SMPS
Diunggah oleh
Sandeep GogadiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SMPS
Diunggah oleh
Sandeep GogadiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SMPS
What is SMPS?
SMPS means Switch Mode Power Supply.
This is used for D.C to D.C conversion.
This works on the principle of switching
regulation. The SMPS system is highly
reliable, efficient, noiseless and compact
because the switching is done at very
high rate in the order of several KHz to
MHz
Necessity
The SMPS regulators are used in B.S.N.L at
various locations like CDOT, E10B and
Transmission systems etc.
SMPS
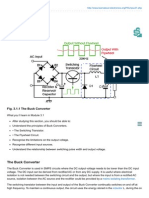
Principle of Switching Regulator
A pulse train drives the base of
switching or pass transistor. When the
voltage to the base is high, the transistor
saturates, when the voltage is low, the
transistor turns off. Here the transistor
functions as a switch. When the transistor
is ON, load current is drawn through
the transistor and choke L. When the
transistor is OFF the load current is
maintained by the energy stored in the
choke L. The current flows through earth,
Diode D, choke, load and earth. Hence
this diode is called Retrieval Diode.
A pulse train drives the base of
switching or pass transistor. When the
voltage to the base is high, the transistor
saturates, when the voltage is low, the
transistor turns off. Here the transistor
functions as a switch. When the transistor
is ON, load current is drawn through
the transistor and choke L. When the
transistor is OFF the load current is
maintained by the energy stored in the
choke L. The current flows through earth,
Diode D, choke, load and earth. Hence
this diode is called Retrieval Diode.
SMPS
Duty cycle of the Transistor D = On Time
On Time + Off Time
(one cycle time)
The output voltage = Input voltage x D
For example
If I/P voltage is 200 volts and D=0.25
O/P voltage = 200 x 0.25 = 50V.
Regulation is achieved by modifying the
Duty cycle. Duty cycle depends on
onetime of transistor, which in turn
depends on the width of the pulse
applied to the base of the transistor,
which is controlled by Pulse width
modulation by regulator circuit
Principle of Regulation
Regulation
The relaxation oscillator produces a square
wave. The square wave is integrated to
get a triangular wave, which drives the
non-inverting input of a triangular to
pulse converter. The pulse train out of
this circuit then drives the Pass
Transistor. The output is sampled by a
voltage divider and fed to a comparator.
The feed back voltage is compared with
a reference voltage. The output of the
comparator then drives the input of the
triangular to pulse converter
Regulation
If the output voltage tries to
increase the comparator produces a
higher output voltage which raises
the reference voltage of the
triangular- to pulse converter. This
makes the pulse that drives the
base of the switching transistor
narrower. That means duty cycle is
reduced. Since the duty cycle is
lower the output becomes less
which tries to cancel almost all the
original increase in output voltage.
Regulation
Conversely, if the regulated output
voltage tries to decrease, the output
of the comparator decreases the
reference voltage of the triangular -to
pulse converter. This makes the
pulse wider and the transistor
conducts for larger time and more
voltage comes out of the L.C.filter.
This cancels out the original decrease
in output voltage
Regulation
Input Section
Block 1 EMI
Block 2 Current limiter
Block 3 Floate
Block 4 Power factor corrector
100khz
Blokck 6-9 DC-DC converter
TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
CENTRE (DOT) for the S.M.P.S. BASED
POWER PLANT GENERIC REQUIREMENTS
(No. G7SMP/-01/01 JULY 04)
Primary application of the rectifiers SMPS
48V-5600W are in the supply of Telecom
equipment. The convection cooled unit may
be operated up to 60oC ambient air
temperature.
The rectifier operates from a nominal 3 X
230 Vac rms (with neutral wire) source.
The mains frequency may vary from 45 Hz
to 65 Hz. Total harmonic distortion (THD)
of the input current wave form is below 5%.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Belum ada peringkat
- Switch Mode Power Supply and Switching RegulatorsDokumen10 halamanSwitch Mode Power Supply and Switching Regulatorsmarcoms75Belum ada peringkat
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Penilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (3)
- Supplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalDokumen21 halamanSupplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalHassan Bin QasimBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen23 halamanChapter 4Arife AbdulkerimBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 LynchDokumen26 halamanTopic 3 Lynchsunil251Belum ada peringkat
- DC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer Change Voltage Push-Pull Circuit Buck-Boost ConvertersDokumen3 halamanDC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer Change Voltage Push-Pull Circuit Buck-Boost Convertersriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- DC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer VoltageDokumen3 halamanDC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer VoltageeeeprabaharanBelum ada peringkat
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Dari EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Belum ada peringkat
- Mod 2Dokumen99 halamanMod 2SREEHARI V ABelum ada peringkat
- TRANSISTORSDokumen13 halamanTRANSISTORSAbad Kurt ChristianBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome To All The Teacher's Of: SmitDokumen30 halamanWelcome To All The Teacher's Of: Smitsrvdhar100% (2)
- Push-Pull ConverterDokumen3 halamanPush-Pull ConverterBill YoungBelum ada peringkat
- Dire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyDokumen49 halamanDire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyAsed ZakirBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Switched Mode Power Supplies.: Fig.3.0.1 Typical SMPS Block DiagramDokumen17 halamanIntroduction To Switched Mode Power Supplies.: Fig.3.0.1 Typical SMPS Block DiagramPhenias ManyashaBelum ada peringkat
- Supplies (SMPS) - The Various Types of Voltage Regulators, Used in Linear Power Supplies (LPS), Fall inDokumen4 halamanSupplies (SMPS) - The Various Types of Voltage Regulators, Used in Linear Power Supplies (LPS), Fall inrakhikrishnarpillaiBelum ada peringkat
- SMPSDokumen5 halamanSMPSGunadevan ChandrasekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Switch Mode Power SupplyDokumen34 halamanSwitch Mode Power Supplyskaarz100% (5)
- Buck ConvertersDokumen4 halamanBuck ConvertersAbenav SankarBelum ada peringkat
- Relay Switch Circuit and Relay Switching CircuitDokumen10 halamanRelay Switch Circuit and Relay Switching CircuitidatscribdBelum ada peringkat
- 6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Dokumen1 halaman6 - L-21 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction to Switched Mode Power Supply TopologiesDokumen21 halamanAn Introduction to Switched Mode Power Supply Topologiesseahate100% (1)
- Final ReviewDokumen19 halamanFinal ReviewSanyam JainBelum ada peringkat
- Electrotherapy 1Dokumen14 halamanElectrotherapy 1Ajay GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding The Basics of A Flyback ConverterDokumen5 halamanUnderstanding The Basics of A Flyback ConverterhoainamnguyenphucBelum ada peringkat
- Transistor As A SwitchDokumen8 halamanTransistor As A SwitchdhingrastoreBelum ada peringkat
- List of ComponentsDokumen13 halamanList of ComponentsBenita AgbagwaraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC ChoppersDokumen55 halamanChapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC Choppersfor lifeBelum ada peringkat
- SMPS PPT Summer Traning by VijayDokumen60 halamanSMPS PPT Summer Traning by VijayVijay Kaplsya86% (7)
- Power Supplies Module 03Dokumen20 halamanPower Supplies Module 03LeonardoXanMBelum ada peringkat
- SMPS TutorialDokumen18 halamanSMPS TutorialUmasankar Peri100% (1)
- Unit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Dokumen12 halamanUnit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Gnanaseharan ArunachalamBelum ada peringkat
- Acknowledgement: The Transistor As A SwitchDokumen12 halamanAcknowledgement: The Transistor As A SwitchRamanpreet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDokumen21 halamanUnit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringAJAY SBelum ada peringkat
- Ex No:6 Modelling and Simulation of Buck and Boost Converter 10.11.2014Dokumen6 halamanEx No:6 Modelling and Simulation of Buck and Boost Converter 10.11.2014dhineshpBelum ada peringkat
- ASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshDokumen13 halamanASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshHemkeshBelum ada peringkat
- Transistor As A Switch - Using Transistor SwitchingDokumen11 halamanTransistor As A Switch - Using Transistor SwitchingDilpreet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Switch Mode Power Supply and Switching RegulatorsDokumen13 halamanSwitch Mode Power Supply and Switching Regulatorsyuj oBelum ada peringkat
- The Transistor As A SwitchDokumen8 halamanThe Transistor As A Switchmajstor100% (1)
- Circuit Diagram and Description of Power Supply UnitDokumen14 halamanCircuit Diagram and Description of Power Supply Unitreddyece402Belum ada peringkat
- Aim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsDokumen6 halamanAim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsShahrukh PinjariBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDokumen34 halamanIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- 1000w Inverter PURE SINE WAVE Schematic DiagramDokumen153 halaman1000w Inverter PURE SINE WAVE Schematic Diagramjeevapillay100% (4)
- Switched Mode Power SupplyDokumen153 halamanSwitched Mode Power SupplyIvan222244Belum ada peringkat
- P 2Dokumen17 halamanP 2AnushreeBelum ada peringkat
- basic dc to dcDokumen36 halamanbasic dc to dcstrelectronicsBelum ada peringkat
- Forward ConverterDokumen1 halamanForward ConverterJeyakumar VenugopalBelum ada peringkat
- T10A Converters and Inverters: Chapter - 4Dokumen11 halamanT10A Converters and Inverters: Chapter - 4lvsaruBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Detection and ControlDokumen16 halamanFire Detection and ControlvaisnanyBelum ada peringkat
- Switching Regulator - Jean Roderick ADokumen16 halamanSwitching Regulator - Jean Roderick AJishnuraj KubandrarajBelum ada peringkat
- 6.1 IC555 TIMER: Circuit ComponentsDokumen8 halaman6.1 IC555 TIMER: Circuit ComponentsManish PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Em ReportDokumen7 halamanEm Reportkashafnasir9977Belum ada peringkat
- SMPSDokumen3 halamanSMPSsahilfriendmailBelum ada peringkat
- Analog PPT 2Dokumen86 halamanAnalog PPT 2Nooman ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual 2Dokumen92 halamanLab Manual 2Joyce GeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- 1D Spring System SimulationDokumen47 halaman1D Spring System SimulationSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Lect01+Syllabus+ +Intro+FEADokumen19 halamanLect01+Syllabus+ +Intro+FEASandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Saracco13 TheoreticalGrounds MC TransportDokumen12 halamanSaracco13 TheoreticalGrounds MC TransportSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Pinter89 Probabilistic InequalitesDokumen21 halamanPinter89 Probabilistic InequalitesSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Zhao14 ChanceConstrainedOptimizationDokumen7 halamanZhao14 ChanceConstrainedOptimizationSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Moosegard95 MC Sampling InverseProblemsDokumen17 halamanMoosegard95 MC Sampling InverseProblemsSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Williams09 MutualInformationDokumen8 halamanWilliams09 MutualInformationSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter3 2015Dokumen56 halamanChapter3 2015Sandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Yang14 BeyondMCDokumen6 halamanYang14 BeyondMCSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Shafer90 BeliefFunctionsDokumen40 halamanShafer90 BeliefFunctionsSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Proppe03 - Equivalent Linearization and MCDokumen15 halamanProppe03 - Equivalent Linearization and MCSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Roberts01 OptimalScaling Metropolis-Hastings AlgorithmsDokumen17 halamanRoberts01 OptimalScaling Metropolis-Hastings AlgorithmsSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Miller65 JointCCPDokumen17 halamanMiller65 JointCCPSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Mira MH Algorithms Delayed RejectionDokumen12 halamanMira MH Algorithms Delayed RejectionSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Heckerman95 BN KnowledgePLUSDataDokumen47 halamanHeckerman95 BN KnowledgePLUSDataSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Heoting99 BMADokumen22 halamanHeoting99 BMASandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Halder11 CharacteristicsSLEDokumen16 halamanHalder11 CharacteristicsSLESandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Kumar12 InformationGuidedSADokumen6 halamanKumar12 InformationGuidedSASandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- An Adaptive Metropolis Algorithm: 1350 7265 # 2001 ISI/BSDokumen20 halamanAn Adaptive Metropolis Algorithm: 1350 7265 # 2001 ISI/BSSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- DuToit11 ProbabilisticCollisionCheckingDokumen7 halamanDuToit11 ProbabilisticCollisionCheckingSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Crandall85 NonGaussian Closure Nonlinear VibrationDokumen8 halamanCrandall85 NonGaussian Closure Nonlinear VibrationSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Dubois92 Evidence BeliefFunctionsDokumen25 halamanDubois92 Evidence BeliefFunctionsSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Brooks95 SimulatedAnnealingDokumen18 halamanBrooks95 SimulatedAnnealingSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Dempster68 Generalization BayesianInferenceDokumen31 halamanDempster68 Generalization BayesianInferenceSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Crandall00 IsSL FlawedDokumen8 halamanCrandall00 IsSL FlawedSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Power Supplies & RegulatorsDokumen15 halamanPower Supplies & RegulatorsNarasimha Murthy YayavaramBelum ada peringkat
- DeMars11 GaussMixtureDokumen20 halamanDeMars11 GaussMixtureSandeep Gogadi100% (1)
- Complete Modular CatalogueDokumen9 halamanComplete Modular CatalogueSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- Telephone Message Recording ConceptsDokumen3 halamanTelephone Message Recording ConceptsSandeep GogadiBelum ada peringkat
- FSK Modulation & DemodulationDokumen5 halamanFSK Modulation & DemodulationPranavBelum ada peringkat
- Clipping and Clamping Circuits PDFDokumen3 halamanClipping and Clamping Circuits PDFKaustubh MallikBelum ada peringkat
- Tuned Collector OscillatorDokumen3 halamanTuned Collector OscillatorHRM, BAPEXBelum ada peringkat
- Ds - 24vin Mini FamilyDokumen15 halamanDs - 24vin Mini Familyalex lzgBelum ada peringkat
- Dual Trace Phase Measurement Method Lissajous Pattern ExperimentDokumen10 halamanDual Trace Phase Measurement Method Lissajous Pattern ExperimentFallou GayeBelum ada peringkat
- Dual Power MOSFET Driver Features: File Number Data Sheet April 1999Dokumen8 halamanDual Power MOSFET Driver Features: File Number Data Sheet April 1999tommyhghBelum ada peringkat
- Mechatronics Interfacing Sensors-1Dokumen50 halamanMechatronics Interfacing Sensors-1Tanvi ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Zynq Pin Number Ultrazed-Eg Net Name Jx1 Pin Number Ultrazed-Eg Net NameDokumen12 halamanZynq Pin Number Ultrazed-Eg Net Name Jx1 Pin Number Ultrazed-Eg Net Namevenugopal mBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Operational AmplifiersDokumen32 halamanIntroduction to Operational Amplifiersjaya1816100% (1)
- Signals and Amplifiers ExplainedDokumen71 halamanSignals and Amplifiers ExplainedJaveria ZaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Logic GatesDokumen14 halamanLogic GatesDivyam JainBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Electronics CicuitsDokumen4 halamanMicro Electronics Cicuitsbalajibs203285Belum ada peringkat
- Lab 9: O A: Perational MplifiersDokumen6 halamanLab 9: O A: Perational MplifiersAhmed ChBelum ada peringkat
- C10 Power Amplifier Current Dumping EnhancementDokumen24 halamanC10 Power Amplifier Current Dumping EnhancementАлексей ГрабкоBelum ada peringkat
- Amc 7834Dokumen93 halamanAmc 7834jessica jonesBelum ada peringkat
- BFW10Dokumen1 halamanBFW10SarinBelum ada peringkat
- Diode Clamper Circuit. by - Engr - Irshad Rahim Memon - PPT Video Online DownloadDokumen9 halamanDiode Clamper Circuit. by - Engr - Irshad Rahim Memon - PPT Video Online DownloadAlejandro100% (1)
- Gateeasy D To A PDFDokumen3 halamanGateeasy D To A PDFShubham kumarBelum ada peringkat
- TestcieeDokumen7 halamanTestcieefallonBelum ada peringkat
- IC & Applications Assignment Designs Filters Generators CircuitsDokumen4 halamanIC & Applications Assignment Designs Filters Generators CircuitsLAKSHMI NARAYANA ANEMIBelum ada peringkat
- TL 3845Dokumen12 halamanTL 3845sarad43Belum ada peringkat
- Avt 721Dokumen4 halamanAvt 721Martins StarastsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Four Combinational Logic Circuits OutlinesDokumen22 halamanChapter Four Combinational Logic Circuits Outlinesmift ademBelum ada peringkat
- AC ANALYSIS AND PWM CIRCUITSDokumen2 halamanAC ANALYSIS AND PWM CIRCUITSairkad0% (1)
- Service Manual 800RBDokumen21 halamanService Manual 800RBCodinasound CaBelum ada peringkat
- 2SC5343Dokumen3 halaman2SC5343Abigail HoobsBelum ada peringkat
- 99.smith CH05BDokumen52 halaman99.smith CH05BAbdullah Ashraf ElkordyBelum ada peringkat
- Refresher Course: Experimental PhysicsDokumen15 halamanRefresher Course: Experimental PhysicsNeelam KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- WT7520Dokumen9 halamanWT7520Inajá FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Cascade Amplifier CircuitDokumen4 halamanCascade Amplifier Circuit4011 Harshada MohiteBelum ada peringkat