Reaksi Anafilaksis
Diunggah oleh
Nova SuryatiDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Reaksi Anafilaksis
Diunggah oleh
Nova SuryatiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Raveinal
Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Department of Internal Medicine
FKUA/RS M Jamil Padang
Reaksi Anaphylaxis
Case 1
Mr. W 65 years old, came to E.R at 2.00 PM. With loss of consciousness
since 20 minute before admission.
PH: twenty minutes before admission, due to his tooth ache he took
amoxilline 500 mg, mephenemic acid 500 mg and dexametasone 0,5 mg
tablets. One or two minute after ingestion those medicine, he felt itchy
almost the whole bodies, followed by nausea vomiting, diaphoresis and
felt down due to unconscious. His family took him right away to the
nearest hospital. No history of drug allergy, or asthma, except history of
wheezing but very rare
On admission he was found soporous, perspiration the whole body.
Pulse not palpable, blood pressure could not be measured. Respiration
rate 28 per minute, heart rate 132/minute. gallop -, wheezing +/+, no
rales, liver/spleen not palpable. Extremities: warm
Case 1
ECG: normal, except sinus tachycardia. He was treated with:
Oksigen 6 liter/minute
Normal saline: free fall (1 liter)
Epinephrine 0,3 ml i.m lateral thigh
Dexamethasone 1 amp i.v
02.10 blood pressure : 50/palp. Pulse 120/minute very weak
Epinephrine 0,3 ml i.m
Ranitidine 1 amp i.v
Diphenhydramine 1 cc i.v
02.20 BP: 70/50 pulse 108/minutes.
Somnolence, contact ,
Dopamine drip was given 5-10 g/kg BW/mnt
BP: 90/70 pulse: 96/minute, apathy, contact
The patient was discharged the next morning with BP 130/80 pulse
80/minute, fully alert, normal activities and advised to visit Allergy Clinic
he was given methylprednisolone tab 16 mg/day, cetirizine 10 mg/day
for 3 days.
Case 2
Mr I 32 years old, come to E.R at 12.00, with general flushing, and itchy
almost the whole bodies 1 hour after he took griseovulvin.
PH: one hour after taking griseovulvin 125 mg, he felt very itchy and
redness the whole body, he also had nausea, vomiting 5 times and felt
sleepy. He slept for almost 1or 2 hours, when he woke up. he still had
itchy, redness of the skin and swollen of his face. No history of drug
allergy before. On arrival at ER, he was fully alert. Pulse: 120/minutes
weak. BP: 85/60, RR 16/minute his skin redness and warm, no wheezing,
abdomen: normal, extremities warm
Th : NaCL 0,9% free fall 1l, 0
2
4 - 6 l/minute, ephineprine 0,3 cc i.m,
Diphenhydramine 1 cc, dexametasone 1 cc 1 amp, ramtidine 1 amp.
12.20 BP: 100/70 HR: 96/minute, fully alert, felt better.
He was observed in E.R for 2 hours and BP 110/80 he was transferred to
the ward and discharged the following day with BP 130/80 and no more
rush or itchy. He was given mprednisolone 16 mg/day and cetrizine 5
mg/day for 3 days
Anafilaksis merupakan reaksi
alergi sistemik yang berat,
dapat menyebabkan kematian,
terjadi secara tiba-tiba
sesudah terpapar oleh alergen
atau pencetus lainnya
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening,
generalized or systemic hypersensitivity reaction
Anaphylaxis
Allergic anaphylaxis Non-allergic anaphylaxis
IgE-mediated anaphylaxis Non-IgE-mediated allergic anaphylaxis
Johansson SGO, et al. Allergy 2001;56:813-824
What is anaphylaxis?
Mechanisms underlying human
anaphylaxis
Human anaphylaxis
Immunologic
Idiopathic
Non-Immunologic
IgE, FcRI
foods, venoms,
latex, drugs
Other
blood products,
immune aggregates,
drugs
Physical
exercise, cold
Other
drugs
Simon FER. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006;117:367-77
Why we should know?
Anaphylaxis can be fatal
Unpredictable and suddenly
Can happen anywhere
Its prevalence increased
Medico legal ?
Epidemiology :
Prevalence of anaphylaxis
1. 1 : 2300 attendees at ED in UK (Stewart & Ewan, 1996)
2. Anaphylaxis hospital discharge 5.6/100.000 (1991 2)
10.2/100.000 (1994 - 5) (Sheik & Alves, 2000)
3. 13.230 admission for anaphylaxis 1990 - 2000 (Gupta,
et al. 2003)
4. 214 death attributed to anaphylaxis in UK 1992 2001
(Pumphrey, 2004)
Anaphylaxis: population study in 5 years
Incidence (annual): 21 per 100.000 person year
133 residents who experienced 154 anaphylactic
episode : - 116 residents 1 episode
- 13 resident 2 episode
- 4 residents 3 episode
53% atopy
68% allergen identified: food, medication and insect
sting
52% allergy consultation
7% hospitalization
1 patient died
Yocum, et al. JACI 1999;104:452-6
Anaphylaxis can be fatal
Be able to recognize the symptoms
Know and avoid the triggers
Have an emergency action plan
Treat it promptly and appropriately
CLINICAL FEATURES
Anaphylaxis symptoms
MOUTH itching swelling of lips and/or tongue
THROAT itching, tightness, closure, hoarseness
SKIN itching, hives, redness, swelling
GUT vomiting, diarrhea, cramps
LUNG shortness of breath, cough, wheeze
HEART weak pulse, dizziness, passing out
NEURO headache, visual loss, loss of
consciousness, incontinence, confusion
Frequency of occurrence of signs &
symptoms of anaphylaxis*+
Signs & symptoms
Cutaneous
Urticaria & angiodema
Flushing
Pruritus without rash
Respiratory
Dyspnea, wheeze
Upper airway angioedema
Rhinitis
Dizziness, syncope, hypotension
Abdominal
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping pain
Miscellaneous
Headache
Substernal pain
Seizure
90%
85-90%
45-55%
2-5%
40-60%
45-50%
50-60%
15-20%
30-35%
25-30%
5-8%
4-6%
1-2%
* On the basis of a compilation of 1865 patients reported in references 1 through 14
+ Percentages are approximations
Grading of anaphylactic reactions according to severity of clinical symptoms
Symptoms
Grade Dermal Abdominal Respiratory Cardiovascular
I Pruritus
Flush
Urticaria
Angiodema
II Pruritus
Flush
Urticaria
Angiodema (not
mandatory)
Nausea
Cramping
Rhinorrhoea
Hoarseness
Dyspnoea
Tachycardia (> 20 bpm)
Blood pressure change (>
20 mmHg systolic)
Arrhytmia
III Pruritus
Flush
Urticaria
Angiodema (not
mandatory)
Vomiting
Defecation
Diarroea
Laryngeal oedema
Bronchospasm
Cyanosis
Shock
IV Pruritus
Flush
Urticaria
Angiodema (not
mandatory)
Vomiting
Defecation
Diarrhoea
Respiratory arrest Cardiac arrest
Bpm = beats perminute
Ring J, Brockow K & Behrendt. History and classification of anaphylaxis. In Anaphylaxis. Novartis Foundation 2004:12
Derajat berat reaksi hipersensitivitas
yang luas
Derajat Gambaran klinik
Ringan (hanya kulit dan jaringan
submukosa)*
Eritema luas,edema periorbita,atau
angioedema
Sedang (keterlibatan
pernapasan,
kardiovaskuler,atau
gastrointestinal
Sesak, stridor, mengi, mual, muntah,
pusing, presinkop diaforesis, rasa
tertekan di dada atau tenggorok atau
sakit perut
Berat (hipoksia,hipotensi,atau
defisit neurologik)
Sianosis, atau SpO2 < 92% pada tiap
tingkat, hipotensi (tek sistolik < 90 mm
Hg pd dewasa), bingung kolaps, hilang
kesadaran atau inkontinens
* Reaksi ringan dapat dibagi lagi, disertai atau tidak ada angiodema
Grading system for generalized
reactions (from Brown 2004)
Grade Defined by
Mild (skin and subcutaneous
tissue only)*
Generalized erythema, urticaria,
periorbital oedema or angiodema
Moderate (features suggesting
respiratory, cardiovascular or
gastrointestinal involvement)
Dyspnoea, stridor, wheeze, nausea,
vomiting, dizziness (presyncope)
Severe (Hypoxia, hypotension
or neurological compromised
Cyanosis or SpO
2
92%, hypotension
(SBP < 90 mm Hg in adults), confusion,
collapse, LOC or incontinence
* The mild grade does not represent anaphylaxis according to the National Institute of Allergy and
Infections Disease-food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network (NIAID-FAAN) definition (Box 2), loss of
consciousness; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Brown SGA. JACI, 2004:114:371-6
Elicitors of anaphylaxis (including anaphylactoid reactions)
Drugs
Foods
Drug and food additives
Occupational substances (e.g. latex)
Animal venoms
Aeroallergens
Seminal fluid
Contact urticariogens
Physical agents (colt, heat, ultraviolet radiation)
Exercise
Echinococcal cyst
Summation anaphylaxis
Underlying disease
Complement factor 1-inactivator deficiency
Systemic mastocytosis
Idiopathic (?)
Ring J, Brockow K & Behrendt. History and classification of anaphylaxis. In Anaphylaxis. Novartis Foundation 2004:12
The causes of anaphylaxis
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
o
f
C
a
s
e
s
Food Drug/Bio Sting Allergen Exercise Idiopathic
Golden DBK, Patterns of anaphylaxis: Acute & late phase features of allergic reactions. In Anaphylaxis. Novartis
foundation 2004: 103
Interval from exposure to first arrest. Drug reaction
were fastest, mostly taking less than 5 minutes
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
<1 1-2 2.1-4.5 4.6-9.9 10-20 21-45 46-99 100-
214
>215
minutes from exposure to first arrest
Food Stings Drug
Pumphrey RSH, Fatal anaphylaxis in the UK, 1992-2001. In Anaphylaxis. Novartis Foundation 2004:121
Suspected cause of death 212 reactions
Sting 47 29 wasp, 4 bee, 14 unidentified
Nuts 32 2 almond, 2 brazil, 1 hazel, 10 peanut, 6 walnut, 11 mixed or
unidentified
Food 13 1 banana, 2 chickpea, 2 fish, 5 milk, 2 crustacean, 1 snail
Food? 18 1 ?fish, 5 during meal, 1 ?grape, 3 ?milk, 3 ?nut, 1 ?sherbet, 1
?strawberry, 1 ?yeast, 1 ?nectarine
Antibiotic 27 1 benzypenicillin, 10 aminopenicillin, 12 cephalosporin, 1
ciprofloxacin, 1 vancomycin, 2 amphotericin
Anesthetic 35 19 suxamethonium, 7 vecuronium, 6 attracurium, 7 at induction
Other drug 15 3 ACE inhibitor, 6 NSAID, 5 gelatines, 2 protamine, 2 vitamin K,
1 Diamox (acetazolamide), 1 etoposide, 1 pethidine, 1 heroin, 1
kabikinase, 1 local anaesthetic
Contrast
media
11 9 iodinated, 1 technetium, 1 fluorescein
Other 3 1 latex, 1 hair dye, 1 hydatid, 1 idiophatic
Pumphrey RSH, Fatal anaphylaxis in the UK, 1992-2001. In Anaphylaxis. Novartis Foundation 2004:118
Mode of death
Drug Sting Food Food? Male Female
Lower airways 11 3 24 11 21 26
Upper + lower airways 6 4 13 3 5 19
Upper airways 7 8 5 3 16 12
Shock + asphyxia 21 4 2 12 15
Shock 32 18 2 23 29
Disseminated
intravascular coagulation
5 1 1 2 4
Pumphrey RSH, Fatal anaphylaxis in the UK, 1992-2001. In Anaphylaxis. Novartis Foundation 2004:120
DIAGNOSIS
Kriteria klinik diagnosis anafilaksis
1
1. Terjadinya gejala penyakit segera (beberapa menit
sampai jam), yang melibatkan kulit, jaringan mukosa,
atau keduanya (urtikaria yang merata, pruritus,atau
kemerahan, edema bibir-lidah-uvula) DAN PALING
SEDIKIT SATU DARI BERIKUT INI :
a. Gangguan pernapasan (sesak, mengi-
bronkospasme, stridor, penurunan Arus Puncak
Ekspirasi (APE), hipoksemia.
b. Penurunan tekanan darah atau berhubungan
dengan disfungsi organ (hipotonia atau kolaps,
pingsan, inkontinens)
Kriteria klinik diagnosis anafilaksis
2
2. Dua atau lebih dari petanda berikut ini yang terjadi
segera setelah terpapar serupa alergen pada penderita
(beberapa menit sampai jam):
a.Keterlibatan kulit-jaringan mukosa (urtikaria yang
merata, pruritus-kemerahan, edema pada bibir-
lidah-uvula)
b.Gangguan pernapasan (sesak, mengi-
bronkospasme, stidor, penurunan APE, hipoksemia)
c.Penurunan tekanan darah atau gejala yang
berhubungan (hipotonia-kolaps, pingsan,
inkontinens)
d.Gejala gastrointestinal yang menetap(kram perut,
sakit, muntah)
Kriteria klinik diagnosis anafilaksis
3
3. Penurunan tekanan darah segera setelah terpapar
alergen (beberapa menit sampai jam)
a. Bayi dan anak : tekanan darah sistolik rendah
(tgt umur), atau penurunan lebih dari 30%
tekanan darah sistolik.
b. Dewasa : tekanan darah sistolik kurang dari 90
mm Hg atau penurunan lebih dari 30% nilai basal
pasi
* Tekanan darah sistolik rendah untuk anak didifinisikan bila < 70 mm
Hg antara 1 bulan sampai 1 tahun, kurang dari (70 mm Hg [2x
umur]) untuk 1 sampai 10 tahun, dan kurang dari 90 mm Hg dari 11
sampai 17 tahun.
TREATMENT
Penatalaksanaan anafilaksis
1. Hentikan pencetus, nilai beratnya dan berikan terapi yang sesuai
Minta bantuan
Adrenalin i.m (paha lateral) 0.01mg/kg boleh sampai 0.5mg
Pasang infuse
Berbaring rata/ tinggikan posisi kaki bila bias
Berikan oksigen aliran tinggi,alat bantu napas/ventilasi bila diperlukan
BILA HIPOTENSI
Akses i.v.tambahan (jarum 14G atau 16G pada orang dewasa) utk
infus NaCl fisiologis. NaCl fisiologis bolus atau infus 20 mL/kg
diberikan secepatnya bila perlu dengan tekanan
Penatalaksanaan anafilaksis
2. Bila respons tidak adekuat, keadaan mengancam kehidupan, atau memburuk:
Pertimbangkan hal-hal berikut
Hipotensi
o Ulangi infuse NaCl fisiologis 10-20 ml/kg dapat mencapai 50 ml/kg dalam 30 menit.
o i.v. atropine 0.02 mg/kg bila bradikardi berat dosis minimum 0.1 mg
o i.v vasopresor untuk mengatasi vasodilatasi. Pada henti jantung adrenalin dapat
ditingkatkan menjadi 3-5 mg setiap 2-3 menit mungkin efektif.
o i.v. glucagons pada pasien yang memakai obat penyekat beta. Dosis orang dewasa
1-5 mg diikuti 5-15 ug/mnt
Bronkospasme
o Inhalasi salbutamol secara kontinyu
o i.v. hidrokortison 5mg/kg diikuti prednisone 1mg/kg maksimal (50 mg) selama 4 hari
Obstruksi saluran napas bagian atas
o Adrenalin inhalasi (5 mg atau 5 ml sediaan adrenalin 1;1000) mungkin membantu.
o Persiapkan tindakan bedah.
Mulai dengan infuse adrenalin sesuai dengan panduan/protocol rumah sakit
ATAU
Ulang adrenalin i.m setiap 3-5 menit
Penatalaksanaan anafilaksis
3 . Lama observasi dan tindak lanjut
1 Observasi paling tidak 4 jam setelah semua gejala dan tanda
menghilang.
Bila memungkinkan periksa kadar triptase serum saat dating, 1 jam
stelahnya, dan sebelum dipulangkan.
Pada kasus yang berat pasien dirawat semalam, terutama pasien
yang mempunyai riwayat reaksi yang berat atau asma yang tidak
terkontrol dan pasien yang datang pada malam hari.
2 Sebelum dipulangkan pasien diberikan penjelasan mengenai alergen
tersangka dan upaya penghindarannya
Setelah dipulangkan pasien dirujuk ke ahli alergi terutama pada kasus
yang sedang berat, dan yang ringan karena alergi makanan yang
disertai asma.
3 Di negara maju setelah dibekali penjelasan dan pelatihan sebagian
pasien di berikan EpiPen yaitu adrenalin 0.3 atau 0.15 mg yang siap
pakai
Pharmacology of epinephrine
Epinephrine
1
-receptor
2
-receptor
1
-adrenergic
receptor
2
-adrenergic
receptor
vasoconstriction
peripheral vascular resistance
mucosal edema
insulin release
neropinephrine release
inotropy
chronotropy
bronchodilation
vasodilation
glycogenolysis
mucosal edema
Estelle FER. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004;113:837-44
Absorption of epinephrine is faster after
intramuscular injection than after
subcutaneous injection
Estelle FER. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004;113:837-44
34 14 (5-120) minutes
p < 0.05
5 10 15 20 25 30 35
8 2 minutes
Time to C
max
after infection (minutes)
Intramuscular
epinephrine
(Epipen)
Subcutaneous
epinephrine
PREVENTION
Education of anaphylaxis
Individuals and their families
Caregivers
Health case professional (doctors, nurses)
First responden
Emergency medical services
Teachers coaches, child care providers
Food industries, restaurant, law makers
Why is follow up is needed ?
Anaphylaxis can occur repeatedly
The trigger need to be confirmed
Long-term preventive strategies need to be
implemented
Sample Chef Card
To the Chef:
WARNING! I am allergic to peanuts. In order to avoid a life-threatening
reaction, I must avoid the following ingredients:
Artificial nuts
Beer nuts
Cold pressed, expelled, or extruded peanut oil
Ground nuts
Mandelonas
Mixed nuts
Monkey nuts
Nut pieces
Peanut
Peanut butter
Peanut flour
Please ensure any utensils & equipment used to prepare my meal, as
well as prep surfaces, are thoroughly cleaned prior to use. Thanks for
your cooperation
Munoz. Anaphylaxis 2004. Wiley, Chichester. P. 265-75
THANK YOU
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mitral Valve Repair: DR - Juli Ismail SPB - SPBTKV Bagian Bedah Fkua/Rsup M.Jamil PadangDokumen22 halamanMitral Valve Repair: DR - Juli Ismail SPB - SPBTKV Bagian Bedah Fkua/Rsup M.Jamil PadangNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury: Review: Blood Research & Transfusion JournalDokumen4 halamanRenal Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury: Review: Blood Research & Transfusion JournalNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Aortic Stenosis: Yerizal Karani MD Cardiology Division Faculty of Medicine Andalas UniversityDokumen29 halamanAortic Stenosis: Yerizal Karani MD Cardiology Division Faculty of Medicine Andalas UniversityNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Ijcri 1056610201566 AbdelreheemDokumen6 halamanIjcri 1056610201566 AbdelreheemNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Randomized Clinical Trial of Antibiotic Therapy Versus Appendicectomy As Primary Treatment of Acute Appendicitis in Unselected PatientsDokumen9 halamanRandomized Clinical Trial of Antibiotic Therapy Versus Appendicectomy As Primary Treatment of Acute Appendicitis in Unselected PatientsNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseDokumen9 halamanBacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Review For General PractitionersDokumen6 halamanIdiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Review For General PractitionersNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- TutorialDokumen13 halamanTutorialNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Miringitis BulosaDokumen1 halamanMiringitis BulosaNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal VariselaDokumen7 halamanJurnal VariselaNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- "Labor and Delivery": Joserizal Serudji Bag/SMF OBGIN FK Unand/RS. M.Djamil PadangDokumen34 halaman"Labor and Delivery": Joserizal Serudji Bag/SMF OBGIN FK Unand/RS. M.Djamil PadangNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Varisela ZosterDokumen19 halamanJurnal Varisela ZosterNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Bartholinitis: DiagnosisDokumen11 halamanBartholinitis: DiagnosisNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Gangguan NutrisiDokumen8 halamanGangguan NutrisiNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Infeksi Jamur OportunistikDokumen27 halamanInfeksi Jamur OportunistikNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Mata Dan KulitDokumen4 halamanFungsi Mata Dan KulitNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Pleno MG 5Dokumen13 halamanPleno MG 5Nova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Case PresentationDokumen12 halamanCase PresentationFrengky PrasetyaBelum ada peringkat
- Anesthetic Death: A Case ReportDokumen4 halamanAnesthetic Death: A Case ReportraisaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 5Dokumen18 halamanLesson 3 5Johncen TrinidadBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System 2Dokumen32 halamanDigestive System 2Johnmer AvelinoBelum ada peringkat
- USPI - Bicillin C-R - Penicillin G Benzathine, Penicillin GDokumen11 halamanUSPI - Bicillin C-R - Penicillin G Benzathine, Penicillin GRoberto Alfredo SáenzBelum ada peringkat
- Airway Obstruction - Types, Causes, and SymptomsDokumen6 halamanAirway Obstruction - Types, Causes, and SymptomsGilbertLiem100% (1)
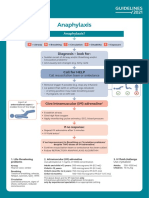
- Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Dokumen1 halamanAnaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Shawn Gaurav JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Lange Q&A: Radiography ExaminationDokumen18 halamanLange Q&A: Radiography ExaminationSamuel JeebanBelum ada peringkat
- The Use of Hyaluronidase in Cosmetic DermatologyDokumen7 halamanThe Use of Hyaluronidase in Cosmetic DermatologyDr. Hilder HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Venofer Venofer Iron Infusion Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanVenofer Venofer Iron Infusion Nursing Care PlanErica Ruth CabrillasBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: College of NursingDokumen14 halamanDrug Study: College of NursingelleBelum ada peringkat
- Allergy Blood Test (IgE)Dokumen5 halamanAllergy Blood Test (IgE)Muhammad RaheemBelum ada peringkat
- Basic and Advance Clinical Outpatient Management For Polillo RHUDokumen122 halamanBasic and Advance Clinical Outpatient Management For Polillo RHUHamilton EscaraBelum ada peringkat
- First Aid ModuleDokumen41 halamanFirst Aid ModuleIza Domingo MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Ryan Cooper - The Precautions of Methylene Blue (2023)Dokumen48 halamanRyan Cooper - The Precautions of Methylene Blue (2023)riickayyBelum ada peringkat
- Food Allergy Basics For All Ages.Dokumen5 halamanFood Allergy Basics For All Ages.Azad HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Certificate For Ascia Anaphylaxis CourseDokumen1 halamanCertificate For Ascia Anaphylaxis Courseapi-532439518Belum ada peringkat
- Shock & Iv Fluids: Dr. Ahmed Khan Sangrasi Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, LUMHS JamshoroDokumen120 halamanShock & Iv Fluids: Dr. Ahmed Khan Sangrasi Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, LUMHS JamshoroTheruna100% (1)
- Nurani Almira Salsabilla-G0018161Dokumen9 halamanNurani Almira Salsabilla-G0018161Rizki AmeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Snake BiteDokumen1 halamanManagement of Snake BiteAfri AdiBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Anaphylactic Shock Journal of Modern Pharmacy 2006Dokumen3 halamanManaging Anaphylactic Shock Journal of Modern Pharmacy 2006Saputro AbdiBelum ada peringkat
- Typhoid Vaccines: What You Need To KnowDokumen2 halamanTyphoid Vaccines: What You Need To KnowRohit KohliBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study NCPDokumen4 halamanDrug Study NCPJustice Ace DaprozaBelum ada peringkat
- RADIESSE Wrinkle Filler Instructions For UseDokumen38 halamanRADIESSE Wrinkle Filler Instructions For UseBetseray100% (1)
- AllergyDokumen19 halamanAllergyAbhi YT0% (1)
- ASCIA Guidelines ADVANCED Acute Management Anaphylaxis Dec2016Dokumen7 halamanASCIA Guidelines ADVANCED Acute Management Anaphylaxis Dec2016SPV DoctorBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Test Bank CH 6-9Dokumen33 halamanPathophysiology Test Bank CH 6-9Joyy86% (7)
- Allergic Manifestation in Oral Cavity. Exudative Polymorphic Erythema. Chronic Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis.Dokumen38 halamanAllergic Manifestation in Oral Cavity. Exudative Polymorphic Erythema. Chronic Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis.Alex DaniciBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphylaxis Anaphylactoid ReactionDokumen8 halamanAnaphylaxis Anaphylactoid Reactionsringeri2Belum ada peringkat
- Acute Renal Failure Complicated by Multiple Bee Stings: A Case Report and Literature ReviewDokumen3 halamanAcute Renal Failure Complicated by Multiple Bee Stings: A Case Report and Literature ReviewHafizah FzBelum ada peringkat