Understanding Oil & Gas Business Lecture E& P
Diunggah oleh
abhishekchhabra3620 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
80 tayangan9 halamanUnderstanding Oil & Gas Business Lecture E& P.pptx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniUnderstanding Oil & Gas Business Lecture E& P.pptx
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
80 tayangan9 halamanUnderstanding Oil & Gas Business Lecture E& P
Diunggah oleh
abhishekchhabra362Understanding Oil & Gas Business Lecture E& P.pptx
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 9
Understanding Oil
& Gas Business
Upstream and Downstream
Oilfield
Processing
Transportation of oil and gas
Gas Processing
Refinery
Petrochemicals
Power Plants and other gas
based industries
UPSTREAM
DOWNSTREAM
Formation of Oil Traps
It is important to have an elementary
understanding on how hydrocarbon is formed
and trapped in the rocks below the earth.
Formation of Traps- Migration of the oil and
gas stopped at traps which were formed due
to various reasons like sedimentation and
convulsions that took place on earth's strata.
Traps are formed by deformation of the rocks,
deposition of rocks or by creation of faults
due to movement of rock strata.
Types of Structural Traps
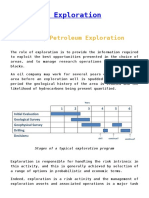
Exploration for Oil and Gas
A commonly used terminology in oil companies,
Exploration & Production (E&P), comprises of
search, discovery and production of oil and gas by
undertaking the following activities:
Licensing
and
agreement
from
the
governments concerned.
Geological
surveys
including
aerial
photography, satellite images to examine nature
of rocks and soil strata and interpretation of
such data.
Geophysical surveys such as seismic surveys.
Interpretation
of data and geological
modeling.
Identifying hydrocarbon resources and their
location based on the interpreted data.
Economic
evaluation
of
the
located
reserves.
Exploratory
drilling
to
establish
commercially viability.
Preparation of field development plan.
Commercially exploiting them by setting
up necessary drilling and production
infrastructure.
Licensing and Agreement:
The first step in exploration of oil obviously is entering
into contract, lease agreement or obtaining licenses
from the governments. Normally the government of the
country carries out a lot of surveys (see next item) to
define a block for exploration and invites bids. The
selected bidder then enters into agreement with the
government. There are two types of arrangements:
Licenses to the exploring company to explore and
produce oil and gas with license fees, royalties (per
unit production) and taxes payable to the state.
Production sharing contracts, in which the state or a
state owned company, is made a partner in the
venture. Normally the initial exploration costs are
borne by the licensee. Revenues earned on
production are first set-off against the costs incurred
by the licensee and the balance amount is shared in
an agreed percentage.
Once the agreement is reached, the exploration
starts.
Geological and Geophysical
Surveys:
Geologists try to develop a model or a map where
hydrocarbon might occur, based on geological
principles.
The map is based on a wide variety of geological
information. They try to locate anticlines and domes
by mapping rock layers coming out of earth's surface.
They use very conventional tools like hand-held
compass, telescope etc. to determine the orientation
of the rock layers. With these instruments geologists
generate drawings and maps of the position and size
of the rock protrusions.
When exploratory wells are drilled, geologists
examine the rock samples and other well data to
make subsurface maps of the reservoir rocks.
Matching up rock layers between wells allows
geologists to draw cross sections in order to find
petroleum traps.
Geophysicists measure the properties and patterns
of sub-surface rock strata by three types of surveys
Magnetic Survey - to determine the strength of the
Earth's magnetic field at a specific location.
Gravity Survey - to determine the strength of the
Earth's gravity at a location.
Seismic Survey - to draw subsurface maps using
sound waves. In seismic survey explosive charges are
detonated in holes drilled by truck mounted rigs at
specific points in the survey area. This rig is called
Thumper Truck.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Oil Gas Accounting 101Dokumen29 halamanOil Gas Accounting 101Dharmendra Pandey100% (2)
- Salem Advocates Bar Association VDokumen17 halamanSalem Advocates Bar Association Vabhishekchhabra36250% (4)
- Coke Vs Pepsi by Harshit GuptaDokumen20 halamanCoke Vs Pepsi by Harshit Guptaabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Oil and Gas AccountingDokumen81 halamanOil and Gas Accountingmike8895100% (1)
- Oil and Gas Accounting OverviewDokumen47 halamanOil and Gas Accounting Overviewtsar_philip2010100% (1)
- Overview of Oil and Gas Accounting & PSC Accounting: Budi HartonoDokumen47 halamanOverview of Oil and Gas Accounting & PSC Accounting: Budi HartonoHariNugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- Googleplex, Mountain View: Designing Interior Spaces at An Urban Scale - Untapped CitiesDokumen11 halamanGoogleplex, Mountain View: Designing Interior Spaces at An Urban Scale - Untapped CitiesDiogo Machado100% (1)
- Archicad Template Checklist v2 0Dokumen7 halamanArchicad Template Checklist v2 0nedblaBelum ada peringkat
- Oil and Gas Drilling 101Dokumen7 halamanOil and Gas Drilling 101lastlandingBelum ada peringkat
- Terminologies in Petroleum IndustryDokumen7 halamanTerminologies in Petroleum Industryarvind_dwivedi100% (1)
- Summary About Nigeria Oil & Gas PDFDokumen108 halamanSummary About Nigeria Oil & Gas PDFDauda Usman50% (2)
- Production Sharing Agreements: Oil Privatisation by Another NameDokumen16 halamanProduction Sharing Agreements: Oil Privatisation by Another NameProtect Florida's BeachesBelum ada peringkat
- Developing Nigeria Oil and Gas Pipeline Using Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (McdaDokumen8 halamanDeveloping Nigeria Oil and Gas Pipeline Using Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (McdaRowland Adewumi100% (8)
- The Introduction To Oil & Gas Industry - The WorkshopDokumen3 halamanThe Introduction To Oil & Gas Industry - The WorkshopFaiz AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Contract AwardedDokumen2 halamanRapid Contract Awardedsurinman2000Belum ada peringkat
- Statoil PresentationDokumen30 halamanStatoil PresentationsergeyalejandroBelum ada peringkat
- IOT TRANSFORMS OIL & GAS INDUSTRYDokumen18 halamanIOT TRANSFORMS OIL & GAS INDUSTRYmanuelsantos2007Belum ada peringkat
- SEP Position On UnitizationDokumen4 halamanSEP Position On UnitizationMichael Creg AffulBelum ada peringkat
- Exxon Mobil Research PaperDokumen16 halamanExxon Mobil Research Paperbmcginnis83Belum ada peringkat
- Formation of Oil and GasDokumen2 halamanFormation of Oil and GasDiana Herrera SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Finman 1Dokumen18 halamanFinman 1Karen LaccayBelum ada peringkat
- Oil & Gas Accounting Overview: PSC, Full Cost, Successful EffortsDokumen47 halamanOil & Gas Accounting Overview: PSC, Full Cost, Successful EffortsAren BennetBelum ada peringkat
- Recent Experience from Multiple Remote Sensing and Monitoring to Improve Oil Spill ResponseDokumen7 halamanRecent Experience from Multiple Remote Sensing and Monitoring to Improve Oil Spill ResponsePavel TatarintsevBelum ada peringkat
- Chaldal Presentation ScriptDokumen4 halamanChaldal Presentation ScriptRobiul HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Mergers and AcquisitionsDokumen18 halamanMergers and AcquisitionsMohil PoojaraBelum ada peringkat
- Key Maritime Logistics StakeholdersTITLEBill of Lading Functions in International TradeDokumen7 halamanKey Maritime Logistics StakeholdersTITLEBill of Lading Functions in International Tradeparidhisahni0% (2)
- Petroleum Licensing and Contracting OverviewDokumen26 halamanPetroleum Licensing and Contracting OverviewZhangHuiChenBelum ada peringkat
- Mini RefineryDokumen12 halamanMini RefinerySaraAwad100% (1)
- Oil & Gas Accounting, May 2011Dokumen9 halamanOil & Gas Accounting, May 2011Sunday Oluwole50% (2)
- BMT Offshore Oil and Gas - Services and SolutionsDokumen12 halamanBMT Offshore Oil and Gas - Services and SolutionsmiguelfensterseiferBelum ada peringkat
- Trial Lecture LNG Refrigeration ProcessesDokumen37 halamanTrial Lecture LNG Refrigeration Processesoliver9191Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Details: Indian Oil Corporation Eprocurement PortalDokumen3 halamanBasic Details: Indian Oil Corporation Eprocurement PortalamitjustamitBelum ada peringkat
- Nigeria LNG Facts & Figures 2012 ReportDokumen104 halamanNigeria LNG Facts & Figures 2012 ReportseguntaiwoBelum ada peringkat
- OPITO FPSO Deck Cargo Handling & Ballast ControlDokumen21 halamanOPITO FPSO Deck Cargo Handling & Ballast ControlChristina OoiBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Oil & Gas Business V1Dokumen5 halamanFundamentals of Oil & Gas Business V1solvedcareBelum ada peringkat
- Kashagan Offshore Oil Field ProjectDokumen5 halamanKashagan Offshore Oil Field ProjectjiokoijikoBelum ada peringkat
- Amenam/Kpono: First OilDokumen49 halamanAmenam/Kpono: First OilOluseun Maraiyesa100% (1)
- Local Content Undpconf Present080327 Olsen1Dokumen54 halamanLocal Content Undpconf Present080327 Olsen1tsar_philip2010100% (1)
- Setting up an LPG Plant in NigeriaDokumen5 halamanSetting up an LPG Plant in NigeriaAJAGUN JOHNSONBelum ada peringkat
- Tax Treatment For Gross Split Production Sharing Contracts in Indonesian Oil and Gas Sector - SSEK Corporate - Commercial Indonesian Law FirmDokumen6 halamanTax Treatment For Gross Split Production Sharing Contracts in Indonesian Oil and Gas Sector - SSEK Corporate - Commercial Indonesian Law FirmDewa Gede Praharyan JayadiputraBelum ada peringkat
- Acquiring Upstream Assets Via Joint Ventures - Akin Gump Straus Hauer & Feld LLPDokumen39 halamanAcquiring Upstream Assets Via Joint Ventures - Akin Gump Straus Hauer & Feld LLPshortmycdsBelum ada peringkat
- Characterizing Oil & Gas Charge Risk with GeochemistryDokumen4 halamanCharacterizing Oil & Gas Charge Risk with GeochemistrysidikBelum ada peringkat
- Ghana's Big Test: Oil's Challenge To Democratic DevelopmentDokumen32 halamanGhana's Big Test: Oil's Challenge To Democratic Developmenttsar_philip2010Belum ada peringkat
- Exploration Geophysics 1Dokumen4 halamanExploration Geophysics 1khalifasaadBelum ada peringkat
- How Oil Drilling Works: From Ancient Seas to Modern ExplorationDokumen5 halamanHow Oil Drilling Works: From Ancient Seas to Modern Explorationgestion integralBelum ada peringkat
- Discover Oil Traps with Seismic SurveysDokumen24 halamanDiscover Oil Traps with Seismic Surveyspintu ramBelum ada peringkat
- Drilling Practices Course ManualDokumen334 halamanDrilling Practices Course ManualAdil Aytekin96% (27)
- Oil Exploration Methods in 40 CharactersDokumen82 halamanOil Exploration Methods in 40 CharactersTushar VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Petroleum ExplorationDokumen22 halamanPetroleum ExplorationAshrafBelum ada peringkat
- Exploration and Lead & ProspectDokumen17 halamanExploration and Lead & ProspectrizkiboyscribdBelum ada peringkat
- Petroleum Exploration MethodsDokumen16 halamanPetroleum Exploration MethodsAshish SinghBelum ada peringkat
- How Oil Drilling Works: Craig C. Freudenrich, PH.DDokumen18 halamanHow Oil Drilling Works: Craig C. Freudenrich, PH.DmohammedBelum ada peringkat
- How Oil Drilling WorksDokumen9 halamanHow Oil Drilling WorksAviiCaphBelum ada peringkat
- How Oil Drilling WorksDokumen11 halamanHow Oil Drilling Workssrm101Belum ada peringkat
- How Oil Drilling WorksDokumen10 halamanHow Oil Drilling WorksAmit WadkarBelum ada peringkat
- ملزمة أسسDokumen9 halamanملزمة أسسAli AbdBelum ada peringkat
- Geotechnical Engineering ReportDokumen25 halamanGeotechnical Engineering ReportAbdullah YucesoyBelum ada peringkat
- Coal Exploration Modern TechDokumen9 halamanCoal Exploration Modern TechLive JhonyBelum ada peringkat
- UPSTREAM Oil and Gas GuidelinesDokumen13 halamanUPSTREAM Oil and Gas GuidelinesLloyd Kenneth CalapanBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Group No.5 ElebareDokumen7 halamanSummary Group No.5 ElebareBayot Aliana Vine A.Belum ada peringkat
- How Oil Drilling WorkDokumen7 halamanHow Oil Drilling WorkGoro BeteBelum ada peringkat
- Extract Crude Oil Production ProcessDokumen35 halamanExtract Crude Oil Production Processsohil vhoraBelum ada peringkat
- Everything About OffshoreDokumen108 halamanEverything About OffshoreVipin DwivediBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Exploration of Geophysical in Oil & Gas Indutry - WikipediaDokumen4 halamanIntroduction of Exploration of Geophysical in Oil & Gas Indutry - WikipediaFaiz AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Aditi Law of MiningDokumen14 halamanAditi Law of Miningabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- New Format of Course Plan - BALLB HSE 2015Dokumen16 halamanNew Format of Course Plan - BALLB HSE 2015abhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- International LawDokumen24 halamanInternational Lawabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- DeepikaDokumen10 halamanDeepikaabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Companies Act 2013 Key Highlights and Analysis in MalaysiaDokumen52 halamanCompanies Act 2013 Key Highlights and Analysis in MalaysiatruthosisBelum ada peringkat
- Lucy v. Mariappa CPCDokumen12 halamanLucy v. Mariappa CPCabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen12 halamanAssignmentabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- College of Legal Studies Assignment OnDokumen7 halamanCollege of Legal Studies Assignment Onabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Mining Assignment ChhabraDokumen13 halamanMining Assignment ChhabraAbhishek ChhabraBelum ada peringkat
- AbhishekDokumen15 halamanAbhishekabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Abhishek CaseDokumen6 halamanAbhishek Caseabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Regulatory Agencies - PPTX 13.1.15Dokumen79 halamanUnit 2 Regulatory Agencies - PPTX 13.1.15abhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Adocxditi Case.Dokumen7 halamanAdocxditi Case.abhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Anirban MajumdarDokumen18 halamanAnirban Majumdarabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Labour Welfare: Factories Act 1948Dokumen23 halamanLabour Welfare: Factories Act 1948abhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding Oil & Gas Business Lecture E& PDokumen9 halamanUnderstanding Oil & Gas Business Lecture E& Pabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Unit-1: Introduction To Health, Safety and Environment Aspects 5.2.14Dokumen30 halamanUnit-1: Introduction To Health, Safety and Environment Aspects 5.2.14abhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding Crude Oil Benchmarks & Pricing MechanismsDokumen13 halamanUnderstanding Crude Oil Benchmarks & Pricing Mechanismsabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- What Is Political Regime?: Synopsis Transitional Phase of International Political RegimesDokumen2 halamanWhat Is Political Regime?: Synopsis Transitional Phase of International Political Regimesabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 HSE Management Systems: - IntegratedDokumen72 halamanUnit 3 HSE Management Systems: - Integratedabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding Crude Oil Benchmarks & Pricing MechanismsDokumen13 halamanUnderstanding Crude Oil Benchmarks & Pricing Mechanismsabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Political RegimesDokumen15 halamanPolitical Regimesabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment III For BALLBDokumen2 halamanAssignment III For BALLBabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Case Analysis Aditi GuptaDokumen4 halamanCase Analysis Aditi Guptaabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- City Gas DistributionDokumen14 halamanCity Gas Distributionabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- City Gas DistributionDokumen14 halamanCity Gas Distributionabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- French Motor Car Co. Ltd. Workers Union Vs. French Motor Car Co. LtdDokumen3 halamanFrench Motor Car Co. Ltd. Workers Union Vs. French Motor Car Co. Ltdabhishekchhabra362Belum ada peringkat
- Air CompressorDokumen21 halamanAir CompressorAjayBelum ada peringkat
- AirlinewaysDokumen32 halamanAirlinewaysOmkar GidlaBelum ada peringkat
- Woodward Speed Setting MechDokumen6 halamanWoodward Speed Setting Mechmanuel1122Belum ada peringkat
- Theories EssayDokumen11 halamanTheories EssayNaim Ahmad MukifBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae New 2017 MD Sajid AlamDokumen6 halamanCurriculum Vitae New 2017 MD Sajid AlamAlam MD SazidBelum ada peringkat
- Inventory Management-Dante v. AriñezDokumen41 halamanInventory Management-Dante v. AriñezJaypee FazoliBelum ada peringkat
- Clearing Pending TransactionsDokumen10 halamanClearing Pending TransactionsVinay ChughBelum ada peringkat
- Project 3Dokumen18 halamanProject 3Jay ParekhBelum ada peringkat
- NASA Configuration Management (CM) Standard (NASA - STD - 00059Dokumen143 halamanNASA Configuration Management (CM) Standard (NASA - STD - 00059yaseenzaidi5117100% (1)
- EpicorAFR InstallGuide 905702EDokumen23 halamanEpicorAFR InstallGuide 905702EVictor MotoliniaBelum ada peringkat
- 08 Network ModelsDokumen2 halaman08 Network ModelsJohn Carlo AmodiaBelum ada peringkat
- Cif PmiDokumen1 halamanCif PmiC.K DavisBelum ada peringkat
- V2 I4 Naniwa Newsletter OFFICIALDokumen4 halamanV2 I4 Naniwa Newsletter OFFICIALNigelBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Dynamics GP 2013 - System Admin Guide PDFDokumen110 halamanMicrosoft Dynamics GP 2013 - System Admin Guide PDFsivextienBelum ada peringkat
- Bek MDPDokumen43 halamanBek MDPluisgalo91143Belum ada peringkat
- CA7 CommandsDokumen9 halamanCA7 CommandsArvindUpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- Plaxis QuatationDokumen3 halamanPlaxis Quatationraaji2002Belum ada peringkat
- SAP Landscape Design - V24Dokumen47 halamanSAP Landscape Design - V24vishnu_kota58Belum ada peringkat
- Work at HeightDokumen10 halamanWork at HeightShoaib RazzaqBelum ada peringkat
- 3HE06512AAAHTQZZA01 - V1 - 5620 SAM Release 9.0 R8 Optical Parameter ReferenceDokumen326 halaman3HE06512AAAHTQZZA01 - V1 - 5620 SAM Release 9.0 R8 Optical Parameter ReferenceKeyson FariasBelum ada peringkat
- SR5080 Booklet Finisher RTBsDokumen22 halamanSR5080 Booklet Finisher RTBsTecnica CPY Copiadoras del ParaguayBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Marketing EmptyDokumen4 halamanMass Marketing EmptyvalenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Rfid Nov'11eng 4Dokumen23 halamanRfid Nov'11eng 4hydisBelum ada peringkat
- Graduate Catalog - Faculty of Engineering - Qatar University 2011-2012Dokumen71 halamanGraduate Catalog - Faculty of Engineering - Qatar University 2011-2012Maher RagehBelum ada peringkat
- EstimateDokumen6 halamanEstimateSansar PanchalBelum ada peringkat
- Mod BDokumen32 halamanMod BRuwina Ayman100% (1)
- AP Electrical Safety SWPDokumen12 halamanAP Electrical Safety SWPjvigforuBelum ada peringkat