Diarrhea
Diunggah oleh
Vilma Delos Reyes0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
48 tayangan15 halamanNursing Care Management 103
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniNursing Care Management 103
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
48 tayangan15 halamanDiarrhea
Diunggah oleh
Vilma Delos ReyesNursing Care Management 103
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 15
Anatomy and Physiology
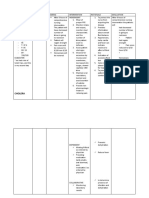
Diarrhea is an increase in the frequency, volume, and
fluid content of the stool. In diarrhea, the water
content of feces is increased usually due to either
malabsoprtion or water secretion in the bowel. It is a
manifestation rather than a primary disease.
Diarrhea may be acute or chronic. Acute diarrhea,
which lasts less than a week is usually due to an
infectious agent. Chronic diarrhea that persists longer
than 3 to 4 weeks may be caused by an inflammatory
disorders, malaabsoprtion and or endocrine disorders.
Overview of the Disease
There are two general types of diarrhea -- acute diarrhea
and chronic diarrhea. Acute diarrhea improves within two
weeks. Chronic diarrhea lasts longer than two weeks.
There are many possible causes of acute diarrhea. A few of
the more common causes include:
Viral infections (see Stomach Flu , Norovirus , or Rotavirus)
Bacterial infections, such those involving Salmonella typhi
and E. coli
Parasites, such as Giardia
Medicines
Anxiety .
Acute Versus Chronic
Infections
Medicines
Certain medical conditions like:
Certain types of surgery, such as gastric bypass surgery
Travel.
Sometimes, the cause of chronic diarrhea remains
unknown. As long as it goes away on its own, an
extensive search for the cause is not usually necessary.
Specific causes of chronic diarrhea
include:
Large watery stools daily
Sign and Symptoms
Specimen analysis, Stool specimen, stool culture
Purpose and description: a sample of stool is collected
for gross and microscopic examination, as well as form
and consistency and color. Gross examination includes
volume and water content and the presence of any
blood, pus, mucus, or excess fat. Microscopic
examination idenstifies the presence of WBCs,
unabsorbed fat and parasites. When an enteric
pathogen is suspected, a stool sample is taken.
Diagnostic
Absorbant and protectant kaolin and pectin
(kaopectate, donagel-MB)
Bismuth subsalicylate (pepto-bismol)
Absorbant preparation act locally in the intestine
to bind substance that can cause diarrhea.
Absorbants are safe and are generally available over
the counter. Their efficacy hasnot been shown to be
somewhat effective in preventing and managing
travellers diarrhea, usually related to contaminated
water supplies. Bismuth salts are also have a protective
and antimicrobial effect.
Medical Treatment
Opium and opium derivatives ( camporated tincture of
opium ( paregoric)
Tincture of opium ( laudanum, opium tincture); Difenoxin
(motofen); Diphenoxylate ( lomotil, lotrol, others);
Loperamide hydrochloride ( Imodium).
This drugs act on the central nervous system to decrease
the motility of the ileum and colon, slowing transit time
and promoting more water absorption. They also
decrease the sensation of a full rectum and increase anal
sphincter tone. Paregoric and tincture opium have a
greater potential for abuse and are prescription drugs
subject to controls under the Federal Controlled
Substance Act of 1970.
Take medication as ecommended at the onset of
diarrhea ad after each loose stool.
These drugs may be a habit forming; use for no more
than 48hrs.
Avoid using alcohol and over the counter cold
preparation while taking these drugs.
These preparations may cause drowsiness, avoid
driving or operating machinery while taking them.
Health teaching for the client
Anticholinergic ( atropine, Belladonna alkaloids (
Donnagel, Donnatal)
Anticholinergic medications reduce bowel spasticity
and acid secretion in the stomach. They are used to
treat diarrhea that is associated with peptic ulcer
disease and irritable bowel syndrome. These are non-
specific drugs; their systemic effects are their major
drawback.
Take only as directed, stop the drug and notify the
physician if you develop eye pain, impaired urination,
constipation.
Do not operate machinery while taking this drug,
drowsiness may occur.
Hard candies help relieve oral dryness associated with
these preparations
Health teaching for the client
Risk for fluid volume deficit
Record intake and output
Monitor vital signs including orthostatic blood pressure
Provide fluid and electrolyte replacement solutions as
indicated.
Nursing diagnosis
Diarrhea
Monitor and record the frequency and characteristics
of bowel movements.
Measure abdominal girth and auscultate bowel
sounds every 8hrs as indicated.
Use standard precautions, including gloves and hand
washing provide ready access to bathroom,
commode and or bedpan.
Administer anti- diarrheal medications as prescribed.
Risk for impaired skin integrity
Assist with the cleaning of perianal area as needed.
Apply protective ointment to the perianal area.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cognitive and Motor DevelopmentDokumen54 halamanCognitive and Motor DevelopmentVilma Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan For CellulitisDokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plan For CellulitisVilma Delos Reyes63% (16)
- Drug StudyDokumen9 halamanDrug StudyVilma Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Incision Drainage ProceduresDokumen35 halamanIncision Drainage ProceduresVilma Delos Reyes100% (1)
- More Than 100 Keyboard Shortcuts Must ReadDokumen6 halamanMore Than 100 Keyboard Shortcuts Must ReadMaayans Nathas100% (1)
- Examples of Reflective Writing: Example 1Dokumen5 halamanExamples of Reflective Writing: Example 1Christina JacobsonBelum ada peringkat
- Standard PracticeDokumen7 halamanStandard PracticeVilma Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinalobstruction 120819104604 Phpapp02Dokumen126 halamanIntestinalobstruction 120819104604 Phpapp02Vilma Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological AssessmentDokumen20 halamanNeurological AssessmentVilma Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Prevalence of Diarrhea Among Severely Malnourished Children Admitted in Government Hospital, Lahore, PakistanDokumen7 halamanPrevalence of Diarrhea Among Severely Malnourished Children Admitted in Government Hospital, Lahore, PakistanOpenaccess Research paperBelum ada peringkat
- Acute EnteritisDokumen12 halamanAcute Enteritishend_aserBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - LoperamideDokumen3 halamanDrug Study - LoperamideCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Management DeshidratationDokumen15 halamanManagement DeshidratationDani G CeñalBelum ada peringkat
- Personal Hygiene and Life Expectancy Improvements Since 1850: Historic and Epidemiologic AssociationsDokumen4 halamanPersonal Hygiene and Life Expectancy Improvements Since 1850: Historic and Epidemiologic AssociationsOutlawHealthBelum ada peringkat
- Elimination Pattern (Fecal) MSPDokumen20 halamanElimination Pattern (Fecal) MSPMuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Jackman2020 Article Medium-chainFattyAcidsAndMonogDokumen15 halamanJackman2020 Article Medium-chainFattyAcidsAndMonogIgor BaltaBelum ada peringkat
- Hygiene Promotion BriefingDokumen8 halamanHygiene Promotion BriefingMekiBelum ada peringkat
- New Suliyat SeminarDokumen21 halamanNew Suliyat SeminarHola MiBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Acting On GitDokumen70 halamanDrugs Acting On GitUkash sukarmanBelum ada peringkat
- Weaning Off Babies From A DiseaseDokumen272 halamanWeaning Off Babies From A DiseaseJun MagdaraogBelum ada peringkat
- DECACHORDS: A Guide to Homeopathic RemediesDokumen66 halamanDECACHORDS: A Guide to Homeopathic RemediesLisiane DuarteBelum ada peringkat
- NCP MeningitisDokumen2 halamanNCP MeningitisARISBelum ada peringkat
- Labor Advisory No. 01-23 Food and Waterborne Disease Prevention and Control in The WorkplaceDokumen2 halamanLabor Advisory No. 01-23 Food and Waterborne Disease Prevention and Control in The WorkplaceRaymond CruzinBelum ada peringkat
- Health Water SanitationDokumen47 halamanHealth Water SanitationMinaYaguelValenzuela100% (1)
- KlindexDokumen2 halamanKlindexPatricia MaglasangBelum ada peringkat
- AKC Dogs Poisonous Plant GuideDokumen1 halamanAKC Dogs Poisonous Plant GuidestallionrpBelum ada peringkat
- Vibrio Cholerae PosterDokumen1 halamanVibrio Cholerae PosterStela MonkBelum ada peringkat
- Performance of Clinical SignsDokumen4 halamanPerformance of Clinical SignsDina AryaniBelum ada peringkat
- C. Difficile-7Dokumen7 halamanC. Difficile-7Suprakkash DasBelum ada peringkat
- Diare PDFDokumen23 halamanDiare PDFGangsar DamaiBelum ada peringkat
- Report of Inservice EducationDokumen35 halamanReport of Inservice EducationAkansha JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Community Health Nursing: I - Definition of TermsDokumen25 halamanCommunity Health Nursing: I - Definition of TermsRichard Ines Valino97% (29)
- Water Borne DiseasesDokumen33 halamanWater Borne DiseasesHeinrichjohannesBelum ada peringkat
- Examination of The Gastrointestinal TractDokumen44 halamanExamination of The Gastrointestinal TractDrNaveen Singh Rajpurohit Kadu100% (1)
- Assignment On Cholera: Submitted ToDokumen17 halamanAssignment On Cholera: Submitted ToEhesanulHaqueSaifBelum ada peringkat
- Routine FecalysisDokumen25 halamanRoutine FecalysisE. B. F.Belum ada peringkat
- DPHO Final EditedDokumen24 halamanDPHO Final EditedBinita ShakyaBelum ada peringkat
- Group 4 Final Paper Bacterial OrganismDokumen55 halamanGroup 4 Final Paper Bacterial OrganismRodriguez, Jhe-ann M.Belum ada peringkat
- Charcoal PDFDokumen12 halamanCharcoal PDFbeedgai100% (1)