CH 4 Bending Stressesnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnn
Diunggah oleh
dudescapeJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CH 4 Bending Stressesnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnn
Diunggah oleh
dudescapeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHAPTER 4: BENDING
STRESSES
1
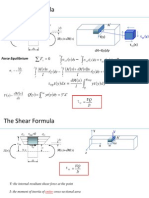
Normal Stresses in Beams -
Bending
2
Normal Stresses in Beams
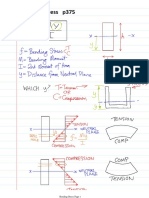
the normal stress in the member, which occurs at a point on the cross-sectional area
farthest away from the neutral axis ( N/m
2
= Pa )
M the resultant internal moment, determined from the method of sections and the
equations of equilibrium and calculated about the neutral axis of the cross section ( Nm )
y the perpendicular distance from the neutral axis to a point farthest away from the
neutral axis. This is where
max
acts ( m )
I the moment of inertia of the cross sectional area about the neutral axis ( m
4
)
R radius of curvature ( m )
E Young Modulus ( N/m
2
= Pa )
3
M = = E
I y R
Flexure formula :
Maximum Stresses at a Cross-
Section
Relationships between
signs of bending
moments and
directions of normal
stresses;
(a) +ve bending
moment.
(b) -ve bending
moment.
4
Properties of Plane Areas
5
Properties of Plane Areas.
6
Properties of Plane Areas.
7
Properties of Plane Areas.
8
Combination Shape
I
X/Y
moment of inertia
A cross sectional area
h length between neutral axis
I = (I
G
+ Ah)1+2+3+.
9
Neutral Axis
Unsymmetric Symmetrical
=
yA
A
10
Here is a place holder for the text. The earth flower on this page can be
removed. Picture from PresenterMedia.com
Picture Page Layout
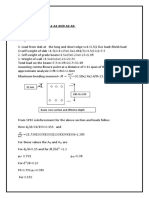
c = y = 0.2/2 = 0.1 m
3kNm
100mm
200mm
I = bh
3
/12 = 0.1 x 0.2
3
/ 12 = 6.667x10
-5
m
4
= Mc
I
= (3kNm)(0.1m)/(6.667x10
-5
m
4
)
= 4.4998 MPa (compression and tension)
12
Example 1: Cantilever Beam
EXAMPLE 2
13
EXAMPLE 3
14
Example 4: Simply Supported Beam
40mm
10mm
100mm
10mm
10mm
80mm
5kN/m
6m
15
Area A :
y
A
= 0.01/2 = 0.005 m;
A
A
= 0.04 x 0.01 = 0.0004 m
2
;
Area B :
y
B
= 0.01 + 0.08/2 = 0.05 m;
A
B
= 0.01 x 0.08 = 0.0008 m
2
Area C :
y
C
= 0.01 + 0.08 + 0.01/2 = 0.095 m;
A
C
= 0.1 x 0.01 = 0.001 m
2
Step 1: Identify value c from neutral axis
40mm
10mm
100mm
10mm
10mm
80mm
A
B
C
Neutral Axis
0
Y
C
Y
B
Y
A
C
1
C
2
c
1
= yA/A
c
1
= [y
A
A
A
+ y
B
A
B
+ y
C
A
C
]/[A
A
+ A
B
+ A
C
]
c
1
= [(0.005 x 0.0004) + (0.05 x 0.0008) + (0.095 x 0.001)] / [0.0004 + 0.0008 + 0.001]
c
1
= 0.062 m
16
Area A :
h
A
= 0.062-0.005=0.057m;
I
A
=3.33x10
-9
m
4
Area B :
h
B
= 0.062-0.050=0.012m;
I
B
= 4.267x10
-7
m
4
Area C :
h
C
= 0.095-0.062=0.033m;
I
C
=8.33x10
-9
m
4
The shape for A,B and C are rectangular Use I = bh
3
/12
Step 2: Determine moment of inertia
40mm
10mm
100mm
10mm
10mm
80mm
A
B
C
Neutral Axis 0
Y
C
Y
B
Y
A
= 0.005m
= 0.05m
= 0.095m
C
1
= 0.062m
C
2
= 0.038m
Total of combination shape; I = (I
G
+ Ah)
I = (I + Ah)
A
+ (I + Ah)
B
+ (I + Ah)
C
= 1.30293x10
-6
m
4
+ 5.419x10
-7
m
4
+ 1.09733x10
-6
m
4
= 2.942x10
-6
m
4
17
Step 3: Determine maximum bending stresses
5kN/m
6m
0 kNm
6m
+22.5kNm
+30kN
-30kN
Shear Force Diagram
Moment Diagram
18
Step 4: Calculate normal stress
I = 2.94216x10
-6
m
4
M
max
=22.5kNm (+ve)
max
= Mc
1
I
= (22.5kN)(0.062)/(2.94216x10
-6
)
= 474.14x10
6
N/m(compression)
= Mc
2
I
= (22.5kN)(0.038)/(2.94216x10
-6
)
= 290.60x10
6
N/m(tension)
compress
tension
40mm
10mm
100mm
10mm
10mm
80mm
A
B
C
Neutral Axis
C
1
= 0.062m
C
2
= 0.038m
19
Maximum bending stress
20
L/2 L/2
L
L
L
M
max
=FL/4
M
max
=FL/8
M
max
=FL
M
max
=FL/2
(F unit N)
(F unit N)
(F unit N/m)
(F unit N/m)
F
F
F
L
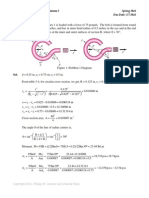
If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M = 20kN.m,
determine the maximum bending stress in the beam.
EXAMPLE 5
21
Example 5: Continue
22
20mm
20mm
20mm
200mm
300m
m
A
B C
Symmetrical
M
Direction bending: POSITIVE BENDING
compres
s
tension
Value c : 0.2m/2 = 0.1m
I = [bh
3
/12]
A
+ [bh
3
/12]
B
+ [bh
3
/12]
C
I = 2[0.02 x 0.2
3
/12] + [0.26 x 0.02
3
/12]
I = 2.684 (10
-5
) m
4
max
= Mc/I = 20(10
3
) x 0.1/2.684 (10
-5
) = 74.5 MPa
M = 20kNm
Example 6
A cast-iron machine part is acted upon by a 3 kNm couple. Knowing E
= 165 GPa and neglecting the effects of fillets, determine (a) the
maximum tensile and compressive stresses, (b) the radius of
curvature.
Example 6: Continue
SOLUTION:
Based on the cross section geometry,
calculate the location of the section centroid
and moment of inertia.
( )
+ = =
'
2
d A I I
A
A y
Y
x
Apply the elastic flexural formula to find
the maximum tensile and compressive
stresses.
I
Mc
m
= o
Calculate the curvature
EI
M
=
1
SOLUTION: Based on the cross section geometry, calculate the location of the
section centroid and moment of inertia.
mm 38
3000
10 114
3
=
=
A
A y
Y
= =
=
=
3
3
3
3 2
10 114 3000
10 4 2 20 1200 30 40 2
10 90 50 1800 90 20 1
mm , mm , mm Area,
A y A
A y y
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
4 9 - 4 3
2 3
12
1
2 3
12
1
2 3
12
1
2
m 10 868 mm 10 868
18 1200 40 30 12 1800 20 90
= =
+ + + =
+ = + =
'
I
d A bh d A I I
x
Example 6: Continue
Apply the elastic flexural formula to find the maximum tensile and compressive stresses.
4 9
4 9
m 10 868
m 038 . 0 m kN 3
m 10 868
m 022 . 0 m kN 3
= =
= =
=
I
c M
I
c M
I
Mc
B
B
A
A
m
o
o
o
MPa 0 . 76 + =
A
o
MPa 3 . 131 =
B
o
Calculate the curvature
( )( )
4 9 -
m 10 868 GPa 165
m kN 3
1
=
=
EI
M
m 7 . 47
m 10 95 . 20
1
1 - 3
=
=
Example 6: Continue
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Engineers Precision Data Pocket ReferenceDari EverandEngineers Precision Data Pocket ReferencePenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- UnaDokumen179 halamanUnahafiniaBelum ada peringkat
- 00 Calculator Techniques 01Dokumen2 halaman00 Calculator Techniques 01vincelord92% (12)
- Design BeamDokumen50 halamanDesign BeammonirithneangBelum ada peringkat
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- 1984Dokumen46 halaman1984Praveen Kumar85% (13)
- Timber DesignDokumen26 halamanTimber DesignRichmon Pangilinan100% (6)
- Mechanical Science for Technicians: Volume 1Dari EverandMechanical Science for Technicians: Volume 1Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Internal CombutionDokumen48 halamanInternal CombutionNURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR100% (7)
- Design of Rectangular Water TankDokumen242 halamanDesign of Rectangular Water Tankmumarbsc7244Belum ada peringkat
- Strap Footing DesignDokumen5 halamanStrap Footing DesignNabin Acharya100% (1)
- Answer Set 5 - Fall 2009Dokumen38 halamanAnswer Set 5 - Fall 2009zachBelum ada peringkat
- ECS 238 - Chapter 2b (Bending and Shear Stresses and in Symmetrical Beams)Dokumen53 halamanECS 238 - Chapter 2b (Bending and Shear Stresses and in Symmetrical Beams)Izzat JalilBelum ada peringkat
- Crack Width Calc - BS 8110Dokumen1 halamanCrack Width Calc - BS 8110Thomas Crowe100% (2)
- Column With Biaxial MomentDokumen26 halamanColumn With Biaxial MomentRajanvmBelum ada peringkat
- Moment of InertiaDokumen20 halamanMoment of Inertiaharipatel1989100% (1)
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringDari EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- 77-9 Design of CranesDokumen10 halaman77-9 Design of Cranesrip111176Belum ada peringkat
- Buzan, Barry - Security, The State, The 'New World Order' & BeyondDokumen15 halamanBuzan, Barry - Security, The State, The 'New World Order' & Beyondyossara26100% (3)
- Span Deflection (Double Integration Method)Dokumen14 halamanSpan Deflection (Double Integration Method)Ikhwan Z.88% (8)
- Theory of Simple Bending - Full1Dokumen62 halamanTheory of Simple Bending - Full1Rahul KasaudhanBelum ada peringkat
- AA-SM-002 TorsionDokumen8 halamanAA-SM-002 TorsionjowarBelum ada peringkat
- ME307-11 Tutorial 9Dokumen9 halamanME307-11 Tutorial 9Mohammed A IsaBelum ada peringkat
- Project Fatigue PDFDokumen219 halamanProject Fatigue PDFdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Project Fatigue PDFDokumen219 halamanProject Fatigue PDFdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Ce234 Technical Study On CFRP - Simbajon - RetchieDokumen15 halamanCe234 Technical Study On CFRP - Simbajon - RetchieRitch SimbajonBelum ada peringkat
- Farm STR ProjectDokumen17 halamanFarm STR ProjectShinyi GanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen30 halamanChapter 3Victoria JungBelum ada peringkat
- Bending StressDokumen53 halamanBending StressManish Shashikant Dharek100% (9)
- Strip MethodDokumen11 halamanStrip MethodAmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- The Shear Formula: Force EquilibriumDokumen9 halamanThe Shear Formula: Force EquilibriummohanBelum ada peringkat
- 125 - 201review Problems SolnsDokumen6 halaman125 - 201review Problems SolnsdfgdfgdfgaaBelum ada peringkat
- Orange Train AnalysisDokumen10 halamanOrange Train AnalysisMuhammad Shaheryar AbidBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment #3 Solution - Spring 2014Dokumen5 halamanAssignment #3 Solution - Spring 2014Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Mekanika Material Latihan Soal Untuk Jurusan Teknik FisikaDokumen17 halamanMekanika Material Latihan Soal Untuk Jurusan Teknik FisikaEsther Kezia SimanjuntakBelum ada peringkat
- Complementary Shear StressDokumen17 halamanComplementary Shear StresscataiceBelum ada peringkat
- Beamsaet 1Dokumen3 halamanBeamsaet 1omar_sool2Belum ada peringkat
- MCR Ste616-A1.13jul19Dokumen5 halamanMCR Ste616-A1.13jul19noli90Belum ada peringkat
- 78 - 9 - HookDokumen14 halaman78 - 9 - Hookrip111176Belum ada peringkat
- Week 6 - Properties PDFDokumen44 halamanWeek 6 - Properties PDFRichie BobbyBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Lab ManualDokumen55 halamanAnsys Lab Manualkrishna8808100% (2)
- Combined Loadings Slides (Revision)Dokumen50 halamanCombined Loadings Slides (Revision)amymikail01Belum ada peringkat
- Ansys WorkDokumen19 halamanAnsys WorkAhmed zia tahirBelum ada peringkat
- Bending StressDokumen14 halamanBending StressDavid TurayBelum ada peringkat
- Beam Tut4Dokumen17 halamanBeam Tut4Cormos RaulBelum ada peringkat
- Tegangan GeserDokumen34 halamanTegangan GeserFithra MaferBelum ada peringkat
- MODULAR QUIZ - 56 - Steel DesignDokumen9 halamanMODULAR QUIZ - 56 - Steel DesignCornelio J. FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of Bending Stress - Part 2 - CanvasDokumen13 halamanTheory of Bending Stress - Part 2 - Canvasraza05421Belum ada peringkat
- Analisis Struktur C6Dokumen47 halamanAnalisis Struktur C6Hazyema HarunBelum ada peringkat
- 4.5 - Design of DRS - Simply SupportedDokumen18 halaman4.5 - Design of DRS - Simply Supportedron thombareBelum ada peringkat
- Transverse Shear Stresses in BeamsDokumen6 halamanTransverse Shear Stresses in BeamsMijhael Anatholi Romero MamaniBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4Dokumen35 halamanLecture 4BoopathiBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh InternetDokumen14 halamanContoh InternetNur Syazwani binti IshakBelum ada peringkat
- (XLL XLL: Beam Example 4 Sheet3Of4 RevDokumen1 halaman(XLL XLL: Beam Example 4 Sheet3Of4 RevlyhalimBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Beams 1design of Beams A1-A2 and A2-A3Dokumen4 halamanDesign of Beams 1design of Beams A1-A2 and A2-A3Sreenathareddy GajjalaBelum ada peringkat
- Prestress Concrete (24-30)Dokumen33 halamanPrestress Concrete (24-30)Prantik Adhar SamantaBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of The SectionDokumen46 halamanProperties of The SectionGiannis TzivBelum ada peringkat
- Report Moment Influence LinesDokumen25 halamanReport Moment Influence LinesUtaya Kumar Veelmurugan100% (1)
- Assignment 1Dokumen13 halamanAssignment 1irfan syafiqBelum ada peringkat
- Solids Lab 2 - 201110737.AL AQEEB FAIQ BIN ROZAIDEDokumen14 halamanSolids Lab 2 - 201110737.AL AQEEB FAIQ BIN ROZAIDEpicul 08Belum ada peringkat
- MODULAR QUIZ - 56 - Steel DesignDokumen9 halamanMODULAR QUIZ - 56 - Steel DesignCornelio J. FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Strength of MatrialDokumen36 halamanStrength of MatrialahmedanyBelum ada peringkat
- Moment of Inertia of Composite SectionsDokumen4 halamanMoment of Inertia of Composite SectionsmkbijuBelum ada peringkat
- EngineerDokumen360 halamanEngineerdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Senju Kun JuDokumen26 halamanSenju Kun JududescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 1Dokumen2 halamanExercise 1dudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- EngineerDokumen5.746 halamanEngineerdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Junniand Sunni90Dokumen54 halamanJunniand Sunni90dudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial EngDokumen3 halamanIndustrial EngdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Auto Mail ReceiverDokumen462 halamanAuto Mail ReceiverdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- SsdsDokumen360 halamanSsdsdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- You Have Dig BickDokumen18 halamanYou Have Dig BickdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- AsdasdcewwecwdcDokumen3.633 halamanAsdasdcewwecwdcdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 PDFDokumen12 halamanTopic 1 PDFdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- BDA 31203 Binding Report FormatDokumen7 halamanBDA 31203 Binding Report FormatdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Level and Flow SystemDokumen47 halamanLevel and Flow SystemdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- OthaDokumen2.847 halamanOthadudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- I Have Dig BickDokumen34 halamanI Have Dig BickdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Level and Flow SystemDokumen2 halamanLevel and Flow SystemdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Unused Rubbish Bin ProjectDokumen21 halamanUnused Rubbish Bin ProjectdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Kanin A MacausadasdsaDokumen3.632 halamanKanin A MacausadasdsadudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Singh ButohDokumen3.633 halamanSingh ButohdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Statement: - Poor Reading Comprehension - Poor Word Recognition - Poor Speech - Poor DecodingDokumen7 halamanProblem Statement: - Poor Reading Comprehension - Poor Word Recognition - Poor Speech - Poor DecodingdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Kanin A Macau Quality ControlDokumen3.632 halamanKanin A Macau Quality ControldudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Kanin A MacausadasdsaDokumen3.632 halamanKanin A MacausadasdsadudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Report On Robbery IncidentDokumen1 halamanReport On Robbery IncidentdudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Kanin A MacauDokumen3.632 halamanKanin A MacaududescapeBelum ada peringkat
- 4 2 CastiglianoDokumen3 halaman4 2 CastiglianodudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computers and Programming: KnowledgeDokumen14 halamanIntroduction To Computers and Programming: KnowledgeAnonymous rpcAOpBelum ada peringkat
- Autocad Command FullDokumen3 halamanAutocad Command FulldudescapeBelum ada peringkat
- Defining The Christian Faith PaperDokumen8 halamanDefining The Christian Faith Paperlin tongBelum ada peringkat
- Blackrock Methods of Delay AnalysisDokumen36 halamanBlackrock Methods of Delay AnalysisAhmed MoubarkBelum ada peringkat
- Data Processing and Management Information System (AvtoBərpaEdilmiş)Dokumen6 halamanData Processing and Management Information System (AvtoBərpaEdilmiş)2304 Abhishek vermaBelum ada peringkat
- Examiners' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2018Dokumen9 halamanExaminers' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2018RafaBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance UDI Compliance DatesDokumen13 halamanGuidance UDI Compliance DatesGigi EssegiBelum ada peringkat
- My TestDokumen18 halamanMy TestBlessmore Chitanha100% (1)
- NewspaperDokumen2 halamanNewspaperbro nabsBelum ada peringkat
- Simon Bolivar PresentationDokumen7 halamanSimon Bolivar Presentationapi-345742212Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2 Management Perspective Son Leadership MotivationDokumen14 halamanAssignment 2 Management Perspective Son Leadership MotivationHoneyVasudevBelum ada peringkat
- MGMT 4Dokumen26 halamanMGMT 4Said GunayBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5Dokumen5 halamanPhysics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5StephanieBelum ada peringkat
- Xafsa 1Dokumen19 halamanXafsa 1Heitham OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 7Dokumen68 halamanLecture 7Gay TonyBelum ada peringkat
- Heating Curve Lab Report - Ava MonizDokumen7 halamanHeating Curve Lab Report - Ava Monizapi-533828039Belum ada peringkat
- Sekonic L 758Dokumen68 halamanSekonic L 758mariosapereiraBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of An Atom Revision PaperDokumen5 halamanStructure of An Atom Revision PaperZoe Kim ChinguwaBelum ada peringkat
- Position Trading Maximizing Probability of Winning TradesDokumen91 halamanPosition Trading Maximizing Probability of Winning Tradescarlo bakaakoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsDokumen26 halamanChapter 2 Fluid StaticsSoban Malik100% (1)
- Annex 1: Homeroom Guidance Monitoring Tool (School Level) Homeroom Guidance Monitoring ToolDokumen2 halamanAnnex 1: Homeroom Guidance Monitoring Tool (School Level) Homeroom Guidance Monitoring ToolMariel Gregore0% (1)
- Scan 03-Jan-2020 PDFDokumen2 halamanScan 03-Jan-2020 PDFPavanSharmaBelum ada peringkat
- RP Poster FinalDokumen1 halamanRP Poster Finalapi-270795195Belum ada peringkat
- N Mon Visualizer OverviewDokumen27 halamanN Mon Visualizer OverviewClaudioQuinterosCarreñoBelum ada peringkat
- 1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104Dokumen57 halaman1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104f.kpobi1473Belum ada peringkat
- Reading The Bible From Feminist, Dalit, Tribal and Adivasi Perspectives (Course Code: BC 107)Dokumen8 halamanReading The Bible From Feminist, Dalit, Tribal and Adivasi Perspectives (Course Code: BC 107)Arun Stanley100% (2)
- Utah Vaccine AdministrationDokumen1 halamanUtah Vaccine AdministrationOffice of Utah Gov. Spencer J. CoxBelum ada peringkat
- DFT UploadDokumen13 halamanDFT Uploadmeghraj01Belum ada peringkat
- Ga2 27:6:23Dokumen1 halamanGa2 27:6:23john HuntBelum ada peringkat
- The Mystery of Putins DissertationDokumen16 halamanThe Mystery of Putins DissertationDoinaCebanuBelum ada peringkat