Analysis of In-Wheel Switched Reluctance Motor: Review-I
Diunggah oleh
Suresh Kumar RDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Analysis of In-Wheel Switched Reluctance Motor: Review-I
Diunggah oleh
Suresh Kumar RHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ANALYSIS OF IN-WHEEL SWITCHED
RELUCTANCE MOTOR
REVIEW-I
BY
SURESH KUMAR R
RRN NO:131232601007
M.Tech -PED-FINAL YEAR
Under the guidance of
Dr .K.N .SRINIVAS
PROFESSOR/EEE
AIM
To design an in-wheel switched reluctance motor and
analyzing its static and dynamic characteristics.
To interface the modelled machine with MATLAB simulink
and predicting its perfomance for electric vehicle operation.
ABSTRACT
In this era of electrified transportation, in-wheel switched
reluctance motor (SRM) is emerging as a prospective
replacement to traditional electric motors especially for large
heavy duty vehicles.
The integration of the motor housing inside the wheel rim
saves significant space and eliminates the need for additional
mechanical parts used in the centralized drive.
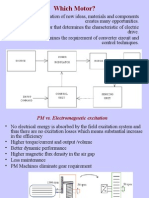
It is desired that electric motors for EVs have high torque, high
efficiency, and high torque density.
In-wheel SRM offer up to 65% improvement in specific torque
over the conventional SRM.
INTRODUCTION
An in-wheel switched reluctance motor (SRM) with high
power density and torque is a special stator-rotor designed by
the Power and Drive Systems Group (PADS) at Cranfield
University in the year 2006.
However , the emerging trends in the electrical propolution
made it as a better one.
Because the rotor decides the torque of the machine. Due to
large diameter of rotor, the torque density is high.
STRUCTURE OF IN-WHEEL SRM
CONSTRUCTION
The motor consists of two parts. Namely,
Stator
Rotor
Stator is made up of silicon-steel stamping with outward
projected poles.
Stator poles carry the field winding.
Stator is mounted on a shaft which is capable of withstanding
vibration and stress.
The stator terminals are connected to the output of the semi-
conductor switches.
ROTOR
Rotor also made up of same material with inward projected
poles.
Rotor carries no winding or magnet.
Due to this construction , the motor has the high thermal
stability and fault tolerance.
Hence the rotor needs the Rotor Position Sensor(RPS) because
the machine operates with the position feedback.
AXIAL-GAP AND RADIAL-GAP MOTORS
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
The motor works on the principle of variable
reluctance.
When the voltage is applied to the stator phase , the
motor creates torque in the direction of increased
inductance.
The rotor moves to the forth coming position of the
maximum inductance.
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF IN-WHEEL SRM
POWER CIRCUIT
ACTIVATION SEQUENCE
ROTOR POSITION
DIMENSIONS OF PROPOSED IN-WHEEL
SRM
Number of phases Nph 4 Air-gap length g 0.9mm
Stator-rotor configuration 16/18 Motor axial length l
m
180mm
Rotor pole pitch
r
20
0
Stator outer radius ros 134.1mm
In-pair stator pole pitch
s
20
0
Rotor inner radius r
ir
135mm
Stator pair-pair pitch spp 45
0
Rotor outer radius r
or
180mm
Stator pole arc
s
8
0
Number of turns N 160
Rotor pole arc
r
8
0
Step angle 5
0
RATING OF IN-WHEEL SRM
PARAMETERS VALUES PARAMETERS VALUES
Output Power 24 kW Maximum Power 40 kW
Rated Power 120 N-m Maximum Torque 200 N-m
Rated Current 35A Base Speed 2000 rpm
FEATURES OF PROPOSED TOPOLOGY
Overcomes the disadvantages of permanent magnet motor
vehicles.
Small in size compared to brushed and pm motors.
The segmented rotor improves the torque over the
conventional SRM.
Reduction in copper loss due to full-pitch winding.
Capable of operating in high temperature
Flux path is independent of the radius of rotor.
.
STATOR ASSEMBLY
ROTOR ASSEMBLY
IN-WHEEL ASSEMBLY
PRACTICAL EXAMPLE
WORK PLAN
Review II
Analysing the static characteristics.
Review III
Analyzing the dynamic characteristics.
REFERENCES
Luk, P.C.K.; Jinupun, P. A Novel In-wheel Switched Reluctance
Motor Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, 2006. VPPC
'06. IEEE, Issue Date: 6-8 Sept. 2006.
Jiongkang Lin ; Cheng, E.K.W. ; Zhu Zhang ; Xiangdang Xue
Experimental investigation of in-wheel switched reluctance motor
driving system for future electric vehicles PESA 2009. 3rd
International Conference on Power Electronics Systems and
Applications, 2009.
Ng, T.W. ; Cheng, K.W.E. ; Xue, X.D Computation of the In-
wheel Switched Reluctance Motor inductance using Finite Element
Method 3rd International Conference on Power Electronics
Systems and Applications, 2009. PESA 2009
REFERENCES
R. Madhavan and B. G. Fernandes, A Novel axial flux
segmented SRM for electric vehicle application, in IEEE
2010 International Conference on Electric Machines, pp. 1-6.
P. C. Desai, M. Krishnamurthy, N. Schofield, A. Emadi: Novel
Switched Reluctance Machine Configuration With Higher
Number of Rotor Poles Than Stator Poles: Concept to
Implementation, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,
Vol. 57 no. 2, pp. 649-659, 2010
I. Husain and M. S. Lslam, Design, modeling and simulation
of and electric vehicle system, in Advance in Electric Vehicle
Technology. Warrendale, PA: SAE, Inc., 1999, pp. 916.
THANK YOU
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter-3 Switch Reluctance Motor Characteristics 3.1 Switched Reluctance MotorDokumen9 halamanChapter-3 Switch Reluctance Motor Characteristics 3.1 Switched Reluctance MotorSree GaneshBelum ada peringkat
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationDari EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Mixer Grinder MotorDokumen6 halamanMixer Grinder MotorKkbhuvan KkBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseDari EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseBelum ada peringkat
- Phasor Diagram and CharacteristicsDokumen8 halamanPhasor Diagram and Characteristicskarthikeyan249Belum ada peringkat
- C1201042329 PDFDokumen7 halamanC1201042329 PDFJOHN MINKHANTBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsDari EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (19)
- Modeling and Simulation of Three Phase Induction Machine Using Written Pole TechnologyDokumen7 halamanModeling and Simulation of Three Phase Induction Machine Using Written Pole TechnologyJOHN MINKHANTBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation & Fabrication of Axial Flux Brushless DC Motor DriveDokumen7 halamanSimulation & Fabrication of Axial Flux Brushless DC Motor DrivePanser PangaribuanBelum ada peringkat
- Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM)Dokumen8 halamanSwitched Reluctance Motor (SRM)Ömer Faruk AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Ev & HVDokumen9 halamanEv & HVsuhas2002kulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- A Very High Speed Switchedreluctance Startergenerator For AircraDokumen7 halamanA Very High Speed Switchedreluctance Startergenerator For AircraAimmadBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3Dokumen29 halamanUnit 3Manabesh MalakarBelum ada peringkat
- Torque Ripple MitigationDokumen20 halamanTorque Ripple MitigationSanjayBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Active Electromagnetic Suspension System: September 2020Dokumen27 halamanReview of Active Electromagnetic Suspension System: September 2020Akshay bypBelum ada peringkat
- Rotary and Linear Switched Reluctance MotorsDokumen12 halamanRotary and Linear Switched Reluctance Motorskarthikeyan249100% (2)
- Brushless DC MotorDokumen17 halamanBrushless DC Motorkrishna015100% (1)
- Chapter-1: Introduction: 1.2 Aim and Objective of ProjectDokumen12 halamanChapter-1: Introduction: 1.2 Aim and Objective of Projectsameerpatel15770Belum ada peringkat
- Thesis Switched Reluctance MotorDokumen6 halamanThesis Switched Reluctance Motormelissalusternorman100% (2)
- PMBLDC Motor DriveDokumen55 halamanPMBLDC Motor DriveSushant SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 037 Takau Full PaperDokumen5 halaman037 Takau Full PaperJose FrancisBelum ada peringkat
- Training 12 Aerospace ApplicDokumen6 halamanTraining 12 Aerospace ApplicvishiwizardBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Control of Axial-Flux Brushless DC Wheel Motors For Electric Vehicles-Part I Multiobjective Optimal Design and AnalysisDokumen10 halamanDesign and Control of Axial-Flux Brushless DC Wheel Motors For Electric Vehicles-Part I Multiobjective Optimal Design and Analysishooshyar100% (1)
- Project On Avtron DriveDokumen39 halamanProject On Avtron Drivenarendramaharana39Belum ada peringkat
- 1 - Switched Reluctance MotorDokumen5 halaman1 - Switched Reluctance MotorHARSHIT TOMARBelum ada peringkat
- Brushed Direct-Current Motors: 5.1 Review of Motor TheoryDokumen32 halamanBrushed Direct-Current Motors: 5.1 Review of Motor TheoryEvren SoydanBelum ada peringkat
- Reluctance MotorDokumen27 halamanReluctance MotorMax Sedric L LaylayBelum ada peringkat
- Motors and DrivesDokumen27 halamanMotors and DrivessifuszBelum ada peringkat
- SRD-vehicle Traction Applications PDFDokumen20 halamanSRD-vehicle Traction Applications PDFEduardo BittencourtBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Motor Basics HandoutDokumen18 halaman6 Motor Basics HandoutTan Yit KeongBelum ada peringkat
- Special Electrical MachinesDokumen62 halamanSpecial Electrical MachinesVineeth Valiyaveedu Vijayan100% (9)
- Optimal Design and Control of Axial-Flux Brushless DC Wheel Motor For Electrical VehiclesDokumen10 halamanOptimal Design and Control of Axial-Flux Brushless DC Wheel Motor For Electrical Vehiclesfre12345Belum ada peringkat
- Suirrel CageDokumen3 halamanSuirrel CageMalepe TemosegoBelum ada peringkat
- ميكا2Dokumen7 halamanميكا2Ahmed M. MuradBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review of Three Phase Induction MotorDokumen7 halamanLiterature Review of Three Phase Induction Motorfvdh47rr100% (1)
- Jansons Institute of Technology: Special Electrical MachinesDokumen98 halamanJansons Institute of Technology: Special Electrical Machineselangoprt1Belum ada peringkat
- BLDCDokumen4 halamanBLDCabhik DasBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Ii SRM QaDokumen20 halamanUnit Ii SRM QaanbuelectricalBelum ada peringkat
- Interior Permanant Magnet Synchronous Machine For Hybrid Electric VehiclesDokumen36 halamanInterior Permanant Magnet Synchronous Machine For Hybrid Electric Vehiclesganeshn1983631Belum ada peringkat
- Seminar Report On Brushless DC MotorDokumen13 halamanSeminar Report On Brushless DC MotorDev Kumar50% (2)
- Motor IqDokumen4 halamanMotor IqPaul HkloBelum ada peringkat
- Vartanian2009 PDFDokumen6 halamanVartanian2009 PDF13sandipBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper On Single Phase Induction MotorDokumen7 halamanResearch Paper On Single Phase Induction Motorgw15ws8j100% (1)
- Unit Ii SRM QaDokumen21 halamanUnit Ii SRM QaanbuelectricalBelum ada peringkat
- Term Paper On DC MotorDokumen4 halamanTerm Paper On DC Motorc5qfb5v5100% (1)
- Reluctance MotorDokumen24 halamanReluctance Motorpraveenpv7100% (1)
- Motors For Mechatronics An IntroductionDokumen80 halamanMotors For Mechatronics An IntroductionJigar M. UpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- Special Electrical Machines Ee2403 PDFDokumen16 halamanSpecial Electrical Machines Ee2403 PDFsamyramu100% (3)
- Written Pole TechnologyDokumen8 halamanWritten Pole TechnologyShruthi ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- ElectricalDokumen157 halamanElectricalnaguBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Design of SynchronousDokumen6 halamanElectromagnetic Design of SynchronousedumacerenBelum ada peringkat
- LSPMDokumen38 halamanLSPMSathiyaraj KondusamyBelum ada peringkat
- The Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsDokumen6 halamanThe Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsGalco IndustrialBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis and Design of Chaos in Switched ReluctanceDokumen20 halamanAnalysis and Design of Chaos in Switched ReluctanceRaaji NattuBelum ada peringkat
- DQ InductanceDokumen11 halamanDQ Inductancegthulasi789193Belum ada peringkat
- Vector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorDokumen51 halamanVector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorFAIZAN ALIBelum ada peringkat
- Reaction PaperDokumen6 halamanReaction PaperAngelo Escoro Dante100% (1)
- DC MotorDokumen6 halamanDC MotorUjjawal ParasarBelum ada peringkat
- Artificial Neural Network Based Space Vector PWM For A Five-Level Diode-Clamped InverterDokumen3 halamanArtificial Neural Network Based Space Vector PWM For A Five-Level Diode-Clamped InverterSuresh Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- 14 - Appendices 1 To 4Dokumen19 halaman14 - Appendices 1 To 4rmsasirajaBelum ada peringkat
- Emerging Hybrid and Electric Vehicles and Their Impact On Energy and EmissionsDokumen42 halamanEmerging Hybrid and Electric Vehicles and Their Impact On Energy and EmissionsSuresh Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- A Seamless Mode Transfer Maximum Power Point Tracking Controller For Thermoelectric Generator ApplicationsDokumen9 halamanA Seamless Mode Transfer Maximum Power Point Tracking Controller For Thermoelectric Generator ApplicationsSuresh Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Power Electronics and Drives Laboratory: Sl. No List of Major EquipmentsDokumen1 halamanPower Electronics and Drives Laboratory: Sl. No List of Major EquipmentsSuresh Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Diagram OF Three Phase Ac Voltage ControllerDokumen1 halamanCircuit Diagram OF Three Phase Ac Voltage ControllerSuresh Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- Three Phase Ac Voltage Controller α = 120, PULSE WIDTH = 30 %Dokumen1 halamanThree Phase Ac Voltage Controller α = 120, PULSE WIDTH = 30 %Suresh Kumar RBelum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen43 halaman1Adithya ChandrasekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Operationalization of Regenerative Design Indicators An Integrated Framework of Design and AnalysisDokumen10 halamanOperationalization of Regenerative Design Indicators An Integrated Framework of Design and AnalysisVera MarinBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electronic For Marine EngineersDokumen45 halamanBasic Electronic For Marine EngineersŞansal DikmenerBelum ada peringkat
- Ductile Fracture & Brittle Fracture PDFDokumen39 halamanDuctile Fracture & Brittle Fracture PDFkoontattBelum ada peringkat
- EPT12 EZ Error CodesDokumen5 halamanEPT12 EZ Error CodesKiều Văn TrungBelum ada peringkat
- 11 de Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Audio KeyDokumen47 halaman11 de Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Audio Keythuy Linh100% (1)
- Hi-Kalibre Actuator ManualDokumen13 halamanHi-Kalibre Actuator Manual柴俊卿Belum ada peringkat
- Volvo: Electrical Wiring DiagramDokumen7 halamanVolvo: Electrical Wiring Diagramrusadi100% (5)
- V B TDokumen12 halamanV B TAshish KatariaBelum ada peringkat
- List Three Examples of Matter Changing From One State To AnotherDokumen31 halamanList Three Examples of Matter Changing From One State To AnotherygjyoBelum ada peringkat
- Som Intelligent Densities Vertical CommunitiesDokumen50 halamanSom Intelligent Densities Vertical CommunitiesRizwan Yousaf CheemaBelum ada peringkat
- Essentials of Economics, 10th Edition (2016)Dokumen468 halamanEssentials of Economics, 10th Edition (2016)Luis EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Dinli ATV Electrical System ManualDokumen15 halamanDinli ATV Electrical System ManualgryzzlyBelum ada peringkat
- Physics NotesDokumen13 halamanPhysics Noteswaheedlakho100% (2)
- Central Lincolnshire Local Plan Core StrategyDokumen370 halamanCentral Lincolnshire Local Plan Core Strategydaniel7120Belum ada peringkat
- Abdul Rasheed (2019-Me-34) Thermodynamic AssignmentDokumen6 halamanAbdul Rasheed (2019-Me-34) Thermodynamic AssignmentAbdul Rasheed GhaziBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Practice QuestionsDokumen12 halamanChemistry Practice QuestionsMfanafuthi0% (1)
- Marketing Plan BMW I3Dokumen20 halamanMarketing Plan BMW I3Nauman MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Quick Exhaust Solenoid Valves: NC NODokumen4 halamanQuick Exhaust Solenoid Valves: NC NOMuhammad AsadBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Interview Questions & Answers: Search For Jobs..Dokumen29 halamanTransformer Interview Questions & Answers: Search For Jobs..shamshadBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Specification of VSK PDFDokumen28 halamanTechnical Specification of VSK PDFmaran.suguBelum ada peringkat
- KKT Chillers PI ECO EngDokumen2 halamanKKT Chillers PI ECO EngjltenorioBelum ada peringkat
- 33-50-14 (Epu301)Dokumen30 halaman33-50-14 (Epu301)BehroozBelum ada peringkat
- 230L2M551 - Cement Mixing EquipmentDokumen43 halaman230L2M551 - Cement Mixing Equipmentyao nestorBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5. Neutron LoggingDokumen72 halamanLecture 5. Neutron LoggingDimash AbdrakhmanovBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Light-Front Dynamics For Pedestrians: 1 PreliminariesDokumen36 halamanAn Introduction To Light-Front Dynamics For Pedestrians: 1 PreliminariesBayer MitrovicBelum ada peringkat
- SREA-ECET (Mechanical) 8 Years Topic Wise Bit Bank-1 PDFDokumen68 halamanSREA-ECET (Mechanical) 8 Years Topic Wise Bit Bank-1 PDFDhanunjay JaguBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluating The Effectiveness of Retrofitting An Existing Hospitality Buildingsia in 2010-2014Dokumen8 halamanEvaluating The Effectiveness of Retrofitting An Existing Hospitality Buildingsia in 2010-2014International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Parts Catalogue: '19 ER300 AKF/AKFA (CL) (Z300)Dokumen87 halamanParts Catalogue: '19 ER300 AKF/AKFA (CL) (Z300)Yeison Cartagena BedoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Development of A Network and Gas Lift Allocation Model For Production Optimization in The Ras Budran FieldDokumen14 halamanDevelopment of A Network and Gas Lift Allocation Model For Production Optimization in The Ras Budran FieldTaiwo Adenike BashorunBelum ada peringkat
- Capacitors: Publishing As Pearson (Imprint) BoylestadDokumen71 halamanCapacitors: Publishing As Pearson (Imprint) BoylestadFaisal UddinBelum ada peringkat