Consumer Behavior: Definition: - What, Why, When, Where and Frequency of Buying
Diunggah oleh
harsha513950 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
15 tayangan28 halamanConsumer buying behavior and types of consumer buying behavior,5 step buyer decision process
Judul Asli
2010 COB
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniConsumer buying behavior and types of consumer buying behavior,5 step buyer decision process
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
15 tayangan28 halamanConsumer Behavior: Definition: - What, Why, When, Where and Frequency of Buying
Diunggah oleh
harsha51395Consumer buying behavior and types of consumer buying behavior,5 step buyer decision process
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 28
3-1
CONSUMER BEHAVIOR : DEFINITION
Consumer Behavior is the study of how
individuals, group and organizations
select, buy, use and dispose of goods,
services, ideas or experiences to satisfy
their needs and wants. (individuals &
households who buy goods and services
for personal consumption.)
To find
What,Why,When, Where and Frequency of
buying
3-2
Consumer Buying Behaviour: Key
Questions
3-3
Who is Important?
Most purchases individual confectionary,
beer, etc
Many decisions by group/family/couple -
(buying centre/decision making unit). There
are 5 roles
Initiator
Starts process, may gather information to aid decision
Influencer
Persuade others in group re the outcome of decision,
typically gathers information and tries to impose their choice
Decider
He/she who pays ultimate power of veto
Buyer
Person who conducts transaction
User
Consumer/user of the product
3-4
What are the choice criteria?
Technical
Reliability
Durability
Performance
Comfort
Taste
Convenience
Economic
Price
Value for money
Life time costs
Residual value
Running costs
Social
Personal
Status
Social
Belonging
Fashion
Self-Image
Ethics
Emotions
3-5
Day of the week? advertise toys on Saturday morning (pester
power) for the afternoon
Stay open on Sunday have the time to review cars, etc
Last minute?
Not buying it in Tescos, Ill buy it on the Kings Road?
It will look and sound cooler
Ill buy it online?
It will sound cooler
Ill buy it at the airport?
When do they buy?
Where do they buy?
3-6
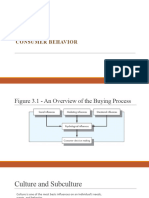
Model of Buyer Behavior
Marketing and
Other Stimuli
Buyers Black Box
Buyers Response
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Economic
Technological
Political
Cultural
Buyer
Characteristics
Buying
Decision
Process
Product Choice
Brand Choice
Dealer Choice
Purchase
Timing
Purchase
Amount
3-7
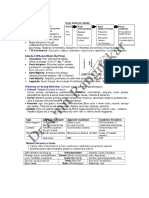
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Culture
Sub-
culture
Social
class
Social
Reference
groups
Family
Roles
and
status
Personal
Age and
life-cycle
Occupation
Economic
situation
Lifestyle
Personality
and
self-concept
Psycho-
logical
Motivation
Perception
Learning
Beliefs and
attitudes
Buyer
Cultural
3-8
Factors Affecting Consumer Behavior:
Culture
Culture
Most basic cause of a person's wants and
behavior.
Values, Perceptions, Wants & Behavior
Social Class
Societys relatively
permanent & ordered
divisions whose members
share similar values,
interests, and behaviors.
Measured by: Occupation,
Income, Education, Wealth
and Other Variables.
Subculture
Groups of people with
shared value systems
based on common life
experiences.
3-9
Groups
Membership
Reference
Factors Affecting Consumer Behavior:
Social
Family
Family of orientation
Family of procreation
Roles and Status
Social Factors
3-10
Reference Group
Primary Reference Group:
Membership Reference
Aspiration reference
Disclaimant reference
Avoidance Group
Secondary Reference Group:
Relation formal but less interaction
Religious ,Trade unions, professional groups
3-11
Factors Affecting Consumer Behavior:
Personal
Personal Influences
Age and Life Cycle
Stage
Occupation
Economic Situation
Lifestyle Identification
Activities, Behavior Opinions
Interests
Personality & Self-Concept
3-12
Psychological
Factors
Motivation
Perception
Learning
Beliefs and
Attitudes
Factors Affecting Consumer Behavior:
Psychological
3-13
Psychological Factors
Motivation
Driving force activities towards unfulfilled needs
and wants
Maslows Hierarchy of needs ( Physical, Safety,
Social,Esteem,Self actualization need )
Perception
Process of selecting ,organizing & interpreting
stimuli into meaningful thoughts & pictures
Learning
Experience
Builds beliefs and attitude towards a product.
3-14
Buying roles
Initiator
Influencer
Decider
Buyer
User
Maintainer
Disposer
3-15
Need Recognition
Information Search
Evaluation of Alternatives
Purchase Decision
Post-purchase Behavior
Buyer Decision Process
3-16
External Stimuli
TV advertising
Magazine ad
Radio slogan
Stimuli in the environment
Internal Stimuli
Hunger
Thirst
A persons normal needs
Need Recognition
Buyer Recognizes a Problem or Need
Step 1:Need Recognition
3-17
Family, friends, neighbors
Most effective source of
information
Advertising, salespeople
Receives most information
from these sources
Mass Media
Consumer-rating groups
Reports
Handling the product
Examining the product
Using the product
Personal Sources
Commercial Sources
Public Sources
Experiential Sources
Step 2: Information Search
3-18
Consumer May Use Careful
Calculations & Logical Thinking
Consumers May Buy on Impulse and
Rely on Intuition
Consumers May Make Buying Decisions
on Their Own.
Consumers May Make Buying Decisions
Only After Consulting Others.
Marketers Must Study Buyers to Find Out
How They Evaluate Brand Alternatives
Step 3: Evaluation of Alternatives
3-19
Purchase Intention
Desire to buy the most preferred brand
Purchase Decision
Brand,Location,Price,Payment,Support Services
Attitudes of
Others
Unexpected
Situational
Factors
Step 4:Purchase Decision
3-20
Consumers Expectations of
Products Performance
Dissatisfied Customer Satisfied Customer!
Products Perceived Performance
Cognitive Dissonance
Step 5 : Post Purchase Behavior
3-21
TOTAL
SET
AWARENESS
SET
CONSIDERATION
SET
CHOICE
SET
DECISION
E.g. Laptops,Mobiles,
Watches,Formal
Suits,Washing
Machine,LCD,Cameras
Sets involved in decision making
3-22
Types of Buying decision behavior
High
Involvement
Significant
Differences
Between brands
Few
Differences
Between brands
Low
Involvement
Complex
Buying
Behavior
Variety-
Seeking
Behavior
Dissonance-
Reducing Buying
Behavior
Habitual
Buying
Behavior
3-23
What is a Business Market?
Business Buyer Behavior refers to the
buying behavior of all the organizations
that buy goods and services for use in the
production of other products and services
that are sold, rented, or supplied to others.
The business market is huge and involves
many more rupees and items than do
consumer markets.
3-24
Difference
Organizational markets
More time
Buyers very few
More specialized and
customized service
High Quantity
Demand more fluctuating
Predominance of raw and
semi finished goods
Minimum intermediaries
Consumer markets
Less time for purchase
process
Higher no of buyers
Customization is tough
Low Quantity
Less fluctuating
Finished goods
Higher intermediaries
3-25
Difference
Consumer buying
behavior
Buy products for
personal, family or
households
No specialized skills and
any member can do it
Not particular about
satisfaction
Buy
Quality and price
Organizational buying
behavior
For further production,
usage in operating and to
resale to other consumers
Specialists
Exact specification
Prefer to lease
Delivery time , technical
assistance ,post service
3-26
Buying Decision process
3-27
Participants in the Business Buying
Process: The Buying Center
Buying Center
Users Gatekeepers
Buyers Deciders
Influencers
3-28
The buyer routinely reorders
something without any
modifications.
Straight Re-buy
Modified Re-buy
New Task
The buyer purchases a
product or service for the
first time.
The buyer wants to modify
product specifications,
prices, terms, or suppliers.
Buying Situations in organization
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Consumer and Business Buyer Behavior: Nathan GeorgeDokumen32 halamanConsumer and Business Buyer Behavior: Nathan GeorgeAjay Roshan P100% (1)
- Consumer Buyer Behavior and Analyzing CompetitionsDokumen38 halamanConsumer Buyer Behavior and Analyzing CompetitionsAbebaw AyeleBelum ada peringkat
- Spencer Tire PurchaseDokumen28 halamanSpencer Tire PurchaseJitendra Choudhary0% (2)
- Customer Buyer BehaviorDokumen3 halamanCustomer Buyer BehaviorLại Nguyễn Hoàng Phương VyBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Influencing Consumer BehaviourDokumen18 halamanFactors Influencing Consumer BehaviourjijuloveuBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4Dokumen21 halamanModule 4omsfadhlBelum ada peringkat
- Buyer Behaviour: The Individual, Risk and InvolvementDokumen22 halamanBuyer Behaviour: The Individual, Risk and InvolvementShaheer BokhariBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Behavior - SlidesDokumen46 halamanConsumer Behavior - SlidesMaria Christina Paredes ConcepcionBelum ada peringkat
- Buying Decision Making Process: - Basic Psychological Processes Important Role in Consumer's Buying DecisionDokumen14 halamanBuying Decision Making Process: - Basic Psychological Processes Important Role in Consumer's Buying DecisionAung Mon ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Amity Consumer BehaviorDokumen240 halamanAmity Consumer BehaviorAjit JainBelum ada peringkat
- CH-1 BB For ClassDokumen50 halamanCH-1 BB For ClassSarah MuktarBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Chap 5 Consumer Market and Buying BehaviorDokumen27 halamanMarketing Chap 5 Consumer Market and Buying Behaviorusama100% (1)
- Introduction To Marketing Management: Chapter 5 & 6Dokumen26 halamanIntroduction To Marketing Management: Chapter 5 & 6pakyashahBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer and Business Buyer Behaviour NotesDokumen7 halamanConsumer and Business Buyer Behaviour NotesSavannah Simone PetrachenkoBelum ada peringkat
- A Presentation On Consumer Decision Making ProcessDokumen23 halamanA Presentation On Consumer Decision Making ProcessKailash KhandeliaBelum ada peringkat
- One Definition: - Consumer BehaviorDokumen23 halamanOne Definition: - Consumer Behaviorsheetal2001Belum ada peringkat
- How Do Households Take Decisions On High Involvement & Low Involvement ProductsDokumen18 halamanHow Do Households Take Decisions On High Involvement & Low Involvement ProductsSreenandan NambiarBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 3 Study GuideDokumen17 halamanExam 3 Study Guide32bballgoBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Model of Consumer BehaviorDokumen41 halamanBasic Model of Consumer BehaviorRohit Kumar100% (1)
- Types of Customer and Customer PurchasingDokumen46 halamanTypes of Customer and Customer PurchasingrahulBelum ada peringkat
- Rural Consumer BehaviourDokumen24 halamanRural Consumer BehaviourAparna ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Research in Understanding Consumer BehaviourDokumen50 halamanRole of Research in Understanding Consumer Behaviouraqib_khan55Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 4: Buyer's BehaviourDokumen38 halamanUnit 4: Buyer's Behaviourअभिषेक रेग्मीBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 05 Understanding Consumer and Business Buyer BehaviorDokumen9 halamanChapter 05 Understanding Consumer and Business Buyer BehaviorLENA WOO XIAO HUIBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 Mkt501: Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviourDokumen44 halamanLecture 5 Mkt501: Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviourannahBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Research Process & Consumer Decision MakingDokumen50 halamanConsumer Research Process & Consumer Decision MakingGazal Atul SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Five: Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDokumen31 halamanChapter Five: Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorVeronica GnanasegaranBelum ada peringkat
- Information Search and EvaluationDokumen37 halamanInformation Search and EvaluationSanjay KhaDkaBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer BehaviorDokumen29 halamanConsumer BehaviorPuneetpal_Sing_6393Belum ada peringkat
- Business Buyer BehaviourDokumen7 halamanBusiness Buyer BehaviourKarthik RaghuramanBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDokumen22 halamanConsumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorCorey PageBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer BehaviourDokumen27 halamanConsumer BehaviourRahul SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- The Buying Decision ProcessDokumen30 halamanThe Buying Decision ProcessBirhanu DesalegnBelum ada peringkat
- Shopper PsychologyDokumen19 halamanShopper PsychologyAfifah MohdBelum ada peringkat
- Cunsumer Buying BehaviorDokumen48 halamanCunsumer Buying Behaviorsherifrafik7633Belum ada peringkat
- Consumer Behavior and Marketing StrategyDokumen42 halamanConsumer Behavior and Marketing Strategysaket2209Belum ada peringkat
- Marketing Management: Buyer BehaviourDokumen27 halamanMarketing Management: Buyer BehaviourAlagu RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer BehaviorDokumen23 halamanConsumer BehaviorArslan SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 2 - Marketing Environment System and Buyer BehaviorDokumen25 halamanUNIT 2 - Marketing Environment System and Buyer BehaviorAnjal ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- MKTG 3 Cons Buying BehDokumen55 halamanMKTG 3 Cons Buying BehSanket GangalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 MKT 422Dokumen23 halamanChapter 3 MKT 4222019863031Belum ada peringkat
- BOM1Dokumen9 halamanBOM1ashwini.swapjobBelum ada peringkat
- Approaches To Customer AnalysisDokumen29 halamanApproaches To Customer AnalysisSyed Maaz HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Module-1: Consumer Behaviour: Consumer Behavior Is The Process Involved WhenDokumen54 halamanModule-1: Consumer Behaviour: Consumer Behavior Is The Process Involved WhenlicopodicumBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Consumer MarketDokumen33 halamanChapter 5 Consumer MarkethhaiderBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-4Relationship Marketing, Consumer BehaviorDokumen33 halamanUnit-4Relationship Marketing, Consumer BehaviorSumaira KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDokumen23 halamanConsumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorArslan SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter ThreeDokumen32 halamanChapter ThreeAlemtsehay AbrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Decision Making Process & Characteristics of Industrial Markets Characteristics of Industrial MarketsDokumen26 halamanConsumer Decision Making Process & Characteristics of Industrial Markets Characteristics of Industrial MarketssagarBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Customer BehaviourDokumen56 halamanUnderstanding Customer BehaviourSameena SayedBelum ada peringkat
- Uganda Matrys Univeristy Consumer Behavior: BY John Tumwesigye 0772406097Dokumen47 halamanUganda Matrys Univeristy Consumer Behavior: BY John Tumwesigye 0772406097kasozi martinBelum ada peringkat
- BBA CH - 4 Buyers BehaviourDokumen29 halamanBBA CH - 4 Buyers BehaviourSuman Samal MagarBelum ada peringkat
- Organizational BuyingDokumen17 halamanOrganizational BuyingShri PanchavisheBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Consumer BehaviourDokumen34 halamanBasics of Consumer Behaviourlogan vBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Buying Process: Janet ItliongDokumen28 halamanConsumer Buying Process: Janet Itliongjanvill_19Belum ada peringkat
- Consumer MarketDokumen26 halamanConsumer MarketMutahar HayatBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneur Buying BehaviorsDokumen62 halamanEntrepreneur Buying Behaviorsnnyairis.skelBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction KLLDokumen13 halamanIntroduction KLLkashak5500Belum ada peringkat
- The New Selling IQ: Combining the Power of Buyer - Seller Intelligence to Optimize Results!Dari EverandThe New Selling IQ: Combining the Power of Buyer - Seller Intelligence to Optimize Results!Belum ada peringkat
- A Consumer’s Guide to Successfully Resolving Any DisputeDari EverandA Consumer’s Guide to Successfully Resolving Any DisputeBelum ada peringkat
- BrandDokumen2 halamanBrandharsha51395Belum ada peringkat
- Question Bank FormatDokumen45 halamanQuestion Bank Formatharsha51395Belum ada peringkat
- Indian IT and ITeS Industry Presentation 010709Dokumen77 halamanIndian IT and ITeS Industry Presentation 010709workosaurBelum ada peringkat
- Godavari Sugar Mills - Assocham CSR Case Study FormatDokumen18 halamanGodavari Sugar Mills - Assocham CSR Case Study Formatapi-3701467Belum ada peringkat
- Marketing ManagementDokumen58 halamanMarketing Managementharsha51395Belum ada peringkat
- Relationship MarketingDokumen17 halamanRelationship Marketingkaushik_ranjan_2Belum ada peringkat
- CobDokumen28 halamanCobharsha51395Belum ada peringkat
- Foucault and History The Lessons of A DisillusionDokumen23 halamanFoucault and History The Lessons of A DisillusionՍմբատ ՀովհաննիսյանBelum ada peringkat
- A Few Points On Effective WritingDokumen15 halamanA Few Points On Effective WritingValerie Marquez100% (5)
- Module 3 - The Artist Mindset in The Early GradesDokumen6 halamanModule 3 - The Artist Mindset in The Early Gradesjennifer cruz50% (2)
- Using Diagnostic Reading MeasuresDokumen6 halamanUsing Diagnostic Reading MeasuresRaquel Theresa FabelaBelum ada peringkat
- Cognitivedevelopmentofthepreschoolers1 141013225827 Conversion Gate01Dokumen40 halamanCognitivedevelopmentofthepreschoolers1 141013225827 Conversion Gate01Garcia MaevellBelum ada peringkat
- Haptic TechnologyDokumen29 halamanHaptic TechnologyRam KishoreBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Practice On Word Formation PDFDokumen0 halamanAdvanced Practice On Word Formation PDFKhiem Vuong100% (1)
- Indirect QuestionsDokumen15 halamanIndirect Questionsfounè diassanaBelum ada peringkat
- Clash of Royalties 2023 (Student Activity Form)Dokumen2 halamanClash of Royalties 2023 (Student Activity Form)Jennaliza AragoBelum ada peringkat
- VroomDokumen34 halamanVroomkemimeBelum ada peringkat
- Multi-GradeEducation Strategy Sector PlanDokumen28 halamanMulti-GradeEducation Strategy Sector PlanjessamaeBelum ada peringkat
- Social CognitionDokumen24 halamanSocial CognitionGrazielle Anne SancejaBelum ada peringkat
- 2023 Curriculum Implementation Wairoa SchoolDokumen9 halaman2023 Curriculum Implementation Wairoa SchoolZhang YolandaBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Tips For Improving Your English Speaking SkillsDokumen14 halaman10 Tips For Improving Your English Speaking Skillsnurulsafiani100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Classifying ObjectsDokumen7 halamanLesson Plan Classifying Objectsangeljazzleidel.salongaBelum ada peringkat
- A Systematic Review of Unsupervised Learning Techniques For Software Defect PredictionDokumen18 halamanA Systematic Review of Unsupervised Learning Techniques For Software Defect PredictionPRABHAKARANBelum ada peringkat
- Course Information Booklet Second Semester January - May 2022Dokumen18 halamanCourse Information Booklet Second Semester January - May 2022RomaBelum ada peringkat
- Logical FallaciesDokumen7 halamanLogical FallaciesIbrahima SakhoBelum ada peringkat
- S 2Dokumen12 halamanS 2api-406786743Belum ada peringkat
- Complexity and Healthcare - An Intro. - K. Sweeney, Et. Al., (Radcliffe, 2002)Dokumen204 halamanComplexity and Healthcare - An Intro. - K. Sweeney, Et. Al., (Radcliffe, 2002)Victor PonomariovBelum ada peringkat
- DLL - MTB 3 - Q2 - W9Dokumen2 halamanDLL - MTB 3 - Q2 - W9Claris MarisgaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment ReportDokumen3 halamanAssessment Reportapi-540101254Belum ada peringkat
- Sample Assessment - HamletDokumen3 halamanSample Assessment - Hamletapi-305114866Belum ada peringkat
- Cutsforth Standards ArtifactsDokumen8 halamanCutsforth Standards ArtifactsSarah CutsforthBelum ada peringkat
- August 2021 The Impact of Technology On Children UaDokumen2 halamanAugust 2021 The Impact of Technology On Children UaMesam JafriBelum ada peringkat
- Athira Innovative LessonDokumen7 halamanAthira Innovative Lessongeetha100% (1)
- Critical IncidentsDokumen14 halamanCritical IncidentsharryharryBelum ada peringkat
- Behavioural Finance Advantages and DisadvantagesDokumen2 halamanBehavioural Finance Advantages and DisadvantagesKartika Bhuvaneswaran NairBelum ada peringkat
- Family StressDokumen36 halamanFamily StressRaymonde Uy100% (1)
- The Role of Society and Culture in The Person's DevelopmentDokumen17 halamanThe Role of Society and Culture in The Person's DevelopmentJoseph Alvin PeñaBelum ada peringkat