Anatomy of Inguinal Canal
Diunggah oleh
Fasih Sami SiddiquiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anatomy of Inguinal Canal
Diunggah oleh
Fasih Sami SiddiquiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anatomy of Inguinal Canal
Group F
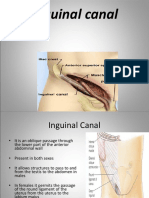
The INGUINAL CANAL is an oblique
intermuscular slit lying above the medial
half of the Inguinal Ligament
It commences at the Deep Inguinal Ring
and terminates at the Superficial Inguinal
Ring
The Superficial Inguinal Ring is an
oblique traingular gap in the aponeurosis
of the External Oblique Abdominal
Muscle located just superolateral to the
Pubic Tubercle. The base of the gap is
the Pubic Crest and the margins are the
crura of the ring.
The Deep Inguinal Ring is an opening in
the Transversalis Fascia that lies about
1.25 cm above the midpoint of the Inguinal
Ligament.
Walls of Inguinal Canal
Anterior Wall: External Oblique Aponeurosis,
assisted laterally by Internal Oblique Muscle.
Posterior Wall: Weak Transversalis Fascia
throughout, strong Conjoint Tendon medially.
Roof: Lower edges of Internal Oblique and
Transversus Abdominis.
Floor: Inrolled lower edge of the Inguinal
ligament, reinforced medially by Lacunar
Ligament.
Structures that pass through the
Inguinal Canal
Males: The Spermatic Cord (Vas Deferens,
Testicular Artery & accompanying Veins,
obliterated remains of Processus Vaginalis,
Genital Branch of Genitofemoral Nerve,
Autonomic Nerves, Lymphatics).
Females: Obliterated Processus Vaginalis,
Round Ligament & Lymphatics from the
Uterus.
Note: The Ilio-inguinal Nerve, although a content of the Inguinal Canal,
does not enter the canal through the deep ring, but by piercing the
Internal Oblique Abdominal Muscle.
Structures Deep to the
Transversalis Fascia
Inferior Epigastric Artery located at the
medial edge of the Deep Inguinal Ring.
The Vas Deferens in Males; Round
Ligament in Females.
The Inguinal Triangle (Hasselbachs Triangle) is
a area bounded laterally by the Inferior Epigastric
Artery, medially by the lateral border of Rectus
Abdominis, and below by the Inguinal Ligament.
Hernias of the Inguinal Region
Inguinal Hernias
occur when soft
tissue, usually
part of the
intestines,
protrudes
through a weak
point or tear in
the abdominal
wall
Direct Hernia: The
Hernial Sac passes
medial to the Inferior
Epigastric Artery,
through Hasselbachs
Triangle.
Indirect Hernia: The
Hernial Sac passes
lateral to the Inferior
Epigastric Artery,
through the Deep
Inguinal Ring.
Course of Hernia
Direct Hernia: Passes through or around
Inguinal Canal
Indirect Hernia: Transverses Inguinal
Canal
Exit of Hernia from Anterior
Abdominal Wall
Direct Hernia: Via Superficial Inguinal
Ring, lateral to Spermatic Cord (rarely
enters Scrotum)
Indirect Hernia: Via Superficial Inguinal
Ring inside the Spermatic Cord
(commonly passes into Scrotum/Labium
Majus)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Surgery Clerkship Oral Exam ReviewDokumen18 halamanSurgery Clerkship Oral Exam Reviewpanther795100% (1)
- Anatomy of OesophagusDokumen25 halamanAnatomy of OesophagusRabi SyedBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Limb: Organization FunctionDokumen33 halamanUpper Limb: Organization FunctionAhmed Nabiel El-Jaliel100% (1)
- Abdomen Test QuestionsDokumen20 halamanAbdomen Test QuestionsRuth AlooBelum ada peringkat
- HydroceleDokumen38 halamanHydroceleAlfie Yannur100% (2)
- 3-Inguinal Canal PDFDokumen58 halaman3-Inguinal Canal PDFN A0% (1)
- Abdominal WallDokumen56 halamanAbdominal WallAHMAD KHANBelum ada peringkat
- Anterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal CanalDokumen35 halamanAnterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal Canalapi-3698357100% (3)
- Clinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachDokumen82 halamanClinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachmackieccBelum ada peringkat
- Female ReproductiveDokumen34 halamanFemale ReproductiveAbdallah A. Abu Mattar100% (2)
- Pelvis and Perineum Lecture NotesDokumen12 halamanPelvis and Perineum Lecture NotesSolomon Seth SallforsBelum ada peringkat
- Popliteal Fossa and LegDokumen40 halamanPopliteal Fossa and LegRaj Shekhar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Flail ChestDokumen3 halaman3 - Flail ChestKrishna Chaitanya GovardhanamBelum ada peringkat
- Arteries of Upper Limb.Dokumen16 halamanArteries of Upper Limb.Shimmering Moon100% (1)
- Colorectal MalignancyDokumen108 halamanColorectal MalignancySatishht SatishBelum ada peringkat
- Osteology Lower Limb, by DR IramDokumen76 halamanOsteology Lower Limb, by DR IramimmmiBelum ada peringkat
- Nerves of Upper LimbDokumen24 halamanNerves of Upper LimbShimmering MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Esophagus and StomachDokumen65 halamanAnatomy of Esophagus and Stomachmackiecc100% (2)
- Upper LimbDokumen31 halamanUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojBelum ada peringkat
- Rectum & Anal CanalDokumen14 halamanRectum & Anal CanalLisa DentonBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Lower LimbDokumen52 halamanAnatomy of Lower Limbdrkhan58Belum ada peringkat
- Large Blood Vessels of The GutDokumen61 halamanLarge Blood Vessels of The GutpoojaBelum ada peringkat
- Nerve InjuryDokumen46 halamanNerve InjuryNofilia Citra CandraBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 Hernia Kuliah FKDokumen50 halaman2019 Hernia Kuliah FKKhairani NurhamidahBelum ada peringkat
- H 4.2 Histology Urinary SystemDokumen52 halamanH 4.2 Histology Urinary SystemF N100% (2)
- Upper LimbDokumen54 halamanUpper LimbMar YBelum ada peringkat
- Femoral Region, Anterior and Medial Compartments of The ThighDokumen49 halamanFemoral Region, Anterior and Medial Compartments of The ThighNolanBelum ada peringkat
- Accessory OrgansDokumen18 halamanAccessory OrgansDaniel AtiehBelum ada peringkat
- Femoral Sheath and Femoral TriangleDokumen23 halamanFemoral Sheath and Femoral TriangleSamiha Haq100% (2)
- Gluteal RegionDokumen34 halamanGluteal Regionlion2chBelum ada peringkat
- Your Guide To The Mrcs International PDFDokumen12 halamanYour Guide To The Mrcs International PDFdevinchi09Belum ada peringkat
- List of Muscles and ActionsDokumen8 halamanList of Muscles and ActionsGiacen0% (1)
- All Bat NotesDokumen1.048 halamanAll Bat NotesAfk SystemBelum ada peringkat
- 4) Mammary Gland 220413 Upnm2Dokumen22 halaman4) Mammary Gland 220413 Upnm2AaronMaroonFive100% (1)
- Clinical Notes On Upper LimbDokumen10 halamanClinical Notes On Upper LimbZllison Mae Teodoro Mangabat100% (1)
- 1 PeritonitisDokumen26 halaman1 PeritonitisGizachew AsimareBelum ada peringkat
- Pelvic WallDokumen56 halamanPelvic WallYousef El bannaBelum ada peringkat
- Erb's PointDokumen14 halamanErb's PointRohit SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Anatomy of HeartDokumen23 halamanSurface Anatomy of HeartKhush Bakht100% (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDokumen23 halamanFemale Reproductive SystemSheena PasionBelum ada peringkat
- Femoral Triangle 1Dokumen20 halamanFemoral Triangle 1USAMA AHMEDBelum ada peringkat
- AXILLADokumen8 halamanAXILLAImmunity RABOTABelum ada peringkat
- 4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingDokumen53 halaman4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingMuhammad TaqwaBelum ada peringkat
- A&P 2 Respiratory Lecture NotesDokumen31 halamanA&P 2 Respiratory Lecture NotesBethanyBelum ada peringkat
- The Human ThoraxDokumen71 halamanThe Human Thoraxbayenn100% (2)
- Anatomy of PeritoneumDokumen61 halamanAnatomy of PeritoneumFirdaus SeptiawanBelum ada peringkat
- ERN Intercoll MRCS Bk2Dokumen48 halamanERN Intercoll MRCS Bk2Rocita HoBelum ada peringkat
- Anterior Triangle of The NeckDokumen6 halamanAnterior Triangle of The NeckHugh JacobsBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Major Arteries of GIDokumen9 halaman3 Major Arteries of GIbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDokumen4 halamanCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catBelum ada peringkat
- Cranial Nerves 7-12Dokumen62 halamanCranial Nerves 7-12jangyBelum ada peringkat
- Axilla and Brachial PlexusDokumen22 halamanAxilla and Brachial Plexusromaisa akhtarBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 201 Upper Limbs Muscles of The Upper Limbs Brachial PlexusDokumen5 halamanBIO 201 Upper Limbs Muscles of The Upper Limbs Brachial PlexusKelly TrainorBelum ada peringkat
- Head and NeckDokumen63 halamanHead and Neckbayenn100% (1)
- Burns InjuryDokumen23 halamanBurns Injurymary_chdhry100% (1)
- Respiratory System 2011Dokumen99 halamanRespiratory System 2011Izzah Atqa100% (1)
- The Shoulder JointDokumen17 halamanThe Shoulder JointBhargavBelum ada peringkat
- 7th-The Alimentary SystemDokumen25 halaman7th-The Alimentary Systemprasun_v100% (1)
- HSB - Head: Anterior: Supraorbital Margin Posterior: Superior Nuchal LineDokumen19 halamanHSB - Head: Anterior: Supraorbital Margin Posterior: Superior Nuchal LineRaki IliganBelum ada peringkat
- Gross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighDokumen20 halamanGross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighOnah ArinzeBelum ada peringkat
- General AnatomyDokumen46 halamanGeneral AnatomyIhab IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Anterior Abdominal Wall& Inguinal Canal 2023Dokumen26 halamanAnterior Abdominal Wall& Inguinal Canal 2023GanapathyGaneshBelum ada peringkat
- Inguinal Canal: DR - Lubna NazliDokumen28 halamanInguinal Canal: DR - Lubna NazliAhmed AminBelum ada peringkat
- Postmortem Changes and The Time of DeathDokumen19 halamanPostmortem Changes and The Time of DeaththehourofarrivalBelum ada peringkat
- WHO Dengue Guidelines 2013Dokumen160 halamanWHO Dengue Guidelines 2013Jason MirasolBelum ada peringkat
- Connecting The Dots: Education and Religious Discrimination in PakistanDokumen139 halamanConnecting The Dots: Education and Religious Discrimination in PakistanonfaithwapoBelum ada peringkat
- Cvs Week 4Dokumen1 halamanCvs Week 4Fasih Sami SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- HERNIAS in PaediatricsDokumen27 halamanHERNIAS in PaediatricsHugh JacobsBelum ada peringkat
- Case Discussion Day 2 - MatulaDokumen1 halamanCase Discussion Day 2 - MatulaTRISHA MATULABelum ada peringkat
- ASSESSING FEMALE MALE GENITALIAS Including The INGUINALDokumen23 halamanASSESSING FEMALE MALE GENITALIAS Including The INGUINALkyla boncacasBelum ada peringkat
- HerniaDokumen37 halamanHerniaNoreen Hannah GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- BLOCK II LMS Quiz AnatomyDokumen27 halamanBLOCK II LMS Quiz AnatomyAshley BuchananBelum ada peringkat
- SURGE Inguinal HerniaDokumen1 halamanSURGE Inguinal Herniairhamni istiqomahBelum ada peringkat
- Scrotum: Imp: Right Testicular TorsionDokumen2 halamanScrotum: Imp: Right Testicular TorsionQuest Medinova Lab ManagerBelum ada peringkat
- ERPM Clinical TrainingDokumen33 halamanERPM Clinical TrainingAmal Perera100% (1)
- Hernia ClassificationDokumen15 halamanHernia ClassificationAgung SetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Hernias Case PresentationDokumen46 halamanHernias Case Presentationraxym17Belum ada peringkat
- Ped Surgery PPT 13th FebDokumen46 halamanPed Surgery PPT 13th FebKASATSABelum ada peringkat
- MEDICON 40000 With Questions NDokumen15 halamanMEDICON 40000 With Questions Nnemalijyothsna3Belum ada peringkat
- Testicle UltrasoundDokumen5 halamanTesticle UltrasoundJan Karl Roelhsen AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- NF DR Concept Map Week 12Dokumen4 halamanNF DR Concept Map Week 12Kyra Bianca R. FamacionBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Pada AnakDokumen6 halamanHernia Pada Anakahmad iffa maududyBelum ada peringkat
- Anterior Abdominal WallDokumen56 halamanAnterior Abdominal WallDebby 003Belum ada peringkat
- 2nd Exams PDFDokumen143 halaman2nd Exams PDFahmed yousefBelum ada peringkat
- Combined Questions FinalDokumen17 halamanCombined Questions FinalrohitBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis HerniaDokumen25 halamanThesis HerniaBhageshwar ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Bates Chapter 13 - Male Genitalia Flashcards - QuizletDokumen10 halamanBates Chapter 13 - Male Genitalia Flashcards - Quizletaznknight323Belum ada peringkat
- 3 Ways To Treat Umbilical Hernia Without Surgery - Pristyn CareDokumen1 halaman3 Ways To Treat Umbilical Hernia Without Surgery - Pristyn CareCasey Rae YanoBelum ada peringkat
- Case Hernia2Dokumen19 halamanCase Hernia2ejkohBelum ada peringkat
- PEDIATRIC NotesDokumen79 halamanPEDIATRIC NotesM A83% (6)
- Fmge Recall Jan 24Dokumen66 halamanFmge Recall Jan 24crgmkps6chBelum ada peringkat
- TAPP HernioplastyDokumen5 halamanTAPP HernioplastyMaryam Alam KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Inguinal CanalDokumen10 halamanAnatomy of Inguinal CanalsaisoniaBelum ada peringkat
- Task SurgeryDokumen32 halamanTask SurgeryRajendranNandhiniBelum ada peringkat