Teaching Guidelines: Patients With Heart Failure
Diunggah oleh
mnazifmauludiJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Teaching Guidelines: Patients With Heart Failure
Diunggah oleh
mnazifmauludiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Teaching
Guidelines:
Patients With Heart Failure
Definition of
Heart Failure
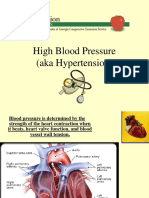
Heart Failure means that the heart is not
pumping as effectively as it should.
When this happens, blood that should be
pumped out of the heart backs up into the
lungs and other parts of the body.
Also is known as CHF (congestive heart
failure)
Causes of Heart Failure
Coronary artery disease: Less blood
reaches the heart muscle due to build up
of cholesterol and fatty deposits.
Damage to the heart muscle or valves:
resulting from disease, infection, or birth
defects
Causes of Heart Failure contd
High blood pressure: When BP is too high,
the heart has to pump harder to keep the
blood circulating; over time the heart
chambers get larger and weaker.
Past heart attacks: cause
damage to the heart
muscle; the remaining
healthy tissue must work
harder.
Symptoms of CHF
Two most common symptoms:
Shortness of Breath as blood backs up
into the lungs
Edema (swelling) as blood backs up into
the legs
Sign or Symptom Why It Happens People with HF
May Experience
Shortness of Breath
(also called dyspnea)
Blood backs up in the
pulmonary veins (the
vessels that return
blood from the lungs to
the heart) because the
heart cant keep up
with the supply. This
causes fluid to leak
into the lungs.
breathlessness
during activity (most
commonly), at rest, or
while sleeping, which
may come on suddenly
and wake them up
difficulty breathing
while lying flat and may
need to prop up the
upper body and head
on two pillows
wake up tired or
feeling anxious and
restless
Sign or Symptom Why It Happens People with HF
May Experience
Persistent Coughing or
Wheezing
Fluid builds up in the
lungs. (same as
previous slide)
Blood backs up in the
pulmonary veins (the
vessels that return
blood from the lungs to
the heart) because the
heart cant keep up
with the supply.
This causes fluid to
leak into the lungs.
coughing that
produces white or pink
blood-tinged phlegm
Sign or Symptom Why It Happens People with HF
May Experience
Buildup of Excess
Fluid in Body Tissues
(Edema)
As blood flow slows,
coming out of the
heart, blood returning
to the heart through the
veins backs up,
causing fluid to build
up in the tissues.
The kidneys are less
able to dispose of
sodium and water, also
causing fluid retention
in the tissues.
Swelling in feet or
legs or weight gain
Shoes may feel tight.
Sign or Symptom Why It Happens People with HF
May Experience
Tiredness, Fatigue The heart cant pump
enough blood to meet
the needs of body
tissues.
The body diverts blood
away from less vital
organs, particularly
muscles in the limbs,
and sends it to the
heart and brain.
a tired feeling all the
time and difficulty with
everyday activities
such as shopping,
climbing stairs,
carrying groceries or
walking
Sign or Symptom Why It Happens People with HF
May Experience
Dizziness or Chest
Pain/Tightness
Certain medications
may cause a drop in
blood pressure.
lightheadness or
dizziness upon
standing from a sitting
position
11
Carry frequently used items around the
house in a basket.
Chop or peel vegetables while sitting.
Place a basket at the bottom of the stairs
to collect items throughout the day (take
them upstairs all at once).
Develop a schedule that paces your
activities with rest periods in between.
Reducing Fatigue
Diet: Decreasing Salt Intake
Sodium makes the
body hold on to fluid.
Thus, the heart has to
work harder to pump the
added fluid.
Decreasing the amount of salt in your diet
is one of the most important things you
can do!
Diet: Decreasing Salt Intake
TIPS:
Take the salt shaker off
the table.
Do not add salt when
cooking.
Use salt substitutes (these
usually contain potassium,
so you should check with
your doctor to see if it is
appropriate for you).
TIPS:
Avoid seasonings such as
bouillon cubes, meat
tenderizer, seasoned salts,
soy sauce, steak or
Worcestershire sauce.
Drain and rinse canned
foods before preparation.
Substitute low sodium
foods.
Use frozen or fresh fruits
and vegetables.
Diet: Decreasing Salt Intake
Foods to avoid (unless there
is a low sodium version):
Pre-seasoned mixes: tacos,
chili, rice, sauces, gravy
Snack foods: pretzels, potato
chips, olives, cheeses, pickles
Fast food (McDonalds, Burger
King, etc.)
Diet: Decreasing Salt Intake
Eating Out
(For the patient that frequently eats out)
Order plain baked potato
or unsalted vegetables
instead of French fries or
onion rings.
Plan ahead: Select a
restaurant where food is
made to order.
Many restaurants honor
special requests for low-fat
or low-salt dishes.
Limit extras before the
meal such as appetizers,
bread and butter; these
contain extra fat and salt.
Read the menu carefully.
Look for these words:
steamed, baked, roasted,
garden fresh, poached,
broiled, grilled.
Eating Out (contd)
(for the patient who frequently eats out)
Read the menu and avoid
Crispy, creamed, rich, buttery,
fried, in cheese sauce, stewed, pot
pie, with bacon or sausage
Choose healthy ethnic foods
(Chinese, Mexican) by asking
which dishes are lower in salt or
fat.
Ask for salad dressings, sauces
or gravies to be served on the
side.
This helps control how much you
use.
Eating Out (contd)
(for the patient who frequently eats out)
Medication Tips
Notify your nurse and doctor of all medications,
medication changes, herbal products or known
allergies to minimize side effects, avoid drug
interactions and avoid allergic reactions.
Take doses at the same
time each day.
Use a weekly pill box to
help keep pills organized.
Common CHF Medications
ACE inhibitors
Capoten (captopril)
Vasotec (enalapril)
Altace (ramipril)
Prinovil or Zestril (lisinopril)
Accupril (quinapril)
Monopril (fosinopril)
Lotensin (benazepril)
Univasc (moexipril)
Common CHF Medications
ACE inhibitors (contd)
These are a type of vasodilator; they cause
the blood vessels to expand, which lowers the
blood pressure and decreases the hearts
workload.
Side effects: cough, weakness, dizziness,
high potassium levels
Check potassium levels regularly.
Common CHF Medications
Diuretics (water-pills)
Lasix (furosemide)
Hydrodiuril (hydrochlorothiazide)
Diuril (chlorothiazide)
Bumex (bumetanide)
Aldactone (spironolactone)
Dyrenium (triamterene)
Others
Common CHF Medications
Diuretics (water-pills) (contd):
A diuretic causes the kidney to remove more
sodium and water from the bloodstream than
usual. This lessens the fluid in the body and
causes the heart to have a decreased
workload.
It also decreases the buildup of fluid in the
lungs, ankles and legs.
Take diuretics in the morning.
Common CHF Medications
Diuretics (water-pills) (contd):
When taking a diuretic you must weigh yourself daily;
your dose may be adjusted depending on the weight
you have gained or lost.
Notify your home health nurse or doctor if you gain 3
pounds in one day or 5 pounds in one week.
Make sure to urinate at least every 2 hours during the
day, and have ready access to a bathroom.
Common CHF Medications
Diuretics (water-pills) (contd):
Many diuretics cause your body to lose
potassium; if you have one of those types,
you may have to add potassium to your diet.
Foods containing potassium:
raisins, prunes, apricots, dates, bananas, cantaloupe,
oranges, greens, spinach, peas, tomatoes, mushrooms,
fresh turkey, fish or beef
Common CHF Medications
Oxygen
Nasal Cannula
Mask
Your doctor has ordered the oxygen flow rate per
minute. Do not change a setting without consulting
your doctor or nurse first.
Higher oxygen flow rates usually do not help.
Side effects: High flow rates increase the risks of
of carbon dioxide buildup in the blood especially in
patients who have lung disease (e.g., COPD).
Common CHF Medications
Vasodilators
Isordil (isosorbide dinitrate)
Apresoline (hydralazine)
These cause blood vessel walls to relax which
allows blood to flow more easily.
Side effects: dizziness or fainting when sitting or
standing quickly, headaches, heart palpitations,
nasal congestion
Common CHF Medications
Digitalis Preparations:
Lanoxin (digoxin)
Digoxin increases the force of the hearts
contraction; it also slows some types of
irregular heart beats.
Levels that are too high can cause loss of
appetite, nausea, vomiting, headaches;
blurred or yellow vision.
Common CHF Medications
Beta Blockers
Coreg (carvedilol)
Lopressor (metoprolol)
Tenormin (Atenolol)
These drugs reduce the heart rate and lower
blood pressure.
Side effects: nausea or weakness; too-low
blood pressure; worsening asthma symptoms
Common CHF Medications
Blood thinners
Coumadin (warfarin)
Heparin, Lovenox
These drugs help prevent blood from clotting
and lessen the chance of getting blood clots
throughout the body.
Many drugs can interact with blood thinners.
Do not take any new medications without
consulting your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Common CHF Medications
Blood thinners contd
Side effects include bleeding tendencies:
Watch for nosebleeds, gums bleeding, bruising
easily.
Notify your home health nurse or doctor
immediately if you are bleeding easily.
You need to have your blood tested for INR
regularly at least once per month (check with
your nurse or doctor for frequency).
CHF HEALTH TRACK
Green
Zone
COMMON SIGNS
No new or worsening of
shortness of breath
No new or worsening swelling
of your hands or feet
No weight gain exceeding
your goal weight
No chest pain or tightness
No decrease in your ability to
maintain your activity level
WHAT TO DO
Continue daily weights.
Take medication as prescribed by your doctor. DO NOT SKIP
DOSES.
Follow low-salt diet.
Keep all physician appointments.
Keep up the
good work!
CHF HEALTH TRACK
Yellow
Zone
COMMON SIGNS
Gained 3 or more pounds
Increased cough
Increased swelling in feet or legs
Increased in shortness of breath with activity
Increase in the number of pillows needed to sleep at
night
New or more frequent chest pain or tightness
New onset of dizziness or lightheadness after standing
up
WHAT TO DO
Your symptoms may mean that you need an
adjustment of your medications.
Call your home health nurse.
If you have one
or more of
these signs,
take QUICK
action!
CHF HEALTH TRACK
COMMON SIGNS
Unrelieved shortness of breath or shortness of breath
at rest
Unrelieved chest pain
Wheezing or chest tightness at rest
Need to sit in chair to sleep
Weight gain or loss of more than 5 pounds
Confusion
A fall related to dizziness or lightheadness
WHAT TO DO
You man need to be evaluated by a physician
right away.
Call your home health nurse or physician right
away.
Red
Zone
If you have one
or more of
these signs,
take
IMMEDIATE
action!
35
Heart Failure is best managed with early
intervention.
Your home health team (nurse, therapist,
or aide) need to be notified early of any
changes in your health status.
Early intervention may prevent a
hospitalization for you or your loved one.
Remember!
This material was adapted by GMCF under contract with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), an
agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The contents presented do not necessarily reflect
CMS policy. Publication No. 8SOW-GA-HH-07-26
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- High Blood Pressure (Aka Hypertension)Dokumen28 halamanHigh Blood Pressure (Aka Hypertension)Ronaleen mislang100% (2)
- Cardio Notes - Heart FailureDokumen11 halamanCardio Notes - Heart FailureNage Lubin100% (1)
- Causes Symptoms Treatment Orthostatic HypotensionDokumen9 halamanCauses Symptoms Treatment Orthostatic HypotensionأحمدالشحاتBelum ada peringkat
- POCUS ProceduresDokumen123 halamanPOCUS Proceduresjaimin 666Belum ada peringkat
- Low Blood Preasure BlogDokumen9 halamanLow Blood Preasure BlogSheffield PharmaciesBelum ada peringkat
- Radiology review questionsDokumen4 halamanRadiology review questionsZafar Khan60% (5)
- Aortic Stenosis AmendillaDokumen31 halamanAortic Stenosis AmendillaVadim BursacovschiBelum ada peringkat
- Med Surge 2 Mod 1 CardiacDokumen13 halamanMed Surge 2 Mod 1 CardiacDirk Buckner100% (2)
- High Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesDari EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney FailureDokumen9 halamanChronic Kidney FailureKrizzy MontanaBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar On Mobile Coronary Care UnitDokumen11 halamanSeminar On Mobile Coronary Care UnitASIR DHAYANI95% (19)
- High Blood Pressure GuideDokumen4 halamanHigh Blood Pressure GuideKhaira CharmagneBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Presentation On Anti-Hypertensive: All India Institute of Medical and Science New Delhi 2021-2022Dokumen12 halamanDrug Presentation On Anti-Hypertensive: All India Institute of Medical and Science New Delhi 2021-2022Priya SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Plan Using "METHOD"Dokumen6 halamanTeaching Plan Using "METHOD"Cassandra73% (11)
- Thyroid StormDokumen16 halamanThyroid StormRaquid MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Gagal Jantung Kongestif DR - YusraDokumen35 halamanGagal Jantung Kongestif DR - YusraSurya ArhBelum ada peringkat
- Understand Congestive Heart FailureDokumen5 halamanUnderstand Congestive Heart FailureOanh HoangBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension: Medlineplus TopicsDokumen31 halamanHypertension: Medlineplus TopicsMcNover Catlin OsamBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension Written ReportDokumen5 halamanHypertension Written ReportKate Felongco CambelBelum ada peringkat
- Federation of Allied Health and Sciences StudentsDokumen16 halamanFederation of Allied Health and Sciences StudentsYelsew Quebral PagidBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 7 High Blood PressureDokumen3 halamanChap 7 High Blood PressureSabina MoolyeBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Kidney DiseaseDokumen6 halamanWhat Is Kidney DiseaseEllie ELLBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is A Disease of Vascular Regulation Resulting From Malfunction ofDokumen4 halamanHypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is A Disease of Vascular Regulation Resulting From Malfunction ofkewpietheresaBelum ada peringkat
- CHF and PyelonephritisDokumen8 halamanCHF and Pyelonephritisveronicaperez03100% (2)
- Written Report CHFDokumen5 halamanWritten Report CHFSarah Michelle NiduaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Hypertension: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDokumen16 halamanUnderstanding Hypertension: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentJheanAlphonsineT.MeansBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension 101028172250 Phpapp01Dokumen16 halamanHypertension 101028172250 Phpapp01DianAyuBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Management for Cardiovascular DisordersDokumen4 halamanNursing Management for Cardiovascular DisordersJohn Colem ImpitBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen9 halamanCardiovascular Diseaseiri_balBelum ada peringkat
- Low Blood PreasureDokumen9 halamanLow Blood PreasureNhs VacancyBelum ada peringkat
- Disease of Human Circulatory System: Submitted To: Jordan Aquino Submitted By: Kenta YamamotoDokumen31 halamanDisease of Human Circulatory System: Submitted To: Jordan Aquino Submitted By: Kenta YamamotoCarl Maga VlogsBelum ada peringkat
- Peripheral Artery Disease - LegsDokumen6 halamanPeripheral Artery Disease - LegsCecil Bhang-i Cacay - PabloBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Failure Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDokumen2 halamanHeart Failure Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDummy AccountBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension NotesDokumen5 halamanHypertension NotesNkosi JupiterBelum ada peringkat
- Heart disease symptoms, causes, prevention and treatmentDokumen5 halamanHeart disease symptoms, causes, prevention and treatment学蒽Belum ada peringkat
- Disease Congenital Heart DiseaseDokumen7 halamanDisease Congenital Heart DiseaseMahesh GanesanBelum ada peringkat
- Diet For Cardiovaskular Disease - ErinetaDokumen8 halamanDiet For Cardiovaskular Disease - ErinetaErin NettaBelum ada peringkat
- ScriptDokumen7 halamanScriptAllen DelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- Nur 200Dokumen13 halamanNur 200Dan MichBelum ada peringkat
- Health Teaching Plan ContentDokumen2 halamanHealth Teaching Plan ContentEdmr Slzar100% (1)
- Left-Sided Heart FailureDokumen3 halamanLeft-Sided Heart FailureKhalid Mahmud ArifinBelum ada peringkat
- Brief DescriptionDokumen13 halamanBrief DescriptionHerson RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension FinalDokumen22 halamanHypertension Finalapi-247079964Belum ada peringkat
- Heart Failure and IschemicDokumen5 halamanHeart Failure and IschemicAbdul Hamid NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Used To Treat CVD: Antihypertensive-Drugs That Reduce High Blood PressureDokumen7 halamanDrugs Used To Treat CVD: Antihypertensive-Drugs That Reduce High Blood PressureNithoo NishBelum ada peringkat
- PDP2 Heart Healthy LP TDokumen24 halamanPDP2 Heart Healthy LP TTisi JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension High Blood Pressure - Feb21Dokumen2 halamanHypertension High Blood Pressure - Feb21Azevedo VenturaBelum ada peringkat
- Family History and Lifestyle Factors Increase Hypertension RiskDokumen8 halamanFamily History and Lifestyle Factors Increase Hypertension Risk4B- BUMANGLAG, Frances Hannah V.Belum ada peringkat
- Hypertension 1Dokumen18 halamanHypertension 1frechel kimBelum ada peringkat
- Strokes: Abdominal Aortic AneurismDokumen5 halamanStrokes: Abdominal Aortic AneurismMaja LucasBelum ada peringkat
- Dasar Terapi RasionalDokumen7 halamanDasar Terapi RasionalADINTA SANIYYAHBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Failure: Cardiac RehabilitationDokumen12 halamanHeart Failure: Cardiac RehabilitationwahyuBelum ada peringkat
- What Is HypertensionDokumen18 halamanWhat Is HypertensionShahzad ShameemBelum ada peringkat
- Hypotention مDokumen7 halamanHypotention مSophy YounanBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines for a Low Sodium DietDokumen18 halamanGuidelines for a Low Sodium Dietradziah_mohdBelum ada peringkat
- U.S. National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health HypertensionDokumen10 halamanU.S. National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health HypertensionShane Santos PeraltaBelum ada peringkat
- Content For HypertensionDokumen5 halamanContent For HypertensionYashika soniBelum ada peringkat
- Congestive Heart Failure PhysiciansDokumen13 halamanCongestive Heart Failure PhysiciansryanmoreBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study For Coronary Artery DiseaseDokumen8 halamanCase Study For Coronary Artery DiseaseGabbii CincoBelum ada peringkat
- Raise Low Blood Pressure Naturally Through DietDokumen5 halamanRaise Low Blood Pressure Naturally Through DietRoy C. EstenzoBelum ada peringkat
- HypertensionDokumen5 halamanHypertensionhamporkBelum ada peringkat
- HypertensionDokumen36 halamanHypertensionmohamedahmedf12345678Belum ada peringkat
- High Blood PressureDokumen2 halamanHigh Blood PressureMuhammad NaveedBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation For ClassDokumen59 halamanCase Presentation For ClassMuhammad HarisBelum ada peringkat
- Achim 2022Dokumen8 halamanAchim 2022BözskeBelum ada peringkat
- The Anatomy and Functions of the Heart in 40 CharactersDokumen7 halamanThe Anatomy and Functions of the Heart in 40 CharactersMarjorie ViescaBelum ada peringkat
- HDFC Life Critical Illness Plus RiderDokumen8 halamanHDFC Life Critical Illness Plus RiderranbirrathiBelum ada peringkat
- Self-propelled cono weeder evaluatedDokumen7 halamanSelf-propelled cono weeder evaluatedSapuniiBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Practice TestDokumen7 halamanCardiac Practice TestroseBelum ada peringkat
- FundamentalsDokumen30 halamanFundamentalsRachel PerandoBelum ada peringkat
- Summary and ConclusionDokumen4 halamanSummary and Conclusionhamodi222Belum ada peringkat
- MagdiDokumen4 halamanMagdiapi-534579275Belum ada peringkat
- Mhps-Ts Newsletter: MHPS Technical Services CorporationDokumen24 halamanMhps-Ts Newsletter: MHPS Technical Services Corporationjonel.javierBelum ada peringkat
- CPC PowerpointDokumen36 halamanCPC Powerpointapi-277377339Belum ada peringkat
- Common Pediatric DiseasesDokumen16 halamanCommon Pediatric Diseasesboxed juiceBelum ada peringkat
- Prevalence of Hypertension Among Women in Ihiagwa, Owerri West LGADokumen67 halamanPrevalence of Hypertension Among Women in Ihiagwa, Owerri West LGAocBelum ada peringkat
- 9th Grade Science Lesson on the Cardiovascular SystemDokumen5 halaman9th Grade Science Lesson on the Cardiovascular SystemOliver VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Sarawak Handbook (1st Edition)Dokumen298 halamanSarawak Handbook (1st Edition)Azim Abd RazakBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiology. Scheme ..Dof3tna - Net... EgyDrDokumen4 halamanCardiology. Scheme ..Dof3tna - Net... EgyDrJilan El SherBiny100% (1)
- NCP PPHDokumen2 halamanNCP PPHMark Joseph Christian100% (1)
- Kertas Kerja PinjamanDokumen18 halamanKertas Kerja PinjamanWan AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Health7 Q4 M1 v4Dokumen31 halamanHealth7 Q4 M1 v4JEMAX SALABelum ada peringkat
- NEW BMLT Stream - Syllabus - PDF - 1961275447 - B.SC - MLTTDokumen24 halamanNEW BMLT Stream - Syllabus - PDF - 1961275447 - B.SC - MLTTadn paramedicalBelum ada peringkat
- Citirea in PalmaDokumen7 halamanCitirea in PalmaAndrei AndelescuBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Surprising Energy SappersDokumen3 halaman8 Surprising Energy Sappersiconm888Belum ada peringkat
- Physiology Comprehensive Exam Pointers PDFDokumen108 halamanPhysiology Comprehensive Exam Pointers PDFRaynalynGimoros100% (1)
- Fibrilacioni Atrial Trajtimi Dhe Diagnoza e TijDokumen8 halamanFibrilacioni Atrial Trajtimi Dhe Diagnoza e TijMarsiano QendroBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative ArrhythmiaDokumen66 halamanPerioperative ArrhythmiaVithal DhulkhedBelum ada peringkat
- Detection of Cardiac Disorder Using MATLAB BasedDokumen4 halamanDetection of Cardiac Disorder Using MATLAB BasedSeira LoyardBelum ada peringkat