Archaea
Diunggah oleh
Hannura Hosea100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
113 tayangan54 halamanBefore microorganisms were known to exist, all life was classified as either animal or plant. The discovery of microbes in the late 17th century required developing a new classification system. Through the 1970s, scientists debated how to classify these new organisms. In 1978, Carl Woese proposed grouping all life into three domains based on cellular structure: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. This three domain system classified organisms as bacteria, archaea, which lack bacteria's peptidoglycan cell walls, or eukaryotes including plants, animals, fungi and protists.
Deskripsi Asli:
archae bacteria is
Judul Asli
12. Archaea
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniBefore microorganisms were known to exist, all life was classified as either animal or plant. The discovery of microbes in the late 17th century required developing a new classification system. Through the 1970s, scientists debated how to classify these new organisms. In 1978, Carl Woese proposed grouping all life into three domains based on cellular structure: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. This three domain system classified organisms as bacteria, archaea, which lack bacteria's peptidoglycan cell walls, or eukaryotes including plants, animals, fungi and protists.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
113 tayangan54 halamanArchaea
Diunggah oleh
Hannura HoseaBefore microorganisms were known to exist, all life was classified as either animal or plant. The discovery of microbes in the late 17th century required developing a new classification system. Through the 1970s, scientists debated how to classify these new organisms. In 1978, Carl Woese proposed grouping all life into three domains based on cellular structure: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. This three domain system classified organisms as bacteria, archaea, which lack bacteria's peptidoglycan cell walls, or eukaryotes including plants, animals, fungi and protists.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 54
Classification of Microorganisms
Before the existence of microbes was known, all organisms
were grouped into either the animal kingdom or the plant
kingdom.
When microscopic organisms with characteristics of animals
and plants were discovered late in the seventeenth century,
a new system of classification was needed. Still, biologists
could not agree on the criteria for classifying these new
organisms until the late 1970s.
At the beginning :
there are two kingdoms
- Monera
- Protista
Earlier classification :
Monera is oldest (earliest cell), prokaryotic
& structurally simple cell
Protista is youngest (latest cell), eukaryotic
& more structurally complex cell
The Protista developed to four
kingdom : Protista, Fungi, plantae
and animalia
Table 10.2
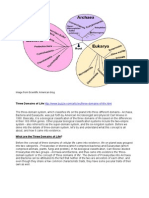
In 1978, Carl Woese devised a system of classification based
on the cellular organization of organisms. It groups all
organisms in three domains as follows:
1. Bacteria (cell walls contain a proteincarbohydrate
complex called peptidoglycan)
2. Archaea (cell walls, if present, lack peptidoglycan)
3. Eukarya, which includes the following:
Protists (slime molds, protozoa, and algae)
Fungi (unicellular yeasts, multicellular molds, and
mushrooms)
Plants (mosses, ferns, conifers, and flowering plants)
Animals (sponges, worms, insects, and vertebrates
The Three-Domain System
Figure 10.1
Euryarchaeota
Crenarchaeo
ta
Korarchaeota
Domains Archaea
In the late 1970s, a distinctive type of prokaryotic cell was
discovered. Most strikingly, the cell walls of these
prokaryotes lacked the peptidoglycan common to most
bacteria. It soon became clear that they also shared many
rRNA sequences, and the sequences were different from
either those of the Domain Bacteria or the eukaryotic
organisms. These differences were so significant that these
organisms now constitute a new taxonomic grouping, the
Domain Archaea.
Bacteria and Archaea
Bacteria and Archaea are both prokaryotes and
their DNA is arranged in circular structures called
plasmids (they have no nucleus and the DNA is not
arranged in chromosomes). Prokaryote derived
from the Greek Pro meaning before and karyon
meaning a kernel [i.e. a nucleus].
However, they have substantial differences in their
biochemistry, cell wall structure and other
molecular details.
Bacteria vs. Archaea
Bacteria are inhibited by antibiotics Streptomycin
and Chloramphenicol but Archaea are not.
Archaea in common with Eukarya have histone
proteins associated with their DNA, have introns
in their DNA, and have several kinds of RNA
polymerase. Bacteria lack these features.
Domain Bacteria
Includes most of the bacteria people are familiar
with including disease-causing species
(Salmonella; Vibrio cholerae which causes
cholera), nitrogen-fixing (Nitrosomonas) and
parasites (Borrelia burgdorferi which causes Lyme
disease).
Bacteria play a major role in decomposition and
many live symbiotically with other organisms
including humans helping to break down or
synthesize foods needed by the host.
contain unique genetic sequences in their rRNA
seem more closely related to Domain Eukarya than to
bacteria
have unique membrane lipids & cell wall construction
live in the most extreme habitats in nature,
extremophiles
adapted to heat salt acid pH, pressure & atmosphere
includes: methane producers, hyperthermophiles,
extreme halophiles, and sulfur reducers
Domain Archaea
Figure 11.27 Archaea. Pyrodictium abyssi, an unusual member of
the archaea found growing in deep-ocean sediment at a
temperature of 110C. The cells are disk-shaped with a
network of tubules (cannulae). Most archaea are more
conventional in their morphology.
The Three-Domain System
Table 10.1
Phyllogenetic tree of archaea
Phylum/Class Order Important Genera Special
Features
DOMAIN ARCHAEA
Crenarchaeota (Gram-Negative)
Desulfurococcales Pryidictium Hyperthermophiles
Sulfolobales Sulfolobus Hyperthermophiles
Euryarchaeota (Gram-Positive to Variable)
Methanobacteriales Methanobacterium Methanogens
Halobacteriales Halobacterium Require high salt
concentration
Halococcus Require high salt
concentration
Phyllogenetic and Metabolic diversity of archaea
A.
B.
for your kind attention
Sahara desert
Life in the extremes
Yellowstone National park
Lake Magadi, Tansania
Yellowstone National Park
Postulated Mars-Biosphere
Mars from Pathfinder
Liquid water only in deep subsurface regions
Life either extinct or in subsurface niches:
ANTARCTICA, 1984
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ebook PDF Microbe 2nd Edition by Michele SwansonDokumen41 halamanEbook PDF Microbe 2nd Edition by Michele Swansonglenda.shawl193Belum ada peringkat
- Importancia de La Inmunología Como Ciencia: August 2018Dokumen23 halamanImportancia de La Inmunología Como Ciencia: August 2018Jorge Alberto López Gómez100% (1)
- What Were The Short and Long Term Consequences of The Black Death On Medieval Society?Dokumen3 halamanWhat Were The Short and Long Term Consequences of The Black Death On Medieval Society?Dushanka Govender78% (9)
- Factors That Influence Microbial Growth in FoodDokumen72 halamanFactors That Influence Microbial Growth in FoodIrham Ibrahim100% (1)
- BIO022 Classification of Microbes (Lecture Outline)Dokumen25 halamanBIO022 Classification of Microbes (Lecture Outline)Butz GeonzonBelum ada peringkat
- Archae 1Dokumen30 halamanArchae 1Sabiha SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Domain Archaea Morphology Physiology BioDokumen38 halamanDomain Archaea Morphology Physiology BioRoshini KuppiliBelum ada peringkat
- Archaebacteria KingdomDokumen13 halamanArchaebacteria KingdomKnnncyber Cafe100% (1)
- Kingdom ArchaeBacteriaDokumen20 halamanKingdom ArchaeBacteriaFrances Jhoy Lolong100% (2)
- The Five Kingdoms of LifeDokumen9 halamanThe Five Kingdoms of LifeKristel Joy Bayaca CabuyadaoBelum ada peringkat
- 3A General - ClassificationDokumen10 halaman3A General - Classificationনাজমুল হক শাহিনBelum ada peringkat
- Systematics of Living Organisms (Biological Classification)Dokumen60 halamanSystematics of Living Organisms (Biological Classification)Ganesh PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomic Classification of Microorganisms - 4CHEB - Group3Dokumen30 halamanTaxonomic Classification of Microorganisms - 4CHEB - Group3Vicente JonathanBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 Domains Clades MainDokumen40 halaman2022 Domains Clades MainaleexpuigcorbeBelum ada peringkat
- BIODIVERSITYDokumen26 halamanBIODIVERSITYRea AnsusBelum ada peringkat
- Archaebacteria: Group MembersDokumen30 halamanArchaebacteria: Group MembersMr MBelum ada peringkat
- How Is Life ClassifiedDokumen4 halamanHow Is Life ClassifiedMustansarWattooBelum ada peringkat
- Three Domains of LifeDokumen2 halamanThree Domains of LifeNishali SamBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Archaea VanessaDokumen8 halamanWhat Is Archaea VanessaArnel MorallosBelum ada peringkat
- Archea: - Ə) Are A Group of Single-Celled Microorganisms. A Single IndividualDokumen14 halamanArchea: - Ə) Are A Group of Single-Celled Microorganisms. A Single IndividualAhsan TareenBelum ada peringkat
- The Domain ArchaeaDokumen3 halamanThe Domain ArchaeatadashiiBelum ada peringkat
- 2.-Domains-Kingdoms-and-Hierarchy 2Dokumen6 halaman2.-Domains-Kingdoms-and-Hierarchy 2Ej FerrerBelum ada peringkat
- Archaebacteria: BY Bibaswan Pritam SristyDokumen25 halamanArchaebacteria: BY Bibaswan Pritam SristySRISTY AGARWALBelum ada peringkat
- Agapan ArchaeanDokumen2 halamanAgapan ArchaeanFoolBelum ada peringkat
- Botany: Biological ClassificationDokumen17 halamanBotany: Biological ClassificationNeeraj VenugopalBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Biodiversity and ClassificationDokumen34 halaman1.1 Biodiversity and ClassificationYoganeesharuban AnbalaganBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction - Clasification - 5 SeptDokumen71 halamanIntroduction - Clasification - 5 Sept14Fika Amaliatus SholihahFMIPABelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 BiodiversityDokumen45 halamanTopic 1 BiodiversityNORLISA SYADINA SHAIFUL AZAMBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ClassificationDokumen6 halamanIntroduction To ClassificationAmelia KaisersinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10Dokumen5 halamanChapter 10Apryll DarlineBelum ada peringkat
- Biological ClassificationDokumen8 halamanBiological Classificationlpc4944Belum ada peringkat
- Domain Bacteria Archaea & VirusesDokumen29 halamanDomain Bacteria Archaea & VirusesS Nadine YP100% (1)
- ArcheaDokumen30 halamanArcheaKomalBelum ada peringkat
- Archaea Domain - Kingdom Archaebacteria 2Dokumen26 halamanArchaea Domain - Kingdom Archaebacteria 2Chrisel BantuganBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Bio200 Chapter 2Dokumen28 halaman6 Bio200 Chapter 2api-153638948Belum ada peringkat
- Kebo 102Dokumen13 halamanKebo 102Ved Prakash SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 BiodiversityDokumen5 halamanModule 4 BiodiversityJohn ForteBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 1-BiodiversityDokumen70 halamanCHP 1-BiodiversitySIMBA The Lion KingBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 10 MicrobiologyDokumen6 halamanCHAPTER 10 MicrobiologyApryll DarlineBelum ada peringkat
- Three Domains of LifeDokumen5 halamanThree Domains of LifeDhanushka WarnakulasooriyaBelum ada peringkat
- ArchaeaDokumen5 halamanArchaeaSara Isabel Gil ZuluagaBelum ada peringkat
- 11biological ClassificationDokumen23 halaman11biological ClassificationSreenjoy ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen4 halamanUntitledAlice KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Biological ClassificationDokumen90 halaman2 Biological Classificationrustama0322Belum ada peringkat
- The Six KingdomsDokumen6 halamanThe Six KingdomsMarta YantiBelum ada peringkat
- Domain Archaea (Shortened)Dokumen28 halamanDomain Archaea (Shortened)Lyka Durian Lamoste100% (1)
- Taxonomy and ClassificationDokumen91 halamanTaxonomy and ClassificationshakiraBelum ada peringkat
- Mawlana Bhashani Science and Technology UniversityDokumen7 halamanMawlana Bhashani Science and Technology UniversityJayed Hassan ZihadBelum ada peringkat
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Iological LassificationDokumen13 halaman© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Iological LassificationKM_ArunBelum ada peringkat
- 2.2classification of MicroorganismsDokumen77 halaman2.2classification of MicroorganismsMa. Isabel A. EnriquezBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5: Lesson 5 - Five Kingdoms, Three DomainsDokumen3 halamanLesson 5: Lesson 5 - Five Kingdoms, Three DomainsKerberos DelabosBelum ada peringkat
- Biology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsDokumen92 halamanBiology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsGideon CavidaBelum ada peringkat
- Homo Sapiens. The Name of Any Species Is TwoDokumen5 halamanHomo Sapiens. The Name of Any Species Is TwoYngrid Bless Z. CadenaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample OnlyDokumen6 halamanSample OnlySeb LlaveBelum ada peringkat
- Microbial TaxonomyDokumen20 halamanMicrobial TaxonomySebna NoushadBelum ada peringkat
- Domains Kingdoms and Hierarchy PDFDokumen5 halamanDomains Kingdoms and Hierarchy PDFEj FerrerBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of OrganismsDokumen2 halamanClassification of Organismsjocelynmillano115Belum ada peringkat
- Biology Tercer ParcialDokumen5 halamanBiology Tercer Parcialvaleriatr14Belum ada peringkat
- Vetriani, 2001Dokumen9 halamanVetriani, 2001Karla GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Science Majorship Hand Outs m18Dokumen11 halamanBiological Science Majorship Hand Outs m18Xenia Mae FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Classification of Bacteria (History of Archaea) 113Dokumen24 halamanMolecular Classification of Bacteria (History of Archaea) 113Meong MeongBelum ada peringkat
- FACT SHEET 2021/2022 Information For Erasmus+ StudentsDokumen5 halamanFACT SHEET 2021/2022 Information For Erasmus+ StudentsHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Sustainability 12 01845 v3Dokumen19 halamanSustainability 12 01845 v3Hannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Land-Use Planning and The Public: Is There An Optimal Degree of Civic Participation?Dokumen15 halamanLand-Use Planning and The Public: Is There An Optimal Degree of Civic Participation?Hannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S2352340921000664 MainDokumen8 halaman1 s2.0 S2352340921000664 MainHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Spatial Patterns of Urbanisation Using Geoinformatics and Spatial MetricsDokumen21 halamanAnalysis of Spatial Patterns of Urbanisation Using Geoinformatics and Spatial MetricsHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Urban Management: Paola Ortiz-B Aez, Pablo Cabrera-Barona, Jan BogaertDokumen12 halamanJournal of Urban Management: Paola Ortiz-B Aez, Pablo Cabrera-Barona, Jan BogaertHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- 6487 13875 1 SM PDFDokumen11 halaman6487 13875 1 SM PDFIvan FardhianzsyahBelum ada peringkat
- Urban Sprawl: Metrics, Dynamics and Modelling Using GIS: ArticleDokumen12 halamanUrban Sprawl: Metrics, Dynamics and Modelling Using GIS: ArticleHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Urban Sprawl Metrics: An Analysis of Global Urban Expansion Using GISDokumen13 halamanUrban Sprawl Metrics: An Analysis of Global Urban Expansion Using GISHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- The UtilityDokumen13 halamanThe UtilityHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Agricultural Bio Diversity in Tropical IndonesiaDokumen22 halamanAgricultural Bio Diversity in Tropical IndonesiaHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- 56 G ProgDokumen27 halaman56 G ProgHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Undergraduate Admission OthersDokumen2 halamanUndergraduate Admission OthersHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- ch19 1Dokumen7 halamanch19 1api-305539170Belum ada peringkat
- (Biol 12) 200 MCQ On Microorganisms + AnswersDokumen23 halaman(Biol 12) 200 MCQ On Microorganisms + Answersjemal12174Belum ada peringkat
- For SchoolDokumen1 halamanFor Schoolapi-252841138Belum ada peringkat
- Micro TaxonomyDokumen29 halamanMicro TaxonomyNishit PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Explorer Unit5 Video TranscriptDokumen2 halamanReading Explorer Unit5 Video TranscriptJean Marie CruzBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Exploring+Biology+TextDokumen43 halaman01 Exploring+Biology+TextKatrina FermocilloBelum ada peringkat
- OCR A Level Biology WebDokumen15 halamanOCR A Level Biology Webscmdesigns2Belum ada peringkat
- Degradation of Sugarcane Vinasse in A Full-Scale Methanogenic UASBDokumen11 halamanDegradation of Sugarcane Vinasse in A Full-Scale Methanogenic UASBProyectos Plantas De Tratamiento De AguaBelum ada peringkat
- Kingdom MoneraDokumen2 halamanKingdom MoneraAlpine SutioBelum ada peringkat
- Bergeys Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyDokumen5 halamanBergeys Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyAnumol LoranceBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDokumen7 halamanWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology PDFDokumen26 halamanMicrobiology PDFAladin herzALLAHBelum ada peringkat
- Diversity in Living Organisms NOTESDokumen15 halamanDiversity in Living Organisms NOTEStejas mittalBelum ada peringkat
- Micro TaxonomyDokumen29 halamanMicro TaxonomyGujulla RahulBelum ada peringkat
- Bose Et Al 2020Dokumen23 halamanBose Et Al 2020Himadri BoseBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Gram-Negative Bacteria and Gram-Positive Bacteria Gram-Negative Bacteria PDFDokumen122 halamanChapter 2 Gram-Negative Bacteria and Gram-Positive Bacteria Gram-Negative Bacteria PDFemiresianaBelum ada peringkat
- Post Lab Report - Exercise 1 - Morphology and Motility of MicroorganismsDokumen23 halamanPost Lab Report - Exercise 1 - Morphology and Motility of MicroorganismsDara KwonBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry and The Organization of Cells-Chap 1Dokumen33 halamanBiochemistry and The Organization of Cells-Chap 1scribdusernumber210% (1)
- ICTV Master Species List 2022 MSL38.v2Dokumen1.654 halamanICTV Master Species List 2022 MSL38.v2Richard ThodéBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Half Microbiology For Allied Health StudentsDokumen497 halaman1st Half Microbiology For Allied Health StudentsFjornBelum ada peringkat
- 1996 - Gupta & Golding - The Origin of The Eukaryotic CellDokumen6 halaman1996 - Gupta & Golding - The Origin of The Eukaryotic Cellvltg_35643Belum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Microbiology: Delivered byDokumen38 halamanFundamentals of Microbiology: Delivered byShahzad AslamBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Biological ClassificationDokumen33 halaman2 Biological Classificationapi-356050743Belum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Biological Science 4th Edition FreemanDokumen14 halamanTest Bank For Biological Science 4th Edition Freemanunbloodystrakeow2Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology & BiochemistryDokumen320 halamanCell Biology & BiochemistryVai SanBelum ada peringkat
- Yadav Et Al. 2018-Psychrotrophic MicrobiomesDokumen44 halamanYadav Et Al. 2018-Psychrotrophic MicrobiomesAjar Nath YadavBelum ada peringkat
- A Guide To Wastewater MicrobiologyDokumen14 halamanA Guide To Wastewater Microbiologyabduyassin8014Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDokumen24 halamanIntroduction To MicrobiologyNguyễn Ngọc NguyênBelum ada peringkat
- Jean-Claude Bertrand, Philippe Normand, Bernard Ollivier, Télesphore Sime-Ngando - Prokaryotes and Evolution-Springer International Publishing (2018)Dokumen401 halamanJean-Claude Bertrand, Philippe Normand, Bernard Ollivier, Télesphore Sime-Ngando - Prokaryotes and Evolution-Springer International Publishing (2018)Vianney BeraudBelum ada peringkat