Introduction To OBG
Diunggah oleh
sindhujojoJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Introduction To OBG
Diunggah oleh
sindhujojoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sindhu Sebastian
Lecturer
FMCON
Midwifery is as old as the history of human species.
Mid With
Wife - Woman
The art of assisting woman
in child birth
The definition term midwife was developed by
international confederation of midwives in
1972.
Midwife: A midwife is a person who, having been
regularly admitted to a midwifery educational
programme, duly recognized in the country in which it
is located, has successfully completed the prescribed
courses or studies in midwifery and has acquired the
requisite qualifications to be registered and or legally
licensed to practice midwifery.(WHO 1992)
Midwifery: is the knowledge necessary to perform the
duties of a midwife.
Obstetrics is a branch of medicine
concerned with the treatment of women
during pregnancy, childbirth birth.
Nursing encompasses autonomous and
collaborative care of individuals of all ages,
families, groups and communities, sick or well
and in all settings. Nursing includes the
promotion of health, prevention of illness, and
the care of ill, disabled and dying people.
Advocacy, promotion of a safe environment,
research, participation in shaping health policy
and in patient and health systems management,
and education are also key nursing roles. (ICN
2002)
Obstetrical nursing : Nursing care given to the
pregnant patient before, during, or after
childbirth.
Midwifery today:
Midwifery education & practice go beyond scope
of practice Outlined in the definition.
Nurse- midwifery
Education- midwifery + nursing+
medicine
Practice- all midwifery + components of nursing+
medicine
QUALITIES OF MIDWIVES
Skill full
Able to assess the women
Health educator
Managing care ability
Professionally competent
good communicator
Team spirit
Counselor
Midwifery is as old as the history of human
species
Archeological evidence of a women in squatting
in childbirth supported by another women from
behind existence of midwifery in 5000 BC
References in old testament
- Hebrew midwives
Hippocrates (460 BC) trained &
Supervised midwives
Aristotle(384-322BC) discussed the
essential qualities of midwife
Soranus -2
nd
centuaryspecialized in OBG
5
th
-15
th
century untrained midwives controlled
practice of midwifery.
In 1513 first book on midwifery was printed in
Germany based on teaching of Soranus (2
nd
century first to specialize OBG-1,500 years).
1540 translated in English (used for 150 years)
doctors excluded from labor room &
midwives assisted in childbirth)
Ambroise Pare founded a school for
midwives in Paris
Louise Bourgeos a midwife recommended
induction of labor for pelvic contraction.
Julius Caeser Aranzi wrote first book for
Italian midwives-17
editions. Advised cesarean
section for contracted pelvis. But term had
come from Latin word caedere means to cut.
William Harvey (1578-1657), father of British
midwifery,wrote 1
st
English textbook on
midwifery. He described fetal circulation and
placenta. First to deliver placenta by massaging
the uterus
French king Louis XIV (1663)
employed a Paris surgeon to attend
his mistresses in labour- honoured with
name accouchear -a person who assists
women in childbirth.
Mauriceau (physician) in
published a Treatise on
midwifery. He
described attitude
of fetus in uterus
Hugh Chamberlen -1965
designed obstetrical forceps.
William smellie explained
labour process .
Pelvimetry, Cephalometry
Forceps delivery
The midwifery chair was
founded in 1726 in university
Edinburgh.
John Leake replaced it with
delivery beds
Charles White stated
that puerperal fever was infectious
and Gordon explained puerperal sepsis
Fielding Ould described normal labour and
performed episiotomy.
Francois recognized fetal heart sound.
James Young used Chloroform first in
obstetrics for anesthesia.
Florence Nightingale conducted training for
midwives in 1862.
Semmelweiss demonstrated causes &
preventive measures for puerperal sepsis.
Louis Pasteur wrote a thesis on it demonstrating
presence of Streptococci in Lochia.
Spencer & Ballyantyne promoted concept of
antenatal care for pregnant women.
Munro Kerr 1926 introduced technique LSCS.
DEVELOPMENT OF MATERNITY SERVICES IN
INDIA
Earlier midwifery was practised by Dais.
In early part of 20
th
century changes in
practices began to occur.
Health Organization
Director General of IM
services+ Surgeon General of
Civil hospitals in States
Administration & maintenance
of associated institutions
Public heath commissioner +
Sanitation Commissioner in
States
Preventive health services
The All India Institute of Hygiene &
Public Health established in 1930 under
Rockefeller foundation which provided
programms for MCH.
1943- Govt. appointed Bhore committee which
recommended PHC for every 40,000 population with
having staff of each unit: 1 institutional nurse, 4
midwivwes & 4 trained dais. Programs for TD & ANMs
were started based on its report.
Training programs for nurses were
Mainly in mission hospitals.
Christian medical College Hospital
Vellore in
Tamil Nadu had nurses training program.
NSs of Mission Hospitals felt need for an organization
of their own by 1911.
1931- a formal institution of nurses was started- Nurses
Auxiliary of Christian medical Association of
India(CMAI)
1964- renamed as Nurses League. They had 2 boards of
nsg.education.
Mid India B.N.E+ B.N.E, south India branch.They had
GNM +ANM courses
1949- Indian Nursing Council
(INC) was Constituted.
It formulated standards for
Nsg.Educ.in the country.
During last five decades N.Edu has advanced.
Midwifery training is included into 3 yr basic
general nsg.program i.e diploma in nsg &
midwifery.
ANM program 2 yrs & MHW-multipurpose
health worker program- 18 months
B.SC+ M.SC courses are also available now.
Edu & practice in institutions approved by SNC
+ INC are mandatory for practicing nsg
+midwifery.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Midwife in My Pocket: Pregnancy, Birth, and Life with a New Baby, Told as It Really IsDari EverandA Midwife in My Pocket: Pregnancy, Birth, and Life with a New Baby, Told as It Really IsBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To MidwiferyDokumen27 halamanIntroduction To MidwiferySHOWMAN DEEPAK100% (2)
- History and Contempary PerspectivesDokumen4 halamanHistory and Contempary PerspectivesManinder SekhonBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 - Introduction To MidwiferyDokumen25 halamanUnit 1 - Introduction To Midwiferypriya100% (1)
- Managing Obstetrical Emergencies & Its ChallengesDokumen58 halamanManaging Obstetrical Emergencies & Its Challengessanthiyasandy100% (1)
- Induction & Management of Labour GuideDokumen45 halamanInduction & Management of Labour GuideLamnunnem HaokipBelum ada peringkat
- Management of PuerperiumDokumen22 halamanManagement of Puerperiumannu panchalBelum ada peringkat
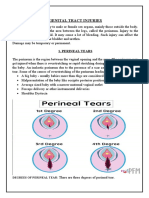
- Genital Tract InjuriesDokumen19 halamanGenital Tract InjuriesMarvella Nongkhar100% (1)
- Independent Midwifery PracticeDokumen18 halamanIndependent Midwifery Practiceneeta rajesh bhide100% (3)
- MCH ProgrammeDokumen14 halamanMCH ProgrammepriyankaBelum ada peringkat
- MINOR DISORDERS OF PREGNANCY FinalDokumen6 halamanMINOR DISORDERS OF PREGNANCY FinalChedupLepcha100% (7)
- Kangroo Mother Care PDFDokumen25 halamanKangroo Mother Care PDFMission Neet-PgBelum ada peringkat
- English Ii Assignment: Midwifery Management in Cephalopelvic DisproportionDokumen14 halamanEnglish Ii Assignment: Midwifery Management in Cephalopelvic DisproportionBintari Ancinonyx JubatusBelum ada peringkat
- Role and Scope of Midwifery PracticeDokumen23 halamanRole and Scope of Midwifery Practicesweta100% (1)
- Independent Nurse PractitionerDokumen14 halamanIndependent Nurse PractitionerKarishma Shroff100% (1)
- Management of PuerperiumDokumen28 halamanManagement of PuerperiumVarna MohanBelum ada peringkat
- Epidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDokumen30 halamanEpidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthNitin Sharma100% (1)
- Examination of PlacentaDokumen2 halamanExamination of PlacentaAnju MargaretBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of postnatal women & nursing managementDokumen26 halamanAssessment of postnatal women & nursing managementakanksha100% (1)
- Topic 7 NURSE MIDWIFERY PRACTITIONER NavjotDokumen7 halamanTopic 7 NURSE MIDWIFERY PRACTITIONER NavjotSimon JosanBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Labor Essential Factors Elements of Uterine Contractions & Physiology of 1 Stage of LaborDokumen88 halamanNormal Labor Essential Factors Elements of Uterine Contractions & Physiology of 1 Stage of LaborAswathy Aswathy100% (1)
- Abortion PP TDokumen42 halamanAbortion PP TDivya ToppoBelum ada peringkat
- Perineal TearsDokumen44 halamanPerineal TearsMagic_OverBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Midwifery PracticeDokumen17 halamanRole of Midwifery PracticeTania ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- Journal PresentationDokumen14 halamanJournal PresentationValarmathiBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal Examination According To WHODokumen6 halamanAntenatal Examination According To WHOManisha ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- Babay Friendly Hospital InitiativeDokumen15 halamanBabay Friendly Hospital InitiativeRajeev NepalBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal Placenta & Umbilical Cord GuideDokumen31 halamanAbnormal Placenta & Umbilical Cord GuideIdiAmadou100% (1)
- 5.theories and Models of MidwiferyDokumen29 halaman5.theories and Models of MidwiferyRatna KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Specific Teaching Objectives Contents Hr Resourse learning activities aids evaluation personDokumen14 halamanSpecific Teaching Objectives Contents Hr Resourse learning activities aids evaluation personsandeepv08100% (1)
- Preparation For ParenthoodDokumen8 halamanPreparation For ParenthoodKoushik ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- AbortionsDokumen99 halamanAbortionsAGERI PUSHPALATHABelum ada peringkat
- Midwifery and Obstetric NursingDokumen9 halamanMidwifery and Obstetric NursingANUM NOORIBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal Uterine Action GuideDokumen27 halamanAbnormal Uterine Action Guidetanmai noolu100% (1)
- Minor Disorders of PregnancyDokumen28 halamanMinor Disorders of PregnancyAbdullahi Suleiman Maka100% (1)
- Family Welfare ServicesDokumen20 halamanFamily Welfare Servicesbemina ja100% (2)
- Assessing KAP of nurses on partograph useDokumen20 halamanAssessing KAP of nurses on partograph usemohapatra dev100% (1)
- BFHIDokumen10 halamanBFHIArchana Sahu100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health IssuesDokumen12 halamanMaternal and Child Health IssuesQudrat Un NissaBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine Malformations PDFDokumen6 halamanUterine Malformations PDFsaritha OrugantiBelum ada peringkat
- Front Page of Lesion PlanDokumen11 halamanFront Page of Lesion Planarchna gargBelum ada peringkat
- Preventive ObstetricsDokumen8 halamanPreventive ObstetricsAnn Merlin JobinBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Historical ReviewDokumen3 halaman1 Historical ReviewNoraBelum ada peringkat
- History of Development of Nursing Profession J CharacteristicsDokumen28 halamanHistory of Development of Nursing Profession J CharacteristicsSushma SwathiBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal Care PPT EchyDokumen14 halamanAntenatal Care PPT EchyYuliana alensi falloBelum ada peringkat
- Third Stage of LabourDokumen39 halamanThird Stage of LabourabydlBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Stage of LaborDokumen79 halaman2nd Stage of LaborJissa DaisonBelum ada peringkat
- Amnioscopy EnglishDokumen2 halamanAmnioscopy EnglishAlya BudiBelum ada peringkat
- Development and Evolution of Nursing Education in IndiaDokumen6 halamanDevelopment and Evolution of Nursing Education in Indiasteffy sojan100% (1)
- A Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Program On Knowledge and Practice Regarding Kangaroo Mother Care Among Post Natal Mothers Having Low Birth Weight Babies 1Dokumen9 halamanA Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Program On Knowledge and Practice Regarding Kangaroo Mother Care Among Post Natal Mothers Having Low Birth Weight Babies 1Manisa ParidaBelum ada peringkat
- Pain Relief in Labour (English)Dokumen60 halamanPain Relief in Labour (English)lieynna4996100% (2)
- Trends in The Midwifery and Obstetrical NursingDokumen26 halamanTrends in The Midwifery and Obstetrical NursingNilakshi Barik Mandal89% (9)
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka Synopsis Proforma For Registration of Subjects For DissertationDokumen14 halamanRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka Synopsis Proforma For Registration of Subjects For Dissertationpavin0% (1)
- Research Proposal WRDDokumen38 halamanResearch Proposal WRDEsha KuttiBelum ada peringkat
- Contemprory Issues in ObstetricsDokumen6 halamanContemprory Issues in ObstetricsDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- SHARONDokumen65 halamanSHARONFaith InstitutionsBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar ON: Baby Friendly Hospital InitiativeDokumen7 halamanSeminar ON: Baby Friendly Hospital InitiativeUmairah BashirBelum ada peringkat
- Genital Tract InjuryDokumen24 halamanGenital Tract InjuryAbdulJabar Riadh100% (1)
- Educational Aims and ObjectivesDokumen49 halamanEducational Aims and Objectivessona100% (2)
- Minor Disorders of Pregnancy For 3rd BSC 2014Dokumen29 halamanMinor Disorders of Pregnancy For 3rd BSC 2014sindhujojo100% (2)
- Adolescent Pregnacy, Unwed Mother, Sexual Violence - 3rd BSC 2014Dokumen236 halamanAdolescent Pregnacy, Unwed Mother, Sexual Violence - 3rd BSC 2014sindhujojo0% (1)
- Abortion - PPT For 2nd MSCDokumen121 halamanAbortion - PPT For 2nd MSCsindhujojo33% (3)
- Certified Nurse MidwifeDokumen21 halamanCertified Nurse MidwifesindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Methods ReportingDokumen13 halamanMethods ReportingsindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Breast FeedingDokumen43 halamanBreast FeedingsindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Records&ReportsDokumen39 halamanRecords&ReportssindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Lie, Presentation Position For 3rd BSC 2014Dokumen33 halamanLie, Presentation Position For 3rd BSC 2014sindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal Care: A Guide to Regular Pregnancy ExaminationsDokumen109 halamanAntenatal Care: A Guide to Regular Pregnancy ExaminationssindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Caserian SectionDokumen100 halamanCaserian SectionsindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Antenatal CareDokumen58 halamanAntenatal Caresindhujojo100% (1)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDokumen44 halamanAbnormal Uterine BleedingsindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Genetic Counseling GNM ClasssDokumen37 halamanGenetic Counseling GNM Classssindhujojo100% (2)
- Genetic Counseling Presentation SummaryDokumen28 halamanGenetic Counseling Presentation SummarysindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Resources Documents Word 5H2j PS RoleOfRNGeneticTestingDokumen2 halamanResources Documents Word 5H2j PS RoleOfRNGeneticTestingsindhujojoBelum ada peringkat
- Test Paper For Paper 1 STAGE 8Dokumen14 halamanTest Paper For Paper 1 STAGE 8Dương Ngọc Cường73% (15)
- High-Risk Pregnancy Factors & CareDokumen19 halamanHigh-Risk Pregnancy Factors & CareRoger Jr PumarenBelum ada peringkat
- New Vistas In: Fetal MedicineDokumen2 halamanNew Vistas In: Fetal MedicineRaviraj TirukeBelum ada peringkat
- Caesarian Section: Case PresentationDokumen23 halamanCaesarian Section: Case PresentationRiza Angela BarazanBelum ada peringkat
- Breech PresentationDokumen35 halamanBreech PresentationPrince Jhessie L. AbellaBelum ada peringkat
- Acog 216 Macrosomia Resumen PDFDokumen3 halamanAcog 216 Macrosomia Resumen PDFOrlando CuellarBelum ada peringkat
- The Sexual Soulmate Pact Susan Bratton PDFDokumen56 halamanThe Sexual Soulmate Pact Susan Bratton PDFyaoyang hung60% (5)
- English Course Family Tree PracticeDokumen13 halamanEnglish Course Family Tree PracticeJulisa OjedaBelum ada peringkat
- WordDokumen49 halamanWordMarko ShabanofOzz0% (1)
- Boy Robin Resume 2 FinalDokumen2 halamanBoy Robin Resume 2 Finalapi-3702572Belum ada peringkat
- Clerking Edited by Nada.H.BDokumen4 halamanClerking Edited by Nada.H.BAbdulrahman NajiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1Dokumen3 halamanChapter 2 Lesson 1John Carldel VivoBelum ada peringkat
- Factors That Can Influence The Counselling Session - Counselling For Maternal and Newborn Health Care - Ncbi BookshelfDokumen15 halamanFactors That Can Influence The Counselling Session - Counselling For Maternal and Newborn Health Care - Ncbi BookshelfNur Ain KhadirBelum ada peringkat
- MCQS On PHYSIOLOGY OF LACTATIONDokumen6 halamanMCQS On PHYSIOLOGY OF LACTATIONnighatkhanBelum ada peringkat
- Gender in The Classroom Daniel Van de KieftDokumen11 halamanGender in The Classroom Daniel Van de Kieftapi-374340003Belum ada peringkat
- The Histori Kebidanan 1Dokumen200 halamanThe Histori Kebidanan 1Delsy NurrizmaBelum ada peringkat
- Research Assignment-Kevin Moore 1Dokumen10 halamanResearch Assignment-Kevin Moore 1api-308654647Belum ada peringkat
- Sexul Tantric En, CarteDokumen129 halamanSexul Tantric En, CarteryankarminBelum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource Was: ATI Maternal Newborn Proctored Exam Study Set 1Dokumen4 halamanThis Study Resource Was: ATI Maternal Newborn Proctored Exam Study Set 1Gina Giammalvo100% (5)
- Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDokumen13 halamanStages of Prenatal DevelopmentTherisse Joy MagtibayBelum ada peringkat
- Memoirs of A Woman of PleasureDokumen8 halamanMemoirs of A Woman of PleasureShy Koo RahBelum ada peringkat
- Amniotic FluidDokumen12 halamanAmniotic FluidprembarnabasBelum ada peringkat
- #185 - People vs. AbulonDokumen3 halaman#185 - People vs. AbulonGenerousdeGuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Nms Utest04 L2 Trial eDokumen11 halamanNms Utest04 L2 Trial eHugo CheungBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER-19-REPRODUCTIVE-SYSTEMDokumen11 halamanCHAPTER-19-REPRODUCTIVE-SYSTEMVanya YeleniaBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep Asuhan Prakonsepsi: Ferina, BD., M.KebDokumen20 halamanKonsep Asuhan Prakonsepsi: Ferina, BD., M.KebRuni LestariBelum ada peringkat
- Forceps DeliveryDokumen30 halamanForceps DeliveryKozang Meong lhaBelum ada peringkat
- ID Viabilitas Spermatozoa Babi Dalam PengenDokumen6 halamanID Viabilitas Spermatozoa Babi Dalam PengenAugust Ridlof RiwuBelum ada peringkat
- Obstetric Emergency - in Primary CareDokumen93 halamanObstetric Emergency - in Primary Careazida90Belum ada peringkat
- Jennifer B. Cagandahan CaseDokumen10 halamanJennifer B. Cagandahan CaseFrank Gernale GolpoBelum ada peringkat
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- The Menopause Manifesto: Own Your Health With Facts and FeminismDari EverandThe Menopause Manifesto: Own Your Health With Facts and FeminismPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (18)
- ADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementDari EverandADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- The Strength and Conditioning Bible: How to Train Like an AthleteDari EverandThe Strength and Conditioning Bible: How to Train Like an AthleteBelum ada peringkat
- All in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayDari EverandAll in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- The 21-Day Self-Love Challenge: Learn How to Love Yourself Unconditionally, Cultivate Confidence, Self-Compassion and Self-WorthDari EverandThe 21-Day Self-Love Challenge: Learn How to Love Yourself Unconditionally, Cultivate Confidence, Self-Compassion and Self-WorthBelum ada peringkat
- The Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouDari EverandThe Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfDari EverandBrain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- What No One Tells You: A Guide to Your Emotions from Pregnancy to MotherhoodDari EverandWhat No One Tells You: A Guide to Your Emotions from Pregnancy to MotherhoodPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (30)
- A Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersDari EverandA Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (71)
- Perimenopause Power: Navigating your hormones on the journey to menopauseDari EverandPerimenopause Power: Navigating your hormones on the journey to menopausePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- What to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Dari EverandWhat to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Younger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondDari EverandYounger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (110)
- The Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenDari EverandThe Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (153)
- Hypnobirthing Meditations: Relaxation And Mindfulness Techniques For Expectant Mothers To Experience A Natural And Positive ChildbirthDari EverandHypnobirthing Meditations: Relaxation And Mindfulness Techniques For Expectant Mothers To Experience A Natural And Positive ChildbirthPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Dark Feminine Energy: Free Your Femme Fatale Ignite Your Irresistible Allure Through Mystique, Sexuality, Femininity, and Elegance to Become the Dark Diva No One Can IgnoreDari EverandDark Feminine Energy: Free Your Femme Fatale Ignite Your Irresistible Allure Through Mystique, Sexuality, Femininity, and Elegance to Become the Dark Diva No One Can IgnorePenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Sacred Womb Healing Meditation Divine feminine alignment: heal ancestral traumas deep wounds, release blocked sexual energies, flow to creativity, overcome the energies of birthing, joy love happyDari EverandSacred Womb Healing Meditation Divine feminine alignment: heal ancestral traumas deep wounds, release blocked sexual energies, flow to creativity, overcome the energies of birthing, joy love happyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- I'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionDari EverandI'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (123)
- Breaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodDari EverandBreaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (33)
- Menopause: All you need to know in one concise manualDari EverandMenopause: All you need to know in one concise manualPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (11)
- Rediscover Your Sparkle: Nourish Your SoulDari EverandRediscover Your Sparkle: Nourish Your SoulPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- I'm So Effing Hungry: Why We Crave What We Crave – and What to Do About ItDari EverandI'm So Effing Hungry: Why We Crave What We Crave – and What to Do About ItBelum ada peringkat
- ROAR: How to Match Your Food and Fitness to Your Unique Female Physiology for Optimum Performance, Great Health, and a Strong, Lean Body for LifeDari EverandROAR: How to Match Your Food and Fitness to Your Unique Female Physiology for Optimum Performance, Great Health, and a Strong, Lean Body for LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (44)
- Women, Food, And Hormones: A 4-Week Plan to Achieve Hormonal Balance, Lose Weight, and Feel Like Yourself AgainDari EverandWomen, Food, And Hormones: A 4-Week Plan to Achieve Hormonal Balance, Lose Weight, and Feel Like Yourself AgainPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (14)
- Skinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!Dari EverandSkinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!Penilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (488)
- Getting My Bounce Back: How I Got Fit, Healthier, and Happier (And You Can, Too)Dari EverandGetting My Bounce Back: How I Got Fit, Healthier, and Happier (And You Can, Too)Belum ada peringkat
- Bumpin': The Modern Guide to Pregnancy: Navigating the Wild, Weird, and Wonderful Journey From Conception Through Birth and BeyondDari EverandBumpin': The Modern Guide to Pregnancy: Navigating the Wild, Weird, and Wonderful Journey From Conception Through Birth and BeyondPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (38)
- After Birth: What Nobody Tells You - How to Recover Body and MindDari EverandAfter Birth: What Nobody Tells You - How to Recover Body and MindPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Mindful Birthing: Training the Mind, Body, and Heart for Childbirth and BeyondDari EverandMindful Birthing: Training the Mind, Body, and Heart for Childbirth and BeyondPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (24)
- The Better Period Food Solution: Eat Your Way to a Lifetime of Healthier CyclesDari EverandThe Better Period Food Solution: Eat Your Way to a Lifetime of Healthier CyclesBelum ada peringkat