Irrigation Methods
Diunggah oleh
Kathir RathJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Irrigation Methods
Diunggah oleh
Kathir RathHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IRRIGATION METHODS
SELECTION OF METHOD OF
IRRIGATION
DECIDED BY AGRICULTURIST
BASIC REQUIREMENTS FOR ADOPTING METHOD
For Light irrigation-at least 6cm depth & Uniform
For Heavy 15cm to 20cm depth
Large flow & Reduction of conveyance losses and
labor cost
Capable to adopt any mechanical farming methods
Over irrigation should be avoided to prevent soil
erosion, leached fertilizers, drainage problem & salt
accumulation
SURFACE IRRIGATION
Supply of irrigation water to the Land by
gravity
2 types (a) Flow irrigation (b) Lift irrigation
Flow irrigation when availing water in higher
level
Lift irrigation- when availing water in lower
level by some mechanical
FLOW IRRIGATION
i. Perennial irrigation
ii. Flood irrigation
iii. Furrow irrigation
iv. Contour forming method
PERENNIAL IRRIGATION
Constant & Continuous water supply
Through storage, canal headworks & canal
distribution system
Direct irrigation water directed to the canal
by constructing weir across the river.
Storage irrigation Dam constructed across
the river to store water throughout the year
& supplied at the time of need.
canal & tank irrigations are examples.
CANAL IRRIGATION
System of a planned network of canals
Main canals, Branch canals, Distributaries and
miniors
TANK IRRIGATION
utilizes the water stored on the upstream of a
small-size dam called bund.
Tanks are generally made out of earth.
Earthen bunds constructed across streams are
called tank bunds or tank banks.
A tank may be isolated or form a pack of
group of tanks
TANK IRRIGATION
FLOOD IRRIGATION
The soil is kept submerged and fully get
saturated by the flooded water.
By using natural rainfall or more watering
brings the crop to maturity
This method is also called as Innundation
Irrigation
Classified into uncontrolled or wild flooding
and controlled flooding.
UNCONTROLLED FLOODING
Water is flooded on an flat which is not
leveled
Typical inundation system
Evidently it is waste of water encouraged in
low cost water availing area
CONTROLLED FLOODING
The water flooding on the land by adopting
certain methodology for control the depth of
water.
Methods are
Free flooding
Border flooding
Check flooding
Basin flooding
FREE FLOODING
BORDER FLOODING
CHECK FLOODING
BASIN FLOODING
FURROW IRRIGATION METHOD
Only wetting of the field is done
Suitable when crops are planted in rows
Longitudinal slope of furrow 2 to 10m for
1000 m length
Spacing of furrows varies from 8 to 30cm
depends on crop
FURROW IRRIGATION METHOD
CONTOUR FARMING METHOD
Used in steep slope hilly areas
Comprises of conducting field operations such
as ploughing, planting, cultivating
First contour generally laid 1.2 to 1.5m
vertically below the top of the hill
CONTOUR FARMING METHOD
LIFT IRRIGATION METHOD
The water has to be lifted by using some
mechanical means, its lift irrigation.
Except lifting operation, water supply done by
any one of the surface irrigation method.
Subsurface water lifted by 2 methods (a) open
well (b) Tube well irrigation
Sometimes surface water from canal, river
also lifted .
LIFT IRRIGATION METHOD
Any water bearing underground formation is
called aquifer.
Aquifers are classified as confined and
unconfined aquifers.
OPEN WELL IRRIGATION
Hole in the ground with 2 to 10m are made.
Depth of penetration below ground water
table may be the order of 3 to 4m.
Generally the avg D/C 0.004m
3
/s
Yield of well determined by pumping test or
recuperation test.
The rate of yield expressed in m
2
/hour or
lit/min
TUBE WELL IRRIGATION
It is resorted to by digging a small hole in the
subsoil formation and lifting the water by
using some type of pump.
To prevent clogging of the tube well, a
perforated metal pipe is driven. Its prevents
the soil particles from entering the hole.
The tube has to be taken atleast 50m into the
water bearing stratum.
It is most suitable where the subsoil formation
is capable of storing water.
SUBSURFACE IRRIGATION
METHODS
Water does not wet the soil surface but
nourishes the plant roots by capillarity.
This method is favoured under the following
conditions
presence of impervious sub soil strata at a
reasonable depth
Water table to exist at deeper depth
Uniform topographic conditions
Permeable soil condition at the root zone
Moderate slope
SUBSURFACE IRRIGATION
METHODS
This method avoiding alkali accumulation and
excess water logging.
Classified in two categories
Natural sub surface irrigation
Artificial sub surface irrigation
NATURAL SUB-SURFACE
IRRIGATION
Water contributes directly to the subsoil.
The favourable condition is that the top
pervious soil(about 2m depth) rests on
impervious stratum.
Water directly supply to subsoil small ditches
of 50 to 100 cm deep and 30cm wide are dug
at a spacing of 60 to 90m from the main
channel.
NATURAL SUB-SURFACE
IRRIGATION
ARTIFICIAL SUBSURFACE
IRRIGATION
Water supply to the roots of the crops by
capillary action, open jointed drains are laid
below the soil.
This method is costly but useful for production
of cash crops on small areas.
Avoided losses of evaporation & deep
percolation.
The pipes are buried 0.3 to 0.4m deep.
Drip irrigation is the main type of artificial
subsurface irrigation.
ARTIFICIAL SUBSURFACE
IRRIGATION
DRIP IRRIGATION
Water is slowly and directly applied to the
root zone of the plants.
This method also called as TRICKLE
IRRIGATION which completely minimizes the
losses by evaporation and percolation.
DRIP IRRIGATION COMPONENTS
OF THE SYSTEM
Head: It consists of a pump to lift water so as produce
the desired pressure.
Fertilizer tank: lifted water passed through this to mix
the fertilizer in water.
Filter: Remove suspended particles to avoid clogging.
Mains & sub-mains: PVC small pipes buried or laid on
the ground.
Laterals: 1 to 1.25m dia pipes length upto 50m and also
called as trickle lines.
Drip nozzles: Fixed on laterals at regular intervals of
about 0.5 to 1m & discharging water at very small rates
of about 5 liters per hour.
DRIP IRRIGATION
DRIP IRRIGATION ORGANIZATION
OF THE SYSTEM
Field is divided into smaller suitable plots.
A secondary line is drawn for each plot.
No of lateral are connected to each secondary
line.
A regulator is fixed in secondary line to
provide a fixed quantity of water.
This system widely practiced in foreign
countries.
DRIP IRRIGATION MERITS
Less requirement of irrigation water
Supply of water is optimum
No soil erosion
suitable for any topography
Reduction in labour cost
Feasibility to irrigate more area with the available
water
Rate of supply of water can be varied through out the
crop period
Suitable for cash crops
Water-logging is prevented
DRIP IRRIGATION DEMERITS
Initial cost is high
Possibility of blocking of nozzles
Shallow root growth
Frequent change of spacing of nozzles
SPRINKLER IRRIGATION METHOD
Ideal rainfall method
Also called as over-head irrigation method.
Water is applied in the form of a spray
Main aluminum supply pipes are fixed at
specified intervals on which sprinkler pipes
with nozzles fixed or rotating type on top are
fixed.
SPRINKLER IRRIGATION METHOD
SPRINKLER IRRIGATION METHOD
SPRINKLER IRRIGATION METHOD
FAVOURABLE CONDITIONS
Any type of topography
Suitable for all gradients of field
Highly permeable soil
Water table is high
Areas where water availability is scarce or difficult
where seasonal water requirement is low
Types of crops which require
Humidity control
Shallow roots
High and frequent watering
SPRINKLER IRRIGATION METHOD
TYPES
Classified into three types
i. Permanent system
ii. Semi-permanent system
iii. Portable system
PERMANENT SYSTEM: pipes are permanently buried
such that they do not interfere with farming operations.
SEMI-PERMANENT SYSTEM: main lines are buried in the
ground while the laterals are portable.
PORTABLE SYSTEM: both main & lateral are portable.
SPRINKLER IRRIGATION METHOD
MERITS
Control of erosion
Uniformity in application of water
Controlled irrigation
Initial land preparation like construction of
borders, ditches are not needed.
Small quantity of water can be effectively used
Control on application of fertilizers
Reduction in crop damage due to frost.
SPRINKLER IRRIGATION METHOD
DEMERITS
Sprinkler pattern may be changed due to wind
Constant need of water for sprinkling
Clean water is always needed
Heavy soil of less permeable can not be useful
High power requirement.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Sanitary Drainage SystemsDokumen21 halamanSanitary Drainage Systemspepito manalotoBelum ada peringkat
- POLYSEED Application Procedure 3.15Dokumen2 halamanPOLYSEED Application Procedure 3.15ALVARO ENRIQUE CANTILLO GUZMANBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Management Case StudyDokumen6 halamanWaste Management Case StudySamuel Takeshi PanBelum ada peringkat
- GE2021 Environmental Science Study MaterialDokumen134 halamanGE2021 Environmental Science Study MaterialSelvakapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal ViskositasDokumen5 halamanJurnal ViskositasAfif Fahza NurmalikBelum ada peringkat
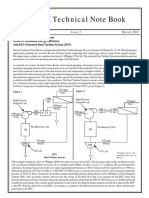
- PEI Technical Note Achieves Maximum Energy Efficiency with Dual Turbine SystemDokumen2 halamanPEI Technical Note Achieves Maximum Energy Efficiency with Dual Turbine System1mmahoneyBelum ada peringkat
- MSDS Milk Powder-1Dokumen3 halamanMSDS Milk Powder-1Asmida HamidBelum ada peringkat
- WORM COMPOSTING - RecyclingSmartDokumen2 halamanWORM COMPOSTING - RecyclingSmartWorm CompostingBelum ada peringkat
- Plastics Convert Iron Ore To Steel Feedstock Recycling in Blast FurnacesDokumen8 halamanPlastics Convert Iron Ore To Steel Feedstock Recycling in Blast FurnacesNancy DanielBelum ada peringkat
- Spill Prevention and ControlDokumen20 halamanSpill Prevention and ControlZaid MubeenBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Water Quality Test LabDokumen12 halaman02 Water Quality Test LabNaj Nasir75% (8)
- Coagulants For Water TreatmentDokumen48 halamanCoagulants For Water Treatmenthafiz zain saeedBelum ada peringkat
- Recycling Implementation in BiliranDokumen2 halamanRecycling Implementation in BiliranJoey Hermusora EspantoBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study on Promoting 3R Waste PracticesDokumen5 halamanCase Study on Promoting 3R Waste PracticesDarren Chelsea PacienciaBelum ada peringkat
- Readymix Brunei Fly Ash 2016Dokumen59 halamanReadymix Brunei Fly Ash 2016LokeBelum ada peringkat
- Disposal of WastesDokumen53 halamanDisposal of WastesPriya Sharma100% (1)
- Process Design BasisDokumen6 halamanProcess Design BasisMufleh Idris100% (3)
- Gap Filling Without Clues: Answer: A. Return B. Lame C. Angry D. Controlled E. Great F. Going G. Carry H. Sent IDokumen3 halamanGap Filling Without Clues: Answer: A. Return B. Lame C. Angry D. Controlled E. Great F. Going G. Carry H. Sent IMaruf Hossain PiashBelum ada peringkat
- PWTLecture8 (SedimentationII)Dokumen55 halamanPWTLecture8 (SedimentationII)JojoBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluating Biological Treatment SystemsDokumen154 halamanEvaluating Biological Treatment SystemsMohamed Salem100% (3)
- DAO 2003-30 Procedural ManualDokumen193 halamanDAO 2003-30 Procedural ManualJoemer Absalon Adorna100% (1)
- Tle 1Dokumen12 halamanTle 1anglcrvrBelum ada peringkat
- APES Chapter 3 NotesDokumen4 halamanAPES Chapter 3 Noteskhushi100% (1)
- Assessment of Forest Suitability in Khuvsgul Province Using Geographic Information System and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making ApproachDokumen11 halamanAssessment of Forest Suitability in Khuvsgul Province Using Geographic Information System and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Approachzul ErdeneBelum ada peringkat
- Namba Park Sub by - SoorajDokumen25 halamanNamba Park Sub by - SoorajsoorajBelum ada peringkat
- Soil Degradation and Conservation ProcessesDokumen37 halamanSoil Degradation and Conservation ProcessessilBelum ada peringkat
- CCL CorporateDokumen21 halamanCCL Corporatevishal_patil_3Belum ada peringkat
- Ginoo at Binibining Trimex # QuestionDokumen2 halamanGinoo at Binibining Trimex # QuestionErichSantosValdeviesoBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 5 Single-Multiple Stage LeachingDokumen29 halamanChap 5 Single-Multiple Stage Leachingqemaismail100% (1)
- Oscar Winning Doc Exposes Climate ThreatDokumen3 halamanOscar Winning Doc Exposes Climate ThreatNadine100% (1)