation Dependent Body parts whole organ diffusely
Cut Surface Oozing of blood from
distended capillaries
Exudation of fluid
mixed with blood
Swelling &
Exudation
Nil May be present
Mucous
membrane
Normal Dull & lusterless
(due to inflammation)
Hollow organs -
stretched
Alternate Stained &
Unstained Areas
Uniform Staining
Nature of change Postmortem Ante mortem
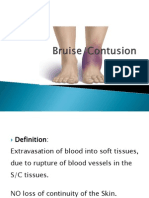
LIVIDITY BRUISE
Situation Dependent body parts Situated anywhere.
Tissue level Epidermal Sub epidermal
surface Not elevated Surface slightly elevated
margins Clearly defined Diffuse
Color Uniform in color Changes with Time
Cause
Distension of capillaries & veins
with blood
Extravasation of blood from
capillaries
Nature of
change
Postmortem Ante mortem
Effect if
Pressure
Pressed spot appears blanched
if PMS not fixed
No color change
Cut Surface Oozing of blood from
distended capillaries which
can be easily washed away
Extravasation of blood in
the surrounding tissue
which can not be
washed away easily
M/E
Blood is found within the Bld.
Vessels.
Blood is found outside the
Bld. Vessels.
MLI
Suggest time since death &
Position of the dead body
Suggest nature of injury &
weapon used
MEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF PM STAINING
1. Reliable Sign of death.
2. Position of body at the time of death & whether position has
been changed.
3. Time since Death.
4. Cause of death (Color).
5. Manner of death (distribution)
6. Mistaken as - Bruise / Pathological condition
Muscle Changes
Primary Relaxation
Immediately after death
Muscles still react to external stimulus
Lower jaw - Droops,
Intraocular tension - Falls, Pupils - Dilate
Muscles - Soft & Flabby, Joints - Flexible.
Sphincters - Relax (incontinence of urine & faeces).
Rigor Mortis
Shortening, Stiffening & Opacity of muscles.
Mechanism of Rigor Mortis
During Life
in Relaxed State
Actin & Myosin interdigitate to a lesser extent
Muscles - Soft & Extensible ( due to presence of ATP)
During Movement
Actin & Myosin interdigitate to greater extent
ATP is converted to ADP & Energy
After Death
Continuous breakdown of ATP
Re-synthesis of ATP occurs till Glycogen is available.
Once glycogen is exhausted - ATP is depleted
Muscles lose Softness, Elasticity & Extensibility.
Fusion of Actin & Myosin into a Dehydrated Gel
Ph of Muscle changes from Alkaline to Acidic (lactic acid).
ONSET OF RIGOR MORTIS
Tested by - Gently bending the joints.
Present in - Voluntary & Involuntary Muscles.
Occurs earlier in - Involuntary muscles.
Does not depend on - Nerve Supply of the muscle
ONSET OF RIGOR MORTIS
Amongst Involuntary muscles - appears in Heart within an hour
Voluntary muscles
Muscles of Eyelids------------3-4 hrs
Muscles of Face----------------4-5 hrs
Neck & Trunk--------------------5-7 hrs
Muscles of Upper limbs------7-9 hrs
Muscles of Lower limbs-----9-11 hrs
Small muscles of Fingers & Toes--11-12 hrs
Disappears in the same order in which it appears
Disappears due to - Autolysis of muscle proteins.
CUTIS ANSERINA (Cutis= Skin Anser =Goose)
RM of Erector Pillae muscles of Skin
Granular Puckered appearance - GOOSE SKIN
Skin papillae stand out prominently with hair standing on end.
Also occurs if - Body is exposed to Cold.
PERIOD OF STAY OF RIGOR MORTIS
It starts in 2-3 hrs after death
Takes about 12 hrs to develop
(from Head to Toe)
Persist for another 12 hrs &
takes about 12 hrs to pass off
Features Observed During RIGOR MORTIS
Partial emptying of heart.
Pupils -Constricted (RM of Iris muscle)
Postmortem delivery.
Rule of 12
Factors Influencing RIGOR MORTIS
(1) AGE
Fetus < 7 month IUL R M does not develop
Fetus > 7month IUL develops & passes off Quickly.
Children & Elderly Develops & passes off Quickly.
(2) PHYSIQUE
Weak Musculature ---- Develops & disappears Quickly
Strong Musculature ---- Develops & disappears Slowly
(3) TEMPERATURE
Develops & Passes off quickly at High temperature.
Develops & disappears Slowly at low temperature.
Factors Influencing RIGOR MORTIS
(4) Exhaustive disease / Convulsions
RM appears & Passes off early.
(5) Death due to Drowning
Appears early due to muscular exhaustion BUT
Lasts longer due to coldness of water.
(6) Septicemia
Rigor Mortis may be absent due to septicemia
MedicoLegal Importance of Rigor Mortis
1. Sure sign of Death.
2. Time since Death.
3. Position of Body at the time of Death &
whether it has been altered after rigor mortis has set in.
4. It may be confused with
Cadaveric Spasm
Heat Stiffening
Cold Stiffening
Gas Stiffening
Conditions Simulating Rigor Mortis
Cold Stiffeness
Extreme Cold for Sufficient Period - Stiffness occurs
(Freezing of Body Fluids &
Hardening of S/C Fat
If kept at Atm. Temp. for sometime - Body becomes Flaccid
After that RM appears.
Gas Stiffening:
Accumulation of Putrefactive Gas in the tissues.
Other putrefactive changes
Cadaveric Spasm / Instantaneous Rigor
Stiffness of Muscles - Immediately after Death
NOT preceded by Primary Relaxation
Preconditions for Cadaveric Spasm
1. Extremely Rapid Death.
2. Great Emotional Stress.
3. Muscles in great physical Activity
Cadaveric spasm - a Vital Phenomenon - Starts immediately before death -
Persists after death - without Primary Relaxation -
Obscure Reason
Other Muscles Undergo Primary Relaxation
Passes off due to decomposition of Muscles
MEDICOLEGAL IMPORTANCE OF CADAVERIC SPASM
Indicates Sudden Death
Emotional Stress and
Physical activity of Muscles at the time of death.
It may indicate - Manner of death.
Suicide - knife/pistol - Found tightly clenched in the hand
Drowning Vegetation / other objects underneath water-
found tightly clenched in hand.
Homicide - Part of Cloth or Hair of the assailant
found in the clenched hand
Secondary Relaxation
RM disappears Muscles become Soft & Flaccid.
Does NOT respond to - Mechanical / Chemical Stimuli.
Muscle Reaction - Again becomes Alkaline.
Secondary Relaxation - Coincides with Onset of Decomposition
PUTRERFACTION / DECOMPOSITION
Last stage of Resolution of Body from - Organic to Inorganic
1) Autolysis 2) Bacterial Action
1. Autolysis = Self Destruction
Enzymes released from Cells -- Liquefy the tissues.
Starts 3-4 hrs after death - Continues steadily for 2-3 days.
2. Bacterial Action
Aerobes & Anaerobes.
Cl. Welchii, Streptococci, E. Coli, B. proteus
Cl. Welchii produce lecithinase - Hydrolyse lecithin of Cell Memb.
Warmth
Moisture
Air accelerates decomposition (Bacterial Growth)
During Life - Organisms are within the large intestine
After Death Org enter Bld. vessels & Spread throughout the Body
Features of Putrefaction
1
st
External Sign - Greenish Discoloration of skin over
Caecum & Flanks
Internal Sign - Under Surface of Liver
(bowel contents - More fluid & Full of Bacteria)
Bacterial Action -- Blood is hemolysed (Hb is released)
-- H
2
S is produced
H
2
S acts on Hb Sulph-metaemoglobin
Features of Putrefaction
Color change over the Caecum & flanks - Appear in 12-24 hrs.
Discoloration Spreads to - Front of Abdomen & External
Genitals.
Patches appear on other Body parts
Whole Body is discolored in next 24 hrs.
Marbling
Veins of Root of Neck, Shoulders & Groins - Visible as Bluish or
Greenish lines
form a mosaic or arborescent pattern known as MARBLING.
Staining of vessel wall by pigments released from decomposed bld
Starts after about 24 hrs of death
prominently seen in 36-48 hrs.
FOUL SMELLING GASES
Simultaneously with the Color change
H
2
S, Ammonia, Methane
Gases accumulate in - S/C tissue, Hollow Viscera &
eventually Solid Viscera.
12-18 hrs Abdomen - Distended.
18-36 or 48 hrs - Gas formation - Abundant - Rigidity Body
Pressure Effect of Gases
1. Bloating of Features
About 36 hrs
Face Swollen, Discolored - Identification impossible
Eyes - Bulge out.
Tongue Black, Protrude Out - mistaken for Strangulation
Breasts - Enormously Swollen.
In 48-72 hrs
Rectum - Protrudes.
Body Surface Expands
Splitting of Skin
Pressure marks - Form previously Well Fitting Clothes
Mark on Neck - Mistaken for Strangulation.
Shifting of PM Staining
Pressure of Gases leads to - Displacement of PM staining
Blood Clots Liquefy (due to decomposition)
Changes in Skin, Hair & Wounds
Putrefactive Blisters/ Blebs (36-48 hrs)
Contain mainly Gas, Little reddish fluid.
Vital Reaction - Absent
If Blister breaks - Patch of Raw Skin - similar to Scald.
Skin gets denuded.
Bruises & Abrasions - become Unrecognizable
Changes in Skin, Hair & Wounds
48-72 hrs
Skin of Hand & Feet - Peel off like Glove & Stocking
Hair - Loose & can be Pulled out easily.
Ante mortem & Postmortem Wounds Oozing of blood
Post mortem Bleeding
Extrusion of Fluid from Nose & Mouth
Gases in Abdomen - Diaphragm is forced upwards
Compress the Lungs & Heart
Blood stained Froth oozes from Nose & Mouth.
Stomach contents - Forced out - Enter the Larynx - Lungs
Stomach contents beyond Secondary Bronchioles indicate -
Inhaled food particles are Ante-mortem in origin (Aspiration)
Emptying of Heart
Upward pressure of Gases on Diaphragm - Chest Compression
Changes in Genitals
After 36 hrs
Genitals - Enormously Swollen
- Oozing of Blood tinged fluid - Mistaken as Sexual Assault
In about 48-72 hrs
Cervix & Uterus Protrude
Pregnant female - Fetus may be Expelled (Postmortem Delivery)
APPEARANCE OF MAGGOTS
Flies are attracted to the Decomposed Body
Flies Lay Eggs ------------------------------18-36 hrs.
Eggs hatch into Maggots (Larva)-------24 hrs
Larvae develop in to Pupae-------------- 4-5 days
Pupae develop in to adult Flies ----------4-5 days
OTHER CHANGES
3-7 days
Teeth - Loose & may fall out.
Skull Sutures in Children - Loose & liquefied brain ooze out
5-12 days
Colliquative Putrefaction begins
Tissues become Soft - Get converted to Semi fluid Black Mass
Abdomen Bursts - Stomach & Intestines Protrude
Soft Tissues separate from Bones.
Body is Skeletonized: 1-3 months.
Bones start decomposing in
1 year in bodies buried - without coffin
3-10 yrs in bodies - Laid in coffins.
Decomposing bones loose wt., become fragile
Bone - Totally destroyed in 10-25 yrs.
Bodies lying exposed on Ground may be skeletonized in <24hrs
Organs which putrefy early (1-2 days)
Organs which putrefy late (2-3 wks)
FACTORS Modifying Decomposition
External Factors
Temperature
At Freezing point - Putrefaction will NOT occur
Starts at 10 C.
Ideal Temp. is 37 C.
At High temperature - Putrefaction is Retarded.
Clothing
Initially - Favors Putrefaction (maintains Body temp)
Later stage - Slows down decomposition
Protects body from Flies & Insects.
External Factors
Moisture
Bodies recovered from Water - Decompose faster
Organs with High moisture - Putrefy faster (Brain)
Air
Presence of Air - Promotes decomposition
Absence of Air - Retards decomposition.
Manner of Burial
Body in Air Tight Coffins Decomposition Retarded.
Bodies buried without Coffins - Decompose Very Fast,
Deep Grave - Putrefy Slowly (Exclusion of Air)
In Water logged Clay soil - Adipocere formation
In Sand & Porous Soil - Mummification
Internal Factors
Age
New Born / Still Born Sterile -Putrefaction occurs only from
invasion of external Organisms
In Adults - It starts from within the body to Outwards.
Condition of the body
Fat & flabby body of Children - Putrefy Rapidly (plenty of moisture
Injured Body Part - Putrefy Early
Gravid & Post partum Uterus - Putrefy Early.
Gender
Little influence on decomposition.
Females dying after Child birth especially due to Septicemia
decompose Rapidly
Cause of Death
Septicemia Decompose Early
Wasting disease (Anemia, Malnutrition) - Putrefaction is retarded
Sudden Death in apparently Healthy person - Decompose slowly
Chronic Heavy metal Poisoning (Arsenic, Antimony) -
Decomposition is retarded (destroy bacteria)
Putrefaction in WATER
Decomposition - More pronounced over Head.
Completely Submerged in Water - Putrefies Slowly
(Exclusion of Air & Low Temp.)
On removal from Water - Bodies putrefy Rapidly (Increased Moisture)
Floatation of Body
Body floats in 1 day in Summers
2-3 days in Winters.
When body floats - Abdomen is Upwards & Spine is Downwards.
Time required for floatation depends on:
Age
New Born, Mature infants - Float Early
Still born or Immature infants Float Late
Sex
Females float sooner (More Fat)
Condition of the Body
Obese Bodies - Float Earlier.
Time required for floatation depends on
Season
Summers - Body floats early (warm water favors putrefaction)
Quality of water
Sea water (High Sp. Gravity) - Floats earlier
Pond (less water) Warmed by Sun rays Early
- Favor putrefaction - Float Early
ADIPOCERE / SAPONIFICATION
ADIPOS = Fat CERA = Wax
Conversion of Unsaturated Liquid Fats (Oleic Acid) to
Saturated Solid Fats (Hydroxy-Stearic Acid & Oxo-Stearic Acid)
by Bacterial Fat Splitting Enzymes (Clostridium)
Properties resemble - Fat & Wax.
Yellowish White,
Greasy,
Wax like,
Rancid smell.
Floats on Water
ADIPOCERE / SAPONIFICATION:
Favors Adipocere formation
Moisture,
Warmth &
Relative Diminution of Air
Cuts Easily, Burns with Yellow Flame
Offensive smell (ammonia & sulphur)
Fresh Adipocere - Soft & Moist
Old - Dry & Brittle.
Involves - Hydrogenation & Hydrolysis of Body Fats.
Occurs at Fatty areas of Cheeks, Breasts, Buttocks, Abdomen
Moisture is derived from - Body tissues (which becomes dry)
In drowning moisture is derived from - Outside Water
- Body tissues are not dehydrated
In Summers
Shortest period required for Adipocere formation 3 wks
Adipocere of a Limb 3-6 wks
Adipocere of Whole body 1 Yr
Medico-Legal Importance
1. Identification (External features are preserved)
2. Cause of Death (injuries are recognizable)
3. Time since Death
4. Indicates place from where body has been recovered
Mummification
Decomposition stops and Body undergoes Mummification
Dehydration / Desiccation of Tissues & Organs due to loss of moisture
Body - Shriveled, Odorless, Dark Black.
Skin is Hard, Dry, Leathery ,
Adheres closely to Shrunken Body.
Organs are Dark Brown / Black, blended together as a Single Mass.
Preservation of features of the Body
Injuries are also Identifiable
Mummification
High Temperature
Absence of Moisture
Air Circulation
Bodies buried in Hot, Dry Soil (Deserts)
Chronic Arsenic / Antimony Poisoning.
Exposed Body parts (Lips, Fingers, Toes) - Mummify first
Time required for complete Mummification 3m- 1yr.
Favors
Mummification
Medico-legal Importance
Identification (External features are preserved)
Cause of Death (injuries are recognizable)
Time since Death
Indicates place from where body has been recovered.
Embalming
Dead Body can be mummified artificially known as Embalming.
Inj. Formaldehyde / Sol. of Lead Sulphide & Potassium Carbonate
in the Femoral Artery, Aorta & Carotids
Done to preserve the Dead Body
for Anatomical Dissection
for Transportation to a long distance
Time Since Death / Post Mortem Interval
Interval between death and postmortem examination.
Extremely important for Crime Investigation.
IO is more concerned in Time of Occurrence of incident
Once TSD is known then by finding the Age of injuries
time of occurrence of incident can be calculated.
Time Since Death / Post Mortem Interval
Physical Changes
1. Stoppage of
CNS, CVS
& Resp. System
2. Flaccid Muscles,
Loss of Skin Elasticity
Along with this
If Body is Still Warm &
without Permanent Haziness of Cornea
TSD will be within 1 hr in Summers
2 hrs in Winters
3. Cooling of the Body
Tropical Countries (India) - Avg Heat Loss 0.5 to 0.7
0
C/ hr
Body attains Env. Temp in 16- 20 hrs
Rate of Cooling - NOT Uniform
More helpful in Temperate Countries
4. Eye Changes
Corneal Opacity - Does NOT give Satisfactory results
Retinal Changes Reliable
5. PM Staining
More Reliable Factor
NOT dependent on many factors (Temp, Humidity, Musculature)
More Reliable during - Early phase
6. Rigor Mortis
Most commonly used to find TSD.
If RM is present all over the Body - Wide Range is given
7. Putrefaction
Amongst Delayed changes - Best factor to find TSD.
Consider various Factors affecting Putrefaction
8. Adipocere & Mummification
Gives Vague idea about TSD
Gross range Days & Weeks
9. Stomach & Intestinal Contents
State of Digestion of Food Contents indicate
Interval between Death & Last meal
If Time of Last meal is known time interval between last
meal and death can be known.
Emptying Time of Stomach (Avg Indian Diet)
of the food passes out of Stomach in 45 to 60 min
of the balance by Next Hour
of the balance by 3
rd
hr
Complete Emptying in 4
th
hr
Carbohydrate Diet gets digested Earliest,
Proteins stay for longer period
Fatty Food empties Last
Emptying of Gastric contents is delayed in
Pyloric Stenosis,
Head Injury,
Unconscious,
Physical Exhaustion
Digested food Residue reaches
Hepatic Flexor of Large intestine ----6 to 8 hrs
Splenic Flexor ---------------------------- 9 to 10 hrs
Pelvic Colon ------------------------------ 12 hrs
10. URINARY BLADDER CONTENTS
Amount of Urine in Bladder - Time Since Last Micturation.
11.Growth of Facial Hair (in persons who regularly shave)
Rate of hair growth is 0.4 mm / day.
If Time of Last Shave is known - Time interval between Shave &
Death can be found.
B) CHEMICAL & BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN BLOOD
After Death - Blood Ph Falls
(Glycolysis, Glycogenolysis --- Lactic Acid & CO
2
Accumulate)
During Secondary Relaxation - Blood Ph Rises Again
(Ammonia accumulates due to Protein breakdown)
Soon after Death - Cl level of Plasma & RBC is Equal.
End of 3
rd
day
Cl level of Plasma - Drops to Half (extra Vascular diffusion)
Blood Mg - Rises 8 Times (diffusion from outside the vessels)
K level - Increase (diffusion from vascular endothelium)
Amino Acid & Non Protein N
2
- Increase after Death
BLOOD ENZYMES (Peak level in blood)
Amylase & Phosphorylase ---------- 36 to 48 hrs.
Transaminase -------------------------- 48 to 60 hrs
Lactic Dehydrogenase --------------- About 4
th
day
c) BIOCHEMICAL Changes in CSF:
Lactic acid , NPN , Amino Acid N
2
increases during
first 15 hrs after death { rise is not uniform}.
d) K+ Conc in Vitreous Humor
Linear relation between rise of k+ Conc. and PMI up to 100 hrs.
Suspended Animation / Apparent Death
Vital Functions of Body (HR,RR) are at such a Low Level
that they cannot be detected by
routine clinical examination.
It may persist for short period (few sec. to min)
It may occur in
New Born Babies, Barbiturate/ Opium overdose,
After anesthesia, Electrocution, Heat Stroke,
Drowning, Shock Prolonged illness (Typhoid)
Voluntarily by Yogis.
Patient can be revived by resuscitation.
In such doubtful cases, death should not be declared
without EEG and ECG record.
PRESUMPTION OF DEATH
Sec 107 IEA
In case of a missing person being alive or dead within 30
yrs, interested party has to prove his death.
SEC 108 IEA
If it is proved that
missing person has not been heard for 7 yrs by those
who would normally have heard of him (relatives) if he
had been alive
then such a person is presumed to be dead.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Quality ChecklistDokumen7 halamanQuality ChecklistVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Martin F Dsouza V Mohd Ishfaq PDFDokumen32 halamanMartin F Dsouza V Mohd Ishfaq PDFVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- PDF 1570500423846Dokumen15 halamanPDF 1570500423846Virendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Strategic Planning and Designing of A Hospital Disaster Manual in A Tertiary Care, Teaching, Research and Referral Institute in IndiaDokumen7 halamanStrategic Planning and Designing of A Hospital Disaster Manual in A Tertiary Care, Teaching, Research and Referral Institute in IndiaVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Kunal SahaDokumen210 halamanKunal SahaVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Medicolegal Book PDFDokumen21 halamanMedicolegal Book PDFVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Gift DeedDokumen4 halamanGift Deedalkaadatia100% (2)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hiv TestDokumen8 halamanHiv TestVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- BloodstainPatternsDokumen24 halamanBloodstainPatternsArif KusumawidjayaBelum ada peringkat
- Medicolegal Book ContentsDokumen5 halamanMedicolegal Book ContentsVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- DNR GuidelinesDokumen20 halamanDNR GuidelinesVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Artificial Insemination Act, DelhiDokumen5 halamanArtificial Insemination Act, DelhiVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- 36 TH Annual Conferenceof North Brochure FinalDokumen8 halaman36 TH Annual Conferenceof North Brochure FinalVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Medicolegal Book PDFDokumen21 halamanMedicolegal Book PDFVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Ins Malhotra V DR A KriplaniDokumen34 halamanIns Malhotra V DR A KriplaniVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Dr. Suresh Gupta Vs Govt. of N.C.T. of Delhi & Anr On 4 August, 2004Dokumen6 halamanDr. Suresh Gupta Vs Govt. of N.C.T. of Delhi & Anr On 4 August, 2004Virendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Forensic PsychiatryDokumen7 halamanForensic PsychiatryVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Medicolegal Book PDFDokumen21 halamanMedicolegal Book PDFVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Reduced oxygenation and asphyxia: causes, signs, and findings in hanging, strangulation, and throttlingDokumen99 halamanReduced oxygenation and asphyxia: causes, signs, and findings in hanging, strangulation, and throttlingVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Types, Causes, and Characteristics of BruisesDokumen20 halamanTypes, Causes, and Characteristics of BruisesVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Medicolegal Book ContentsDokumen5 halamanMedicolegal Book ContentsVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- DR - VP Singh - Medrecon (FINAL)Dokumen45 halamanDR - VP Singh - Medrecon (FINAL)Virendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Than A To LogyDokumen21 halamanThan A To LogyVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Forensic Medicine: Dr. Vpsingh Medicolegal ConsultantDokumen32 halamanForensic Medicine: Dr. Vpsingh Medicolegal ConsultantVirendar Pal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- OPD Network ListDokumen354 halamanOPD Network ListSHAIKH ABDUL AZIZ salim bashaBelum ada peringkat
- Covidsafe Application Privacy Impact AssessmentDokumen78 halamanCovidsafe Application Privacy Impact AssessmentMichael Smith100% (1)
- Newborn Care Volume 1 2020-1Dokumen192 halamanNewborn Care Volume 1 2020-1Shyvonne PeirisBelum ada peringkat
- Brosur Suction Pro 72Dokumen4 halamanBrosur Suction Pro 72Anonymous tbJ24554Belum ada peringkat
- Do Your Genes Make You A CriminalDokumen39 halamanDo Your Genes Make You A CriminalParisha SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Eo No. 013 - 2018 Reorganization of BhertDokumen2 halamanEo No. 013 - 2018 Reorganization of BhertAnne Kimberly Peñalba BabaanBelum ada peringkat
- DR Reddy'sDokumen28 halamanDR Reddy'sAbhinandan BoseBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- ASP ProductsDokumen33 halamanASP ProductsSerghei Barba100% (1)
- Everett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookDokumen46 halamanEverett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookJessica OlsonBelum ada peringkat
- Regional Studies in Marine ScienceDokumen11 halamanRegional Studies in Marine ScienceBOUCHNANBelum ada peringkat
- Remote Working A Dream Job British English Advanced c1 c2 GroupDokumen5 halamanRemote Working A Dream Job British English Advanced c1 c2 GroupNick ManishevBelum ada peringkat
- Stericon Plus BioindicatorDokumen4 halamanStericon Plus Bioindicatorupt labkeswanbaliBelum ada peringkat
- Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes To Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) CourseDokumen11 halamanSuccess Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes To Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) CourseanthonyBelum ada peringkat
- Healy Professional DeviceDokumen1 halamanHealy Professional DeviceBramarish KadakuntlaBelum ada peringkat
- Article Text Batuk EfektifDokumen7 halamanArticle Text Batuk EfektifWelang 102Belum ada peringkat
- Benign Breast DiseaseDokumen26 halamanBenign Breast DiseaseMedicine 0786Belum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- HSE List of PublicationsDokumen12 halamanHSE List of PublicationsDanijel PindrićBelum ada peringkat
- Adult Health - Soap Note 5Dokumen3 halamanAdult Health - Soap Note 5api-546259691100% (3)
- Enemies of BeerDokumen24 halamanEnemies of Beerpana0048100% (1)
- Function: What Is The Skeletal System?Dokumen6 halamanFunction: What Is The Skeletal System?Mr. Christian ParabuacBelum ada peringkat
- Maharashtra State Bams Private Colleges Fess.Dokumen2 halamanMaharashtra State Bams Private Colleges Fess.Bhavesh RajpurohitBelum ada peringkat
- Posters Whofic 2020Dokumen107 halamanPosters Whofic 2020Kristel HurtadoBelum ada peringkat
- PIDSR Other DiseasesDokumen45 halamanPIDSR Other DiseasesMichelle TuraBelum ada peringkat
- Emotional Dysregulation in Adult ADHD What Is The Empirical EvidenceDokumen12 halamanEmotional Dysregulation in Adult ADHD What Is The Empirical EvidenceVo PeaceBelum ada peringkat
- The Cell Cycle and Cancer WorksheetDokumen3 halamanThe Cell Cycle and Cancer WorksheetAngie Pyatt KarrakerBelum ada peringkat
- Use of Essential Oils Following Traumatic Burn Injury A Case StudyDokumen12 halamanUse of Essential Oils Following Traumatic Burn Injury A Case StudyShandaPrimaDewiBelum ada peringkat
- IFUk en 310250 07 PDFDokumen14 halamanIFUk en 310250 07 PDFKhaled AlkhawaldehBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 3rd ESO Full DossierDokumen54 halamanBiology 3rd ESO Full DossierNinaBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis-Android-Based Health-Care Management System: July 2016Dokumen66 halamanThesis-Android-Based Health-Care Management System: July 2016Noor Md GolamBelum ada peringkat
- Stefan White, Andrew Sinclair (Auth.), John M. Hutson, Garry L. Warne, Sonia R. Grover (Eds.) - Disorders of Sex Development_ an Integrated Approach to Management-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (20Dokumen327 halamanStefan White, Andrew Sinclair (Auth.), John M. Hutson, Garry L. Warne, Sonia R. Grover (Eds.) - Disorders of Sex Development_ an Integrated Approach to Management-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (20Aakanksha MehtaBelum ada peringkat