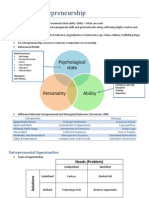
2-Types of Entrepreneurship
Diunggah oleh
SaadiahMansurHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2-Types of Entrepreneurship
Diunggah oleh
SaadiahMansurHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MODULE 2
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Objectives
To disseminate and intensify knowledge on the different types of entrepreneurship
and entrepreneurs.
To differentiate the differences based on entrepreneurial activities as well as the
functions assumed by the entrepreneurs.
Learning outcomes
Classify the types of entrepreneurship and entrepreneurs into proper context without
any difficulty.
Differentiate and articulate the different types of entrepreneurship and
entrepreneurs that exist in the current entrepreneurship literature.
Explain the differentiating factors based on based on the respective entrepreneurial
activities and functions of the entrepreneurs.
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Topics
Introduction
Entrepreneurship Versus Entrepreneur
Types of Entrepreneurship
Types of Entrepreneurs
Summary
INTRODUCTION
Entrepreneurship is a process of identifying
the opportunity, converting the opportunity
into marketable products or services using
creative and innovative means, and through
the process creates value and wealth to the
society.
Entrepreneurs are individual who undertake
entrepreneurial process
ENTREPRENEURSHIP VERSUS
ENTREPRENEUR
Entrepreneurship refers
to an entrepreneurial
process
Entrepreneur is the
individual that executes
the process.
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP
1) Corporate
Entrepreneurship
2) Private or
independent
entrepreneurship
3)
Intrapreneurship
4) Social
entrepreneurship
5) Public Sector
Entrepreneurship
6) Academic
Entrepreneurship
1) Corporate Entrepreneurship
Refers to the entrepreneurial activities carried
out in large corporations.
Large companies have to continually expand
and diversify their entrepreneurial activities in
order to sustain their existence by creating
new products or services to their customers.
Entrepreneurial activities in the corporate
setting can be seen at different stages or
scopes.
2) Private or independent
entrepreneurship
Refers to entrepreneurship activities of private
or independent firms where the
entrepreneurship process is most prevalent.
Independent entrepreneurship contributes to
the nations economy in terms of providing
jobs and value added initiatives.
3) Intrapreneurship
Innovative corporate management strategy that
encourages employees within an organization to
create new product ideas.
Often associated with larger companies that have
taken notice of the rise in entrepreneurial activity
in recent years
These firms endeavour to create an environment
wherein creative employees can pursue new
ways of doing things and new product ideas
within the context of the corporation
4) Social entrepreneurship
Refers to the entrepreneurial activities carried
out by social enterprises, NGOs and charitable
organizations.
Involves recognition of a social problem and the
application of the entrepreneurial approach to
organize, create and manage a venture to achieve
the social objectives or social ROI (return on
investment).
Eg economic- based social entrepreneurship is
Grahmeen Bank in Bangladesh
5) Public Sector Entrepreneurship
Refers to entrepreneurial activities carried out
by government-linked companies (GLCs) or
state-owned enterprises.
These companies were formed as part of the
nations privatization programme
Example: State Economic Corporations
(SEDCs)
6) Academic Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurial activities in academic and
research institutions mainly involve research
and development new products, processes,
systems, materials, etc.
Also known as knowledge entrepreneurship.
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURS
1) Corporate Entrepreneurs
who manage large corporations usually public
listed companies
Either employed or own shares in the
corporation
Known as intrapreneur
Are professionals
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURS
2) Independent Entrepreneurs
Pure type of entrepreneur
They are independent , own and manage own
company
Usually exhibit extensive entrepreneurial
characteristics
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURS
3) Social Entrepreneurs
Exist in social organizations or enterprises
Known as social leader of agents of
transformation
Their roles in instilling an entrepreneurial
mind-set to their respective target groups
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURS
4) Public Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs found in public sector
organizations including government-linked
companies and state-owned enterprises
Applying entrepreneurship principles in
managing
Do not own the companies
TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURS
5) Academic Entrepreneurs
Exist in most institution of higher learning and
research and development organization
Involved in entrepreneurial activities that lead
to innovation and commercialization of R & D
Known as knowledge entrepreneurs
OTHER VARIANTS OF ENTREPRENEURS
Serial Entrepreneurs
Those who continuously start new ventures and sell off the
venture at a later stage
Lifestyle Entrepreneurs
Start new ventures out of their passion rather than solely
for profit
Nascent Entrepreneurs
Those aspire to take up entrepreneurship as a career
option
Necessity Entrepreneurs
Are involved in entrepreneurial activities not by their own
choice
OTHER VARIANTS OF ENTREPRENEURS
Technopreneurs
Entrepreneurial persons who are technology savvy and earn a
fortune using their expertise in the respective technologies
Intrapreneur
A person within a large corporation who takes direct responsibility
for turning an idea into a profitable finished product through
assertive risk-taking and innovation
Agripreneurs
Involved in entrepreneurial activities in the agriculture sector
Infopreneurs
Those who utilize information as commodity for sale
Edupreneur
Those involved in setting up educational institutions privately with
the objective to make profit
SUMMARY
The classification of entrepreneurship
are:
based on the type of entrepreneurial
activities carried out in specific organization
and
based on their roles and functions in the
specific type of organization
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter 2 Types of EntrepreneurshipDokumen38 halamanChapter 2 Types of Entrepreneurshipbryan9422100% (2)
- Introduction to Entrepreneurship Unit IDokumen34 halamanIntroduction to Entrepreneurship Unit I16R01A05H7 16R01A05H7Belum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDokumen70 halamanEntrepreneurship DevelopmentsaranBelum ada peringkat
- Day-5-6 Concept of Entrepreneur & EntrepreneurshipDokumen19 halamanDay-5-6 Concept of Entrepreneur & EntrepreneurshipGaurav SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- International MarketingDokumen48 halamanInternational MarketingAshish100% (1)
- Women Entrepreneurship in NepalDokumen15 halamanWomen Entrepreneurship in NepalSudeep Parajuli100% (1)
- EEM QuizDokumen8 halamanEEM Quizlokesh_bhatiyaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Entrepreneurial Management Module New4 1Dokumen7 halaman4 Entrepreneurial Management Module New4 1Class LectureBelum ada peringkat
- Short Questions On EntrepreneursDokumen5 halamanShort Questions On Entrepreneursvini2710100% (1)
- Notes On EntrepreneurshipDokumen4 halamanNotes On EntrepreneurshipAtharva Inamdar40% (5)
- Chapter 13 - Entrepreneurial Strategy: Generating and Exploiting New EntriesDokumen15 halamanChapter 13 - Entrepreneurial Strategy: Generating and Exploiting New EntriesArman86% (7)
- ECC 4 Module 2Dokumen5 halamanECC 4 Module 2Trixie Mendoza Torres100% (1)
- Business Ethics and Social ResponsibilityDokumen18 halamanBusiness Ethics and Social Responsibilitynisarg_100% (1)
- Introduction to Entrepreneurship: Key Concepts and FunctionsDokumen34 halamanIntroduction to Entrepreneurship: Key Concepts and Functionssamuel lireBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Notes On Ent Chapter 1Dokumen12 halamanRevision Notes On Ent Chapter 1XB 9 Vishwa Rajgor100% (1)
- Types of EntrepreneurDokumen27 halamanTypes of EntrepreneurGing Castillano-LumsodBelum ada peringkat
- The Role of Entrepreneurs in Driving Economic GrowthDokumen66 halamanThe Role of Entrepreneurs in Driving Economic GrowthSherin SunnyBelum ada peringkat
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP: THE KEY CONCEPTSDokumen34 halamanENTREPRENEURSHIP: THE KEY CONCEPTSChandrika. MBBelum ada peringkat
- Entrep Hand OutDokumen25 halamanEntrep Hand OutKnightmare9871Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDokumen41 halamanIntroduction To EntrepreneurshipchinchouBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Reasons Why Intrapreneurship Is ImportantDokumen8 halaman5 Reasons Why Intrapreneurship Is ImportantGab NaparatoBelum ada peringkat
- Notes 1. Introduction To Entrepreneurship Discussion Case StudyDokumen12 halamanNotes 1. Introduction To Entrepreneurship Discussion Case StudyGastor Hilary Mtweve100% (1)
- SOLVED PAST PAPERS (Short Questions Only)Dokumen5 halamanSOLVED PAST PAPERS (Short Questions Only)Zain LauBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurship: Lalit ChikkerDokumen30 halamanEntrepreneurship: Lalit ChikkerNJ Culla100% (1)
- Module 8 Theories of EntrepreneurshipDokumen48 halamanModule 8 Theories of EntrepreneurshipNikita SangalBelum ada peringkat
- The Concept of EntrepreneurshipDokumen11 halamanThe Concept of EntrepreneurshipAlpesh PatelBelum ada peringkat
- RCA 204 Entrepreneurial Competency GuideDokumen20 halamanRCA 204 Entrepreneurial Competency Guideneemarawat11100% (2)
- Self Help Groups: BY N.Manoj KumarDokumen14 halamanSelf Help Groups: BY N.Manoj KumarManoj Kumar NBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Forms of Business Ownership Part-IIDokumen18 halamanChapter 2 - Forms of Business Ownership Part-IIQwRasel0% (1)
- Emerging Trends in EntrepreneurshipDokumen4 halamanEmerging Trends in EntrepreneurshipAdil Shrestha0% (1)
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDokumen46 halamanCorporate Social ResponsibilityALLYSON GWYNETH NOVICIOBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of Good Governance and CSRDokumen24 halamanDefinition of Good Governance and CSRDanna Marie BanayBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurship and Small Business ManagementDokumen12 halamanEntrepreneurship and Small Business Managementkhushboo chandaniBelum ada peringkat
- EntrepreneurshipDokumen4 halamanEntrepreneurshipNicolae MgnBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurial LeadershipDokumen11 halamanEntrepreneurial LeadershipKimii Dora100% (1)
- Enterpreneur BehaviourDokumen17 halamanEnterpreneur BehaviourangelaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter One: The Concepts of Entrepreneurship and EntrepreneurDokumen17 halamanChapter One: The Concepts of Entrepreneurship and Entrepreneurras dawitBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15 Lecture 1 CSR & EthicsDokumen15 halamanChapter 15 Lecture 1 CSR & Ethicsanuraag1710Belum ada peringkat
- Topic 14 - Emerging Trends in EntrepreneurshipDokumen15 halamanTopic 14 - Emerging Trends in EntrepreneurshipAG Atc UumBelum ada peringkat
- Opportunity RecognitionDokumen87 halamanOpportunity Recognitionigottest90% (10)
- Entrepreneurship Study NotesDokumen336 halamanEntrepreneurship Study NotesSekar Murugan100% (3)
- Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDokumen13 halamanIntroduction To EntrepreneurshipDwiki Satria WibawaBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of EntrepreneurshipDokumen6 halamanTheories of EntrepreneurshipGadin PaoloBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Social EnterprisesDokumen20 halamanIntroduction To Social EnterprisesS.Rengasamy67% (9)
- EntrepreneurshipDokumen19 halamanEntrepreneurshipmathew00785% (27)
- Revision Questions and Answer For End Semester ExaminationDokumen7 halamanRevision Questions and Answer For End Semester ExaminationFaheem Easa Abdulla Moosa33% (3)
- Entrepreneur Strategic Decision MakingDokumen11 halamanEntrepreneur Strategic Decision MakingKintu MunabangogoBelum ada peringkat
- Opportunity Recognition: Module No. 11 by BSN Ii A - Group 6Dokumen74 halamanOpportunity Recognition: Module No. 11 by BSN Ii A - Group 6Fe P. ImbongBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurial StrategiesDokumen62 halamanEntrepreneurial StrategiesSantosh NepalBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-1 Product Management - Basic ConceptsDokumen9 halamanUnit-1 Product Management - Basic Conceptsbhar4tpBelum ada peringkat
- Innovation Management NotesDokumen4 halamanInnovation Management NotesMohd Izzudin100% (1)
- Theories OF Entrepreneurship: Monirba (Allahabad University) Supported byDokumen27 halamanTheories OF Entrepreneurship: Monirba (Allahabad University) Supported bymanishkanojia_79% (19)
- Chap3 EntrepreneurDokumen41 halamanChap3 EntrepreneurAnonymous hzr2fbc1zMBelum ada peringkat
- Entre=PPTDokumen199 halamanEntre=PPTmogesalemu573Belum ada peringkat
- Ali Usman: Entrepreneurship and Small Business ManagementDokumen43 halamanAli Usman: Entrepreneurship and Small Business Managementjisanus5salehinBelum ada peringkat
- PS 306.2 Entrepreneurship Management: Vinay KrishnaDokumen33 halamanPS 306.2 Entrepreneurship Management: Vinay KrishnaVinay KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 8 Recording PDFDokumen15 halamanLecture 8 Recording PDFHermain Fayyaz KarimBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 1-EntreprenuershipDokumen20 halamanCHAPTER 1-EntreprenuershipRonit TandukarBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-1 Nature of Enterpreneurship Up DatedDokumen42 halamanCh-1 Nature of Enterpreneurship Up Dateddini best100% (1)
- Chapter OneDokumen30 halamanChapter Oneyomif tamiruBelum ada peringkat
- Iso TS 16949 - 2002-IatfDokumen29 halamanIso TS 16949 - 2002-IatfDennis SantiBelum ada peringkat
- Replenishment Planning - Process StepsDokumen1 halamanReplenishment Planning - Process StepsNishu NishuBelum ada peringkat
- Akl Soal 3 - Kelompok 2Dokumen9 halamanAkl Soal 3 - Kelompok 2M KhairiBelum ada peringkat
- STFC - Public Issue of NCDs - Final Prospectus - JSA - June 16 2011 - 1Dokumen522 halamanSTFC - Public Issue of NCDs - Final Prospectus - JSA - June 16 2011 - 1charan6969Belum ada peringkat
- Petition For Issuance of Letter of AdministrationDokumen4 halamanPetition For Issuance of Letter of AdministrationMa. Danice Angela Balde-BarcomaBelum ada peringkat
- 5443 - Global Supply Chain Management2.2Dokumen22 halaman5443 - Global Supply Chain Management2.2douglas gacheru ngatiiaBelum ada peringkat
- Leadership Styles Leadership Styles Leadership StylesDokumen1 halamanLeadership Styles Leadership Styles Leadership StylesDIY TaskerBelum ada peringkat
- 9706 s10 QP 41Dokumen8 halaman9706 s10 QP 41roukaiya_peerkhanBelum ada peringkat
- Seven Dimensions of Corporate IdentityDokumen25 halamanSeven Dimensions of Corporate IdentityRaquel Tedesco Peruzzo100% (2)
- ISO 14001 2015 Upgrade ChecklistDokumen10 halamanISO 14001 2015 Upgrade ChecklistDariush Rumi100% (1)
- All Intermediate ChapterDokumen278 halamanAll Intermediate ChapterNigus AyeleBelum ada peringkat
- Organised Securities MarketsDokumen4 halamanOrganised Securities MarketsNipun Sachdeva50% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts of Strategic ManagementDokumen6 halamanChapter 1 - Basic Concepts of Strategic ManagementMay JennBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacovigilance Systems Master File (PSMF) : Dr. Varun Sharma Senior Project LeaderDokumen22 halamanPharmacovigilance Systems Master File (PSMF) : Dr. Varun Sharma Senior Project LeaderEldaniz Hasanov100% (2)
- Tech & Ops Trends in Wealth Management 2021: Key Developments Explained by Top Industry ExpertsDokumen33 halamanTech & Ops Trends in Wealth Management 2021: Key Developments Explained by Top Industry Expertsvk2012Belum ada peringkat
- Job Opportunity Sales: An Opportunity You Can't MissDokumen2 halamanJob Opportunity Sales: An Opportunity You Can't MissKarThik VanKadaruBelum ada peringkat
- Finacle X Pnbrep & PNBRPT Menus: List of PNBREP Reports - PNBREP - 1Dokumen17 halamanFinacle X Pnbrep & PNBRPT Menus: List of PNBREP Reports - PNBREP - 1Amit67% (3)
- Product Release Oracle Banking Treasury Management Release 14.6.0.0.0 File NameDokumen64 halamanProduct Release Oracle Banking Treasury Management Release 14.6.0.0.0 File NamenajusmaniBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank: Test Bank For Financial Management Principles and Applications 13Th Edition TitmanDokumen15 halamanTest Bank: Test Bank For Financial Management Principles and Applications 13Th Edition TitmanCharles FilerBelum ada peringkat
- Training ReportDokumen17 halamanTraining ReportprabhatBelum ada peringkat
- Kotler Pom17e PPT 01Dokumen33 halamanKotler Pom17e PPT 01solehah sapie100% (1)
- Chap 7Dokumen20 halamanChap 7Ika ChillayBelum ada peringkat
- Board Meeting Requirements and ComplianceDokumen20 halamanBoard Meeting Requirements and ComplianceMansi Saini100% (1)
- Focusing Surecash, Bkash, Ipay, Upay: April 30, 2019Dokumen65 halamanFocusing Surecash, Bkash, Ipay, Upay: April 30, 2019আবদুল্লাহ আল মাহমুদBelum ada peringkat
- Mpa AssignmentDokumen8 halamanMpa AssignmentSanah SahniBelum ada peringkat
- Kumpulan Quiz UAS AkmenDokumen23 halamanKumpulan Quiz UAS AkmenPutri NabilahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7Dokumen15 halamanChapter 7YnaBelum ada peringkat
- BC Annual Report 2018 - SEC Form 17-A PDFDokumen252 halamanBC Annual Report 2018 - SEC Form 17-A PDFKyle BacaniBelum ada peringkat
- Articles of IncorporationDokumen6 halamanArticles of IncorporationKimberly GallaronBelum ada peringkat
- Classical Management TheoryDokumen7 halamanClassical Management Theorysimren171100% (1)