CISC y RISC Architectures
Diunggah oleh
IvanArias20 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
52 tayangan12 halamanThis document compares and contrasts CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) and RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) architectures. CISC uses large, complex instructions that can perform multiple operations in one instruction, while RISC uses simpler instructions that are optimized to perform single operations. Historically, CISC was developed when memory was slow and expensive, so complex instructions reduced memory accesses. Later, RISC emerged as memory speeds increased and studies showed CISC instructions went underutilized. CISC trades off more cycles per instruction for fewer instructions total, while RISC aims to minimize cycles per instruction at the cost of more total instructions. Examples show a multiplication operation requiring one instruction in CISC versus four instructions in
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
CISC y RISC Architectures.pptx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document compares and contrasts CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) and RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) architectures. CISC uses large, complex instructions that can perform multiple operations in one instruction, while RISC uses simpler instructions that are optimized to perform single operations. Historically, CISC was developed when memory was slow and expensive, so complex instructions reduced memory accesses. Later, RISC emerged as memory speeds increased and studies showed CISC instructions went underutilized. CISC trades off more cycles per instruction for fewer instructions total, while RISC aims to minimize cycles per instruction at the cost of more total instructions. Examples show a multiplication operation requiring one instruction in CISC versus four instructions in
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
52 tayangan12 halamanCISC y RISC Architectures
Diunggah oleh
IvanArias2This document compares and contrasts CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) and RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) architectures. CISC uses large, complex instructions that can perform multiple operations in one instruction, while RISC uses simpler instructions that are optimized to perform single operations. Historically, CISC was developed when memory was slow and expensive, so complex instructions reduced memory accesses. Later, RISC emerged as memory speeds increased and studies showed CISC instructions went underutilized. CISC trades off more cycles per instruction for fewer instructions total, while RISC aims to minimize cycles per instruction at the cost of more total instructions. Examples show a multiplication operation requiring one instruction in CISC versus four instructions in
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 12
CISC y RISC Architectures
Ivn Alberto Arias Galvis
Universidad Nacional de Colombia
Sede Manizales
14 de Agosto de 2012
1
Meaning and characteristics of CISC
Both refers to the machine (microprocessor)
instruction set architecture ISA.
CISC: Complex instruction set computer.
large instruction set
instructions can perform very complex operations,
powerful assembly language
variable instruction formats
large number of addressing modes
few registers
machine instructions implemented with microcode
2
Meaning and characteristics of RISC
RISC: Reduced instruction set computer.
relatively few instructions
simple addressing modes, only load/store
instructions
access memory
uniform instruction length
many registers
no microcode
pipelined instruction execution
3
History I
In the beginning the memory was an invaluable
resource, and the access time was pretty slow,
so the instructions was powerful enough to
develop complex operations and only occupy one
memory space, which only had to be acceded
one time, this was the principal goal of CISC,
additionally the reduction of semantic gap and
the incipiency of compilers was a problem to
overcome.
4
History II
The advance in memory speed and studies that
demonstrated that a wide part of the CISC
instructions was actually unused leaded to the
research of a computing based in elemental
instructions and pipelined execution.
5
Processor performance
The CISC approach attempts to minimize the
number of instructions per program, sacrificing
the number of cycles per instruction.
RISC does the opposite, reducing the cycles per
instruction at the cost of the number of
instructions per program
6
Comparison
7
CISC RISC
Emphasis on hardware Emphasis on software
Includes multi-clock complex
instructions
Single-clock, reduced instruction
only
Memory-to-memory:
"LOAD" and "STORE" incorporated
in
Instructions
Register to register:
"LOAD" and "STORE" are
independent instructions
Small code sizes, high cycles per
second
Low cycles per second, large code
Sizes
Transistors used for storing
complex
Instructions
Spends more transistors on
memory registers
Machines Using CISC and RISC
Architectures
CISC:
Intel 80486
RISC:
ARM
MIPS
PowerPC
8
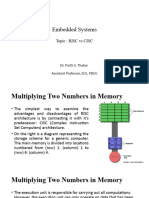
Example: CISC Approach for a product
of two operands
CISC Approach
CISC design would try to finish the task in the minimum
possible instructions by implementing hardware which could
understand and execute series of operations. Thus the
processor would come with a specific instruction MUL in its
instruction set. MUL will loads the two values from the
memory into separate registers, multiplies the operands in the
execution unit, and then stores the product in the appropriate
location. So, the entire task of multiplying two numbers can
be completed with one instruction:
MUL 1:3, 4:2
MUL is referred to as a "complex instruction" as it operates
directly on the computer's memory banks and does not
require the programmer to explicitly call any loading
or storing functions.
9
Example:RISC Approach for a product
of two operands
RISC processors use simple instructions that can be executed within
a clock cycle. Thus, MUL instruction will be divided into three
instructions.
i) "LOAD," which moves data from the memory bank to a
register,
ii) "PROD," which finds the product of two operands located
within the registers, and
iii) "STORE," which moves data from a register to the memory
banks.
In order to perform the task, a programmer would need to code four
lines of assembly:
LOAD A, 1:3
LOAD B, 4:2
PROD A, B
STORE 1:3, A
10
Bibliography
http://www.engineersgarage.com/articles/risc-
and-cisc-architecture
http://users.abo.fi/mats/codeopt2011/handouts
/Processors.pdf
Example
11
Thanks
Questions
12
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- C Programming for the PIC Microcontroller: Demystify Coding with Embedded ProgrammingDari EverandC Programming for the PIC Microcontroller: Demystify Coding with Embedded ProgrammingBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Computer SystemsDokumen16 halamanStructure of Computer SystemsMussie KebedeBelum ada peringkat
- Risc Cisc in Microcontroller and MicroprocessorDokumen31 halamanRisc Cisc in Microcontroller and Microprocessormanvir kaurBelum ada peringkat
- Cisc & Risc: Mr. Sunanda DasDokumen19 halamanCisc & Risc: Mr. Sunanda DasTowsif100% (1)
- The Simplest Way To Examine The Advantages and Disadvantages of RISC Architecture Is by Contrasting It With ItDokumen11 halamanThe Simplest Way To Examine The Advantages and Disadvantages of RISC Architecture Is by Contrasting It With ItsaadawarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 07 RISCDokumen62 halamanChapter 07 RISCBinod SAdhikariBelum ada peringkat
- Instruction Set ArchitectureDokumen4 halamanInstruction Set ArchitectureashuBelum ada peringkat
- Session2 - Introduction To RISC and CISCDokumen4 halamanSession2 - Introduction To RISC and CISCHillary MurungaBelum ada peringkat
- CISC Vs RISC and I286, I386, I486Dokumen12 halamanCISC Vs RISC and I286, I386, I486Manash MandalBelum ada peringkat
- PPT4 - Module 1Dokumen15 halamanPPT4 - Module 1sammy CBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Organization and Architecture: CLSC & RiscDokumen15 halamanComputer Organization and Architecture: CLSC & RiscJayanta SikdarBelum ada peringkat
- Cisc Vs RiscDokumen3 halamanCisc Vs RiscGeorgiana DanilaBelum ada peringkat
- RISC and CISC - Eugene ClewlowDokumen17 halamanRISC and CISC - Eugene Clewlowilg1Belum ada peringkat
- Risc and Cisc: by Eugene ClewlowDokumen17 halamanRisc and Cisc: by Eugene ClewlowRamnath PraveenBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Computer Architecture 1 1Dokumen118 halamanAdvanced Computer Architecture 1 1SharathMenonBelum ada peringkat
- Risc and Cisc: by Eugene ClewlowDokumen17 halamanRisc and Cisc: by Eugene ClewlowSampathhhhh Sai TadepalliBelum ada peringkat
- RISC Vs CISCDokumen10 halamanRISC Vs CISCbrijesh.gec21Belum ada peringkat
- (Computer Architecture CIA-3) : (By: Nikhil Kumar Yadav) (Roll. No.: 1847241) (Date of Submission: 06-09-2019)Dokumen8 halaman(Computer Architecture CIA-3) : (By: Nikhil Kumar Yadav) (Roll. No.: 1847241) (Date of Submission: 06-09-2019)NIKHIL KUMAR YADAV 1847241Belum ada peringkat
- Mod5 1Dokumen18 halamanMod5 1welcome to my worldBelum ada peringkat
- The Simplest Way To Examine The Advantages and Disadvantages of RISC Architecture Is by Contrasting It With ItDokumen4 halamanThe Simplest Way To Examine The Advantages and Disadvantages of RISC Architecture Is by Contrasting It With ItMushawatuBelum ada peringkat
- Risc and Cisc: Computer ArchitectureDokumen17 halamanRisc and Cisc: Computer Architecturedress dressBelum ada peringkat
- Task 5Dokumen3 halamanTask 5Fajri RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Risc A Cisc PDokumen10 halamanRisc A Cisc PAlexander KirosBelum ada peringkat
- RISC Architecture and Super Computer: Prof. Sin-Min Lee Department of Computer Science San Jose State UniversityDokumen85 halamanRISC Architecture and Super Computer: Prof. Sin-Min Lee Department of Computer Science San Jose State UniversityAvneet JohalBelum ada peringkat
- Jan Marie Veatrice M. Pacia 4-ECE: What Are Cisc and Risc Architecture? How Do They Differ From Each Other?Dokumen6 halamanJan Marie Veatrice M. Pacia 4-ECE: What Are Cisc and Risc Architecture? How Do They Differ From Each Other?Jan Marie Veatrice PaciaBelum ada peringkat
- RISC Architecture: Prof. Sin-Min Lee Department of Computer Science San Jose State UniversityDokumen69 halamanRISC Architecture: Prof. Sin-Min Lee Department of Computer Science San Jose State UniversityArgneshu GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Risc and CiscDokumen17 halamanRisc and CiscAyazBelum ada peringkat
- Risc and CiscDokumen20 halamanRisc and Ciscprathapreddy420Belum ada peringkat
- Lec 3Dokumen20 halamanLec 3Prateek GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- RISC vs. CISCDokumen12 halamanRISC vs. CISCafaakiBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Arcitecture Assignment: Risc-Reduced Instruction Set ComputerDokumen5 halamanComputer Arcitecture Assignment: Risc-Reduced Instruction Set ComputerantoBelum ada peringkat
- MPMC (Unit 01) Part 02Dokumen39 halamanMPMC (Unit 01) Part 02bovas.biju2021Belum ada peringkat
- CSS 548 Joshua LoDokumen13 halamanCSS 548 Joshua LoliuylBelum ada peringkat
- Risc PropertiesDokumen2 halamanRisc PropertiesSwetha RamBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation RISC Vs CISCDokumen13 halamanPresentation RISC Vs CISCafaakiBelum ada peringkat
- Coa 9Dokumen4 halamanCoa 9adadaBelum ada peringkat
- General IntroductionDokumen29 halamanGeneral IntroductionMisrak kassahunBelum ada peringkat
- Cisc Vs Risc: Multiplying Two Numbers in MemoryDokumen4 halamanCisc Vs Risc: Multiplying Two Numbers in MemoryItz Sami UddinBelum ada peringkat
- Risc Arcitecture (Reduced Instructuion Set Computers) by PrateekDokumen14 halamanRisc Arcitecture (Reduced Instructuion Set Computers) by Prateekprateek1706Belum ada peringkat
- Risc and Cisc: By: Farheen Masood Sania ShahzadDokumen17 halamanRisc and Cisc: By: Farheen Masood Sania ShahzadAlia BashirBelum ada peringkat
- Risc Vs CiscDokumen1 halamanRisc Vs CiscPrateek SanchetiBelum ada peringkat
- Cisc and Risc NotesDokumen3 halamanCisc and Risc NoteskavitaBelum ada peringkat
- Complex Instruction Set ComputerDokumen17 halamanComplex Instruction Set ComputerkangkanpaulBelum ada peringkat
- Von Neumann Architecture vs. HarvardDokumen22 halamanVon Neumann Architecture vs. Harvardkaleab seleshiBelum ada peringkat
- Parallel Processing Chapter - 2: Basics of Architectural DesignDokumen29 halamanParallel Processing Chapter - 2: Basics of Architectural DesignGetu GeneneBelum ada peringkat
- Assembly IntroductionDokumen31 halamanAssembly Introductionsohaibislam202Belum ada peringkat
- Computer Architect AssignmentDokumen2 halamanComputer Architect AssignmentINAMBelum ada peringkat
- Risc and Cisc Processors: by Chimi DorjiDokumen9 halamanRisc and Cisc Processors: by Chimi DorjiChencho DorjiBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT-1 Introduction To MicrocontrollersDokumen8 halamanUNIT-1 Introduction To MicrocontrollerssupriyaBelum ada peringkat
- W5 - L3 - Inst Set Archi-RISC CISCDokumen34 halamanW5 - L3 - Inst Set Archi-RISC CISCNeel RavalBelum ada peringkat
- Microprocessor UNIT - IVDokumen87 halamanMicroprocessor UNIT - IVMani GandanBelum ada peringkat
- Microprocess OR & Computer Architecture: 14CS253 / UE14CS253Dokumen12 halamanMicroprocess OR & Computer Architecture: 14CS253 / UE14CS253Prathik GSBelum ada peringkat
- ISA ModelsDokumen5 halamanISA ModelsFahad Tanveer MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Architecture Lesson 2 (Instruction Set Architecture)Dokumen9 halamanComputer Architecture Lesson 2 (Instruction Set Architecture)ghassanBelum ada peringkat
- Risc Vs Cisc: Multiplying Two Numbers in MemoryDokumen4 halamanRisc Vs Cisc: Multiplying Two Numbers in MemoryFiq WaggBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Cisc RiscDokumen37 halaman03 Cisc RiscahmedBelum ada peringkat
- RISC vs. CISCDokumen3 halamanRISC vs. CISCladukhushi09Belum ada peringkat
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.Dari EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.Belum ada peringkat
- Microcontroller Weightage Revised 2019-20Dokumen4 halamanMicrocontroller Weightage Revised 2019-20lalaBelum ada peringkat
- Csen2011 - Computer Organization & ArchitectureDokumen2 halamanCsen2011 - Computer Organization & ArchitectureAsha Pavani KBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter1 - The 8051Dokumen16 halamanChapter1 - The 8051Aaron Lewis DinkinBelum ada peringkat
- Intel Core I7 Comparison ChartDokumen1 halamanIntel Core I7 Comparison ChartEveling ValdiviezoBelum ada peringkat
- Microprocessor MP Exercise QuestionsDokumen3 halamanMicroprocessor MP Exercise QuestionsShack WebsterBelum ada peringkat
- Skylake ArchitectureDokumen31 halamanSkylake ArchitecturekrantiBelum ada peringkat
- White Paper - Cortex-M For Beginners - 2016 (Final v3) PDFDokumen25 halamanWhite Paper - Cortex-M For Beginners - 2016 (Final v3) PDFjuanitoingBelum ada peringkat
- AVR Exam Sheets V5.1-1Dokumen12 halamanAVR Exam Sheets V5.1-1nancyrazzak5Belum ada peringkat
- How To Unlock Intel CPU.Dokumen4 halamanHow To Unlock Intel CPU.uswa shafiqBelum ada peringkat
- ISA 2 Regular Solution-1Dokumen4 halamanISA 2 Regular Solution-1mqtmqyBelum ada peringkat
- FIR Filters: ELG6163 Miodrag BolicDokumen11 halamanFIR Filters: ELG6163 Miodrag Bolicchums_23Belum ada peringkat
- U3 PIC 18F Microcontroller InterruptsDokumen59 halamanU3 PIC 18F Microcontroller Interruptsmadhukar v nimbalkarBelum ada peringkat
- Intel 8088 (8086) Microprocessor Structure: Haibo Wang ECE Department Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 62901Dokumen16 halamanIntel 8088 (8086) Microprocessor Structure: Haibo Wang ECE Department Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 62901Chandrashekhar PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Cpu, Mobo, Gpu, Server, 15.12Dokumen1 halamanCpu, Mobo, Gpu, Server, 15.12ElmiExtremodBelum ada peringkat
- Pipeline Hazards: Christos Kozyrakis Stanford UniversityDokumen48 halamanPipeline Hazards: Christos Kozyrakis Stanford UniversityMo LêBelum ada peringkat
- 8051 Instruction Set: Machine Code, Opcode, Operand and Assembly InstructionDokumen19 halaman8051 Instruction Set: Machine Code, Opcode, Operand and Assembly Instructionharshad lokhandeBelum ada peringkat
- Me 3311 - MCPLC Unit Du 1 Study NotesDokumen4 halamanMe 3311 - MCPLC Unit Du 1 Study Notessivaeeinfo100% (1)
- CPU Organization Bindu AgarwallaDokumen22 halamanCPU Organization Bindu AgarwallaNobodyBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Micro DevicesDokumen17 halamanAdvanced Micro DevicesAris MabangloBelum ada peringkat
- About Intel Virtualization Supported CPUsDokumen11 halamanAbout Intel Virtualization Supported CPUsasimalampBelum ada peringkat
- 170 Infrared KeyboxDokumen1 halaman170 Infrared KeyboxzulBelum ada peringkat
- Which of The Following Is Not A Computer Functional Block?Dokumen7 halamanWhich of The Following Is Not A Computer Functional Block?Lady Anne CruzBelum ada peringkat
- 8051 InterruptDokumen21 halaman8051 InterruptarunvittoBelum ada peringkat
- Arria 10 Product TableDokumen2 halamanArria 10 Product Tablesmith1011Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 06 Computer Organization and Design, Fifth Edition: The Hardware/Software Interface (The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Computer Architecture and Design) 5th EditionDokumen57 halamanChapter 06 Computer Organization and Design, Fifth Edition: The Hardware/Software Interface (The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Computer Architecture and Design) 5th EditionPriyanka Meena100% (1)
- S11 InterruptsDokumen69 halamanS11 InterruptsThesisRequirementBelum ada peringkat
- Itanium MicroprocessorrDokumen16 halamanItanium MicroprocessorrAmmar Al-KindyBelum ada peringkat
- LogDokumen2 halamanLogATS TLBelum ada peringkat
- Ec2304 LP III EceDokumen5 halamanEc2304 LP III EcesunvenkatBelum ada peringkat
- Hardware MultithreadingDokumen4 halamanHardware MultithreadingRevathi Krishnan100% (1)