FIB Quizlet - Autonomic Cardiac Regulation
Diunggah oleh
pr3tt1Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
FIB Quizlet - Autonomic Cardiac Regulation
Diunggah oleh
pr3tt1Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
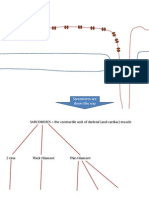
ATP
Pacemaker Cell
1 2
3
cAMP
GDP
GTP
cAMP
cAMP
cAMP
4
5
6
7
8
Na
+
Sympathetic Regulation of Cardiac
Pacemaker Cells
Effect: ____?_____ heart rate
1. ______?______ sympathetic neurons (short) have cell bodies in the
_____?____of spinal cord grey matter between the _?_and _?_ vertebrae.
2. At the ___?____ ganglia, they release ______?______ onto ___?____ ACh
receptors (nAChR) on _______?_______ sympathetic neurons.
3. These neurons (long) release ________?________ onto cardiac
pacemaker cells.
4. NE binds to adrenergic ____?_____.
5. The ______?______ that associates with this GPCR has an alpha subunit
called _____?____. GDP is swapped for __?__. The subunit has no role.
6. The activated G
s
stimulates ____?______, causing ___?___ levels to rise.
7. ____ binds to ___?__. More occupied binding sites on HCN means an
increased probability of HCN ____?____.
8. Increased _____?____ causes the slope of the ____?_____ to become
_____?_____, meaning we get to threshold faster, meaning our heart rate
will ____?____.
Pacemaker Cell
1
2
3
GDP
GTP
4
5
7 Na
+
8 K
+
Parasympathetic Regulation of Cardiac
Pacemaker Cells
Effect: _____?______ heart rate
1. ________?______ parasympathetic neurons (long) have cell bodies
in the ____?_____, in the _______?__________.
2. In the wall of the heart, at the parasympathetic ____?_____ ganglion,
they release _______?______ onto nicotinic receptors (nAChR) on
________?______ parasympathetic neurons.
3. These neurons (short) release _____?_____ onto cardiac pacemaker cells.
4. ACh binds to ________?_______ GPCR.
5. The ______?______ that associates with this GPCR has an alpha subunit
called ________?________. __?__ is swapped for ___?___.
6. The activated G
i
____?____ adenylyl cyclase, causing no increase in
____?____.
7. Very little of it binds to ___?____ , which means a decreased probability
of HCN _____?_____. Low ______?______ causes the slope of the ramp
potential to become ____?_____, meaning we take longer to reach
threshold, meaning our heart rate _____?_____.
8. Additionally, the subunit can associate with inward rectifying K+
channels (GIRK), facilitating _____?_____ and driving the membrane
potential even further from threshold.
6
Answers
Spoiler Alert!
ATP
Pacemaker Cell
1 2
3
cAMP
GDP
GTP
cAMP
cAMP
cAMP
4
5
6
7
8
Na
+
Sympathetic Regulation of Cardiac
Pacemaker Cells
Effect: Increase heart rate
1. Preganglionic sympathetic neurons (short) have cell bodies in the lateral
horn of spinal cord grey matter between the T1 and L3 vertebrae.
2. At the sympathetic chain ganglia, they release acetylcholine (ACh) onto
nicotinic ACh receptors (nAChR) on postganglionic sympathetic neurons.
3. Postganglionic sympathetic neurons (long) release norepinephrine (NE)
onto cardiac pacemaker cells.
4. NE binds to adrenergic GPCR.
5. The GTP-binding protein that associates with this GPCR has an alpha
subunit called G
s
(s = stimulatory). GDP is swapped for GTP. The
subunit has no role.
6. The activated G
s
stimulates adenylyl cyclase, causing cAMP levels to rise.
7. cAMP binds to HCN. More occupied cAMP binding sites on HCN means an
increased probability of HCN opening.
8. Increased sodium influx causes the slope of the ramp potential to become
steeper, meaning we get to threshold faster, meaning our heart rate will
increase.
Pacemaker Cell
1
2
3
GDP
GTP
4
5
7 Na
+
8 K
+
Parasympathetic Regulation of Cardiac
Pacemaker Cells
Effect: Decrease heart rate
1. Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons (long) have cell bodies
in the brainstem, in the motor nucleus of CN X (vagus nerve).
2. In the wall of the heart, at the parasympathetic cardiac ganglion, they
release acetylcholine (ACh) onto nicotinic ACh receptors (nAChR) on
postganglionic parasympathetic neurons.
3. Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons (short) release ACh onto cardiac
pacemaker cells.
4. ACh binds to muscarinic GPCR.
5. The GTP-binding protein that associates with this GPCR has an alpha
subunit called G
i
(i = inhibitory). GDP is swapped for GTP.
6. The activated G
i
inhibits adenylyl cyclase, causing no increase in cAMP.
7. Very little cAMP binds to HCN. Fewer occupied cAMP binding sites on HCN
means a decreased probability of HCN opening. Low sodium permeability
causes the slope of the ramp potential to become less steep, meaning we
take longer to reach threshold, meaning our heart rate decreases.
8. Additionally, the subunit can associate with inward rectifying K+
channels (GIRK), facilitating K+ efflux and driving the membrane potential
even further from threshold.
6
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Brain & Spinal CordDokumen1 halamanBrain & Spinal Cordpr3tt1Belum ada peringkat
- Dates To Remember: Aurora Quest K-8Dokumen7 halamanDates To Remember: Aurora Quest K-8pr3tt1Belum ada peringkat
- Writing Assignment 4Dokumen1 halamanWriting Assignment 4pr3tt1Belum ada peringkat
- Writing Assignment #2 (Unit I, Module 2) PSY210 - Psychology of The Individual in ContextDokumen1 halamanWriting Assignment #2 (Unit I, Module 2) PSY210 - Psychology of The Individual in Contextpr3tt1Belum ada peringkat
- Neuromuscular Synapse and SarcomeresDokumen4 halamanNeuromuscular Synapse and Sarcomerespr3tt1Belum ada peringkat
- Day Times (Mountain Standard) Location Tutors: Summer 2014 Tutor Schedule For BMS 300Dokumen1 halamanDay Times (Mountain Standard) Location Tutors: Summer 2014 Tutor Schedule For BMS 300pr3tt1Belum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Osmosis High-Yield Physiology - Medicalstudyzone - Com (Sürüklenen)Dokumen87 halamanOsmosis High-Yield Physiology - Medicalstudyzone - Com (Sürüklenen)Dilay MercimekBelum ada peringkat
- HIGH CENTERS DR. BARBON and DR VILA 1Dokumen15 halamanHIGH CENTERS DR. BARBON and DR VILA 1Yami C.Belum ada peringkat
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Test Bank DownloadDokumen24 halamanHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Test Bank DownloadVeronica Mayhew100% (20)
- Sns vs. Ans: Somatic Nervous System (SNS)Dokumen20 halamanSns vs. Ans: Somatic Nervous System (SNS)dave_1128Belum ada peringkat
- Bio Sci QuestionsDokumen45 halamanBio Sci QuestionsAiza BaleñaBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Sistem Saraf ManusiaDokumen6 halamanSoalan Sistem Saraf ManusiaRabiatul AdawiyyahBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation (Final)Dokumen35 halamanCase Presentation (Final)Denie BoyonasBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular Accident: "A Case Study Presentation"Dokumen35 halamanCerebrovascular Accident: "A Case Study Presentation"Kristine YoungBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Study On MigraineDokumen35 halamanA Case Study On MigraineRitu ShewaniBelum ada peringkat
- 4-TOPICAL DIAGNOSIS-clinical AnatomyDokumen61 halaman4-TOPICAL DIAGNOSIS-clinical AnatomyMuhammad SyauqadBelum ada peringkat
- Naval StudiesDokumen106 halamanNaval StudiesPhil InkleyBelum ada peringkat
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDokumen50 halamanPeripheral Nervous SystemaveryBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System-2022-23 Asi̇stDokumen101 halamanNervous System-2022-23 Asi̇stYiğit GündüzBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology TestDokumen10 halamanPhysiology TestGanta ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen8 halamanHuman Anatomy and Physiologyzairis21Belum ada peringkat
- Forward Head Posture Affects Your BrainDokumen4 halamanForward Head Posture Affects Your Brainchandni saxenaBelum ada peringkat
- BPT First Year Syllabus Rabindranath Tagore UniversityDokumen33 halamanBPT First Year Syllabus Rabindranath Tagore Universitysubhu7678Belum ada peringkat
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDokumen13 halamanAutonomic Nervous SystemSreejesh Rk100% (1)
- #05 Autonomic Pharmacology v2Dokumen122 halaman#05 Autonomic Pharmacology v2tasnemaldaherBelum ada peringkat
- Albert Ellis-The Art and Science of LoveDokumen292 halamanAlbert Ellis-The Art and Science of Loveinnersensation100% (3)
- Pharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Dokumen166 halamanPharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Adimera TsehayeBelum ada peringkat
- FINALSDokumen19 halamanFINALSOdyBelum ada peringkat
- B SC Nursing Syllabus INC PDFDokumen183 halamanB SC Nursing Syllabus INC PDFsohini bhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Dokumen7 halamanChapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Krisha AvorqueBelum ada peringkat
- Acidity Theory of AtherosclerosisDokumen46 halamanAcidity Theory of Atherosclerosissecretary6609Belum ada peringkat
- Hes 006 Term 2Dokumen18 halamanHes 006 Term 2Crishel Anne Cristobal100% (1)
- Nervous System CompleteDokumen21 halamanNervous System CompleteChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangBelum ada peringkat
- Meningitis (Deadly Diseases and Epidemics) (PDFDrive)Dokumen121 halamanMeningitis (Deadly Diseases and Epidemics) (PDFDrive)Islamiyatul Hayati MiswanBelum ada peringkat
- Body CoordinationDokumen17 halamanBody CoordinationHAMIDAH BINTI JAAFAR MoeBelum ada peringkat
- FINALS NCM 106 Lesson 1 Part 1 Drugs Acting in The Central and Peripheral Nervous System Week 1Dokumen4 halamanFINALS NCM 106 Lesson 1 Part 1 Drugs Acting in The Central and Peripheral Nervous System Week 1Rayanna MaligaBelum ada peringkat