Factoring Services
Diunggah oleh
amygurlDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Factoring Services
Diunggah oleh
amygurlHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Factoring Services
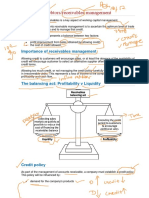
What is Factoring
Factoring is a financial transaction whereby a
business sells its accounts receivable (i.e.,
invoices) to a third party (called a factor) at a
discount in exchange for immediate money
with which to finance continued business.
Factoring differs from a bank loan in
three main ways.
First, the emphasis is on the value of the
receivables (essentially a financial asset), not
the firms credit worthiness.
Secondly, factoring is not a loan it is the
purchase of a financial asset (the receivable).
Finally, a bank loan involves two parties
whereas factoring involves three.
The three parties directly involved are: the one
who sells the receivable, the debtor, and the
factor.
The receivable is essentially a financial asset
associated with the debtors liability to pay
money owed to the seller (usually for work
performed or goods sold).
The seller then sells one or more of its invoices
(the receivables) at a discount to the third party,
the specialized financial organization (the factor),
to obtain cash.
The sale of the receivables essentially transfers
ownership of the receivables to the factor,
indicating the factor obtains all of the rights and
risks associated with the receivables.
Accordingly, the factor obtains the right to
receive the payments made by the debtor for the
invoice amount and must bear the loss if the
debtor does not pay the invoice amount.
Usually, the account debtor is notified of the sale
of the receivable, and the factor bills the debtor
and makes all collections.
In factoring, a financial institution (factor) buys
the accounts receivable of a company (Client) and
pays up to 80%(rarely up to 90%) of the amount
immediately on agreement.
Factoring company pays the remaining amount
(Balance 20%-finance cost-operating cost) to the
client when the customer pays the debt.
Collection of debt from the customer is done
either by the factor or the client depending upon
the type of factoring.
RBI issued guidelines for factoring services in
1990.
The first factoring company SBI Factors and
Commercial Ltd. Started operation in April,
1991.
Factoring companies in India
Canbank Factors Limited: http://www.canbankfactors.com
SBI Factors and Commercial Services Pvt. Ltd: http://www.sbifactors.com
The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Ltd: http://www.hsbc.co.in/1/2/corporate/trade-and-
factoring-services
Foremost Factors Limited: http://www.foremostfactors.net
Global Trade Finance Limited: http://www.gtfindia.com
Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India Ltd:
https://www.ecgc.in/Portal/productnservices/maturity/mfactoring.asp
Citibank NA, India: http://www.citibank.co.in
Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI): http://www.sidbi.in/fac.asp
Standard Chartered Bank: www.standardchartered.co.in
A major advantage of Factoring is that it is a
form of off balance sheet financing.
Forfaiting
In trade finance, forfaiting involves the
purchasing of receivables from exporters.
The forfaiter will take on all the risks involved
with the receivables.
It is different from the factoring operation in the
sense that forfaiting is a transaction based
operation while factoring is a firm based
operation
meaning, in factoring, a firm sells all its
receivables while in forfaiting, the firm sells one
of its transactions.
Benefits for using forfaiting include
eliminating risks (political, transfer and
commercial risks) and improving cashflows.
Increases cash flow.
Forfaiting converts a credit-based transaction
in to a cash transaction.
Forfeiting is without recourse to the seller.
The purchase is in the form of discounting the
documents covering the entire risk of non
payment in collection.
Recourse Factoring
Under a recourse factoring arrangement,
factor has recourse to the client if the
receivables factored turns out to be
irrecoverable.
Factor does not assume credit risks associated
with the receivables.
Non Recourse Factoring
Under a non recourse factoring arrangement,
factor does not have recourse to the client if
the receivables factored turns out to be
irrecoverable.
The loss arising out of the irrecoverable
receivables is borne by him, as a
compensation for which he charges a higher
commission.
Legal Aspects of Factoring
There is no codified legal framework for
factoring in India.
Regulated under the law of Contract.
Legal relationship largely determined by the
terms of the contract.
Factoring versus Bill Discounting
Bill discounting is always with recourse while
factoring can be either with recourse or
without recourse.
Bill Discounting does not involve assignment
of debt as is the case with factoring.
Bill Discounting
Bill discounting is a fund based service
provided by finance companies.
An endorsed bill of exchange is handed over
for ready money.
The margin between the ready money and the
face value of the bill is called Discounting of
Bills.
Bill of exchange
Suppose a seller sells goods or merchandise to
a buyer.
In most cases, the buyer would like to
purchase on credit.
The seller draws a Bill of exchange of a given
maturity on the buyer.
The seller has now assumed the role of a
creditor and is called the drawer of the Bill.
The buyer who is the debtor, is called the
drawee.
The seller then sends the bill to the buyer who
acknowledges it by writing his acceptance on
the bill.
In order to prevent misuse, the RBI placed
several restrictions on the bill discounting
mechanism.
As a result, Bill discounting has substantially
declined in importance.
Questions for Revision
What is factoring ? How is it different from
A Bank Loan
Forfaiting
Bill Discounting
The End
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Factoring MBADokumen9 halamanFactoring MBADilip SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Factoring Project ReportDokumen15 halamanFactoring Project ReportSiddharth Desai100% (3)
- Factoring Vs ForfeitingDokumen27 halamanFactoring Vs ForfeitingShruti AshokBelum ada peringkat
- FactoringDokumen22 halamanFactoringRaju MahatoBelum ada peringkat
- FACTORINGDokumen6 halamanFACTORINGsadathnooriBelum ada peringkat
- M. Com IV Semester Paper: Financial Services Module: Factoring and ForfaitingDokumen19 halamanM. Com IV Semester Paper: Financial Services Module: Factoring and ForfaitingAishwarya100% (1)
- Different Types of Factoring: Financial Transaction Accounts Receivable Invoices Factor DiscountDokumen4 halamanDifferent Types of Factoring: Financial Transaction Accounts Receivable Invoices Factor DiscountSunaina Kodkani100% (1)
- External Commercial BorrowingDokumen14 halamanExternal Commercial BorrowingKK SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Receivable & Payable Management PDFDokumen7 halamanReceivable & Payable Management PDFa0mittal7Belum ada peringkat
- Raymond WC MGMTDokumen66 halamanRaymond WC MGMTshwetakhamarBelum ada peringkat
- ForfeitingDokumen18 halamanForfeitingAchal KhandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- NBFCDokumen37 halamanNBFCMukul Babbar100% (2)
- Summer Training in Intex TechnologyDokumen37 halamanSummer Training in Intex TechnologyMj PayalBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Bank LendingDokumen23 halamanBasics of Bank LendingRosestella PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- Working CapitalDokumen56 halamanWorking CapitalharmitkBelum ada peringkat
- Receivables Management SelfDokumen36 halamanReceivables Management Selfnitik chakmaBelum ada peringkat
- Bank Finance For Working CapitalDokumen12 halamanBank Finance For Working CapitalAjilal KadakkalBelum ada peringkat
- Investigation into the Adherence to Corporate Governance in Zimbabwe’s SME SectorDari EverandInvestigation into the Adherence to Corporate Governance in Zimbabwe’s SME SectorBelum ada peringkat
- Under CapitalizationDokumen10 halamanUnder CapitalizationNMRaycBelum ada peringkat
- Accounts Receivable Management Practices and Growth of SMEDokumen165 halamanAccounts Receivable Management Practices and Growth of SMELuke Robert HemmingsBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment On FactoringDokumen5 halamanAssignment On FactoringVISHNU. M. K MBA 2018Belum ada peringkat
- Merchant BankingDokumen19 halamanMerchant BankingMiral PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Factoring & Forfeiting: Learning ObjectivesDokumen7 halamanFactoring & Forfeiting: Learning ObjectivesLohith SanjeevBelum ada peringkat
- Banking Report On KYC, NPA & FactoringDokumen19 halamanBanking Report On KYC, NPA & FactoringKaushal Patel100% (1)
- Debt SecuritisationDokumen16 halamanDebt SecuritisationAbhishek SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Internship Report On RBBDokumen32 halamanInternship Report On RBBAmrit sanjyalBelum ada peringkat
- Financing Working Capital - Naveen SavitaDokumen7 halamanFinancing Working Capital - Naveen SavitaMurli SavitaBelum ada peringkat
- Ba7022 Merchant Banking and Financial ServicesDokumen214 halamanBa7022 Merchant Banking and Financial ServicesRitesh RamanBelum ada peringkat
- Receivables ManagementDokumen33 halamanReceivables ManagementArjun SanalBelum ada peringkat
- Banking Sector ReformsDokumen27 halamanBanking Sector ReformsArghadeep ChandaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDokumen13 halamanAssignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDavinder Singh Banss0% (1)
- Innovative Financial ServicesDokumen9 halamanInnovative Financial ServicesShubham GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Working Capital Management in Steel IndustryDokumen54 halamanWorking Capital Management in Steel IndustryPrashant Singh50% (2)
- Assignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDokumen13 halamanAssignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDavinder Singh BanssBelum ada peringkat
- Q. 16 Functions of A Merchant BankerDokumen3 halamanQ. 16 Functions of A Merchant BankerMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Bank of Maharashtra: Commercial Banking SystemDokumen13 halamanA Study On Bank of Maharashtra: Commercial Banking SystemGovind N VBelum ada peringkat
- Bills Discounting, Factoring & ForfaitingDokumen23 halamanBills Discounting, Factoring & ForfaitingVineet HaritBelum ada peringkat
- Leasing CompaniesDokumen19 halamanLeasing CompaniesAsad AliBelum ada peringkat
- Presented By: 1. Pravin Gavali 2. Vickram Singh MIT-MBA (Finance)Dokumen24 halamanPresented By: 1. Pravin Gavali 2. Vickram Singh MIT-MBA (Finance)shrikant_gaikwad100Belum ada peringkat
- Pre-Shipment-Post-Shipment 14519Dokumen24 halamanPre-Shipment-Post-Shipment 14519aeeeBelum ada peringkat
- Credit Facility in BankDokumen45 halamanCredit Facility in BankAbhas AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Designing Capital StructureDokumen13 halamanDesigning Capital StructuresiddharthdileepkamatBelum ada peringkat
- Core Risks in BankingDokumen9 halamanCore Risks in BankingVenkatsubramanian R IyerBelum ada peringkat
- IntershipDokumen65 halamanIntershipainashaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Financial System MbaDokumen85 halamanFinancial System MbamallikamathewsBelum ada peringkat
- NSDL Case StudyDokumen3 halamanNSDL Case StudyDeepshikha Goel100% (1)
- Dear Pooja and GroupDokumen3 halamanDear Pooja and GroupVijay YadavBelum ada peringkat
- STATE FINANCIAL CORPORATIONS (SFCS)Dokumen10 halamanSTATE FINANCIAL CORPORATIONS (SFCS)Ankush Kumar RanaBelum ada peringkat
- BASEL I, II, III-uDokumen43 halamanBASEL I, II, III-uMomil FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Hire Purchase and LeasingDokumen30 halamanHire Purchase and LeasingShreyas Khanore100% (1)
- Credit Management of RetailersDokumen35 halamanCredit Management of Retailershemal dhuriBelum ada peringkat
- Factoring ServicingDokumen25 halamanFactoring ServicingTanya JaliBelum ada peringkat
- Non Convertible DebenturesDokumen3 halamanNon Convertible DebenturesAbhinav AroraBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Receivable Management & Its ImpactDokumen70 halamanA Study On Receivable Management & Its Impactlmbhagya100% (2)
- Account Receivable ManagementDokumen41 halamanAccount Receivable ManagementUtkarsh Joshi100% (2)
- P 17-1 Cash Distribution Plan and Entries - Installment: RequiredDokumen5 halamanP 17-1 Cash Distribution Plan and Entries - Installment: RequiredGhitha Afifah HurinBelum ada peringkat
- CICA Condo RulesDokumen52 halamanCICA Condo Rulesoldchanter100% (1)
- Ethics Finance SyllabusDokumen6 halamanEthics Finance SyllabusAfiqah RasidiBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneur : Group or Individual Creativity Technique Alex Faickney OsbornDokumen3 halamanEntrepreneur : Group or Individual Creativity Technique Alex Faickney OsbornAkshay KamathBelum ada peringkat
- Deal Contingent Transactions: Presented by Robert M. Lichten, JRDokumen18 halamanDeal Contingent Transactions: Presented by Robert M. Lichten, JRPrashantK100% (1)
- Company Law-II ProjectDokumen22 halamanCompany Law-II ProjectAbhinavParasharBelum ada peringkat
- RSM FinalDokumen29 halamanRSM FinalNihal LamgeBelum ada peringkat
- Forward MarketDokumen25 halamanForward Marketsamihaz02Belum ada peringkat
- Uid46434 UCCD Financial Accounting Question PaperDokumen7 halamanUid46434 UCCD Financial Accounting Question PaperPhoenixFirebrdBelum ada peringkat
- Form No.92-Affidavit of LossDokumen2 halamanForm No.92-Affidavit of LossMaica PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Secured Transactions OutlineDokumen121 halamanSecured Transactions Outlinemaureen P100% (2)
- Capital Asset Pricing Model SAPMDokumen18 halamanCapital Asset Pricing Model SAPMarmailgmBelum ada peringkat
- Futures Vs Forward PricingDokumen51 halamanFutures Vs Forward PricingLatiff JaleelBelum ada peringkat
- DWDDokumen2 halamanDWDCrystal EricksonBelum ada peringkat
- ExercisesDokumen3 halamanExercisesrhumblineBelum ada peringkat
- Dividend Policy PDFDokumen20 halamanDividend Policy PDFHrithika AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Geofredo E. Mabunga and Froilan D. Cabaltera For Petitioners. Gella, Danguilan, Fuentes, Ferrer, Samson & Associates For Private RespondentDokumen49 halamanGeofredo E. Mabunga and Froilan D. Cabaltera For Petitioners. Gella, Danguilan, Fuentes, Ferrer, Samson & Associates For Private RespondentRuth HephzibahBelum ada peringkat
- Loan Application FormDokumen9 halamanLoan Application FormrohitBelum ada peringkat
- WyckoffDokumen1 halamanWyckoffRatulBelum ada peringkat
- Marine Cargo Claims ProcedureDokumen16 halamanMarine Cargo Claims ProcedureSunday Oluwole100% (1)
- Sap Cin User GuideDokumen56 halamanSap Cin User Guidedurgadreamline100% (2)
- Optimal Option:: SUNY's Personal Retirement Plan As A Model For Pension ReformDokumen32 halamanOptimal Option:: SUNY's Personal Retirement Plan As A Model For Pension ReformJimmyVielkindBelum ada peringkat
- KBA - Accounting and BookkeepingDokumen8 halamanKBA - Accounting and BookkeepingKBA Accounting & Bookkeeping Services LLCBelum ada peringkat
- Action To Recover DamagesDokumen4 halamanAction To Recover DamagesSui100% (1)
- Solution Homework 2Dokumen2 halamanSolution Homework 2Ishaa Siddiqui100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Problems AnswersDokumen11 halamanChapter 3 Problems AnswersOyunboldEnkhzayaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Q&ADokumen19 halamanChapter 4 - Q&APro TenBelum ada peringkat
- Inflation Accounting New CourseDokumen11 halamanInflation Accounting New CourseAkshay Mhatre100% (1)
- Economics AssignmentDokumen8 halamanEconomics Assignmentchandanprakash30Belum ada peringkat