Ballou 01
Diunggah oleh
rajuahmedtDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ballou 01
Diunggah oleh
rajuahmedtHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1-1
Business Logistics/Supply
ChainA Vital Subject
The supply chain is simply another way of
saying the whole process of business.
Chapter 1
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
Warehousing
Warehousing
Transportation
Transportation
Vendors/plants/ports
Transportation
Factory
Transportation
Customers
Information
flows
The Immediate Supply Chain for an Individual Firm
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-2
1-3
Logistics Defined
Logistics is the process of planning, implementing and
controlling the efficient, cost-effective flow and storage
of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods
and related information from the point of origin to point
of consumption for the purpose of conforming to
customer requirements.
Council of Logistics Management
Supply Chain Management Defined
SCM is the integration of all activities associated with the
flow and transformation of goods from raw materials
through to end user, as well as information flows, through
improved supply chain relationships, to achieve a
sustainable competitive advantage.
Handfield and Nichols
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-4
Demand forecasting
Purchasing
Requirements planning
Production planning
Manufacturing inventory
Warehousing
Material handling
Packaging
Finished goods inventory
Distribution planning
Order processing
Transportation
Customer service
Strategic planning
Information services
Marketing/sales
Finance
Supply Chain
Management
Supply Chain
Management
Logistics
Purchasing/
Materials
Management
Physical
Distribution
Activity fragmentation to 1960
Activity Integration 1960 to 2000 2000+
Demand forecasting
Purchasing
Requirements planning
Production planning
Manufacturing inventory
Warehousing
Material handling
Packaging
Finished goods inventory
Distribution planning
Order processing
Transportation
Customer service
Strategic planning
Information services
Marketing/sales
Finance
Supply Chain
Management
Supply Chain
Management
Logistics
Purchasing/
Materials
Management
Physical
Distribution
Activity fragmentation to 1960
Activity Integration 1960 to 2000 2000+
Evolution of Supply Chain Management
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
Supply Chain Schematic
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-5
1-6
The Logistics/SC Mission
Getting the right goods or services
to the right place, at the right time,
and in the desired condition at the
lowest cost and highest return on
investment.
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-7
A Revised Strategy is Generating
Great Top Management Interest
Historical perspective of distribution:
The last frontier of cost economies
The contemporary view:
Distribution is a new frontier for demand
generationa competitive weapon.
Peter Drucker, 1962
Both views are
now important!
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-8
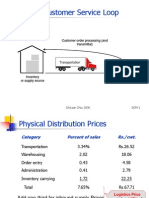
Customers
Transportation
Inventory
or supply source
Customer order processing (and
transmittal)
Customers
Transportation
Inventory
or supply source
Customer order processing (and
transmittal)
Critical Customer Service
Loop
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-9
Category Percent of sales $/cwt.
Transportation 3.34% $26.52
Warehousing 2.02 18.06
Order entry 0.43 4.58
Administration 0.41 2.79
Inventory carrying 1.72 22.25
Total 7.65% $67.71
Physical Distribution Costs
Add one-third for inbound supply costs
Source: Herb Davis & Company
Logistics cost
are about 10% of
sales w/o
purchasing costs
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-10
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1
9
9
2
1
9
9
4
1
9
9
6
1
9
9
8
2
0
0
0
2
0
0
2
Year
D
a
y
s
82
84
86
88
90
92
94
96
%
Order Cycle Time,
Days
Product
Availability--%
orders
Product
Availability--% line
items
Customer Service Performance
Source: Herb Davis & Company
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-11
Costs are high
About 10.5% of GDP domestically
About 12% of GDP internationally
A range of 4 to 30% of sales for individual firms, avg. about 10%
A high as 70-80% of sales if purchasing and production are
included
Customers are more demanding of the supply chain
Desire for quick response
Desire for mass customization
An integral part of company strategy
Generate revenue
Improve profit
Logistical lines are lengthening
Local vs. long distance supply
Logistics is a key to trade and an increased standard of living
Law of comparative economic advantage applies
Logistics adds value
Time and place utilities
Significance of Logistics
1-12
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
Costs are lower than K-Mart or
Target Stores
CEO is a former logistician
Wal-Mart is the largest retailer in
the world!
1-13
Effect on Logistics Foreign Outsourcing
Profit
G & A
Marketing
Logistics
Overhead
Materials
Labor
Profit
G & A
Marketing
Logistics
Overhead
Materials
Labor
Tariffs
Increase
Reduction
Increase
Domestic sourcing Foreign sourcing
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
Scope of the Supply Chain for Most Firms
Physical distribution
Physical supply
(Materials management)
Business logistics
Sources of
supply
Plants/
operations
Customers
Transportation
Inventory maintenance
Order processing
Acquisition
Protective packaging
Warehousing
Materials handling
Information maintenance
Transportation
Inventory maintenance
Order processing
Product scheduling
Protective packaging
Warehousing
Materials handling
Information maintenance
Focus firms internal supply chain
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-14
1-15
Primary
- Setting customer service goals
- Transportation
- Inventory management
- Location
Secondary, or supporting
- Warehousing
- Materials handling
- Acquisition (purchasing)
- Protective packaging
- Product scheduling
-
Order processing
Key Activities/Processes
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-16
Focus
Company
Suppliers
Suppliers
suppliers
Customers
Customers/
End users
Acquire Convert Distribute
The Supply Chain is Multi-Enterprise
Product and information flow
Scope in
reality
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-17
Reality of SC Scope
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-18
SUPPLY
CHAIN
MANAGEMENT
Activity and process
administration
The Multi-Dimensions of SC
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-19
P
L
A
N
N
I
N
G
O
R
G
A
N
I
Z
I
N
G
C
O
N
T
R
O
L
L
I
N
G
Transport Strategy
Transport fundamentals
Transport decisions
Customer
service goals
The product
Logistics service
Ord. proc. & info. sys.
Inventory Strategy
Forecasting
Inventory decisions
Purchasing and supply
scheduling decisions
Storage fundamentals
Storage decisions
Location Strategy
Location decisions
The network planning process
P
L
A
N
N
I
N
G
O
R
G
A
N
I
Z
I
N
G
C
O
N
T
R
O
L
L
I
N
G
Transport Strategy
Transport fundamentals
Transport decisions
Customer
service goals
The product
Logistics service
Ord. proc. & info. sys.
Inventory Strategy
Forecasting
Inventory decisions
Purchasing and supply
scheduling decisions
Storage fundamentals
Storage decisions
Location Strategy
Location decisions
The network planning process
Study Framework
The focus is
here
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-20
Customer
service goals
The product
Logistics service
Information sys.
Inventory Strategy
Forecasting
Storage fundamentals
Inventory decisions
Purchasing and supply
scheduling decisions
Storage decisions
Transport Strategy
Transport fundamentals
Transport decisions
Location Strategy
Location decisions
The network planning process
The Logistics Strategy Triangle
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
PRODUCTION/
OPERATIONS
Sample activities:
Quality control
Detailed production
scheduling
Equipment maint .
Capacity planning
Work measurement
& standards
LOGISTICS
Sample
activities:
Transport
Inventory
Order
processing
Materials
handling
Interface
activities:
Product
scheduling
Plant
location
Purchasing
MARKETING
Sample
activities:
Promotion
Market
research
Product
mix
Sales force
management
Interface
activities:
Customer
service
standards
Pricing
Packaging
Retail
location
Production-
logistics
interface
Marketing-
logistics
interface
Relationship of Logistics to
Marketing and Production
Internal Supply Chain
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-21
Relationship of Logistics to Marketing
Product
Price
Promotion
Place-Customer
service levels
Inventory
carrying costs
Lot quantity
costs
Order processing
and information
costs
Transport
costs
Warehousing
costs
L
o
g
i
s
t
i
c
s
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-22
1-23
Relationship of Logistics to Production
Coordinates through scheduling and strategy
make-to-order or make-to-stock
An integral part of the the supply chain
Affects total response time for customers
Shares activities such as inventory planning
Costs are in tradeoff
Production lot quantities affect inventory
levels and transportation efficiency
Production response affects transportation
costs and customer service
Production and warehouse location are
interrelated
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-24
Logistics/SC in Diverse Areas
Manufacturingmost common
Environmentcausing restrictions
Serviceemerging opportunities
Non-profitslittle explored
Militarylong history
CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
1-25
Contemporary Logistics Terms
Value stream/logistics process
Quick response and flexible
manufacturing
Mass customization
Supply chain management/
collaborative logistics
Reverse logistics
Service logistics
Continuous replenishment
Lean logistics
Integrated logistics
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Business Logistics Supply ChainDokumen25 halamanBusiness Logistics Supply ChainavilesfabianBelum ada peringkat
- PPP SCM Chapter1 (Supply Chain Management)Dokumen29 halamanPPP SCM Chapter1 (Supply Chain Management)Mahfuz Raihan100% (1)
- Vital Subject of Business Logistics/Supply ChainDokumen27 halamanVital Subject of Business Logistics/Supply ChainAbu SyeedBelum ada peringkat
- SCM and Logistics FundamentalsDokumen33 halamanSCM and Logistics FundamentalsLinus ArvhimsBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Customer Service Loop: Customer Order Processing (And Transmittal) Customer Order Processing (And Transmittal)Dokumen23 halamanCritical Customer Service Loop: Customer Order Processing (And Transmittal) Customer Order Processing (And Transmittal)Linus ArvhimsBelum ada peringkat
- Business Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital SubjectDokumen25 halamanBusiness Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital SubjectRavi100% (1)
- 1 - Supply ChainDokumen20 halaman1 - Supply ChainWilliam KmiloBelum ada peringkat
- Ballou 01Dokumen27 halamanBallou 01Student_BUBelum ada peringkat
- Logistics Strategy PlanningDokumen25 halamanLogistics Strategy PlanningSyed Tauseef Chowdhury0% (1)
- Ballou 02Dokumen16 halamanBallou 02brunomarinoneBelum ada peringkat
- Ballou 02Dokumen16 halamanBallou 02Anonymous l0G1fdBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to International Logistics: Course Objectives & Key ConceptsDokumen13 halamanIntroduction to International Logistics: Course Objectives & Key ConceptsrtpanditBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain ManagementDokumen131 halamanSupply Chain ManagementChristopher WheelerBelum ada peringkat
- Business Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital SubjectDokumen32 halamanBusiness Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital Subjectmamun gaziBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To The Course Jing Yuan Feb, 2008Dokumen47 halamanIntroduction To The Course Jing Yuan Feb, 2008artwaniparasBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDokumen30 halamanOverview of Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementTrúc Ly Cáp thịBelum ada peringkat
- Logistics and Supply Chain ManagmentDokumen21 halamanLogistics and Supply Chain ManagmentmbashriksBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 scm1Dokumen37 halamanChapter 1 scm1solomon guadeBelum ada peringkat
- MK 223: Distribution and Logistics Management: General IntroductionDokumen40 halamanMK 223: Distribution and Logistics Management: General IntroductionAshiraf SomiBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain ManagementDokumen43 halamanSupply Chain ManagementAbdulAhadBelum ada peringkat
- Ballou 01Dokumen10 halamanBallou 01Laila NaqviBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Global Logistics IntroductionDokumen47 halaman1 Global Logistics IntroductionChanTheFireGodBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain First ChapterDokumen32 halamanSupply Chain First ChapterJunaid Jamshaid100% (1)
- History & Evolution of Supply Chain ManagemantDokumen41 halamanHistory & Evolution of Supply Chain ManagemantGreeshma100% (7)
- Supply Chain Optimization - Jose PintoDokumen199 halamanSupply Chain Optimization - Jose Pintomanujosephv8752Belum ada peringkat
- Department of Management Studies, BSA Crescent Institute of Science & TechnologyDokumen32 halamanDepartment of Management Studies, BSA Crescent Institute of Science & Technologydangerous saifBelum ada peringkat
- Module I Part 3Dokumen21 halamanModule I Part 3zapzahtBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Management PresentationDokumen71 halamanSupply Chain Management Presentationabir1986100% (1)
- Logistics Management Lecture IDokumen16 halamanLogistics Management Lecture INabendu MajiBelum ada peringkat
- Business Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital SubjectDokumen13 halamanBusiness Logistics/Supply Chain-A Vital SubjectAhmed MaherBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Management PPT 2Dokumen65 halamanSupply Chain Management PPT 2Harris LodhiBelum ada peringkat
- Business Logistics/Supply Chain - A Vital SubjectDokumen18 halamanBusiness Logistics/Supply Chain - A Vital SubjectCamilo AvilaBelum ada peringkat
- Diploma in Logistics ManagementDokumen1 halamanDiploma in Logistics ManagementSubhash ChanderBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Version 2Dokumen37 halamanSupply Chain Version 2Abdelhamid Harakat100% (1)
- Supply ChainDokumen32 halamanSupply ChainAkhil SardaBelum ada peringkat
- SCM - Chapter 01Dokumen68 halamanSCM - Chapter 01Talha6775Belum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Drivers ObstaclesDokumen22 halamanSupply Chain Drivers ObstaclesRikudo Akyoshi0% (1)
- Supply Chain MGTDokumen42 halamanSupply Chain MGTYash RoxsBelum ada peringkat
- Logistics Management Module- Supply Chain ImperativeDokumen19 halamanLogistics Management Module- Supply Chain ImperativeAbhishek JainBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)Dokumen40 halamanSupply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)Abdur RajakBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Supply Chain ManagementDokumen5 halamanBasics of Supply Chain Managementsowmen1988Belum ada peringkat
- SCM MFM Session 1Dokumen25 halamanSCM MFM Session 1Avilash PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Ballou 05Dokumen15 halamanBallou 05brunomarinoneBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Management & LogisticsDokumen26 halamanSupply Chain Management & LogisticsDeepika WaliaBelum ada peringkat
- KUL 1 Chopra INTRO Sept2011Dokumen48 halamanKUL 1 Chopra INTRO Sept2011Uge HolicBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan Ke 5 SCM DriversDokumen36 halamanPertemuan Ke 5 SCM DriversOwen TBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Logistics Management Unit-1Dokumen34 halamanIntroduction to Logistics Management Unit-1etiBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain & LogisticsDokumen44 halamanSupply Chain & LogisticsashwinsudaBelum ada peringkat
- OMGT2085 - Topic01 - Overview of Logistics & Supply Chain ManagementDokumen39 halamanOMGT2085 - Topic01 - Overview of Logistics & Supply Chain ManagementMelissa OrtizBelum ada peringkat
- ISM Notes Part IIDokumen20 halamanISM Notes Part IIGeet GoelBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Logistics Management at Lintas FreightDokumen39 halamanA Study On Logistics Management at Lintas FreightDatta SairamBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Management: A Presentation by K.Abhishek (20G25A0303) Organisation:-SDSC (SHAR)Dokumen19 halamanSupply Chain Management: A Presentation by K.Abhishek (20G25A0303) Organisation:-SDSC (SHAR)kuppani abhiBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Logistics Management: James R. StockDokumen12 halamanStrategic Logistics Management: James R. Stockprincipito240% (1)
- Supply Chain ManagementDokumen76 halamanSupply Chain Managementsreejith_eimt13Belum ada peringkat
- SCM PPT - Module 1Dokumen40 halamanSCM PPT - Module 1rnaganirmita67% (6)
- Logistics in Manufacturing, Supply Chain, and DistributionDari EverandLogistics in Manufacturing, Supply Chain, and DistributionBelum ada peringkat
- Procedure and Documentation in Supply Chain Management: Business strategy books, #1Dari EverandProcedure and Documentation in Supply Chain Management: Business strategy books, #1Belum ada peringkat
- Demand Driven Material Requirements Planning (DDMRP): Version 2Dari EverandDemand Driven Material Requirements Planning (DDMRP): Version 2Belum ada peringkat
- Logistics Management: Principles, Strategies, Technologies, Terms, and Q&ADari EverandLogistics Management: Principles, Strategies, Technologies, Terms, and Q&ABelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 67 01 InvDokumen45 halamanChapter 67 01 Invhaymanotandualem2015Belum ada peringkat
- Study on inventory management at Micon EngineersDokumen39 halamanStudy on inventory management at Micon EngineersAnbalagan AnbaBelum ada peringkat
- Good StorageDokumen20 halamanGood Storageziaddd100% (1)
- ch16 Logistics and Supply-Chain ManagementDokumen24 halamanch16 Logistics and Supply-Chain ManagementLuxBelum ada peringkat
- SCM Session IV Transportation ManagementDokumen213 halamanSCM Session IV Transportation Managementtushar nehruBelum ada peringkat
- Freight Clearing and Forwarding ProceduresDokumen285 halamanFreight Clearing and Forwarding ProceduresSerdar Kontaş88% (17)
- Guerrero Book Chapter1 - Cost Acoounting Basic Concepts and The Job Order Cost CycleDokumen6 halamanGuerrero Book Chapter1 - Cost Acoounting Basic Concepts and The Job Order Cost CycleJenny Brozas JuarezBelum ada peringkat
- Storage and Ware Housing of Agricultural ProductsDokumen14 halamanStorage and Ware Housing of Agricultural ProductsPragyan SarangiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1.1 Introduction To Distribution ManagementDokumen25 halamanChapter 1.1 Introduction To Distribution Management有川静寂Belum ada peringkat
- MSC Thesis - Zelalem LemmaDokumen74 halamanMSC Thesis - Zelalem LemmaWubshet ShimelsBelum ada peringkat
- Ecobulk MX: Perfect For Transport and StorageDokumen1 halamanEcobulk MX: Perfect For Transport and Storagearachman297988Belum ada peringkat
- Sap Help For Idoc WT in EwmDokumen59 halamanSap Help For Idoc WT in EwmAbhishek Nandi50% (2)
- Business Studies Class 11 Study Material Chapter 1Dokumen17 halamanBusiness Studies Class 11 Study Material Chapter 1crystal pathshalaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Amul's End-to-End Supply Chain FrameworkDokumen26 halamanAnalysis of Amul's End-to-End Supply Chain FrameworkDaya100% (2)
- A Study On The Raw Material Warehouse at Tumakuru Plant With Reference To Rane Engine Valve LimitedDokumen93 halamanA Study On The Raw Material Warehouse at Tumakuru Plant With Reference To Rane Engine Valve LimitedSrinivasan SubbiahBelum ada peringkat
- Ahmed Kamel Shalash: 386 King Faisal Street, Giza, Egypt Mob: 01005525526-01272727382 EmailDokumen4 halamanAhmed Kamel Shalash: 386 King Faisal Street, Giza, Egypt Mob: 01005525526-01272727382 EmailAhmed HamzaBelum ada peringkat
- Standards VNA WarehouseDokumen1 halamanStandards VNA WarehouseAnonymous FZs3yBHh7Belum ada peringkat
- Indira Institute of Management PGDM, Pune: TopicDokumen14 halamanIndira Institute of Management PGDM, Pune: TopicFahad DhanseBelum ada peringkat
- Imran's C.VDokumen4 halamanImran's C.VimranrafiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Initiatives of Baskin Robbins India inDokumen20 halamanSupply Chain Initiatives of Baskin Robbins India inVinod RamachandraBelum ada peringkat
- Warehouse Management - AuthorizationsDokumen17 halamanWarehouse Management - AuthorizationsriazscribdBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain Procurement Inventory Manager in Lake Charles LA Resume Monica SoileauDokumen4 halamanSupply Chain Procurement Inventory Manager in Lake Charles LA Resume Monica SoileauMonicaSoileauBelum ada peringkat
- AJIO-JIT Return and SPF PolicyDokumen11 halamanAJIO-JIT Return and SPF PolicyAshish MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Rishi INTERNSHIP REPORT LANDMARK GROUP, PDFDokumen61 halamanRishi INTERNSHIP REPORT LANDMARK GROUP, PDFParas Mangle100% (1)
- Coca Cola PracticumDokumen4 halamanCoca Cola PracticumKabunian Dakila Acio IIIBelum ada peringkat
- Materials - Management 1Dokumen100 halamanMaterials - Management 1Kumar GauravBelum ada peringkat
- Alcisa & Pick GMBH: Small Food-Product Distributor Generates Value With Sap® Standard SolutionDokumen4 halamanAlcisa & Pick GMBH: Small Food-Product Distributor Generates Value With Sap® Standard SolutionJan HarvestBelum ada peringkat
- FTWZDokumen16 halamanFTWZNik100% (1)
- 07 - LandE - Cat - Architectural FacadeDokumen123 halaman07 - LandE - Cat - Architectural FacadeTHAMMANOON REAMAMATAKULBelum ada peringkat