HPTLC
Diunggah oleh
Free Escort ServiceJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
HPTLC
Diunggah oleh
Free Escort ServiceHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Presented by:
NILESH S.JAWALKAR
Guided by:
S.R.KALE
Pune University
1
Introduction
Principle of HPTLC
Difference between HPTLC & TLC
Features of HPTLC
Instrumentation
Steps involved in HPTLC
Rf value
Factor affecting HPTLC
References
2
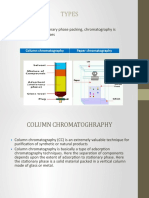
Chromatography: method used for separation
of the multi-component mixture.
HPTLC-High Performance Thin Layer
Chromatography.
It is a sophisticated & automated form of
TLC.
3
Same theoretical principle of TLC.
Separation may result due to
adsorption phenomenon.
4
HPTLC TLC
Particle size 4-8m 5-20m
5
Sorbent layer 100m 250m
Efficiency High Less
Separations 3-5cm 10-15cm
Analysis time greatly reduced slower
Development
chamber
Less amount of
mobile phase
More amount
Simple & rapid
Several analysts work simultaneously
Lower separation time
Less cost
Low maintenance cost
Low mobile phase consumption per sample
No interference from previous analysis
Visual detection possible
6
Sample Preparation
Selection of
chromatography layer
Pre-washing
Pre-conditioning
Application of sample
Chromatography development
Detection of spots
Scanning & documentation
7
Normal phase chromatography: non polar solvent
Reversed phase chromatography: polar solvent
Selection of chromatography layer
Depends on nature of material to be separated
Commonly used(silica gel, alumina)
8
It is purification step
Mainly methanol is used
Essential for quantitative evaluation
Stability testing
9
Also called Chamber Saturation
Low polarity mob. Phase:- no need
High polar mob. Phase:- desirable
For reverse phase saturate chamber with polar
solvent
Sample application
1-5 l
Linomat IV Applicator
10
Linomat lV applicator
11
Ascending development
Descending development
Horizontal development
Problem encountered
Tailing
Diffusion
12
Generally, detection by iodine vapour
Alternatively by
Visual detection at 254nm UV-Light
Detection at 365nm UV-Light
13
Use white light
Registered absorption spectra
Lamp & detector are placed
450m above surface of HPTLC
plate
45 angle bet. Lamp & detector
14
Rf = Zs
Zo
Where,
Rf = Retardation factor
Zs = distance of centre of spot from starting line(mm)
Zo = distance of solvent front from starting line(mm)
15
Type of stationary phase
Mobile phase
Layer thickness
Temperature
Mode of development
Amount of sample
Dipping zone
others
16
Kasture A.V A text book of
Pharmaceutical Analysis (Instrumental
methods), 14
th
edition, page no.28-30
Elke Hahn Deinstrop Applied TLC, 2
nd
edition
Site www.Google.com (Google images)
17
You
18
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Electroanalysis: Theory and Applications in Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Media and in Automated Chemical ControlDari EverandElectroanalysis: Theory and Applications in Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Media and in Automated Chemical ControlBelum ada peringkat
- HPTLCDokumen23 halamanHPTLCShaise Jacob100% (2)
- Chiral Separation Techniques A Practical Approach 2nd Edition (G. Subramanian)Dokumen348 halamanChiral Separation Techniques A Practical Approach 2nd Edition (G. Subramanian)LeandreggBelum ada peringkat
- Column Chromatography 2Dokumen24 halamanColumn Chromatography 2syed shayanBelum ada peringkat
- Column Chromatography in Chemistry Is A Method Used To Purify Individual Chemical Compounds From Mixtures of CompoundsDokumen12 halamanColumn Chromatography in Chemistry Is A Method Used To Purify Individual Chemical Compounds From Mixtures of CompoundsHuzaini IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 26 Chromatographic SeparationDokumen32 halamanChapter 26 Chromatographic SeparationBhavesh NayakBelum ada peringkat
- The DARK Side of Total Synthesis: Strategies and Tactics in Psychoactive Drug ProductionDokumen24 halamanThe DARK Side of Total Synthesis: Strategies and Tactics in Psychoactive Drug Production943909Belum ada peringkat
- HPLC Pharma 25-1-09-Numbered-All PrintDokumen19 halamanHPLC Pharma 25-1-09-Numbered-All PrintshulalevinBelum ada peringkat
- Chromatography: Analytical Chromatography Is Used To Determine The Existence and Possibly Also TheDokumen5 halamanChromatography: Analytical Chromatography Is Used To Determine The Existence and Possibly Also Themaria ayubBelum ada peringkat
- Chromatographic Techniques of AnaylsisDokumen39 halamanChromatographic Techniques of Anaylsispratik satiBelum ada peringkat
- BW Mass Spectrometry - ZeeshanDokumen59 halamanBW Mass Spectrometry - ZeeshanAdnan RoonjhaBelum ada peringkat
- Chromatography TheoryDokumen32 halamanChromatography TheoryRajath KanchanBelum ada peringkat
- Adsorption ChromatographyDokumen4 halamanAdsorption ChromatographyIman FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- ElectrophoresisDokumen7 halamanElectrophoresisnavedBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation HPLCDokumen25 halamanPresentation HPLCSunil Murkikar (GM - PMI Quality Operations)Belum ada peringkat
- LC MS PDFDokumen44 halamanLC MS PDFhugoboss_darkBelum ada peringkat
- GC AASGasChromatography AtomicAbsorptionspectrometry Advancedspectralanalysis MPHARMACYMPCTDokumen9 halamanGC AASGasChromatography AtomicAbsorptionspectrometry Advancedspectralanalysis MPHARMACYMPCTSubhasish DashBelum ada peringkat
- HPLC 4Dokumen39 halamanHPLC 4Naveen YaparthiBelum ada peringkat
- TBOC FMOC Protocols in Peptide SynthesisDokumen30 halamanTBOC FMOC Protocols in Peptide Synthesissantosh kumar sahoo100% (1)
- Ion ChromatographyDokumen2 halamanIon ChromatographyalexpharmBelum ada peringkat
- Chromatography: Definition and OverviewDokumen9 halamanChromatography: Definition and OverviewPradipkumar PanchalBelum ada peringkat
- HPLC by EktaDokumen42 halamanHPLC by EktaEkta SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Impurity Profiling and Drug Characterization: Backdrop and ApproachDokumen17 halamanImpurity Profiling and Drug Characterization: Backdrop and ApproachBaru Chandrasekhar RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Question About HPLCDokumen3 halamanQuestion About HPLCNicoleta MihalceaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental LC-MS Orbitrap Mass Analyzers PDFDokumen30 halamanFundamental LC-MS Orbitrap Mass Analyzers PDFAlonso HurtadoBelum ada peringkat
- iCE 3000 Series Pre-Installation Manual: Part Number 9499 500 30031Dokumen28 halamaniCE 3000 Series Pre-Installation Manual: Part Number 9499 500 30031Compras FisicoquimicoBelum ada peringkat
- Size Exclusion ChromatographyDokumen14 halamanSize Exclusion ChromatographyAYUSH NAIRBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Metabolism: Presenter:-Dr Swaroop H S Moderator: - DR Ananya ChakrabortyDokumen38 halamanDrug Metabolism: Presenter:-Dr Swaroop H S Moderator: - DR Ananya Chakrabortyadinda keanayaBelum ada peringkat
- Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC)Dokumen32 halamanSupercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC)masruri123Belum ada peringkat
- HPLC Column Instru TroubleshootingDokumen61 halamanHPLC Column Instru TroubleshootinglabanacabreraBelum ada peringkat
- Mdma by HPLCDokumen5 halamanMdma by HPLCCarolmariaBelum ada peringkat
- Secrets of SPEDokumen47 halamanSecrets of SPERafael Armando ZaldañaBelum ada peringkat
- 6.1.135.ephedrine Hydrochloride (Ephedrini Hydrochloridum)Dokumen2 halaman6.1.135.ephedrine Hydrochloride (Ephedrini Hydrochloridum)Kevin DonalBelum ada peringkat
- HPLC Opt ManualDokumen21 halamanHPLC Opt ManualHà Lê HảiBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of ChromatographyDokumen8 halamanPrinciples of ChromatographylordniklausBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Specifications HPLC - ProminenceDokumen4 halamanTechnical Specifications HPLC - ProminenceMaría José OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Mini PrepDokumen6 halamanMini PrepWilson GomargaBelum ada peringkat
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDokumen8 halamanThin Layer ChromatographyIsabel RinconBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance Guide ICP-MSDokumen100 halamanMaintenance Guide ICP-MSSimone GiacomelliBelum ada peringkat
- Screening of Antidiabetic Drugs: Presented ByDokumen35 halamanScreening of Antidiabetic Drugs: Presented BysharonBelum ada peringkat
- Chiral Separation TechniquesDokumen360 halamanChiral Separation TechniquesKelvin Law100% (1)
- Absorbance and Fluorescence Spectroscopies of Green Fluorescent ProteinDokumen24 halamanAbsorbance and Fluorescence Spectroscopies of Green Fluorescent ProteinMadel Tutor ChaturvediBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - Iii ChromatographyDokumen18 halamanUnit - Iii ChromatographyUdayaraj NagarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Spec Methods TheoryDokumen88 halamanMass Spec Methods Theorykunasahu1Belum ada peringkat
- Agilent LC-MS PrimerDokumen36 halamanAgilent LC-MS Primer0921py100% (2)
- Mass SpectrosDokumen47 halamanMass SpectrosEdward PittsBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Pharmaceutical AnalysisDokumen4 halamanAdvanced Pharmaceutical AnalysisRezaul RazibBelum ada peringkat
- Basics Fundamentals of Liquid Chromatography HPLCDokumen35 halamanBasics Fundamentals of Liquid Chromatography HPLCDr-Abdulsamie Hassan Alta'eeBelum ada peringkat
- Application of HPLCDokumen11 halamanApplication of HPLCIts KazmiBelum ada peringkat
- Questions HPLCDokumen10 halamanQuestions HPLCMariz MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia AnalisisDokumen75 halamanKimia AnalisisQonita NitaBelum ada peringkat
- Column and Thin Layer ChromatographyDokumen5 halamanColumn and Thin Layer ChromatographyChamzelle100% (1)
- HPLCDokumen15 halamanHPLCSk AnamBelum ada peringkat
- Development of MRM Method - MRM and Acquity Water SystemDokumen8 halamanDevelopment of MRM Method - MRM and Acquity Water SystemoctavianistrateBelum ada peringkat
- Drug TargetDokumen35 halamanDrug Targetsri nurlatipahBelum ada peringkat
- GC MS MSDokumen12 halamanGC MS MSLý VươngBelum ada peringkat
- Size Exclusion ChromatographyDokumen3 halamanSize Exclusion ChromatographyGhanshyam UpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Methods for Major and Modified Nucleosides - HPLC, GC, MS, NMR, UV and FT-IRDari EverandAnalytical Methods for Major and Modified Nucleosides - HPLC, GC, MS, NMR, UV and FT-IRBelum ada peringkat
- Inflammation in Schizophrenia and DepressionDokumen9 halamanInflammation in Schizophrenia and DepressionFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Walid Sarhan F. R. C. PsychDokumen46 halamanWalid Sarhan F. R. C. PsychFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanism For The Ability of 5Dokumen2 halamanMechanism For The Ability of 5Free Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Reliablity Validity of Research Tools 1Dokumen19 halamanReliablity Validity of Research Tools 1Free Escort Service100% (1)
- Reliability and ValidityDokumen15 halamanReliability and Validityapi-260339450Belum ada peringkat
- Role of Nutraceuticals in Health Promotion: Swati Chaturvedi, P. K. Sharma, Vipin Kumar Garg, Mayank BansalDokumen7 halamanRole of Nutraceuticals in Health Promotion: Swati Chaturvedi, P. K. Sharma, Vipin Kumar Garg, Mayank BansalFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Nutraceuticals: Let Food Be Your MedicineDokumen32 halamanNutraceuticals: Let Food Be Your MedicineFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- ABSTRACT (QBD: A Holistic Concept of Building Quality in Pharmaceuticals)Dokumen1 halamanABSTRACT (QBD: A Holistic Concept of Building Quality in Pharmaceuticals)Free Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- ResumeDokumen3 halamanResumeFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Quality by Design On PharmacovigilanceDokumen1 halamanQuality by Design On PharmacovigilanceFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Nutraceutical Role in Health CareDokumen1 halamanNutraceutical Role in Health CareFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Is Built in by Design, Not Tested inDokumen1 halamanQuality Is Built in by Design, Not Tested inFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Optimizing Quality by Design in Bulk Powder & Solid Dosage: Smt. Bhoyar College of Pharmacy, KamteeDokumen3 halamanOptimizing Quality by Design in Bulk Powder & Solid Dosage: Smt. Bhoyar College of Pharmacy, KamteeFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- 2415 14725 4 PBDokumen13 halaman2415 14725 4 PBFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Tablet Coating: Why Coat Tablets?Dokumen12 halamanTablet Coating: Why Coat Tablets?Free Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- T.Shivakumar: Kottam Institute of Pharmacy Jntu, A.PDokumen45 halamanT.Shivakumar: Kottam Institute of Pharmacy Jntu, A.PFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Tablets:: Tablets May Be Defined As SolidDokumen13 halamanTablets:: Tablets May Be Defined As SolidFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- 102i Eng Screen 02Dokumen14 halaman102i Eng Screen 02Free Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- BIOASSAYDokumen16 halamanBIOASSAYFree Escort ServiceBelum ada peringkat
- Bioassay & BiostandardisationDokumen51 halamanBioassay & BiostandardisationFree Escort Service100% (1)
- DestyRestiaet AlDokumen8 halamanDestyRestiaet AlBlokV 19Belum ada peringkat
- High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) : A Modern Analytical Tool For Chemical AnalysisDokumen7 halamanHigh Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) : A Modern Analytical Tool For Chemical AnalysisTamanna NarsinghaniBelum ada peringkat
- J. Comb. Chem. 2003, 5, 645-652Dokumen8 halamanJ. Comb. Chem. 2003, 5, 645-652Tsung-Chih ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Sucrose EsteresDokumen72 halamanSucrose EsteresWaltoy DinizBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Manual CHE102 Chemistry LabDokumen41 halamanLaboratory Manual CHE102 Chemistry LabSushil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- A Novel Combination of The Essential Oils of CinnamomumDokumen5 halamanA Novel Combination of The Essential Oils of Cinnamomumasa chiBelum ada peringkat
- Kromatografi Lapis Tipis-Densitometri Untuk Analisis Residu Pestisida Diazinon Dalam Sawi Hijau (Brassica Juncea L.)Dokumen5 halamanKromatografi Lapis Tipis-Densitometri Untuk Analisis Residu Pestisida Diazinon Dalam Sawi Hijau (Brassica Juncea L.)Yocca AsmaraBelum ada peringkat
- Chromotography LabDokumen5 halamanChromotography LabTutlalee WinesBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Outline - Exercise 5Dokumen6 halamanLaboratory Outline - Exercise 5Majestic RavenBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae: Core StrengthsDokumen6 halamanCurriculum Vitae: Core StrengthsNareshBelum ada peringkat
- PH Euro 3.1.1Dokumen30 halamanPH Euro 3.1.1ryad bmzaBelum ada peringkat
- Nitroanilne TLCDokumen23 halamanNitroanilne TLCzatty kim100% (1)
- s00226 018 1057 3Dokumen15 halamans00226 018 1057 3Aeric HalzBelum ada peringkat
- Extracción Ácida, Identificación de Alcaloides y Cromatografía en Capa Fina en Cáscara de Solanum Tuberosum L. "Papa"Dokumen6 halamanExtracción Ácida, Identificación de Alcaloides y Cromatografía en Capa Fina en Cáscara de Solanum Tuberosum L. "Papa"Joe RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- 0456e PDFDokumen2 halaman0456e PDFtrimujisantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Forensic Chemistry - Laboratory Manual ANDREWS 2001 PDFDokumen75 halamanForensic Chemistry - Laboratory Manual ANDREWS 2001 PDFjavier chavezBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 7 ChromatographyDokumen10 halamanExp 7 ChromatographyNur AidaBelum ada peringkat
- FSTEM, CTD, Philippine Normal University, Taft Avenue, Malate, ManilaDokumen12 halamanFSTEM, CTD, Philippine Normal University, Taft Avenue, Malate, ManilaRENYRICK MANALOTOBelum ada peringkat
- Formal Report Expt 5Dokumen6 halamanFormal Report Expt 5AnonymouscatBelum ada peringkat
- Ol9b02887 Si 001 PDFDokumen297 halamanOl9b02887 Si 001 PDFNathan LongBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrolysis of P-NitroacetanilideDokumen2 halamanHydrolysis of P-NitroacetanilideAshmika Singh58% (12)
- Chalcone Derivative Synthesis 1Dokumen35 halamanChalcone Derivative Synthesis 1Ankit Kumar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Thioctic AcidDokumen2 halamanThioctic AcidThippeswamy MbBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 2Dokumen6 halamanActivity 2MARKUS GERARD REYESBelum ada peringkat
- 10 1 1 185 674Dokumen10 halaman10 1 1 185 674Dr.Siju MuraleedharanBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation and Characterization of Saponins From Moringa OleiferaDokumen10 halamanIsolation and Characterization of Saponins From Moringa OleiferaAhsani ZakyBelum ada peringkat
- Quantification of Adulteration in Traded Ayurvedic Raw Drugs Employing Machine Learning Approaches With DNA Barcode DatabaseDokumen16 halamanQuantification of Adulteration in Traded Ayurvedic Raw Drugs Employing Machine Learning Approaches With DNA Barcode Databasengocan886979Belum ada peringkat
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDokumen6 halamanThin Layer ChromatographyVictoria ReaganBelum ada peringkat
- Formulation and Evaluation of A Syrup Based On BalDokumen10 halamanFormulation and Evaluation of A Syrup Based On BalemilBelum ada peringkat
- Quantitative Analysis and Thin Layer Chromatography of CarbohydratesDokumen4 halamanQuantitative Analysis and Thin Layer Chromatography of CarbohydratesKaycee Allen FranciscoBelum ada peringkat