Heating and Coolings
Diunggah oleh
Megan CollinsDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Heating and Coolings
Diunggah oleh
Megan CollinsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Heating and
Cooling
MS ANNEAR
Unit Description
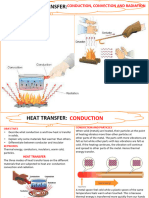
Heat Transfer: Conduction
Process by which thermal energy is
transferred from one place to another
Most significant in solids, important in liquids
and of lesser importance in gases
Materials that conduct readily are referred to
as good conductors and materials that
conduct heat poorly are referred to as
insulators
How?
Heat Transfer by molecular collisions
Kinetic Molecular Theory of matter (Particles in a solid are constantly
vibrating within the crystal structure and interact with neighbouring
particles)
If one part of a material is heated then the particles in that region
will vibrate more rapidly and transfer energy to neighbouring
particles.
Process is slow: mass of each particle is large and their vibrational
velocities are relatively low, therefore are slow to pass on their
vibrational energies.
Substance that purely rely on this method of conduction are likely to
be poor conductors: plastic, glass, wood, paper, ceramic and
concrete
How?
Heat transfer by free electrons
Metals and some other substances contain electrons that are not
involved in a particular chemical bond and are free to move
through the solid. These are referred to as delocalised.
These electrons have a very small mass compared to atoms and
even a small energy gain from heating will result in a very large fain
in velocity.
These delocalised electrons transfer heat energy throughout the
whole material very quickly.
Therefore good electrical conductors are also good heat
conductors.
Factors affecting thermal
conduction
The rate at which heat energy is transferred through any object will
depend upon the:
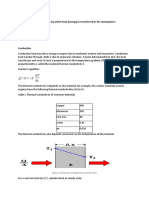
Temperature difference across material [T]
Thickness of material [L]
Surface area [A]
Nature of material (thermal conductivity) [k]
Thus heat transfer (energy per time) through a material is given by
=
A
Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat energy within a fluid (liquid or
gas).
If one part of the fluid is heated the material there will expand and
become less dense. The hotter material, being less dense, will rise
and the colder denser materials will tend to sink.
Even though liquids and gases are not good conductors they can
transfer heat quite rapidly through convection.
This circulation of a material due to convection, is called a
convection current.
Convection
What happens to the smoke once the candle is places underneath
the chimney/exit tube.
Explain by observation and by description of particles
Convection: Sea Breeze vs Land Breeze
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gM0d3fGew-0
Radiation
Common Knowledge that the earth is heated by the sun through
the suns radiation.
Heat energy usually transferred by action of particles.
Radiation represents a case where heat is transferred without the
movement of particles
Particles?
Radiation
Radiation represents a case where heat is transferred without the
movement of particles
Radiation is another expression for electromagnetic waves (which
include visible, ultraviolet and infrared light)
Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (c) and can be
focused, refracted and reflected
Radiation follows other wave-like phenomenon as when in contact
with an object radiation is partly reflected, partly transmitted and
partly absorbed.
The absorbed part transfers heat energy to the absorbing object
causing it to rise in temp.
Radiation is emitted from all objects who temp is above absolute
zero (-273
0
) Thermograph / heat signature
Radiation: Emission and Absorption
All objects emit some radiation, but all do not emit or absorb at
same rates. Eg. Matt black surfaces emit radiant energy at a greater
rate than shiny, light coloured surfaces.
Black matt surface heat up faster than shiny light surfaces. Black
matt surfaces also cool down faster. Eg. Car radiator painted black
to increase emission of energy collected from car engine by
conduction and convection.
Other factors that affect rate of both emission and absorption of
radiation:
Surface area
Temperature
Wavelength of incident radiation
Surface colour and texture (emissivity e, varies in between 0 and 1)
1:better emission and absorption (black rough) 0: poor emission and
absorption (white shiny)
6.8 and Set 11 Review
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Heat Transfer ProjectDokumen68 halamanHeat Transfer ProjectsubratorajBelum ada peringkat
- Prp-1018 Thermal & Moisture Transport Database For Common BLDG & Insulating MaterialsDokumen229 halamanPrp-1018 Thermal & Moisture Transport Database For Common BLDG & Insulating Materialsjdietz4Belum ada peringkat
- CMO 9, S. 2008 - Approved - PS For BSMEDokumen17 halamanCMO 9, S. 2008 - Approved - PS For BSMEzakibrant23100% (1)
- 1538 2000 PDFDokumen27 halaman1538 2000 PDFRafaelBelum ada peringkat
- Astm D572 PDFDokumen4 halamanAstm D572 PDFPriyadarshini KrishnaswamyBelum ada peringkat
- ME2121-2 Lab ReportDokumen14 halamanME2121-2 Lab ReportZu Jian LeeBelum ada peringkat
- 06 Thermochemistry Lecture NotesDokumen10 halaman06 Thermochemistry Lecture Notesarora_bbBelum ada peringkat
- HT Lecture Notes - 0Dokumen41 halamanHT Lecture Notes - 0SUPRADEEP GBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationDokumen29 halamanModule 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationVishnupriya B.Belum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Chapter One and TwoDokumen74 halamanHeat Transfer Chapter One and TwoTariku Negash100% (2)
- Heat Transfer Chapter OneDokumen36 halamanHeat Transfer Chapter OneteddiyfentawBelum ada peringkat
- Conduction, Convection and RadiationDokumen6 halamanConduction, Convection and RadiationKyaw Win TunBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 Transmission of HeatDokumen18 halamanLecture 4 Transmission of Heatdinesh11rBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Chapter One and Two-171102112832Dokumen74 halamanHeat Transfer Chapter One and Two-171102112832shouxun JiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Basic Concepts of Heat TransferDokumen27 halamanIntroduction and Basic Concepts of Heat TransferAbishek GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Modes of Heat TransferDokumen6 halamanModes of Heat TransferfaisalBelum ada peringkat
- There Are Three Mechanisms by Which Heat (Energy) Is Transferred in The AtmosphereDokumen3 halamanThere Are Three Mechanisms by Which Heat (Energy) Is Transferred in The Atmospheremohd firdaus bin ibrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Interface Mass TraDokumen26 halamanInterface Mass TraWahid AliBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer: From (Non-Conventional Energy Sources (OE-ME 701D) Continuous Assessment 2 (CA 2)Dokumen44 halamanHeat Transfer: From (Non-Conventional Energy Sources (OE-ME 701D) Continuous Assessment 2 (CA 2)Prabhat RoutBelum ada peringkat
- 2.3 Thermal ProcessesDokumen6 halaman2.3 Thermal ProcesseshaiderBelum ada peringkat
- HT - Unit 1 - Final.Dokumen40 halamanHT - Unit 1 - Final.Chanti DasariBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYDokumen150 halamanChemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYGustavo Gonzalez ServaBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Introduction and Basic Concepts PDFDokumen18 halaman1-Introduction and Basic Concepts PDFsara sofeaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.0 HeatTransfer - Intro On Conduction Convection RadiationDokumen24 halaman1.0 HeatTransfer - Intro On Conduction Convection RadiationGharamBelum ada peringkat
- Secondary Two Science Worksheet Types of Heat Transfer 31jan2015Dokumen2 halamanSecondary Two Science Worksheet Types of Heat Transfer 31jan2015SoniaAlexBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter OneDokumen16 halamanIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter Oneabdi dejeneBelum ada peringkat
- Physics STPM HEAT TRANSFERDokumen23 halamanPhysics STPM HEAT TRANSFERRed Jagung Fish100% (3)
- Heat TransferDokumen47 halamanHeat TransferMuthukrishagalsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Heat Transfer and Basic Concepts: Faculty of Chemical EngineeringDokumen19 halamanChapter 1: Introduction To Heat Transfer and Basic Concepts: Faculty of Chemical EngineeringSunita JobliBelum ada peringkat
- Course: Heat Transfer (MEC301)Dokumen13 halamanCourse: Heat Transfer (MEC301)wonderBelum ada peringkat
- CHE F241 Lecture 1-8 - 01 - 2019Dokumen50 halamanCHE F241 Lecture 1-8 - 01 - 2019Vaibhav SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Modes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationDokumen63 halamanModes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationKelly ObrienBelum ada peringkat
- Activity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferDokumen7 halamanActivity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferSquidward TentaclesBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment #1Dokumen8 halamanExperiment #1Talha AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Alexis Muhirwa Thermodynamics HandoutsDokumen115 halamanAlexis Muhirwa Thermodynamics HandoutsAlexis MUHIRWABelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 7Dokumen10 halamanLesson 7Stephen Maina NjorogeBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer 2Dokumen24 halamanHeat Transfer 2AshMere MontesinesBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Is The Transition ofDokumen11 halamanHeat Transfer Is The Transition of3m3hBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Mechanisms 2022Dokumen25 halamanHeat Transfer Mechanisms 2022PABLO VICENTE REBOLLOSO SALINASBelum ada peringkat
- HT Lecture 01 Modes of HeatTransferDokumen29 halamanHT Lecture 01 Modes of HeatTransferYashaswiniBelum ada peringkat
- Scha1301 - 033251 1 65Dokumen65 halamanScha1301 - 033251 1 65danifexBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicssDokumen5 halamanPhysicsschionumaraliaBelum ada peringkat
- Heat 1 PDFDokumen22 halamanHeat 1 PDFHendrik Ongki S 921224Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass TransferDokumen40 halamanIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass TransferHugo MartinsBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal PropertiesDokumen27 halamanThermal PropertiesLouise UmaliBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment: 1. ConductionDokumen16 halamanAssignment: 1. ConductionPradnya PariBelum ada peringkat
- Heat ConductionDokumen4 halamanHeat ConductionImtiaz Alam0% (1)
- L4 Heat Transfer Mechanisms PDFDokumen26 halamanL4 Heat Transfer Mechanisms PDFgebreslassie gereziherBelum ada peringkat
- Comprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementDokumen33 halamanComprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementAhmed MobarkiBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer (Introduction) : For Chemical EngineersDokumen12 halamanHeat Transfer (Introduction) : For Chemical EngineersAbhishek PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Class 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferDokumen15 halamanClass 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferShadmanSakiefHridoyBelum ada peringkat
- CHEE 3101 Heat Transfer-HODokumen109 halamanCHEE 3101 Heat Transfer-HO080 Priyanshu mishraBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes - Heat and Mass TransferDokumen371 halamanLecture Notes - Heat and Mass Transferakzh100% (3)
- Chap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalDokumen25 halamanChap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalSBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 FinaleDokumen16 halamanChapter 1 Finalemuhammad izzulBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer: Introduction To ConductionDokumen17 halamanHeat Transfer: Introduction To Conductionنزار الدهاميBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Rwanda PolytechnicsDokumen78 halamanEngineering Thermodynamics - Rwanda PolytechnicsAlexis MUHIRWABelum ada peringkat
- Submitted By:: Amr Ibrahem Abd Elrazek Okasha / Yousif Mohamed Yousif Bayoumy / Mohamed SamerDokumen11 halamanSubmitted By:: Amr Ibrahem Abd Elrazek Okasha / Yousif Mohamed Yousif Bayoumy / Mohamed SamerAmr OkashaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Conduction?Dokumen9 halamanWhat Is Conduction?Ali Usman AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Conduction, Convection, RadiationDokumen64 halamanConduction, Convection, RadiationMuhammad Iqbal Rasyidi0% (1)
- Heat VsDokumen9 halamanHeat VsRenuga77Belum ada peringkat
- Week: 3: Mechanisms of Heat TransferDokumen19 halamanWeek: 3: Mechanisms of Heat TransferAhmad AimanadhifBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture No 1Dokumen75 halamanLecture No 1Raza AnsariBelum ada peringkat
- Heatvs Tem2Dokumen18 halamanHeatvs Tem2Ross Adrales GeleraBelum ada peringkat
- Cables, Conduits and Trunking: 4.1 - Cable Insulation Materials 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6Dokumen40 halamanCables, Conduits and Trunking: 4.1 - Cable Insulation Materials 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6aryo bimo surya putraBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Pengantar Reaktor KimiaDokumen16 halaman1 - Pengantar Reaktor KimiaRyrynArianyBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDokumen17 halamanIntroduction To Thermodynamicsfruitsok81Belum ada peringkat
- HEAT Class 7Dokumen50 halamanHEAT Class 7Raynaah100% (1)
- WS4530-En Risk Analysis For CORRESIC SE Type Heat Exchanger According To PED 2014-68-EUDokumen2 halamanWS4530-En Risk Analysis For CORRESIC SE Type Heat Exchanger According To PED 2014-68-EUViajante_santosBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Fluid Heating SolutionsDokumen8 halamanThermal Fluid Heating SolutionsJosé Pedro MagalhãesBelum ada peringkat
- Home Assignment-7 - (Assignment Problems)Dokumen2 halamanHome Assignment-7 - (Assignment Problems)Rounak MajumdarBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Simulation and Practical Setup of Melting of Phase Change Material For Heat Storage Application With Effect of Mechanical VibrationDokumen26 halamanNumerical Simulation and Practical Setup of Melting of Phase Change Material For Heat Storage Application With Effect of Mechanical VibrationAditya PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Iot Based Mini Refrigerator Using Pelter Module: A Project ReportDokumen61 halamanIot Based Mini Refrigerator Using Pelter Module: A Project ReportL02 ARUN ABelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Formula: Thursday, 18 March 2021 10:32 PMDokumen35 halamanHeat Transfer Formula: Thursday, 18 March 2021 10:32 PMJAN NESRALI YUMULBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Constructional Steel Research: Karlo Sele Š, Mato Peri Ć, Zdenko Tonkovi ĆDokumen9 halamanJournal of Constructional Steel Research: Karlo Sele Š, Mato Peri Ć, Zdenko Tonkovi ĆasdfBelum ada peringkat
- Kinetics and Thermo by Amarendra VijayDokumen257 halamanKinetics and Thermo by Amarendra VijayRamBelum ada peringkat
- Work Sheet 1 2022Dokumen6 halamanWork Sheet 1 2022Fikadu GonfaBelum ada peringkat
- 6.12 Platform and Pipeline Pressure Let Down System Design Philosophy PDFDokumen20 halaman6.12 Platform and Pipeline Pressure Let Down System Design Philosophy PDFDonald.KBelum ada peringkat
- JEE Advanced 2022 Physics AnalysisDokumen1 halamanJEE Advanced 2022 Physics AnalysisDaksh KhandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- JSS 0256-01Dokumen149 halamanJSS 0256-01jagadi582895100% (3)
- Design of Liquid Piston Stirling EngineDokumen62 halamanDesign of Liquid Piston Stirling Enginechaitanyaamin100% (1)
- Tutorial PTT 108 Material and Energy Balance: ID = Inner diameter = 1-in. Volume flowrate = 3.00 gal/min A =πrDokumen6 halamanTutorial PTT 108 Material and Energy Balance: ID = Inner diameter = 1-in. Volume flowrate = 3.00 gal/min A =πrMohd FaizBelum ada peringkat
- Rotary Screw Compressors CSD / CSDX Series: With The World-Renowned SIGMA PROFILEDokumen11 halamanRotary Screw Compressors CSD / CSDX Series: With The World-Renowned SIGMA PROFILEВасилий ЗотовBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 2 (A)Dokumen3 halamanTutorial 2 (A)Damien Marley100% (1)
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDokumen44 halamanLecture 1 IntroductionAlex HebertBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal PhysicsDokumen184 halamanThermal Physicskumarvaibhav123Belum ada peringkat
- Second Term SS1 PhysicDokumen23 halamanSecond Term SS1 PhysicADEYI KAYODE SAMUELBelum ada peringkat
- Hamid2018 PDFDokumen48 halamanHamid2018 PDFАрсенийBelum ada peringkat