STR - Implementation - Abridged Aug Sep 14
Diunggah oleh
ankit2740 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
37 tayangan19 halamanThis document discusses strategy implementation and the key factors involved. It states that while strategy is formulated by top management, implementation requires involvement across the organization. Effective implementation depends on aligning organizational structure, systems, culture and ensuring a fit between these and the strategy. The McKinsey 7S framework is also discussed, which identifies seven interrelated factors including strategy, structure, systems, skills, style, staff and shared values (culture). Changing organizational culture is identified as particularly challenging for implementing new strategies.
Deskripsi Asli:
business strategy
Judul Asli
Str__Implementation_Abridged Aug Sep 14
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document discusses strategy implementation and the key factors involved. It states that while strategy is formulated by top management, implementation requires involvement across the organization. Effective implementation depends on aligning organizational structure, systems, culture and ensuring a fit between these and the strategy. The McKinsey 7S framework is also discussed, which identifies seven interrelated factors including strategy, structure, systems, skills, style, staff and shared values (culture). Changing organizational culture is identified as particularly challenging for implementing new strategies.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
37 tayangan19 halamanSTR - Implementation - Abridged Aug Sep 14
Diunggah oleh
ankit274This document discusses strategy implementation and the key factors involved. It states that while strategy is formulated by top management, implementation requires involvement across the organization. Effective implementation depends on aligning organizational structure, systems, culture and ensuring a fit between these and the strategy. The McKinsey 7S framework is also discussed, which identifies seven interrelated factors including strategy, structure, systems, skills, style, staff and shared values (culture). Changing organizational culture is identified as particularly challenging for implementing new strategies.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 19
Strategy Implementation
Prof Ashish K Mitra
Implementation is a key component of strategic
Management.
Strategy is formulated and approved by the top
management but people across the
organization is involved in its
implementation. Implementation realizes the
intent of the proposed strategy.
Implementation can also be referred to as
process by which strategies & policies are put
into action by programs, budgets and
procedures , Annual Operating plans supported
by performance measurement. Translate Strategic Planning
actions to Job descriptions & KRAs
The implementation of strategy puts to test an
organizations ability to allocate resources,
design structures and systems (processes),
formulate functional objectives, and plan for
operational effectiveness.
Porters view of competitive strategy focused
on the external world of industry structure
and the strategy of the competitors.In contrast,
Prahalad & Hamel focused on the internal
world of a companys strategic architecture
consisting of all its resources and
competencies , and how it was leveraged.
A rational view-taking into considerations both
these approaches is that strategy is a dynamic
& evolutionary process of finding external
opportunities into which the competencies can
be meshed to provide competitive advantage.
These two views are connected through the
strategy implementation process. Even though
strategy may be deciding what to do based on
external /competitive considerations, implementation
is about getting it done through the use of resources
and competencies.
A superior strategy needs a superior ability to
execute. This comes from the portfolio of
resources & competencies.
The superiority can be maintained by continuously
improving on the strategic architecture, both by
strengthening existing competencies and by developing
or acquiring new ones.
Since implementation is done through large
number of people across the organization ( now
a days, often an extended one), it requires the
capacity to design good environments that
motivates and effectively coordinates
activities of people in the organization.
One of the important element in providing the
above is the organization structure. Another
one is the organizational culture, which
determines the atmosphere within the
organization.
The skill of management lies in the realm of
design of structures, systems and mechanisms
to guide and motivate the actions of the
employees.
Without a proper fit between strategy and
organizational design, various elements required
for implementation will not move in harmony,
ultimately leading to inefficient use of facilities
and failure.
For many organizations the chief challenge is
insufficient entrepreneurialism, a failure to
motivate top talent to seize opportunities and
make most of them.
For some, the problem is an inability to develop ,
apply, and capture value from new technologies
and practices, and to forge value creating
linkages between processes in business units,
and core functions. The design of the
organization must take all these factors into
consideration.
Too much emphasis on the best strategy
with inadequate consideration to
implementation aspects may turn out to be
inferior to second best strategy but
implementation aspects properly buttoned up.
(Planning School vs Process View)
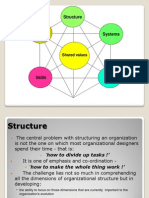
Key Implementation Tasks
Having formulated a Strategy , its implementation
process involves
Designing appropriate Organizational Structure
Designing appropriate processes & control systems
Achieving a fit between strategy, structure and control
systems ( organizational design) & creating the right
environment in the organization
Then managing strategic changes
Strategy implementation Refers to how a company
should create, use and combine organizational structure,
systems, and culture to pursue strategies that lead to a
competitive advantage and superior performance
Organizational
structure
Strategic
Control
Systems
Organizational
Culture
Coordinates
and
Motivates
employees
To achieve superior
profitability
Efficiency
Quality
Innovation
Responsiveness
to customers
Implementing Strategy through Organizational Structure,
Control Systems and Culture
For gaining
competitive
advantage
Manage
Strategic
Changes
structure
Strategy
Skills
Staff
Style
Systems
Shared
Values
The McKinsey 7-S Framework
SHARED VALUES
LEADS TO CULTURE
McKinsey 7-S Framework ( also
explains meaning of Culture)
Just like every individual has a personality , every
organization has an equivalent aspect called -
culture. It is an intangible, ever present theme that
provides meaning, direction and the basis for action.
As personality influences behavior of an individual, the
shared assumption of beliefs and values among a firms
members influence opinions and actions within a firm.
McKinsey 7-S framework highlights the importance of
shared values which leads to culture of the
organization as a whole. It forms the nucleus of the
framework.
Strategy : A framework / set of decisions and
actions aimed at gaining a sustainable
competitive advantage
Structure: The way the organizations units
relate to each other in accomplishing successful
implementation of strategies; The organization
chart who reports to whom, how tasks are both
divided up and integrated.
Systems: The procedures, rules, regulations &
routines that characterizes how important work
is done, the flow of processes. Includes both
formal & informal systems, Financial systems,
appraisal systems etc.
Style: How key managers behave in achieving
the organizational goals, how managers
collectively spend time and attention. How the
management acts is more important than what
management says.
Staff: How companies develop their employees
and shape basic values. Includes selection,
placement, training of employee, compensation.
Skills: An organizations dominant capabilities
and competencies.
Shared Values: The interconnecting centre of
McKinseys model is shared values What the
organization stands for and what it believes in-
the shared vision of the company.
Shared Value is strongly related to the culture of the
company the commonly held beliefs, mindsets, and
assumptions that shapes an organization behaves.
The seven elements are distinguished in so called hard
Ss and Soft Ss
The hard elements strategy, structure and systems are
easy to identify ( found in strategy documents,
organization plans & other documents). Management
has some control over the hard elements & can exercise
influence over them.
The four soft elements are difficult to describe, are
continuously evolving & changing, and are determined
by people at work in the organization.
The 7 S framework highlights the
importance of interrelated and
interconnected factors within the
organization & their roles in strategy
implementation.
It is often difficult to identify which of the
seven factors would be the driving force in
changing an organization at a point of time.
Perhaps the 3 hard Ss are within more
effective control of management.
What is Culture, and Why it is important?
Organization cultures can be viewed as systems of
shared values ( about what is important) &
beliefs (about how things work)
that shape a companys behavioral norms ( the way we
do things around here)
A value is an enduring preference for a mode of
conduct or an end-state . Managers are frequently
unaware that their daily activities are usually governed by
culture and shared values
Organizational culture & values lead to givens, or what
is taken for granted , about how work is to be done & how
one should interact with others. Culture automatically
shapes the way members see their world and behave.
Organizational culture has inertial effect, is deeply
rooted in beliefs & values that members have internalized
Changing culture is a slow, demanding process.
How inadequacy of structure, systems &
culture can impede bringing strategic changes
Assume a Firm takes a strategic decision
to put thrust on bringing new innovative
offerings, new products continuously in
the market.
Despite its stated new strategic direction, it
is worried some months later, Why it still
takes a long time to make a decisions on
issues related to bringing a new product in
the market?
Delays could be because of Culture : people are
risk averse, culture of a failure viewed in a
condemning manner
Delays could be because of Structure : there
could be lack of co-ordination between different
people from different departments. Say lack of
co-ordination between sales, R&D and
manufacturing department.
Delays could be due to lack of systems to
provide timely and reliable inputs to managers
to act. Co-ordinate effort. The approval systems
could be very cumbersome & slow.
Strategic Control Operational Control
Basic
Question
Are we in RIGHT
Direction?
How are we performing?
Aim Proactively
continuously
questioning
Allocation & use of Resources
Main
Concern
Steering the
Organization
Action Control
Focus External
Environment
Internal Organization
Excise of
Control
Top Management,
Long term
Executive / middle management,
Generally Annual / short term
Main
Techniques
Environ scanning,
questioning,
reviewing
Budgets, schedules, & MBO
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Affidavit of Explanation PassportDokumen1 halamanAffidavit of Explanation Passportfennyrose nunalaBelum ada peringkat
- AS Unit 1 Revision Note Physics IAL EdexcelDokumen9 halamanAS Unit 1 Revision Note Physics IAL EdexcelMahbub Khan100% (1)
- McKinsey 7's ModelDokumen21 halamanMcKinsey 7's ModeldipikarathodBelum ada peringkat
- 7s ModelDokumen18 halaman7s ModelUJJAL SAHU100% (2)
- Human Aspects of Strategy ImplementationDokumen48 halamanHuman Aspects of Strategy ImplementationDiksha Sinha100% (5)
- Organisational StructureDokumen10 halamanOrganisational Structuresajid bhattiBelum ada peringkat
- 5fcef6e7-HSM 2015 Student Edition IN3 V2Dokumen788 halaman5fcef6e7-HSM 2015 Student Edition IN3 V2Ashvath Srinivas100% (2)
- Mckinsey 7S Framework: Strategic Management Tom Peters, Robert Waterman, Julien PhilipsDokumen11 halamanMckinsey 7S Framework: Strategic Management Tom Peters, Robert Waterman, Julien Philipssonal jainBelum ada peringkat
- Structure: Shared ValuesDokumen12 halamanStructure: Shared ValuesPrem TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- McKinsey 7 S FrameworkDokumen9 halamanMcKinsey 7 S FrameworkRahul GautamBelum ada peringkat
- McKensie 7S mODELDokumen9 halamanMcKensie 7S mODELEngineering Pasanga DaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management Unit 4: Dr. Meenakshi SharmaDokumen45 halamanStrategic Management Unit 4: Dr. Meenakshi SharmarohitBelum ada peringkat
- MIS: A Tool For Management ProcessDokumen42 halamanMIS: A Tool For Management ProcessAmit SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management: Strategy ImplementationDokumen49 halamanStrategic Management: Strategy ImplementationEhsan AliBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT-II (HR Policies & Strategies)Dokumen36 halamanUNIT-II (HR Policies & Strategies)monika sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen40 halamanChapter 4Roopa YadavBelum ada peringkat
- SM Chapter 6Dokumen27 halamanSM Chapter 6Almaz GetachewBelum ada peringkat
- STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Unit 4Dokumen48 halamanSTRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Unit 4Social MediaBelum ada peringkat
- Bus 5a - Strategic ManagementDokumen16 halamanBus 5a - Strategic ManagementJerah TorrejosBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Evaluation and ControlDokumen44 halamanStrategic Evaluation and ControlSruthz DivakarlaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy ImplementationDokumen30 halamanStrategy ImplementationmayankBelum ada peringkat
- Management, Leadership, and Internal OrganizationDokumen28 halamanManagement, Leadership, and Internal OrganizationShihan Salim شيهن سليمBelum ada peringkat
- OD Week 3Dokumen53 halamanOD Week 3Hazel GasconBelum ada peringkat
- IHRM - Module 2Dokumen22 halamanIHRM - Module 2HooHaa RtvBelum ada peringkat
- Group Assignment For OBDokumen30 halamanGroup Assignment For OBluldavidyianBelum ada peringkat
- McKinsey 7S ModelDokumen6 halamanMcKinsey 7S ModelNikhil Manocha100% (1)
- DrSaraKhan 2661 16690 2 SHRM8Dokumen24 halamanDrSaraKhan 2661 16690 2 SHRM8Urooj MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy ImplementationDokumen82 halamanStrategy ImplementationJoshua Laryea100% (1)
- Strategy Implementation and EvaluationDokumen21 halamanStrategy Implementation and EvaluationShibanta SarenBelum ada peringkat
- Mcob Unit-2Dokumen44 halamanMcob Unit-2Sharma GsrBelum ada peringkat
- Business Organization: and ManagementDokumen21 halamanBusiness Organization: and ManagementChristian ZebuaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic ManagementDokumen149 halamanStrategic ManagementKALBE ABD GHANIBelum ada peringkat
- Business Policy and Strategies NotesDokumen25 halamanBusiness Policy and Strategies NotesKathleen Mae Salenga FontalbaBelum ada peringkat
- SLC McKinsey7SModel LectureManuscriptDokumen3 halamanSLC McKinsey7SModel LectureManuscriptMarlon P. TuizaBelum ada peringkat
- OrgDevt Jortil 0812Dokumen50 halamanOrgDevt Jortil 0812Merlajoy VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management: Strategy ImplementationDokumen86 halamanStrategic Management: Strategy ImplementationBryan Joseph JumawidBelum ada peringkat
- Models Organizational Change and Development: Mohammad Jonaed Kabir Associate Professor Dba, IiucDokumen25 halamanModels Organizational Change and Development: Mohammad Jonaed Kabir Associate Professor Dba, IiucSoyed Mohammed Zaber HossainBelum ada peringkat
- A List of OD InterventionsDokumen4 halamanA List of OD InterventionsJafarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6Dokumen22 halamanChapter 6Mebre WelduBelum ada peringkat
- Fit Concept and Configuration Perspective in Strategic ManagementDokumen4 halamanFit Concept and Configuration Perspective in Strategic ManagementMridul KatochBelum ada peringkat
- Work RedesignDokumen3 halamanWork RedesignJayasree Nadindla100% (1)
- The Mckinsey 7-S FrameworkDokumen9 halamanThe Mckinsey 7-S FrameworkMarlvern ZifambaBelum ada peringkat
- 7S ModelDokumen15 halaman7S ModelRupashi GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Solved Qustion Pe 4 YearDokumen974 halamanSolved Qustion Pe 4 Yearrdadmal2001Belum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen65 halamanUntitledSusmita BaruwalBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic ImplementationDokumen8 halamanStrategic ImplementationAnjali KedareBelum ada peringkat
- L 26 Unit 2 - McKinsey's 7 SDokumen7 halamanL 26 Unit 2 - McKinsey's 7 SUtsav SinghalBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic ManagementDokumen15 halamanStrategic Managementtanoris581Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1Dokumen46 halamanLesson 1Lyana DagoocBelum ada peringkat
- Organizational Design & StructureDokumen27 halamanOrganizational Design & Structurekary2907900% (1)
- McKinsey 7S ModelDokumen12 halamanMcKinsey 7S Modelmahmoud elsrogyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen41 halamanChapter 5AgatBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14 Notes PDFDokumen8 halamanChapter 14 Notes PDFIrish MagbanuaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy PPT Ch6Dokumen40 halamanStrategy PPT Ch6Habtamu mamoBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy Implementation and ControlDokumen71 halamanStrategy Implementation and Controlmilee0005100% (1)
- Unit 4Dokumen51 halamanUnit 4Shweta SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Numan PresentationDokumen25 halamanNuman Presentationnuman muradBelum ada peringkat
- 7S Analysis - A SampleDokumen18 halaman7S Analysis - A Samplebkginting6300100% (5)
- 2.2 Approaches To ManagementDokumen25 halaman2.2 Approaches To ManagementMohamed LisaamBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy Implementation: Amity Business SchoolDokumen33 halamanStrategy Implementation: Amity Business Schoolshark akhtarBelum ada peringkat
- MC Kinsey 7Dokumen15 halamanMC Kinsey 7Anjani PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsDari EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Effect 1 WalkthroughDokumen143 halamanMass Effect 1 Walkthroughandyt10Belum ada peringkat
- Climate Change Forests and Forest Management An O-Wageningen University and Research 481068Dokumen145 halamanClimate Change Forests and Forest Management An O-Wageningen University and Research 481068gulnuromar034Belum ada peringkat
- John Lear UFO Coverup RevelationsDokumen30 halamanJohn Lear UFO Coverup RevelationscorneliusgummerichBelum ada peringkat
- 20 Dumbbell WorkoutsDokumen7 halaman20 Dumbbell WorkoutsAlessandro BenedettiBelum ada peringkat
- Guide Item Dota 2Dokumen11 halamanGuide Item Dota 2YogaWijayaBelum ada peringkat
- UnderstandQUIC MoreDokumen12 halamanUnderstandQUIC MoreONEmillion knowledgeBelum ada peringkat
- At The End of The Lesson, The Students Will Be Able To Apply The Indefinite Articles in The Given SentencesDokumen11 halamanAt The End of The Lesson, The Students Will Be Able To Apply The Indefinite Articles in The Given SentencesRhielle Dimaculangan CabañezBelum ada peringkat
- Investment ChecklistDokumen3 halamanInvestment ChecklistArpan chakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Walsh January Arrest Sherrif Records Pgs 10601-10700Dokumen99 halamanWalsh January Arrest Sherrif Records Pgs 10601-10700columbinefamilyrequest100% (1)
- Article ReviewDokumen3 halamanArticle ReviewRAMADEVI A/P THANAGOPAL MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Slide Marine Cadastre 2Dokumen15 halamanSlide Marine Cadastre 2ajib KanekiBelum ada peringkat
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDokumen29 halamanDownloaded From Manuals Search EnginehaivermelosantanderBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 5 DLL ENGLISH 5 Q3 Week 2Dokumen7 halamanGrade 5 DLL ENGLISH 5 Q3 Week 2Armie Joimie ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Camp High Harbour at Lake LanierDokumen3 halamanCamp High Harbour at Lake LaniermetroatlantaymcaBelum ada peringkat
- Grid / Hippodamian Model: Hippodamus of MiletusDokumen34 halamanGrid / Hippodamian Model: Hippodamus of MiletusVriti SachdevaBelum ada peringkat
- แบบฝึกหัด subjuctiveDokumen6 halamanแบบฝึกหัด subjuctiveรัฐพล ทองแตงBelum ada peringkat
- Estudio - Women Who Suffered Emotionally From Abortion - A Qualitative Synthesis of Their ExperiencesDokumen6 halamanEstudio - Women Who Suffered Emotionally From Abortion - A Qualitative Synthesis of Their ExperiencesSharmely CárdenasBelum ada peringkat
- Juzaili Alias SSB Jadual Perubahan PDP Dan Penilaian AlternatifDokumen1 halamanJuzaili Alias SSB Jadual Perubahan PDP Dan Penilaian Alternatifkar afiBelum ada peringkat
- Using Open-Ended Tools in Facilitating Mathematics and Science LearningDokumen59 halamanUsing Open-Ended Tools in Facilitating Mathematics and Science LearningDomina Jayne PagapulaanBelum ada peringkat
- Painter Decorator Curriculum Eng l1 2 3 CC 404c.404dDokumen100 halamanPainter Decorator Curriculum Eng l1 2 3 CC 404c.404dM.a. KhaderBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Project Asad AliDokumen16 halamanBiology Project Asad Alisikander.a.khanixd26Belum ada peringkat
- Agricultural LocationDokumen26 halamanAgricultural LocationPrince MpofuBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Communication I Assignment (Advertisement)Dokumen13 halamanMarketing Communication I Assignment (Advertisement)Serene_98Belum ada peringkat
- OsteomyelitisDokumen10 halamanOsteomyelitismustafaBelum ada peringkat
- browningsong 안동Dokumen68 halamanbrowningsong 안동yooBelum ada peringkat
- USMLE Step 2 CK Exam - Overview - Examination Content - Test Format - EligibilityDokumen7 halamanUSMLE Step 2 CK Exam - Overview - Examination Content - Test Format - EligibilityJamesHowsonBelum ada peringkat
- HTTP WWW - Aphref.aph - Gov.au House Committee Haa Overseasdoctors Subs Sub133Dokumen3 halamanHTTP WWW - Aphref.aph - Gov.au House Committee Haa Overseasdoctors Subs Sub133hadia duraniBelum ada peringkat