Edited Presentation For Bipv System
Diunggah oleh
dt_chopra64530 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
72 tayangan7 halamanPhotovoltaics directly convert sunlight into electricity using solar panels made of photovoltaic cells. Building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) incorporate solar cells into building materials like the roof or facade. A BIPV system simultaneously generates electricity and serves as part of the building envelope. It is estimated that nearly 50% of global energy demand is from buildings, so BIPV helps reduce this consumption by generating power on-site.
Deskripsi Asli:
Edited Presentation for Bipv System
Judul Asli
Edited Presentation for Bipv System
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniPhotovoltaics directly convert sunlight into electricity using solar panels made of photovoltaic cells. Building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) incorporate solar cells into building materials like the roof or facade. A BIPV system simultaneously generates electricity and serves as part of the building envelope. It is estimated that nearly 50% of global energy demand is from buildings, so BIPV helps reduce this consumption by generating power on-site.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
72 tayangan7 halamanEdited Presentation For Bipv System
Diunggah oleh
dt_chopra6453Photovoltaics directly convert sunlight into electricity using solar panels made of photovoltaic cells. Building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) incorporate solar cells into building materials like the roof or facade. A BIPV system simultaneously generates electricity and serves as part of the building envelope. It is estimated that nearly 50% of global energy demand is from buildings, so BIPV helps reduce this consumption by generating power on-site.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Definitions
1. Photovoltaics(PV) is a method
ofgenerating
electrical
powerby
convertingsolar radiationintodirect
currentelectricityusingsemiconducto
rsthat exhibit thephotovoltaic effect.
2. Photovoltaic
power
generation
employssolar panelscomposed of a
number ofsolar cellscontaining a
photovoltaic material.
3. The direct conversion of sunlight to
electricity occurs without any moving
parts or environmental emissions
during operation.
1. Solar cells produce direct current
electricity from sun light which can be
used to power equipment or to recharge
a battery.
2. When more power is required than a
single cell can deliver, cells are
electrically connected together to form
photovoltaic modules, or solar panels.
3. Photovoltaic
power
capacity
is
measured as maximum power output
under standardized test conditions (STC)
in "Wp" (Watts peak).
4. The actual power output at a particular
point in time may be less than or
greater than this standardized, or
"rated,"
value,
depending
on
1. Cells require protection from the
environment and are usually packaged
tightly behind a glass sheet.
2. Solar cells can be incorporated into the
faade of a building, complementing or
replacing traditional view or spandrel
glass.
3. Photovoltaics may be incorporated into
awnings and saw-tooth designs on a
building faade. These increase access
to direct sunlight while providing
additional architectural benefits such as
passive shading.
4. Photovoltaics can also be used in
roofing systems & in skylight systems
Building Integrated Photo Voltaic
(BIPV)
1. Building Integrated Photo Voltaic
(BIPV) refers to photovoltaic cells
and
modules
which
can
be
integrated as part of the building
structure, and therefore can replace
conventional
building
materials,
rather
than
being
installed
afterwards.
2. A Building Integrated Photovoltaics
(BIPV) system consists of integrating
photovoltaics modules into the
building envelope, such as the roof
or the faade. By simultaneously
serving
as
building
envelope
material and power generator.
1. A Building Integrated Photovoltaics
(BIPV) system consists of integrating
photovoltaics modules into the
building envelope, such as the roof
or the faade. By simultaneously
serving
as
building
envelope
material and power generator.
2. Buildings are major consumers of
energy
in
their
construction,
operation and maintenance.
3. It is estimated that almost 50per
cent of the global energy demand is
due to buildings.
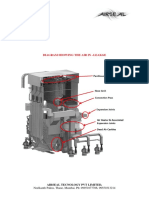
A complete BIPV system includes:
the PV modules (which might be thin-film or
crystalline, transparent, semi-transparent, or opaque);
a charge controller, to regulate the power into and out
of the battery storage bank (in stand-alone systems);
a power storage system, generally comprised of the
utility grid in utility-interactive systems or, a number
of batteries in stand-alone systems;
power conversion equipment including an inverter to
convert the PV modules' DC output to AC compatible
with the utility grid;
backup power supplies such as diesel generators
(optional-typically employed in stand-alone systems);
and
appropriate support and mounting hardware, wiring,
and safety disconnects.
PV ROOF SLATE MODULE
SPECIFICATION
STC Standard Test Conditions:
1000 W/m2 , 25 C solar cell temperature.
PTC PVUSA Test Conditions:
1000 W/m2, 20 C ambient and 1 m/s wind speed.
NOCT - Nominal Operating Cell Temperature [C]:
cell temperature under 800 W/ m2, 20 C air temperature , 1m/s
wind
speed, with open-circuited modules installed in an open rack
configuration
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Projectreport REDokumen15 halamanProjectreport REUnzillahBelum ada peringkat
- Anupam Vinay Surin 12PS05F P & Es, NitkDokumen20 halamanAnupam Vinay Surin 12PS05F P & Es, NitkchethanBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2Dokumen33 halamanModule 2Vibin NivasBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On Solar Module Manufacturing Unit (250-300 Mw/annum)Dokumen12 halamanProject Report On Solar Module Manufacturing Unit (250-300 Mw/annum)EIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers50% (2)
- Chapter 2 Solar PowerDokumen112 halamanChapter 2 Solar PowerBewnet GetachewBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter OneDokumen36 halamanChapter OneStanleyBelum ada peringkat
- How A PV System Works - pdf-20200211100803465Dokumen9 halamanHow A PV System Works - pdf-20200211100803465ahmed abusnoubarBelum ada peringkat
- PHOTOVOLTAICSDokumen27 halamanPHOTOVOLTAICSbrian otienoBelum ada peringkat
- CH 5 PDFDokumen24 halamanCH 5 PDFМихаил МироновBelum ada peringkat
- CH 5Dokumen24 halamanCH 5Михаил МироновBelum ada peringkat
- CH 5 PDFDokumen24 halamanCH 5 PDFAhmed MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- SDPV31306Dokumen65 halamanSDPV31306Mr. K.S. Raghul Asst Prof MECHBelum ada peringkat
- Fiche 4 2 Solar Photovoltaic PDFDokumen18 halamanFiche 4 2 Solar Photovoltaic PDFhitosnapBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Sizing of Stand Alone Solar Power SystemDokumen6 halamanDesign and Sizing of Stand Alone Solar Power Systemनिपुण कुमार100% (1)
- Solar Cell System Design-2Dokumen12 halamanSolar Cell System Design-2spotifyladderBelum ada peringkat
- PV-Wind Hybrid SystemsDokumen24 halamanPV-Wind Hybrid SystemssahitBelum ada peringkat
- SDPV31306Dokumen65 halamanSDPV31306bdsisira100% (1)
- Training Module Photovoltaic Project Analysis: Clean Energy Project Analysis Course Speaker'S NotesDokumen14 halamanTraining Module Photovoltaic Project Analysis: Clean Energy Project Analysis Course Speaker'S NotespikermiBelum ada peringkat
- TH - EnglishDokumen87 halamanTH - EnglishBacamarteBelum ada peringkat
- Inspeccion Sistema SolarDokumen8 halamanInspeccion Sistema SolarManuel TorijaBelum ada peringkat
- Photovoltaics (PV) : Solar ElectricityDokumen2 halamanPhotovoltaics (PV) : Solar ElectricityDaisy100% (1)
- Applications of Solar CellDokumen5 halamanApplications of Solar CellVenkatappa Rao TumuBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Cell TechnologiesDokumen7 halamanSolar Cell TechnologiesAditya AthimoolamBelum ada peringkat
- Peres Unit 3Dokumen86 halamanPeres Unit 3ulaganathanBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Technology: Seminar ContentsDokumen19 halamanSolar Technology: Seminar ContentsObichere OnyekachiBelum ada peringkat
- Photovoltaic Module: Application in BuildingsDokumen2 halamanPhotovoltaic Module: Application in Buildingssusmita sethiBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Solar Electric System With Its Various ComponentsDokumen7 halamanTypes of Solar Electric System With Its Various ComponentsNgoc Thach PhamBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Sizing of Solar Photovoltaic Systems R2Dokumen125 halamanDesign and Sizing of Solar Photovoltaic Systems R2Andrei TaranuBelum ada peringkat
- 22661-RET Notes-UNIT 02Dokumen25 halaman22661-RET Notes-UNIT 02jayeshdeore398Belum ada peringkat
- Photovoltaic CellDokumen17 halamanPhotovoltaic CellKams Parmar100% (1)
- The Fundamentals of Photovoltaic SystemsDokumen5 halamanThe Fundamentals of Photovoltaic SystemsrajuanthatiBelum ada peringkat
- Power Point Presentation On SOLAR POWER BASED UPSDokumen30 halamanPower Point Presentation On SOLAR POWER BASED UPSrasoashley50% (6)
- 3.1 Uee2521 RRPDokumen36 halaman3.1 Uee2521 RRPmohammad2110959Belum ada peringkat
- PV-Wind Hybrid SystemsDokumen24 halamanPV-Wind Hybrid Systemsrihatrivedi_069Belum ada peringkat
- A10020115 KTI AJER InternasionalDokumen15 halamanA10020115 KTI AJER Internasionalarief ndartoBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Charge Controller Using MicrocontrollerDokumen8 halamanSolar Charge Controller Using MicrocontrollerNikhil PottabathiniBelum ada peringkat
- Photo Voltaic SeDokumen3 halamanPhoto Voltaic SeGani LalamBelum ada peringkat
- Design & Sizing of Stand-Alone Solar Power Systems A House IraqDokumen7 halamanDesign & Sizing of Stand-Alone Solar Power Systems A House IraqHamidBelum ada peringkat
- Solar PanelDokumen101 halamanSolar PanelHarshvardhan Upadhyay100% (1)
- Design of A 50 KW Solar PV Rooftop SystemDokumen9 halamanDesign of A 50 KW Solar PV Rooftop SystemvmramakrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- ChaptersDokumen47 halamanChaptersAitha DeepakBelum ada peringkat
- History of Solar PowerDokumen3 halamanHistory of Solar PowersmshivaBelum ada peringkat
- Solar PV Project ReportDokumen19 halamanSolar PV Project Reportpriyanka chaudhary67% (18)
- Design and Sizing of A Stand-Alone Solar Power Systems For A House in IraqDokumen7 halamanDesign and Sizing of A Stand-Alone Solar Power Systems For A House in IraqLuis Perez Marquez100% (1)
- Group3-SECT W.answersDokumen44 halamanGroup3-SECT W.answersJustino BalaneBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Panel: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDokumen18 halamanSolar Panel: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchEr Dinesh TambeBelum ada peringkat
- EsquivelVilchisA TermoApl 36 PhotovoltaicSystem Nov152014Dokumen9 halamanEsquivelVilchisA TermoApl 36 PhotovoltaicSystem Nov152014EsquivelAndiieBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Electric Photovoltaic Modules Photovoltaic (PV) PowerDokumen13 halamanSolar Electric Photovoltaic Modules Photovoltaic (PV) PowerJboar TbenecdiBelum ada peringkat
- PV Farm Report NotesDokumen5 halamanPV Farm Report NoteshappyBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Activity Sheet No. 3: Deass-Iid-H-50)Dokumen7 halamanLearning Activity Sheet No. 3: Deass-Iid-H-50)Einor odenrabBelum ada peringkat
- Photovoltaic (PV) : and Copper Indium Selenide/sulfideDokumen6 halamanPhotovoltaic (PV) : and Copper Indium Selenide/sulfidetroy_asubBelum ada peringkat
- Photovoltaic Inverters TechnologyDokumen8 halamanPhotovoltaic Inverters TechnologynikunjBelum ada peringkat
- 120 Ds Standardcompliantcomponentsfrphotovoltaicapplications en 2945 201701171054541374Dokumen24 halaman120 Ds Standardcompliantcomponentsfrphotovoltaicapplications en 2945 201701171054541374cc_bauBelum ada peringkat
- Grid Connected PV System: More InfoDokumen11 halamanGrid Connected PV System: More Infosai karthikBelum ada peringkat
- Design of A 50 KW Solar PV Rooftop SystemDokumen9 halamanDesign of A 50 KW Solar PV Rooftop SystemKo Mya SanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-3 SPTDokumen6 halamanUnit-3 SPT222 PiyushBelum ada peringkat
- Project Topic:Solar Panel: Worked By:lavdimir Ferraj& Briken Shehaj Accepted From Prof - Sonila DaiuDokumen16 halamanProject Topic:Solar Panel: Worked By:lavdimir Ferraj& Briken Shehaj Accepted From Prof - Sonila DaiuBriken ShehajBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-2 SPTDokumen6 halamanUnit-2 SPT222 PiyushBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Matters Solar GuideDokumen23 halamanEnergy Matters Solar Guideamir100% (1)
- Water Supply in The Rural AreasDokumen169 halamanWater Supply in The Rural Areasdt_chopra64530% (1)
- Corrected Dankuni Eia and EmpreportDokumen35 halamanCorrected Dankuni Eia and Empreportdt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- Water Supply Methodology SaqaDokumen7 halamanWater Supply Methodology Saqadt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- Spacing Between Exiting and New FoundationDokumen1 halamanSpacing Between Exiting and New Foundationdt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- Nhai Proof Consultant Approval Bareilley Vijay ConstructionDokumen2 halamanNhai Proof Consultant Approval Bareilley Vijay Constructiondt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- Definition of HighwayDokumen6 halamanDefinition of Highwaydt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- Safety Checklist For Road Construction SitesDokumen10 halamanSafety Checklist For Road Construction Sitesdt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- BBS Format in FPSDokumen4 halamanBBS Format in FPSdt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- References HorticultureDokumen94 halamanReferences Horticulturedt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- Testing Report FormatDokumen6 halamanTesting Report Formatdt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- Activity (Work) ScheduleDokumen3 halamanActivity (Work) Scheduledt_chopra6453100% (1)
- Critical Path Method: Times (In Days)Dokumen2 halamanCritical Path Method: Times (In Days)dt_chopra6453Belum ada peringkat
- PumpsDokumen115 halamanPumpsMehmet Yılmaz100% (1)
- Components of Nuclear ReactorDokumen17 halamanComponents of Nuclear ReactormrinalBelum ada peringkat
- 560w Solar PanelDokumen2 halaman560w Solar PanelFoto ProdajaBelum ada peringkat
- OECD - Electricity Information 2003.-Organization For Economic Cooperation & Development (Set. 2003)Dokumen779 halamanOECD - Electricity Information 2003.-Organization For Economic Cooperation & Development (Set. 2003)Abdallah MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Casale Technologies For New Grass-Roots PlantsDokumen10 halamanCasale Technologies For New Grass-Roots PlantsNguyen Thanh SangBelum ada peringkat
- AIRSEAL A Leakage SolutionDokumen6 halamanAIRSEAL A Leakage SolutionAbhishek JainBelum ada peringkat
- GB Additional ValvesDokumen16 halamanGB Additional ValvesSmolovic SrdjanBelum ada peringkat
- Section 1: Theory of Heat Unit 3: Refrigeration and RefrigerantsDokumen43 halamanSection 1: Theory of Heat Unit 3: Refrigeration and Refrigerantslemuel ramirezBelum ada peringkat
- CCB VRLA Battery CatalogueDokumen6 halamanCCB VRLA Battery Catalogueomh129Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter Two Literature ReviewDokumen6 halamanChapter Two Literature ReviewMcLeo AliriBelum ada peringkat
- Water Cooled Chiller Performance Qualification Report: Godrej OneDokumen16 halamanWater Cooled Chiller Performance Qualification Report: Godrej OneAnurag KumbhareBelum ada peringkat
- Flame StabilityDokumen11 halamanFlame StabilityMir Reza Negahban100% (1)
- Standards Issued 2017 PDFDokumen1 halamanStandards Issued 2017 PDFEnrique L BlancoBelum ada peringkat
- Safety Talk: Fired HeatersDokumen58 halamanSafety Talk: Fired HeatersSaleem ChohanBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Power PlantDokumen50 halamanThermal Power PlantQasim KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Product People & Company Oryon Watermill GroupDokumen20 halamanProduct People & Company Oryon Watermill GroupDeddy LesmanaBelum ada peringkat
- Rumus Dasar Well ControlDokumen2 halamanRumus Dasar Well Controlwindaru kusumaBelum ada peringkat
- WFO Global Offshore Wind Report HY1 2022Dokumen9 halamanWFO Global Offshore Wind Report HY1 2022João Mendonça SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Pumps, Fans, Blowers, and CompressorsDokumen68 halamanPumps, Fans, Blowers, and CompressorsBren SisonBelum ada peringkat
- Xeno Energy XL-060F Spec SheetDokumen1 halamanXeno Energy XL-060F Spec SheetRadiation Monitoring RadonBelum ada peringkat
- Ecf-Rtc Roof Fan PDFDokumen12 halamanEcf-Rtc Roof Fan PDFFIRMANSYAHBelum ada peringkat
- Is 9404 - 2002 - Identification of Pipeline Used in Thermal Power Plants - Colour CodeDokumen8 halamanIs 9404 - 2002 - Identification of Pipeline Used in Thermal Power Plants - Colour CodeUppala Krishna ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Fiche TechniqueDokumen3 halamanFiche Techniquenacer zidiBelum ada peringkat
- Pump Basic Types & OperationDokumen1 halamanPump Basic Types & Operationmark navarreteBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Piping EngineeringDokumen43 halamanBasics of Piping EngineeringAyushBelum ada peringkat
- 1 DESIGN AND COSTING OF 10KW Solar ModuleDokumen7 halaman1 DESIGN AND COSTING OF 10KW Solar ModuleYash PratapBelum ada peringkat
- BAC Condensers SCONv06EN PDFDokumen2 halamanBAC Condensers SCONv06EN PDFMahmoud KawlesBelum ada peringkat
- Trends Report 2023 - RatedPowerDokumen52 halamanTrends Report 2023 - RatedPowerJuan FrancoBelum ada peringkat
- 5KW MPSG Off-Grid Solar Power System Quotation - 202104Dokumen1 halaman5KW MPSG Off-Grid Solar Power System Quotation - 202104Alberto Chacon PinzonBelum ada peringkat