Condition Monitoring
Diunggah oleh
AbdullaHanèèfaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Condition Monitoring
Diunggah oleh
AbdullaHanèèfaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
VIBRATION ANALYSIS ON
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP in B P C L
Kochi Refinery
Batch members
Athul thilak
Abdulla.H
Elisha yohannan george
Jerrin varghese
Introduction
Maintenance
Maintenance is defined as a set of activities
performed on all plants and machineries to
maintain the at the same at prime condition in
economical ways for smooth running of the
plants
Types of maintenance
Preventive maintenance
condition monitoring
breakdown maintenance
turn around maintenance
Condition Monitoring
Definition
Conditional monitoring is a method of
monitoring the condition of equipment and
machinery, which are in running condition
in respective plants.it is a type of
predictive maintenance.
Types of condition monitoring
Online
offline
Vibration monitoring can be used for
Fans
Blowers
Pumps
Compressors
Turbines
Engines
Pumps
Definision
Pump is an equipment which transfers fluids from one
point to another by pressurizing the fluid
Parts of pump
Casing
Impeller
Shaft
Bearings
Mechanical seals
Vibration analysis
Vibration
Vibration is defined as the cyclic or
Oscillating motion of a machine component
From its position of rest.
Vibration analysis helps in detercting the problem
in initial stages before they cause any damage
to machine
Vibration is caused by
Exciting force
Freedom for movement
Characteristics of vibration
Frequency
Amplitude
Displacement
Velocity
Acceleration
Phase
Acceleration Envelop
Vibration Displacement (Peak
to Peak)
The total distance traveled by the
vibrating part from one extreme limit of
travel to the other extreme limit of travel
is referred to as the peak to peak
displacement, it is expressed in
micrometers (.001 milli meter).It is
generally at low frequencies displacement
may be the best indicator vibration
severity; typically in the frequency range
below 600 VPM.
Vibration Acceleration
Acceleration is closely related to force, and
relatively large forces can occur at high
frequencies even through the
displacement and velocity may be very
small. It is normally expressed in gsE.
Why Velocity normally used?
It gives amplitude weighing to all vibration
frequencies.
It is the only measurement parameter
where the overall vibration level can be
applied directly to a standard of vibration
severity that is when the frequencies of
vibration are unknown.
Most rotating machines produce
frequencies between 600 rpm to 12000
rpm where velocity is the most
responsive.
Vibration velocity is direct indicator
fatigue since it takes in to account both
displacement and frequency.
A measurement of overall vibration
velocity only is valid indicator of the
overall condition of a machine whether
vibration is simple (one frequency) or
more than frequency).
Vibration Velocity
It is the vibration displacement per
unit time. It is expressed in mm/s.
Vibration occurring in the 600 to 60000
CPM frequency range are generally best
measured using vibration velocity.
Vibration Frequency
The amount of time required to complete
one full cycle of vibration pattern is called
the period of vibration. Whereas vibration
frequency is the measure of the number
of complete cycles that occur in a
specified period of time. Frequency is
related to the period of vibration pattern
by the simple formula:
Frequency=1/period
The set of activities carried out
Detection
Analysis
Correction
Verification
Where to measure vibration
Usually for a pup readings are taken at
four different locations namely:
Motor Non Drive End (MNDE)
Motor Drive End (MDE)
Pump Drive End (PDE)
Pump Non Drive End (PNDE)
location readings are taken in
three directions they are
Vertical
Horizontal
Axial
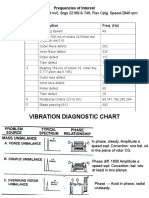
IDENTIFYING THE MOST
COMMON MACHINERY
PROBLEM
Vibration due to unbalance
Vibration due to Misalignment
Vibration due to Eccentricity
Vibration due to Drive Belts
Vibration due to Electrical Faults
Vibration due to Rubbing
Vibration due to Bearings failure
SKF
It is the machine used for measuring the
vibration.
Accelerometer is connected to this
machine.
It is connected to the system using the
cable RS 232.
SKF
SKF Machine Analyst Version
2.2
The diagnosis software, saves the
condition data, presents it in
straightforward diagrams and charts, and
provides a convenient analysis of all
stored condition information.
spectrum
FFT
The transition from time domain
waveform to frequency domain spectrum
is accomplished by the Fast Fourier
Transform(FFT).A graphic depiction of the
mathematical process. The first plot
shows a normal, complex time waveform.
The complex time waveform is broken
down into a series of individual sine
waves, each one at a single frequency.
Frequency=1/period
SPECTRUM ANALYSIS
UNBALANCE CONDITION
Unbalance of rotating machine parts is perhaps the
easiest problem to pinpoint with confidence. it is due to
the non coincident of centre of mass with centre of
rotation, uncomplicated by other problems and In most
cases the data from an unbalanced condition show
CHARACTERISTICS
The vibration frequency is 1 x RPM of the
unbalanced part.
The amplitude is proportional to amount
of unbalance.
The amplitude of vibration in horizontal
and axial readings is greater than
Vertical reading(for couplings).
4. generally the ratios are,
Horizontal:axial:vertical=5:4:1
Vibration due to
Misalignment
Although machines may be well aligned
initially, several factors can affect
alignment including:
1.Operating Temperature
2.Setting of the base of foundation
3.Deterioration or shrinkage of grouting
CHARACTERISTICS
The vibration frequency is 1 x RPM; also 2
x RPM and 3 x RPM if the misalignment is
severe.
The amplitude of vibration is proportional
to misalignment.
The amplitude of vibration is high in axial
as well as the radial direction. This can be
reduced by aligning the parts at operating
temperature.
Three basic types of
misalignment
1.OFFSET MISALIGNMENT
2. ANGUALR MISALIGNMENT
3. COMBINATION ANGULAR/OFFSET
MISALIGNMENT
1. Offset misalignment causes vibration at
2*rpm
2. Angular misalignment causes vibrations at
1*rpm
3. Combinations of angular and offset
misalignments may show a combination of
1*,2*, and 3*rpm.
4. Axial reading is more than horizontal and
vertical.
Vibration due to Eccentricity
Eccentricity is happens when actual centre
of rotation differs from the geometric
centerline. It is actually a common source of
unbalance. Eccentricity can also result in
reaction forces that cannot be corrected by
simple balancing. The largest vibration occurs
at a frequency equal to 1 x RPM, similar to
unbalance but it is not. So when frequency is
1 x RPM check for unbalance and eccentricity.
Vibration due to Drive Belts
The part of machine that causing the
trouble will appear under the strobe light
of your analyzer. Thus the frequency of
vibration is key factor in determining the
nature of the trouble. Belt defects usually
show higher amplitude of vibration in the
direction that is parallel to the belt
tension.
Vibration due to Electrical
Faults
Common causes of electromagnetic
troubles are;
1.Rotor not round
2.Eccentric armature journals
3.Rotor and stator misaligned
4.Elliptical stator bore
5.Open or shorted windings
6.Shorted rotor iron
The frequency of vibration resulting
from electrical problems will be 1 x RPM.
They generally responds to the amount of
load placed on the motor as the load
changes amplitude readings also changes.
Vibration due to Rubbing
Rubbing between stationary and
rotating parts of a machine can generate
vibration at 1 x RPM, 2 x RPM and higher
frequencies. Continuous friction due to
rubbing can excite high frequency
resonance in other part of the machine
and is likely the amplitude and phase
readings will be very instable.
Vibration due to Bearings
failure
When a rolling element bearing
develops flows in the raceways and/or
rolling element, there are actually a
number of vibration frequency
characteristics that result depending up on
the extent deterioration
The primary causes of
bearing failure
1.Contamination , Including moisture
2.Overstress
3.Lack of lubrication
4.Defects created after manufacturing
ball bearing give off four distinct
frequencies
1.Fundamental train frequency(FTF)
2.Ball spin frequency(BS)
3.Outer race frequency(OR)
4.Inner race frequency(IR)
FORMULAE
FTF=rps/2[1-(Bd/pd)*cos
BS=pd/2Bd(rps)[1-(Bd/pd)*cos
OR=N(FTF)
IR=N(rps-FTF)
Where
Rps=revolutions per second of inner
race
Bd=ball diameter
Pd=pitch diameter
N=number of balls
=contact angle
FACTORS FOR MULTIPLICATION
Bearing FTF BS OR IR
FAG 6311
0.378 1.928 3.024 4.976
SKF 6311
0.382 2.003 3.057 4.943
NTN 6311
0.384 2.040 3.072 4.928
SPIKE ENERGY
A measurement design to detect low
amplitude transient impacts generated
Within ultrasonic frequency range by
microscopic surface flaws in rolling
element bearings and gears .
The acceleration signal is
processed via high pass filter and a peak
detection
The value is expressed in units of
gSE
OTHER SOURCES OF
ULTRASONIC FREQUENCIES
Cavitations
High pressure steam and air flow
Turbulence in liquids and air
Rubbing(seals,rotors,belts,guards etc)
Impact excitation(looseness or inherent in
the machines operation)
Electrical arcing
CAVITATION
As an impellers move through a fluid,low
pressure areas are formed as the fluid
accelerates around and moves past the
blades move, the lower the pressure
around it can become. As it reaches
vapour pressure ,the fliud vapourizes and
forms small bubbles of gas called
cavitation
Cavitation in pump occur in two
different forms
1. SUCTION CAVITATION
2.DISCHARGE CAVITATION
.Vibration due to Mechanical
Looseness
Mechanical looseness, and the resulting
pounding action, produces a vibration at a
frequency that is often at 2*RPM and
higher multiples of a rotating speed. This
vibration might be the result of loose
mounting bolts, excessive bearing
clearance, or a crack in the structure or
bearing pedestal.
Characteristics
harmonics indicate severe conditions of
looseness
Shows sine wave that has clipped
By changing the load and observing the
looseness can be detected
RESONANCE
Resonance is the condition whereby
the driving force applied to a structural
part is close to its natural frequency and
amplification occurs. The source of the
driving force is most likely residual
imbalance in a rotating machine attached
to the structure or broadband turbulence
due to fluid motion
charecteristics
Resonance are highly speed
sensitive,depending to some extent on
damping.damping not only decreases the
maximum amplitude of vibration but also
broadens out the response curve.rotors
also have resonances,called critical
speeds.according to the formula
F=mr
The vibratory force should increase as the
square of speed.this is true in low-speed
range.
correction
After detecting and anlysiing the
corrective action shoud be taken.
After the correction again the vibration is
measured for ensuring whether the
problem is solved.
MAINTENANCE STRATEGY
Maintenance is defined as a set of
activities performed on all plant &
machineries, to maintain the same at
prime condition for smooth running for
achievement of organizational objective.
THANKING YOU
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Introduction To Basic Vibration AnalysisDokumen162 halamanIntroduction To Basic Vibration AnalysisΡαφαηλ Καμ.100% (2)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisDari EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- 2015 KOBELCO Defect PDFDokumen25 halaman2015 KOBELCO Defect PDFayushBelum ada peringkat
- Condition Monitoring of Centrifugal Blower Using Vibration Analysis PDFDokumen10 halamanCondition Monitoring of Centrifugal Blower Using Vibration Analysis PDFJose PradoBelum ada peringkat
- Machinery Vibration Analysis & MaintenanceDokumen43 halamanMachinery Vibration Analysis & MaintenanceEduardo Castillo100% (1)
- BalancingDokumen138 halamanBalancingJeinnerCastroBelum ada peringkat
- Aws D1.1 D1.1M-2010Dokumen569 halamanAws D1.1 D1.1M-2010Abraham Aby100% (4)
- Hydraulic and Structural Design of Super PassageDokumen25 halamanHydraulic and Structural Design of Super PassageCPK100% (2)
- Vibration Standardss ISO10816Dokumen24 halamanVibration Standardss ISO10816Aswartha Technical Services67% (3)
- Vibration Analysis and Machine Condition MonitoringDokumen33 halamanVibration Analysis and Machine Condition Monitoringmustafa100% (1)
- Autodyn Theory ManualDokumen235 halamanAutodyn Theory ManualAndre OliveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Machinery Diagnostic PlotsDokumen16 halamanMachinery Diagnostic Plotsfazzlie100% (1)
- Vibration Assessment Quiz To Determine Entry Vs Analysis IDokumen2 halamanVibration Assessment Quiz To Determine Entry Vs Analysis IAhmad DanielBelum ada peringkat
- VIBration Basic MILDokumen687 halamanVIBration Basic MILtrinadhuluBelum ada peringkat
- Optimizing Condition MonitoringDokumen113 halamanOptimizing Condition Monitoringasheervada100% (5)
- Analysis Level I Course: Introduction to CVCM and Typical Machinery Problems Detected by Vibration AnalysisDokumen265 halamanAnalysis Level I Course: Introduction to CVCM and Typical Machinery Problems Detected by Vibration AnalysisSaadKianiBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Training Program On Vibration AnalysisDokumen24 halamanBasic Training Program On Vibration AnalysisMohamed Al-OdatBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration ANALYSIS StandardsDokumen24 halamanVibration ANALYSIS Standardsho-faBelum ada peringkat
- Autocorrelation: 131 CAT IV Part 1 - Signal Processing SlidebookDokumen8 halamanAutocorrelation: 131 CAT IV Part 1 - Signal Processing SlidebookLe Thanh Hai100% (2)
- ISO Vibration Analysis Certification Exam Cat I Part 3 Signal Processing Ali M Al-ShurafaDokumen1 halamanISO Vibration Analysis Certification Exam Cat I Part 3 Signal Processing Ali M Al-ShurafaMohammed Kamel Tony100% (1)
- RCM - Optimize Maintenance with Reliability Centred MaintenanceDokumen46 halamanRCM - Optimize Maintenance with Reliability Centred MaintenanceTong Bbm100% (1)
- Vibration AnalysisDokumen11 halamanVibration AnalysisSofyan HakikiBelum ada peringkat
- Grundfos Design HVACDokumen68 halamanGrundfos Design HVACmishraenggBelum ada peringkat
- Order Analysis ToolkitDokumen16 halamanOrder Analysis ToolkitManuel Enrique Salas FernándezBelum ada peringkat
- Procdure For Valve TestDokumen19 halamanProcdure For Valve TestAbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Motor Diagnostics Defect Frequencies and Data ColleDokumen51 halamanElectric Motor Diagnostics Defect Frequencies and Data ColleSubrata Dubey50% (2)
- Asset Condition Monitoring Techniques Concemino 060712 PDFDokumen49 halamanAsset Condition Monitoring Techniques Concemino 060712 PDFAnonymous OFwyjaMy100% (1)
- 11 PeakVue OverviewDokumen38 halaman11 PeakVue OverviewAhmad Syahroni100% (1)
- Vibration and Shock Isolation-Advanced Antivibration ComponentsDokumen55 halamanVibration and Shock Isolation-Advanced Antivibration Componentshiginio.moro6182Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Vibration Analysis Programs (40Dokumen52 halamanIntroduction to Vibration Analysis Programs (40Sam100% (3)
- AMPLITUDE MODULATION Versus BEATSDokumen5 halamanAMPLITUDE MODULATION Versus BEATSHaitham YoussefBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Monitoring AnalysisDokumen102 halamanVibration Monitoring AnalysisAlangghya Susatya Adigama100% (1)
- Vibration MonitoringDokumen67 halamanVibration MonitoringApurv Khandelwal100% (4)
- VibMatters Current IssueDokumen19 halamanVibMatters Current IssueUsman JabbarBelum ada peringkat
- FRP PipeDokumen4 halamanFRP PipealvinchuanBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Basics 2Dokumen82 halamanVibration Basics 2lomesh021Belum ada peringkat
- Modified Assesment Check ListDokumen28 halamanModified Assesment Check ListAbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringDari EverandMechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Strength of Materials (S.O.M.) Model Question Paper (Q.P.) SolutionDokumen16 halamanStrength of Materials (S.O.M.) Model Question Paper (Q.P.) SolutionProf. P. H. Jain92% (13)
- Fault Identification and Monitoring in Rolling Element BearingDokumen234 halamanFault Identification and Monitoring in Rolling Element BearingRushikesh DandagwhalBelum ada peringkat
- Piezoelectric Accelerometers and Vibration Pre AmplifiersDokumen160 halamanPiezoelectric Accelerometers and Vibration Pre Amplifiersavoid11Belum ada peringkat
- SKF - Tech Associates of CharlotteDokumen57 halamanSKF - Tech Associates of Charlotteiatorres100% (4)
- Vibration Field Guide (For the Newbie Vibration Analyst)Dari EverandVibration Field Guide (For the Newbie Vibration Analyst)Belum ada peringkat
- Vibration Vs UltrasoundDokumen8 halamanVibration Vs UltrasoundallmcbeallBelum ada peringkat
- Ultrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentDari EverandUltrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Why Phase Information Is Important For Diagnosing Machinery ProblemsDokumen3 halamanWhy Phase Information Is Important For Diagnosing Machinery ProblemsdinhdtBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Measurements On Slow Speed MachineryDokumen9 halamanVibration Measurements On Slow Speed MachineryMohd Asiren Mohd SharifBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Analysis For Machinery Health DiagnosisDokumen12 halamanVibration Analysis For Machinery Health Diagnosiskoniks519Belum ada peringkat
- Vibration Analysis For Reciprocating CompressorsDokumen48 halamanVibration Analysis For Reciprocating CompressorsJose PradoBelum ada peringkat
- Ultrasound For Slow Speed Bearing Monitoring - RonTangen PDFDokumen67 halamanUltrasound For Slow Speed Bearing Monitoring - RonTangen PDFaabejaroBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Diagnostic Chart1Dokumen16 halamanVibration Diagnostic Chart1Anand KumarBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 18436 Category IVDokumen2 halamanISO 18436 Category IVzona amrullohBelum ada peringkat
- AnalysisDokumen44 halamanAnalysisMounicaRasagyaPallaBelum ada peringkat
- A Practical Introduction To Condition Monitoring of RollingDokumen14 halamanA Practical Introduction To Condition Monitoring of Rollingsatya_chagantiBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Key - HydraugeoDokumen5 halamanAnswer Key - HydraugeoBryan YuBelum ada peringkat
- Gearbox Vibration Analysis - Analysis Techniques: The Peril of Wall Chart' AnalystsDokumen18 halamanGearbox Vibration Analysis - Analysis Techniques: The Peril of Wall Chart' AnalystsRICARDO OLIVEROBelum ada peringkat
- Detection of Ski Slopes in Vibration SpectrumsDokumen7 halamanDetection of Ski Slopes in Vibration SpectrumsjeyaselvanmBelum ada peringkat
- Why Industrial Bearings Fail: Analysis, Maintenance, and PreventionDari EverandWhy Industrial Bearings Fail: Analysis, Maintenance, and PreventionBelum ada peringkat
- Cat II Course PDFDokumen153 halamanCat II Course PDFMohammad Zainullah Khan100% (2)
- Low Frequency EvaluationDokumen13 halamanLow Frequency EvaluationthrillerxBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 18436 Category I Vibration Analyst Training TopicsDokumen2 halamanISO 18436 Category I Vibration Analyst Training TopicsDean LofallBelum ada peringkat
- Case Studies #4: Gearbox DefectDokumen13 halamanCase Studies #4: Gearbox DefectMiguel VillegasBelum ada peringkat
- Rotating Machine Fault Diagnostics Using VibrationDokumen234 halamanRotating Machine Fault Diagnostics Using VibrationJose PradoBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration BasicsDokumen120 halamanVibration Basicspradeep.selvarajan100% (1)
- Detect Machinery Faults by Using Peak VueDokumen13 halamanDetect Machinery Faults by Using Peak VueHarold Alconz100% (2)
- Orbit Steam Turbine Seal Rub - OrbitDokumen14 halamanOrbit Steam Turbine Seal Rub - OrbitHatem Ali100% (3)
- Vibration Analysis Training & Certification Courses by Predict InstituteDokumen7 halamanVibration Analysis Training & Certification Courses by Predict InstitutefaisalBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Health MonitoringDari EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasBelum ada peringkat
- ISO Vibration Analysis Certification Exam Cat I Part 3 Signal Processing Ali M Al-Shurafa PDFDokumen1 halamanISO Vibration Analysis Certification Exam Cat I Part 3 Signal Processing Ali M Al-Shurafa PDFMohammed Kamel TonyBelum ada peringkat
- Mobius Institute Ultrasound Brochure June 2022Dokumen10 halamanMobius Institute Ultrasound Brochure June 2022nino16041973Belum ada peringkat
- AWS Solutions Architect Certification TrainingDokumen13 halamanAWS Solutions Architect Certification TrainingAbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration Analysis Exam QuestionsDokumen1 halamanVibration Analysis Exam QuestionsZegera Mgendi0% (1)
- Womens Rights in Islam Regarding Marriage and DivorceDokumen15 halamanWomens Rights in Islam Regarding Marriage and DivorceMinazBelum ada peringkat
- Ultrasonic LaminationTestingDokumen2 halamanUltrasonic LaminationTestingAlper GmBelum ada peringkat
- COVID National Guidelines FINAL 18 March-1 PDFDokumen51 halamanCOVID National Guidelines FINAL 18 March-1 PDFAbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Accumulator Skid g62-8k-Cp-009 (Sfny Tp21) - 11.03.2019Dokumen2 halamanAccumulator Skid g62-8k-Cp-009 (Sfny Tp21) - 11.03.2019AbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Consumable ControlDokumen2 halamanConsumable ControlAbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Space MGMTDokumen5 halamanSpace MGMTOnkar HaridasBelum ada peringkat
- Focused Assessment Report: 6285-6286-PP-QA-010Dokumen2 halamanFocused Assessment Report: 6285-6286-PP-QA-010AbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Innterview QuestionsDokumen2 halamanInnterview QuestionsAbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Deepak 02Dokumen3 halamanDeepak 02AbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- CS - PP12 00 Ha Me Aph 131Dokumen72 halamanCS - PP12 00 Ha Me Aph 131AbdullaHanèèfaBelum ada peringkat
- Carta Maestra de Soldadura y CortDokumen7 halamanCarta Maestra de Soldadura y CortAlejandro Del Valle TovarBelum ada peringkat
- Img 1536Dokumen1 halamanImg 1536Dennis Dale FanogaBelum ada peringkat
- 1786 Principes D'hydrauliqueDokumen21 halaman1786 Principes D'hydrauliqueFabio Ferraz de CarvalhoBelum ada peringkat
- Extended Abstract Filipa East Da Camara, n72626Dokumen12 halamanExtended Abstract Filipa East Da Camara, n72626nnnnnaaaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Disha DPP (Topicwise)Dokumen413 halamanDisha DPP (Topicwise)pegasuspretty903Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment - 1 Solution PDFDokumen7 halamanAssignment - 1 Solution PDFDavid StuartBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Transport Processes 1: 1 Course Outline and Reading MaterialDokumen29 halamanFundamentals of Transport Processes 1: 1 Course Outline and Reading MaterialAbhimanyu DubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Discovery of Hall EffectDokumen6 halamanDiscovery of Hall EffectJerome MeccaBelum ada peringkat
- Compressible Fluid Flow Short QuestionsDokumen2 halamanCompressible Fluid Flow Short QuestionsAkhil AswinBelum ada peringkat
- TNPSC Ae / Overseer/Jdo / Ri / Surveyor / Draftsman TRB Polytechnic / EnggDokumen46 halamanTNPSC Ae / Overseer/Jdo / Ri / Surveyor / Draftsman TRB Polytechnic / Engggopala krishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Setting Up A Case For Turbomachinery Problems: Openfoam Kurs 2009 Håkan Nilsson Olivier PetitDokumen33 halamanSetting Up A Case For Turbomachinery Problems: Openfoam Kurs 2009 Håkan Nilsson Olivier PetitBryan ArcilaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 7 Long QuizDokumen4 halamanGrade 7 Long QuizMisraim Perlas VillegasBelum ada peringkat
- ABET Course Syllabus ChE 346 Heat TransferDokumen2 halamanABET Course Syllabus ChE 346 Heat TransferYahya IsiedBelum ada peringkat
- Analyzing cantilever beam shear force and bending moment using MD-Solid softwareDokumen7 halamanAnalyzing cantilever beam shear force and bending moment using MD-Solid softwarefawad naeemBelum ada peringkat
- PHS 212 - Spring 2017 - Syllabus (A & B)Dokumen2 halamanPHS 212 - Spring 2017 - Syllabus (A & B)Fares FadlallahBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Cie Sound P1.Dokumen10 halamanIGCSE Cie Sound P1.Payail Parineeta PalBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics: Physics Topic 2 (Kinematics) O-LevelsDokumen10 halamanKinematics: Physics Topic 2 (Kinematics) O-LevelsSalmanBelum ada peringkat
- 2002, Princeton University Physics Department, Edward J. GrothDokumen8 halaman2002, Princeton University Physics Department, Edward J. GrothOmegaUserBelum ada peringkat
- Analisis Struktur C2Dokumen18 halamanAnalisis Struktur C2Hazyema HarunBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Dokumen20 halamanThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongBelum ada peringkat
- 18307apni KakshaDokumen38 halaman18307apni KakshaVaibhav2006Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanics: Confirming Archimedes' PrincipleDokumen2 halamanMechanics: Confirming Archimedes' PrincipleFattihiEkhmalBelum ada peringkat